El Paso (; ; or ) is a city in and the
county seat
A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or parish (administrative division), civil parish. The term is in use in five countries: Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, and the United States. An equiva ...
of
El Paso County, Texas
El Paso County is the westernmost county in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, the population was 865,657, making it the ninth-most populous county in the state of Texas. Its county seat is the city of El Paso, the sixth-mos ...
, United States. The
2020
The year 2020 was heavily defined by the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to global Social impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, social and Economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, economic disruption, mass cancellations and postponements of even ...
population of the city from the
U.S. Census Bureau was 678,815,
making it the
22nd-most populous city in the U.S., the most populous city in
West Texas
West Texas is a loosely defined region in the U.S. state of Texas, generally encompassing the desert climate, arid and semiarid climate, semiarid lands west of a line drawn between the cities of Wichita Falls, Texas, Wichita Falls, Abilene, Texa ...
, and the
sixth-most populous city in Texas.
Its
metropolitan statistical area covers all of El Paso and
Hudspeth counties in Texas, and had a population of 868,859 in 2020.
El Paso stands on the
Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( or ) in the United States or the Río Bravo (del Norte) in Mexico (), also known as Tó Ba'áadi in Navajo language, Navajo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the Southwestern United States a ...
across the
Mexico–United States border
The international border separating Mexico and the United States extends from the Pacific Ocean in the west to the Gulf of Mexico in the east. The border traverses a variety of terrains, ranging from urban areas to deserts. It is the List of ...
from
Ciudad Juárez
Ciudad Juárez ( , ; "Juárez City"), commonly referred to as just Juárez (Lipan language, Lipan: ''Tsé Táhú'ayá''), is the most populous city in the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. It was k ...
, the most populous city in the Mexican state of
Chihuahua. On the U.S. side, the
El Paso metropolitan area forms part of the larger
El Paso–Las Cruces combined statistical area with
Las Cruces, New Mexico
Las Cruces (; ; lit. 'the crosses') is the List of municipalities in New Mexico, second-most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico and the county seat, seat of Doña Ana County, New Mexico, Doña Ana County. As of the 2020 United States ce ...
, which has a population of 1,098,541.
These three cities form a combined international
metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region consisting of a densely populated urban area, urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories which share Industry (economics), industries, commercial areas, Transport infrastructure, transport network ...
sometimes referred to as the
''Paso del Norte'' or the ''Borderplex''. The region of 2.7 million people constitutes the largest bilingual and binational workforce in the
Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the 180th meridian.- The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Geopolitically, ...
.
The city is home to three publicly traded companies, and former
Western Refining, now
Marathon Petroleum
Marathon Petroleum Corporation is an petroleum industry in the United States, American petroleum refining, marketing, and transportation company headquartered in Findlay, Ohio. The company was a wholly owned subsidiary of Marathon Oil until a cor ...
, as well as home to the Medical Center of the Americas, the only medical research and care provider complex in West Texas and Southern New Mexico, and the
University of Texas at El Paso
The University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP) is a public university, public research university in El Paso, Texas, United States. Founded in 1913 as the State School of Mines and Metallurgy, it is the third oldest academic component of the Univers ...
, the city's primary university. The city hosts the annual
Sun Bowl college football postseason game, the second-oldest
bowl game
In North America, a bowl game, or simply bowl, is one of a number of postseason college football games primarily played by NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS) teams. For most of its history, the FBS did not use a playoff tourname ...
in the country. El Paso has a strong federal and military presence.
William Beaumont Army Medical Center,
Biggs Army Airfield
Biggs Army Airfield (formerly Biggs Air Force Base) is a United States Army military airbase located on the Fort Bliss military base in El Paso, Texas.
History Biggs Field/Biggs Army Airfield (1916–47)
On 15 June 1919, following an attack ...
, and
Fort Bliss
Fort Bliss is a United States Army post in New Mexico and Texas, with its headquarters in El Paso, Texas. Established in 1848, the fort was renamed in 1854 to honor William Wallace Smith Bliss, Bvt.Lieut.Colonel William W.S. Bliss (1815–1853 ...
are located in the area. Also headquartered in El Paso is the
Drug Enforcement Administration
The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) is a Federal law enforcement in the United States, United States federal law enforcement agency under the U.S. Department of Justice tasked with combating illicit Illegal drug trade, drug trafficking a ...
domestic field division 7,
El Paso Intelligence Center,
Joint Task Force North,
United States Border Patrol
The United States Border Patrol (USBP) is a Federal law enforcement in the United States, federal law enforcement agency under the U.S. Customs and Border Protection, United States Customs and Border Protection (CBP) and is responsible for secu ...
El Paso Sector, and U.S. Border Patrol Special Operations Group.
El Paso is a five-time
All-America City Award winner, winning in 1969, 2010, 2018, 2020, and 2021, and ''
Congressional Quarterly
''Congressional Quarterly'', or ''CQ'', is an American publication that is part of the privately owned publishing company CQ Roll Call, which covers the United States Congress. ''CQ'' was formerly acquired by the U.K.-based Economist Group and ...
'' ranked it in the top-three safest large cities in the United States between 1997 and 2014, including holding the title of the safest city between 2011 and 2014. El Paso is also
the second-largest absolute-majority-Hispanic city in the United States (after
San Antonio
San Antonio ( ; Spanish for " Saint Anthony") is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the most populous city in Greater San Antonio. San Antonio is the third-largest metropolitan area in Texas and the 24th-largest metropolitan area in the ...
), with 81% of its residents being
Hispanic
The term Hispanic () are people, Spanish culture, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or broadly. In some contexts, Hispanic and Latino Americans, especially within the United States, "Hispanic" is used as an Ethnici ...
,
and the largest city in the US with an absolute Hispanic majority throughout all its history.
History
Early years
The El Paso region has had human settlement for thousands of years, as evidenced by
Folsom points from
hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, esp ...
s found at
Hueco Tanks. This suggests 10,000 to 12,000 years of human habitation. The earliest known cultures in the region were maize farmers. When the
Spanish arrived, the
Manso,
Suma, and
Jumano tribes populated the area. These were subsequently incorporated into the ''
mestizo
( , ; fem. , literally 'mixed person') is a term primarily used to denote people of mixed European and Indigenous ancestry in the former Spanish Empire. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to people who are culturall ...
'' culture, along with immigrants from central Mexico, captives from
Comanchería, and ''
genízaros'' of various ethnic groups. The
Mescalero Apache were also present.
The
Chamuscado and Rodríguez Expedition trekked through present-day El Paso and forded the Rio Grande where they visited the land that is present-day New Mexico in 1581–1582. The expedition was led by Francisco Sánchez, called "El Chamuscado", and Fray Agustín Rodríguez, the first Spaniards known to have walked along the Rio Grande and visited the Pueblo Indians since Francisco Vásquez de Coronado 40 years earlier. Spanish explorer
Don Juan de Oñate was born in 1550 in
Zacatecas, Zacatecas, Mexico, and was the first
New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
(Mexico) explorer known to have rested and stayed 10 days by the
Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( or ) in the United States or the Río Bravo (del Norte) in Mexico (), also known as Tó Ba'áadi in Navajo language, Navajo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the Southwestern United States a ...
near El Paso, in 1598, celebrating a
Thanksgiving Mass there on April 30, 1598. Four survivors of the
Narváez expedition,
Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca
Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca (; 1488/90/92"Cabeza de Vaca, Alvar Núñez (1492?-1559?)." American Eras. Vol. 1: Early American Civilizations and Exploration to 1600. Detroit: Gale, 1997. 50-51. Gale Virtual Reference Library. Web. 10 December ...
,
Alonso del Castillo Maldonado
Alonso del Castillo Maldonado (died after 1547) was an early Spanish explorer in the Americas. He was one of the last four survivors of the original members of the 1527 Narváez expedition, along with Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca, Andrés Dorant ...
,
Andrés Dorantes de Carranza
Andrés Dorantes de Carranza (ca. 1500 – 1550s), was an early Spanish explorer in the Americas. He was one of the four last survivors of the Narváez expedition, along with Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca, Alonso del Castillo Maldonado, and ...
, and an enslaved native of
Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
,
Estevanico, are thought to have crossed the Rio Grande into present-day Mexico about 75 miles south of El Paso in 1535. El Paso del Norte (present-day
Ciudad Juárez
Ciudad Juárez ( , ; "Juárez City"), commonly referred to as just Juárez (Lipan language, Lipan: ''Tsé Táhú'ayá''), is the most populous city in the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. It was k ...
) was founded on the south bank of the Río Bravo del Norte (Rio Grande), in 1659 by
Fray Garcia de San Francisco. In 1680, the small village of El Paso became the temporary base for Spanish governance of the territory of New Mexico as a result of the
Pueblo Revolt, until 1692, when
Santa Fe was reconquered and once again became the capital.
The
Texas Revolution
The Texas Revolution (October 2, 1835 – April 21, 1836) was a rebellion of colonists from the United States and Tejanos (Hispanic Texans) against the Centralist Republic of Mexico, centralist government of Mexico in the Mexican state of ...
(1836) was generally not felt in the region, as the American population was small, not more than 10% of the population. However, the region was claimed by Texas as part of the treaty signed with Mexico and numerous attempts were made by Texas to bolster these claims, but the villages that consisted of what is now El Paso and the surrounding area remained essentially a self-governed community with both representatives of the Mexican and Texan governments negotiating for control until Texas irrevocably took control in 1846.
During this interregnum, 1836–1848, Americans nonetheless continued to settle the region. As early as the mid-1840s, alongside long extant Hispanic settlements such as the Rancho de Juan María Ponce de León, Anglo-American settlers such as
Simeon Hart and
Hugh Stephenson had established thriving communities of American settlers owing allegiance to Texas.
Stephenson, who had married into the local Hispanic aristocracy, established the
Rancho de San José de la Concordia, which became the nucleus of Anglo-American and Hispanic settlement within the limits of modern-day El Paso, in 1844: the Republic of Texas, which claimed the area, wanted a chunk of the Santa Fe trade. During the
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War (Spanish language, Spanish: ''guerra de Estados Unidos-México, guerra mexicano-estadounidense''), also known in the United States as the Mexican War, and in Mexico as the United States intervention in Mexico, ...
, the
Battle of El Bracito was fought nearby on Christmas Day, 1846. The
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo officially ended the Mexican–American War (1846–1848). It was signed on 2 February 1848 in the town of Villa de Guadalupe, Mexico City, Guadalupe Hidalgo.
After the defeat of its army and the fall of the cap ...
effectively made the settlements on the north bank of the river part of the US, separate from Old El Paso del Norte on the Mexican side.
[''El Paso, A Borderlands History'', by W.H. Timmons, pp. 74, 75] The present New Mexico–Texas boundary placing El Paso on the Texas side was drawn in the
Compromise of 1850
The Compromise of 1850 was a package of five separate bills passed by the United States Congress in September 1850 that temporarily defused tensions between slave and free states during the years leading up to the American Civil War. Designe ...
.
El Paso remained the largest settlement in New Mexico as part of the Republic of Mexico until its cession to the U.S. in 1848, when the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo specified the border was to run north of El Paso De Norte around the
Ciudad Juárez Cathedral
The Our Lady of Guadalupe Cathedral (), also Ciudad Juárez Cathedral, is a Catholic cathedral church dedicated to the Virgin of Guadalupe that is located in Ciudad Juárez in the border state of Chihuahua, in Mexico, in the area called Historical ...
which became part of the state of Chihuahua.
El Paso County was established in March 1850, with
San Elizario as the first county seat. The United States Senate fixed a boundary between Texas and New Mexico at the 32nd parallel, thus largely ignoring history and topography. A military post called the "Post opposite El Paso" (meaning opposite El Paso del Norte, across the Rio Grande) was established in 1849 on Coons' Rancho beside the settlement of Franklin, which became the nucleus of the future El Paso, Texas; after the army left in 1851, the rancho went into default and was repossessed; in 1852, a post office was established on the rancho bearing the name El Paso as an example of
cross-border town naming until El Paso del Norte was renamed Juarez in 1888. After changing hands twice more, the El Paso company was set up in 1859 and bought the property, hiring
Anson Mills to survey and lay out the town, thus forming the current street plan of downtown El Paso.
In ''Beyond the Mississippi'' (1867),
Albert D. Richardson, traveling to California via coach, described El Paso as he found it in late 1859:
The Texan town of El Paso had four hundred inhabitants, chiefly Mexicans. Its businessmen were Americans, but Spanish was the prevailing language. All the features were Mexican: low, flat adobe buildings, shading cottonwoods under which dusky, smoking women and swarthy children sold fruit, vegetables, and bread; habitual gambling universal, from the boys' game of pitching ''quartillas'' (three-cent coins) to the great saloons where huge piles of silver dollars were staked at monte. In this little village, a hundred thousand dollars often changed hands in a single night through the potent agencies of Monte and poker. There were only two or three American ladies, and most of the whites kept Mexican mistresses. All goods were brought on wagons from the Gulf of Mexico and sold at an advance of three or four hundred percent on Eastern prices.
From hills overlooking the town, the eye takes in a charming picture—a far-stretching valley, enriched with orchards, vineyards, and cornfields, through which the river traces a shining pathway. Across it appears the flat roofs and cathedral towers of the old Mexican El Paso; still further, dim misty mountains melt into the blue sky.

During the
Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
,
Confederate military forces were in the area until it was captured by the Union
California Column in August 1862. It was then headquarters for the
5th Regiment California Volunteer Infantry from August 1863 until December 1864.
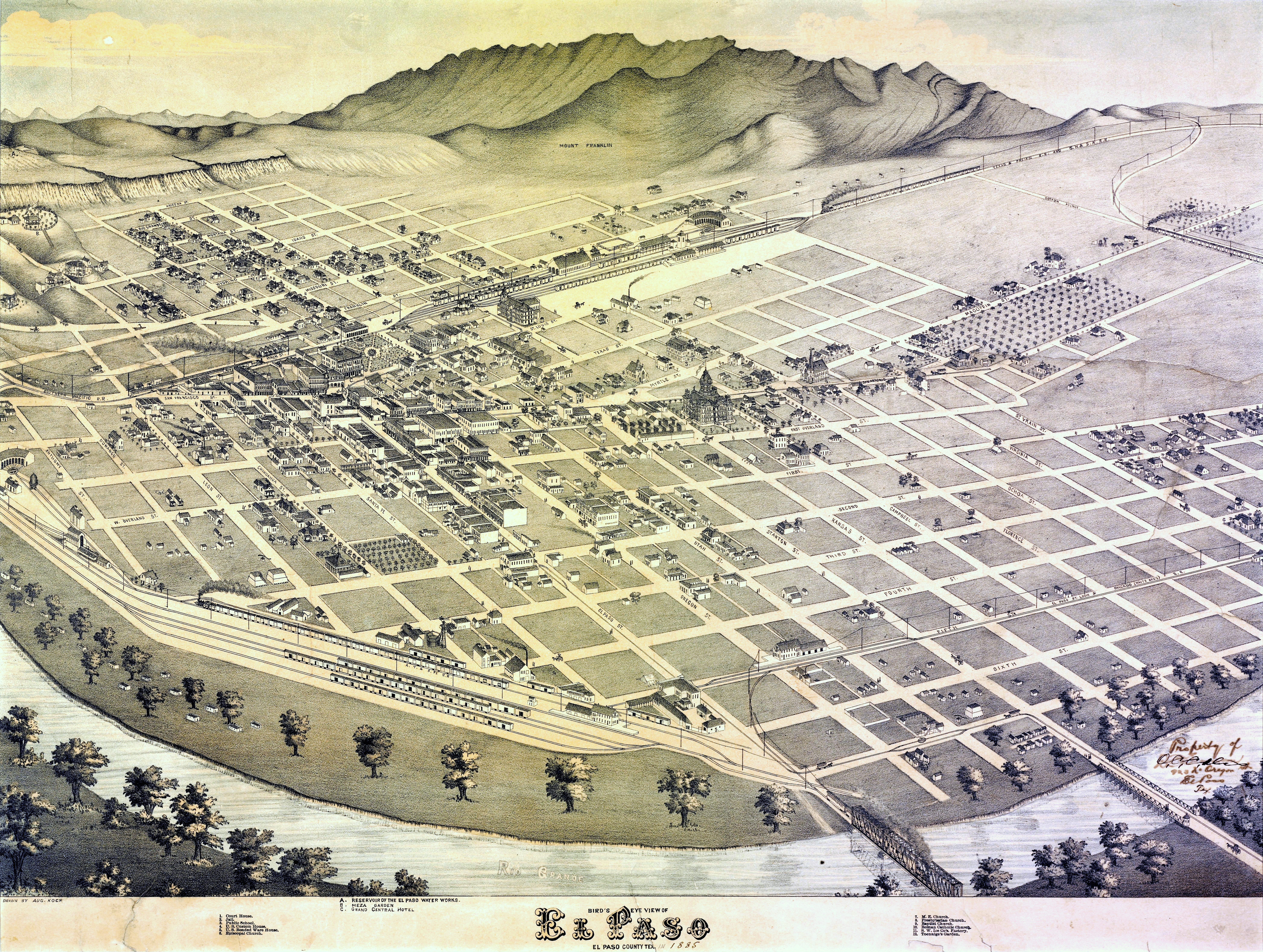
After the Civil War's conclusion, the town's population began to grow as white Texans continued to move into the villages and soon became the majority. El Paso itself, incorporated in 1873, encompassed the small area of communities that had developed along the river. In the 1870s, a population of 23 non-Hispanic Whites and 150 Hispanics was reported.
With the arrival of the
Southern Pacific,
Texas and Pacific, and
Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe railroads in 1881, the population boomed to 10,000 by the 1890 census, with many Anglo-Americans, recent immigrants, old Hispanic settlers, and recent arrivals from Mexico. The location of El Paso and the arrival of these more wild newcomers caused the city to become a violent and wild
boomtown
A boomtown is a community that undergoes sudden and rapid population and economic growth, or that is started from scratch. The growth is normally attributed to the nearby discovery of a precious resource such as gold, silver, or oil, although t ...
known as the "Six-shooter Capital" because of its lawlessness.
Indeed, prostitution and gambling flourished until World War I when the
Department of the Army
The United States Department of the Army (DA) is one of the three military departments within the United States Department of Defense. The DA is the federal government agency within which the United States Army (U.S.) is organized. It is led ...
pressured El Paso authorities to crack down on vice (thus "benefitting" vice in neighboring Ciudad Juárez). With the suppression of the vice trade and in consideration of the city's geographic position, the city continued into developing as a premier manufacturing, transportation, and retail center of the U.S. Southwest.
1900–present


In 1909, the
El Paso Chamber of Commerce hosted U.S. President
William Howard Taft
William Howard Taft (September 15, 1857March 8, 1930) served as the 27th president of the United States from 1909 to 1913 and the tenth chief justice of the United States from 1921 to 1930. He is the only person to have held both offices. ...
and Mexican President
Porfirio Díaz
José de la Cruz Porfirio Díaz Mori (; ; 15 September 1830 – 2 July 1915) was a General (Mexico), Mexican general and politician who was the dictator of Mexico from 1876 until Mexican Revolution, his overthrow in 1911 seizing power in a Plan ...
at a planned summit in El Paso, Texas, and Ciudad Juárez, Mexico, a historic first meeting between the Presidents of the two countries, and also the first time an American President crossed the border into Mexico. However, tensions rose on both sides of the border, including threats of assassination; so the
Texas Rangers, 4,000 U.S. and Mexican troops, U.S. Secret Service agents, FBI agents, and U.S. marshals were all called in to provide security.
Frederick Russell Burnham
Major (rank), Major Frederick Russell Burnham Distinguished Service Order, DSO (May 11, 1861 – September 1, 1947) was an American scout and world-traveling adventurer. He is known for his service to the British South Africa Company and to t ...
, a celebrated scout, was put in charge of a 250-strong private security detail hired by
John Hays Hammond
John Hays Hammond (March 31, 1855 – June 8, 1936) was an American mining engineer, diplomat, and philanthropist. He amassed a sizable fortune before the age of 40. An early advocate of deep mining, Hammond was given complete charge of Cecil R ...
, who in addition to owning large investments in Mexico, was a close friend of Taft from Yale and a U.S. vice presidential candidate in 1908. On October 16, the day of the summit, Burnham and Private C.R. Moore, a Texas Ranger, discovered a man
holding a concealed
palm pistol standing at the Chamber of Commerce building along the procession route in El Paso. Burnham and Moore captured, disarmed, and arrested the assassin within only a few feet of Taft and Díaz. By 1910, an overwhelming number of people in the city were Americans, creating a settled environment, but this period was short-lived as the
Mexican Revolution
The Mexican Revolution () was an extended sequence of armed regional conflicts in Mexico from 20 November 1910 to 1 December 1920. It has been called "the defining event of modern Mexican history". It saw the destruction of the Federal Army, its ...
greatly impacted the city, bringing an influx of refugees—and capital—to the bustling boom town. Spanish-language newspapers, theaters, movie houses, and schools were established, many supported by a thriving Mexican refugee middle class. Large numbers of clerics, intellectuals, and businessmen took refuge in the city, particularly between 1913 and 1915. Ultimately, the violence of the Mexican Revolution followed the large Mexican diaspora, who had fled to El Paso. In 1915 and again in 1916 and 1917, various Mexican revolutionary societies planned, staged, and launched violent attacks against both Texans and their political Mexican opponents in El Paso. This state of affairs eventually led to the vast
Plan de San Diego, which resulted in the murder of 21 American citizens.
The subsequent reprisals by a local militia soon caused an escalation of violence, wherein an estimated 300 Mexicans and Mexican-Americans lost their lives. These actions affected almost every resident of the entire Rio Grande Valley, resulting in millions of dollars of losses; the result of the Plan of San Diego was long-standing enmity between the two ethnic groups.
Simultaneously, other Texans and Americans gravitated to the city, and by 1920, along with the U.S. Army troops, the population exceeded 100,000, and non-Hispanic Whites once again were in the clear majority. Nonetheless, the city increased the segregation between Mexicans and Mexican-Americans with non-Hispanic Whites. One prominent form of segregation, in the form of immigration controls to prevent disease, allegedly was abused to create
nonconsensual pornographic
Pornography (colloquially called porn or porno) is sexually suggestive material, such as a picture, video, text, or audio, intended for sexual arousal. Made for consumption by adults, pornographic depictions have evolved from cave paintings ...
images of women distributed in local bars. These rumors along with the perceived hazard from
kerosene
Kerosene, or paraffin, is a combustibility, combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in Aviation fuel, aviation as well as households. Its name derives from the Greek (''kērós'') meaning " ...
baths led to the
1917 Bath riots. As a result of the increased segregation, the Catholic Church attempted to garner the Mexican-American community's allegiance through education and political and civic involvement organizations, including the National Catholic Welfare Fund. In 1916, the Census Bureau reported El Paso's population as 53% Mexican and 44% Non-Hispanic whites. Mining and other industries gradually developed in the area. The
El Paso and Northeastern Railway was chartered in 1897, to help extract the natural resources of surrounding areas, especially in southeastern New Mexico Territory. The 1920s and 1930s had the emergence of major business development in the city, partially enabled by
Prohibition-era bootlegging.
The military demobilization, and agricultural economic depression, which hit places like El Paso first before the larger
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
was felt in the big cities, though, hit the city hard. In turn, as in the rest of the United States, the
Depression era overall hit the city hard, and El Paso's population declined through the end of World War II, with most of the population losses coming from the non-Hispanic White community. Nonetheless, they remained the majority to the 1940s.
During and following the war, military expansion in the area, as well as oil discoveries in the
Permian Basin, helped to engender rapid economic expansion in the mid-1900s. Copper smelting,
oil refining, and the proliferation of low-wage industries (particularly garment making) led to the city's growth. Additionally, the departure of the region's rural population, which was mostly non-Hispanic White, to cities like El Paso, brought a short-term burst of capital and labor, but this was balanced by additional departures of middle-class Americans to other parts of the country that offered new and better-paying jobs. In turn, local businesses looked south to the opportunities afforded by cheap Mexican labor. Furthermore, the period from 1942 to 1956 had the
bracero program, which brought cheap Mexican labor into the rural area to replace the losses of the non-Hispanic White population. In turn, seeking better-paying jobs, these migrants also moved to El Paso. By 1965, Hispanics once again were a majority. Meanwhile, the postwar expansion slowed again in the 1960s, but the city continued to grow with the annexation of surrounding neighborhoods and in large part because of its significant economic relationship with Mexico.
The Farah Strike, 1972–1974, occurred in El Paso, Texas. This strike was originated and led by Chicanas, or Mexican-American women, against the Farah Manufacturing Company, due to complaints against the company inadequately compensating workers. ''Texas Monthly'' described the Farah Strike as the "strike of the century".
On August 3, 2019, a
terrorist shooter espousing
white supremacy
White supremacy is the belief that white people are superior to those of other races. The belief favors the maintenance and defense of any power and privilege held by white people. White supremacy has roots in the now-discredited doctrine ...
killed 23 people at a
Walmart
Walmart Inc. (; formerly Wal-Mart Stores, Inc.) is an American multinational retail corporation that operates a chain of hypermarkets (also called supercenters), discount department stores, and grocery stores in the United States and 23 other ...
and injured 22 others.
Geography
El Paso is located at the intersection of three states (Chihuahua, New Mexico, and Texas) and two countries (Mexico and the U.S.). It is the only major Texas city in the
Mountain Time Zone
The Mountain Time Zone of North America keeps time by subtracting seven hours from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) when standard time ( UTC−07:00) is in effect, and by subtracting six hours during daylight saving time ( UTC−06:00). The ...
.
Ciudad Juarez was once in the
Central Time Zone
The North American Central Time Zone (CT) is a time zone in parts of Canada, the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It ...
, but both cities are now on Mountain Time.
El Paso is closer to the capital cities of four other states:
Phoenix, Arizona
Phoenix ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of cities and towns in Arizona#List of cities and towns, most populous city of the U.S. state of Arizona. With over 1.6 million residents at the 2020 census, it is the ...
( away);
Santa Fe, New Mexico
Santa Fe ( ; , literal translation, lit. "Holy Faith") is the capital city, capital of the U.S. state of New Mexico, and the county seat of Santa Fe County. With over 89,000 residents, Santa Fe is the List of municipalities in New Mexico, fourt ...
( away);
Ciudad Chihuahua, Chihuahua, ( away), and
Hermosillo
Hermosillo (), formerly called Pitic (as in ''Santísima Trinidad del Pitic'' and ''Presidio del Pitic''), is a city in the center of the northwestern Mexican state of Sonora. It is the municipal seat of the Hermosillo municipality, the state's ...
, Sonora ( away)—than it is to the capital of its own state,
Austin ( away). It is closer to
Los Angeles, California
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
( away) than it is to
Orange, Texas ( away), the easternmost town in the same state as this city.
El Paso is located within the
Chihuahuan Desert, the easternmost section of the
Basin and Range Region. The
Franklin Mountains extend into El Paso from the north and nearly divide the city into two sections; the west side forms the beginnings of the
Mesilla Valley, and the east side expands into the desert and lower valley. They connect in the central business district at the southern end of the mountain range.
The city's elevation is above sea level.
North Franklin Mountain is the highest peak in the city at above sea level. The peak can be seen from in all directions. Additionally, this mountain range is home to the famous natural red-clay formation, the Thunderbird, from which the local
Coronado High School gets its mascot's name. According to the
United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, econ ...
, the city has a total area of .
The
Franklin Mountains State Park,
one of the largest urban parks in the United States, lies entirely in El Paso, extending from the north and dividing the city into several sections along with Fort Bliss and
El Paso International Airport.
The
Rio Grande Rift, which passes around the southern end of the Franklin Mountains, is where the Rio Grande flows. The river defines the border between El Paso and Ciudad Juárez to the south and west until the river turns north of the border with Mexico, separating El Paso from
Doña Ana County, New Mexico.
Mt. Cristo Rey, an example of a
pluton, rises within the Rio Grande Rift just to the west of El Paso on the New Mexico side of the Rio Grande. Nearby volcanic features include
Kilbourne Hole and
Hunt's Hole, which are
Maar volcanic craters west of the Franklin Mountains.
On November 8, 2023, a 5.3 magnitude
Earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they ...
struck the El Paso region. The epicenter of the earthquake was 22 miles (35 kilometers) southwest of
Mentone, according to the
USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an government agency, agency of the United States Department of the Interior, U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geograp ...
Cityscape
Tallest buildings


El Paso's second-tallest building, the Wells Fargo Plaza, was built in the early 1970s as State National Plaza. The black-windowed,
building is famous for its 13 white horizontal lights (18 lights per row on the east and west sides of the building, and seven bulbs per row on the north and south sides) that were lit at night. The tower did use a design of the United States flag during the
July 4
Events Pre-1600
* 362 BC – Battle of Mantinea: The Thebans, led by Epaminondas, defeated the Spartans.
* 414 – Emperor Theodosius II, age 13, yields power to his older sister Aelia Pulcheria, who reigned as regent and procla ...
holidays, as well as the American hostage crisis of 1980, and was lit continuously following the
September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, also known as 9/11, were four coordinated Islamist terrorist suicide attacks by al-Qaeda against the United States in 2001. Nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercial airliners, crashing the first two into ...
in 2001 until around 2006. During the Christmas holidays, a design of a Christmas tree was used, and at times, the letters "UTEP" were used to support University of Texas at El Paso athletics. The tower is now only lit during the holiday months, or when special events take place in the city.
Neighborhoods
= Downtown and central El Paso
=

This part of town contains some of the city's oldest and most historic neighborhoods. Located in the heart of the city, it is home to about 44,993 people. Development of the area started in 1827 with the first resident, Juan Maria Ponce de Leon, a wealthy merchant from Paso del Norte (present-day Ciudad Juárez), who built the region's first structure establishing Rancho Ponce within the vicinity of S. El Paso Street and Paisano Dr. when the city was barely beginning. Today, central El Paso has grown into the center of the city's economy and a thriving urban community. It contains numerous historic sites and landmarks, many in the
Sunset Heights district. Other historic districts in this area include the Rio Grade Avenue Historic District, Segundo Barrio Historic District, and the Magoffin Historic District. It is close to the El Paso International Airport, the international border, and Fort Bliss. It is part of the
El Paso Independent School District
The El Paso Independent School District (or EPISD) is the largest school district serving El Paso, Texas, El Paso, Texas (United States, USA). Originally organized in 1883, it is currently the largest district in the Texas Education Agency's E ...
.

Dr. James Day, an El Paso historian, said that downtown's main business area was originally centered between Second Avenue (now Paisano Drive) and San Francisco Avenue. At a later point, the main business area was centered around Stanton Street and Santa Fe Street. In the late 1800s, most of the
White American
White Americans (sometimes also called Caucasian Americans) are Americans who identify as white people. In a more official sense, the United States Census Bureau, which collects demographic data on Americans, defines "white" as " person having ...
residents lived to the north of the non-White areas, living in brick residences along Magoffin, Myrtle, and San Antonio Avenues.
Hispanic-American residents lived in an area called
Chihuahuita ("little
Chihuahua"), which was located south of Second Avenue and west of Santa Fe Street. Several African Americans and around 300 Chinese Americans also lived in Chihuahuita. Many of the Chinese Americans participated in the building of railroads in the El Paso area. Another downtown neighborhood is
El Segundo Barrio, which is near the Mexico–U.S. border.
= Northwest El Paso
=
Better known as West El Paso or the West Side, the area includes a portion of the Rio Grande floodplain upstream from downtown, which is known locally as the Upper Valley and is located on the west side of the
Franklin Mountains. The Upper Valley is the greenest part of the county due to the Rio Grande. The West Side is home to some of the most affluent neighborhoods within the city, such as the Coronado Hills, Country Club, and Three Hills neighborhoods. It is one of the fastest-growing areas of El Paso. The main high schools in the westside include
Canutillo High School,
Coronado High School (El Paso, Texas), and
Franklin High School (El Paso, Texas)
Franklin High School is a public high school located on the west side of El Paso, Texas, which is part of the El Paso Independent School District. It opened in 1993. Its name refers to the nearby Franklin Mountains. Although the student populati ...
.
= West-central El Paso
=

West-central El Paso is located north of Interstate 10 and west of the Franklin Mountains.
The University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP) and the Cincinnati Entertainment district are located in the heart of the area. Historic districts
Kern Place and
Sunset Heights are in this part of town.
Kern Place was founded in 1914 by
Peter E. Kern, for whom the neighborhood was named.
The homes of Kern Place are unique in architecture and some were built by residents themselves.
One of the better known homes is the Paul Luckett Home located at 1201 Cincinnati Ave. above Madeline Park, and is made of local rock. It is known as "The Castle" due to its round walls and a crenelated rooftop.
Kern Place is extremely popular with college and university students. The area is known for its glitzy entertainment district, restaurants and coffee shops that cater to both business patrons and university students. After UTEP's basketball and football games, UTEP fans pack the Kern Place area for food and entertainment at Cincinnati Street, a small bar district. This bar scene has grown over the years and has attracted thousands to its annual
Mardi Gras block party
A block party or street party is a party in which many members of a single community congregate, either to observe an event of some importance or simply for mutual solidarity and enjoyment. The name comes from the form of the party, which ofte ...
, as well as after sporting events or concerts. Young men and women make up the
majority
A majority is more than half of a total; however, the term is commonly used with other meanings, as explained in the "#Related terms, Related terms" section below.
It is a subset of a Set (mathematics), set consisting of more than half of the se ...
of the crowds who stop in between classes or after work.
Sunset Heights is one of the most historic areas in town, which has existed since the latter part of the 1890s. Many wealthy residents have had their houses and mansions built on this hill. Although some buildings have been renovated to their former glory, many have been neglected and have deteriorated. During the Mexican Revolution widely popular revolutionary leader
Pancho Villa
Francisco "Pancho" Villa ( , , ; born José Doroteo Arango Arámbula; 5 June 1878 – 20 July 1923) was a Mexican revolutionary and prominent figure in the Mexican Revolution. He was a key figure in the revolutionary movement that forced ...
owned and resided in this area during the 1910s. During the 1910 Mexican Revolution many Mexicans fled Mexico and settled in Sunset Heights.
= Northeast El Paso
=

This part of town is located north of
central El Paso and east of the Franklin Mountains. Development of the area was extensive during the 1950s and 1960s. It is one of the more ethnically diverse areas in the city due to the concentration of military families. The Northeast has not developed as rapidly as other areas, such as
east El Paso and northwest El Paso, but its development is steadily increasing. The population is expected to grow more rapidly as a result of the troop increase at Ft. Bliss in the coming years. The area has also gained recognition throughout the city for the outstanding high-school athletic programs at
Andress High School,
Parkland High School,
Irvin High School, and
Chapin High School.
In May 2021 a major developer announced plans for a Master Planned Community in the Northeast modeled after Scarborough's Sunfield Master Planned Community in Buda, Texas. The first phase of the development is to include about 2,500 homes, 10-acre park, walking trails, a four-acre resort-like area with a lazy river, kiddy splash pad, pool, grass areas, and a food truck area, the developers reported. Jessica Herrera, director of the city of El Paso Economic and International Development Department, in a statement released by the developers, said Campo del Sol will generate hundreds of millions of dollars in tax revenues, "which will stimulate other growth and development on the north side of town".
= East El Paso
=
The area is located north of Interstate 10, east of Airway Blvd., and south of Montana Ave. It is the largest and fastest growing area of town with a population over 200,000. It includes the 79936 ZIP Code, which was considered in 2013 as the most populous in the nation with over 114,000 people.
= Mission Valley
=
Formerly known as the lower valley, it includes part of Eastside and all lower valley districts. It is the third-largest area of the city, behind east El Paso and central El Paso. Hawkins Road and Interstate 10 border the Mission Valley. This location is considered the oldest area of El Paso, dating back to the late 16th century when present-day Texas was under the rule of
New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
.
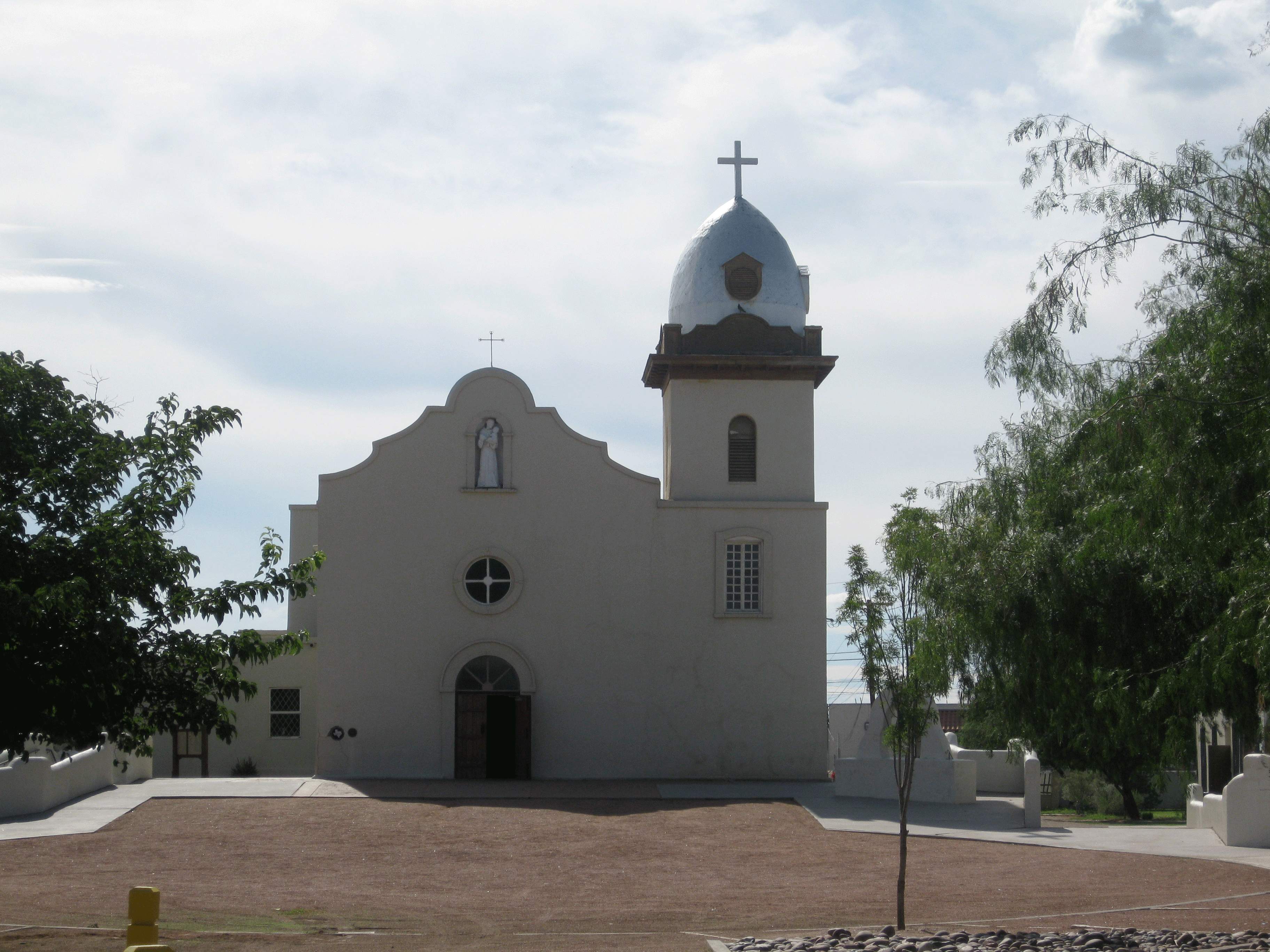

In 1680, the Isleta Pueblo tribe revolted against the Spaniards who were pushed south to what is now El Paso. Some Spaniards and tribe members settled here permanently. Soon afterward, three Spanish missions were built; they remain standing, currently functioning as churches:
Ysleta Mission-1682 (La Misión de Corpus Christi y de San Antonio de la Ysleta del Sur/Our Lady of Mt. Carmel),
Socorro Mission-1759 (Nuestra Señora de la Purísima Concepción del Socorro)-1759, and
San Elizario Chapel (Capilla de San Elcear)-1789.
On April 30, 1598, the northward-bound Spanish conquistadors crossed large sand dunes about 27 miles south of present-day downtown El Paso. The expeditionaries and their horses reportedly ran toward the river, and two horses drank themselves to death.
Don Juan de Oñate, a New Spain-born conquistador of Spanish parents, was an expedition leader who ordered a big feast north of the Río Grande in what is now San Elizario. This was the first documented and true Thanksgiving in North America. Oñate declared''
la Toma'' (taking possession), claiming all territory north of the Río Grande for King
Philip II of Spain
Philip II (21 May 152713 September 1598), sometimes known in Spain as Philip the Prudent (), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from 1580, and King of Naples and List of Sicilian monarchs, Sicily from 1554 until his death in 1598. He ...
.
Ysleta Del Sur Pueblo (related to the insurgent Isleta Pueblo Tribe) is also located in this valley. The Tigua is one of three Indian tribes in Texas whose sovereignty is recognized by the United States government. Ysleta is spelled with a "Y" because 19th-century script did not differentiate between a capital "Y" and a capital "I".
Some people in this area and its twin city across the river, Ciudad Juárez, are direct descendants of the Spaniards.
= Texas and New Mexico suburbs
=
El Paso is surrounded by many cities and communities in both Texas and New Mexico. The most populated suburbs in Texas are
Socorro,
Horizon City, Fort Bliss, and San Elizario. Other Texas suburbs are
Anthony,
Canutillo,
Sparks,
Fabens, and
Vinton.
Although
Anthony,
Santa Teresa,
Sunland Park, and
Chaparral
Chaparral ( ) is a shrubland plant plant community, community found primarily in California, southern Oregon, and northern Baja California. It is shaped by a Mediterranean climate (mild wet winters and hot dry summers) and infrequent, high-intens ...
lie adjacent to El Paso County, they are considered to be part of the
Las Cruces, New Mexico
Las Cruces (; ; lit. 'the crosses') is the List of municipalities in New Mexico, second-most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico and the county seat, seat of Doña Ana County, New Mexico, Doña Ana County. As of the 2020 United States ce ...
metropolitan area by the United States Census Bureau.
Climate

El Paso has a
hot desert climate
The desert climate or arid climate (in the Köppen climate classification ''BWh'' and ''BWk'') is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in desert ...
(
Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (1951–2014), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author ...
''BWh'') featuring hot summers, with little humidity, and cool to mild, dry winters. Rainfall averages per year, much of which occurs from June through September, and is predominantly caused by the
North American Monsoon. During this period, southerly and southeasterly winds carry moisture from the Pacific, the
Gulf of California
The Gulf of California (), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Vermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja California peninsula from ...
, and the
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
into the region. When this moisture moves into the El Paso area and places to the southwest, orographic lift from the mountains, combined with strong daytime heating, causes
thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustics, acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorm ...
s, some severe enough to produce flash flooding and hail, across the region.
The sun shines 302 days per year on average in El Paso, 83% of daylight hours, according to the
National Weather Service
The National Weather Service (NWS) is an Government agency, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government that is tasked with providing weather forecasts, warnings of hazardous weather, and other weathe ...
; from this, the city is nicknamed "The Sun City". Due to its arid, windy climate, El Paso often experiences sand and dust storms during the dry season, particularly during the springtime between March and early May. With an average wind speed often exceeding and gusts that have been measured at over , these wind storms kick up large amounts of sand and dust from the desert, causing loss of visibility.

El Paso and the nearby mountains also receive snow. Weather systems have produced over of snow on several occasions. In the 1982–1983 winter season, three major snowstorms produced record seasonal snowfall. On December 25–26, 1982, of snow fell, producing a white Christmas for the city.
[ This was followed by another on December 30–31, 1982. On April 4–7, 1983, of snow fell on El Paso, bringing the seasonal total to nearly . On December 13–14, 1987, a record storm dumped over of snow on El Paso, and two weeks later (December 25–26), another fell, bringing the monthly total for December 1987 to an all-time record high of of snow.] One example of El Paso's varying climate at its most extreme was the damaging winter storm of early February 2011, which caused closures of schools, businesses, and City Hall. The snow, which was light, stopped after about a day, but during the ensuing cold episode, municipal utilities went into a crisis. The high temperature on February 2, 2011, was , the lowest daily maximum on record. In addition, the low temperature on February 3 was , breaking the monthly record low set during the cold wave of 1899.
One example of El Paso's varying climate at its most extreme was the damaging winter storm of early February 2011, which caused closures of schools, businesses, and City Hall. The snow, which was light, stopped after about a day, but during the ensuing cold episode, municipal utilities went into a crisis. The high temperature on February 2, 2011, was , the lowest daily maximum on record. In addition, the low temperature on February 3 was , breaking the monthly record low set during the cold wave of 1899.[ Loss of desert vegetation, such as Mexican/California palm trees, oleanders, and iceplants to the cold weather was one of the results. Two local power plants failed, forcing El Paso Electric to institute ]rolling blackout
A rolling blackout, also referred to as rota or rotational load shedding, rota disconnection, feeder rotation, or a rotating outage, is an intentionally engineered electrical power shutdown in which electricity delivery is stopped for non-over ...
s over several days, and electric wires were broken, causing localized blackouts. Many water utility pipes froze, causing areas of the city to be without water for several days.
Monthly means range from in December to in July, but high temperatures typically peak in June before the monsoon arrives, while daily low temperatures typically peak in July or early August with the higher humidity the monsoon brings (translating to warmer nights). On average, 42 night lows are at or below freezing, with 118 days of + highs and 28 days of + highs annually; extremely rarely do temperatures stay below the freezing mark all day.National Weather Service
The National Weather Service (NWS) is an Government agency, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government that is tasked with providing weather forecasts, warnings of hazardous weather, and other weathe ...
since 1879.
Flooding
 Although the average annual rainfall is only about 8.8 in (225 mm), many parts of El Paso are subject to occasional flooding during intense summer monsoonal thunderstorms. In late July and early August 2006, up to of rain fell in a week, the flood-control reservoirs overflowed and caused major flooding citywide. The city staff estimated damage to public infrastructure at $21 million, and to private property (residential and commercial) at $77 million. Much of the damage was associated with development in recent decades in arroyos protected by flood-control dams and reservoirs, and the absence of any storm drain utility in the city to handle the flow of rain water.
Although the average annual rainfall is only about 8.8 in (225 mm), many parts of El Paso are subject to occasional flooding during intense summer monsoonal thunderstorms. In late July and early August 2006, up to of rain fell in a week, the flood-control reservoirs overflowed and caused major flooding citywide. The city staff estimated damage to public infrastructure at $21 million, and to private property (residential and commercial) at $77 million. Much of the damage was associated with development in recent decades in arroyos protected by flood-control dams and reservoirs, and the absence of any storm drain utility in the city to handle the flow of rain water.
Demographics
At the 2010 U.S. census, 649,121 people, 216,694 households, and 131,104 families resided in the city. The 2019 U.S. Census Bureau estimates determined El Paso had a population of 681,728, an increase of 5.2% since the 2010 census.
German communities
By 1996, a German community existed in El Paso, as the German Air Force headquarters for North America is in El Paso. A German school in El Paso serves all grade levels, though as of 1996, most of its students begin attending American schools at the secondary level. The German school is on Fort Bliss
Fort Bliss is a United States Army post in New Mexico and Texas, with its headquarters in El Paso, Texas. Established in 1848, the fort was renamed in 1854 to honor William Wallace Smith Bliss, Bvt.Lieut.Colonel William W.S. Bliss (1815–1853 ...
.
Religion
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
is the largest religion in the city and its metropolitan statistical area. Nearly 45% of its population claimed affiliation with the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
in 2020; they are served by the Roman Catholic Diocese of El Paso. Protestants
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
form a minority of Christians in the city limits, and the remainder of the non-Christian population were followers of Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
, Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
, or eastern faiths, including Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
or Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
. The irreligious made the second largest non-Christian group.
Economy
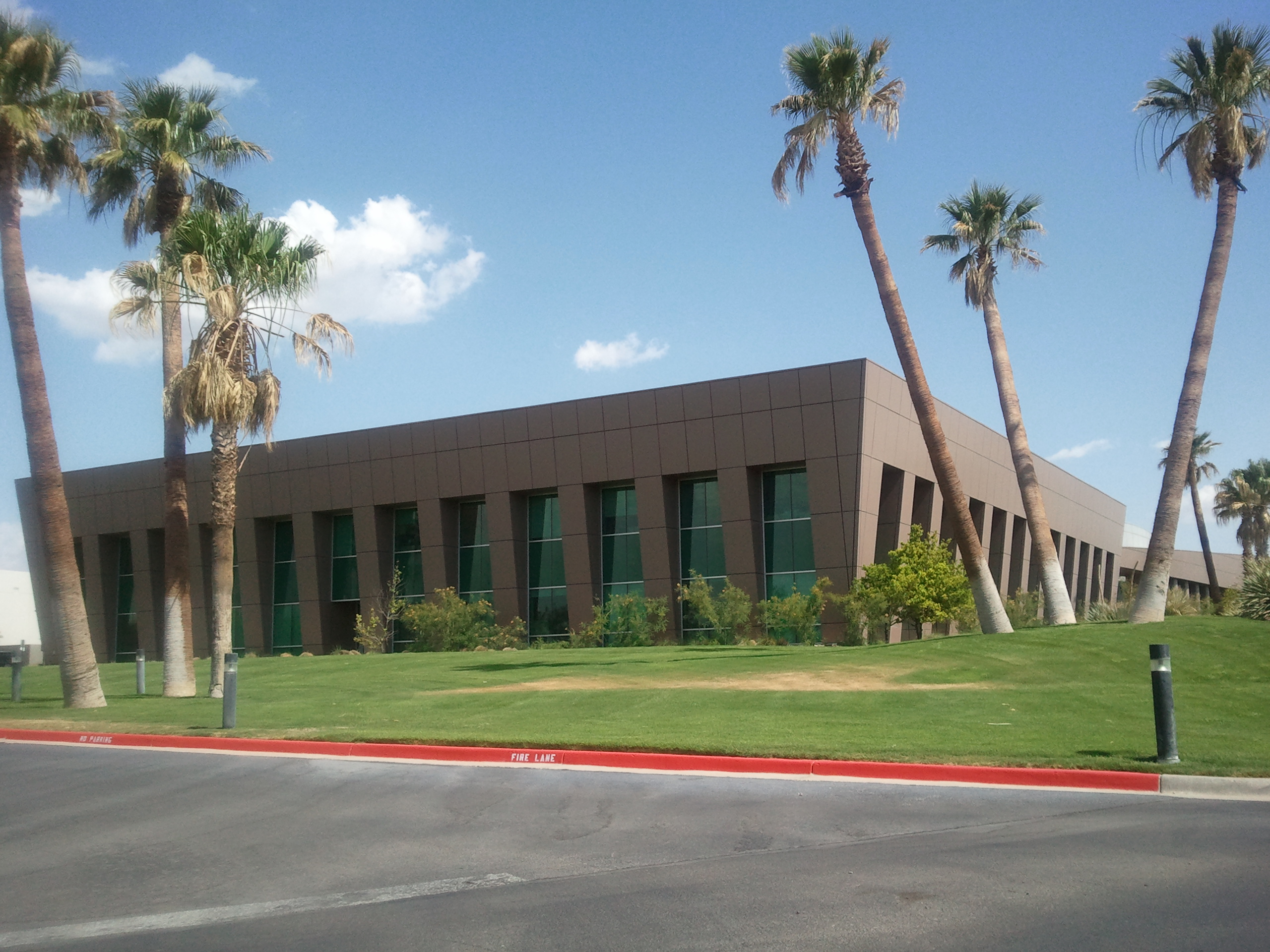 El Paso has a diversified economy focused primarily within
El Paso has a diversified economy focused primarily within international trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories because there is a need or want of goods or services. (See: World economy.)
In most countries, such trade represents a significan ...
, military, government civil service, oil and gas
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geologi ...
, health care, tourism, and service
Service may refer to:
Activities
* Administrative service, a required part of the workload of university faculty
* Civil service, the body of employees of a government
* Community service, volunteer service for the benefit of a community or a ...
sectors. The El Paso metro area had a GDP of $29.03 billion in 2017. There was also $92 billion worth of trade in 2012. Over the past 15 years the city has become a significant location for American-based call centers
A call centre (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling) or call center (American English, American spelling; American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, see spelling differences) is a managed capability th ...
. Cotton, fruit, vegetables, and livestock are also produced in the area. El Paso has added a significant manufacturing sector with items and goods produced that include petroleum, metals, medical devices, plastics, machinery, defense-related goods, and automotive parts. On July 22, 2020, Amazon announced plans to open the first 625,000 square foot fulfillment center in El Paso. Owing to its location on a border, the city is the second-busiest international crossing point in the U.S. behind San Diego
San Diego ( , ) is a city on the Pacific coast of Southern California, adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a population of over 1.4 million, it is the List of United States cities by population, eighth-most populous city in t ...
.
El Paso is home to one ''Fortune ''500 company, Western Refining, which is listed on the New York Stock Exchange
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE, nicknamed "The Big Board") is an American stock exchange in the Financial District, Manhattan, Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It is the List of stock exchanges, largest stock excha ...
(NYSE). This makes the city one of six Texas metro areas to have at least one ''Fortune'' 500 company call it home; the others being Houston
Houston ( ) is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in the U.S. state of Texas and in the Southern United States. Located in Southeast Texas near Galveston Bay and the Gulf of Mexico, it is the county seat, seat of ...
, Dallas-Fort Worth, San Antonio
San Antonio ( ; Spanish for " Saint Anthony") is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the most populous city in Greater San Antonio. San Antonio is the third-largest metropolitan area in Texas and the 24th-largest metropolitan area in the ...
, Austin, and Corpus Christi. The second publicly traded company is Helen of Troy Limited
Helen of Troy Limited is an American publicly traded designer, developer and worldwide marketer of consumer brand-name housewares, health and home, and beauty products under owned and licensed brands. It is the parent corporation of OXO Interna ...
, a NASDAQ
The Nasdaq Stock Market (; National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations) is an American stock exchange based in New York City. It is the most active stock trading venue in the U.S. by volume, and ranked second on the list ...
-listed company that manufactures personal health-care products under many labels, such as OXO, Dr. Scholl's, Vidal Sassoon, Pert Plus, Brut, and Sunbeam
A sunbeam, in meteorological optics, is a lightbeam, beam of sunlight that appears to radiate from the position of the Sun. Shining through openings in clouds or between other objects such as mountains and buildings, these beams of light scatter ...
, and the third is El Paso Electric listed on the NYSE, a public utility
A public utility company (usually just utility) is an organization that maintains the infrastructure for a public service (often also providing a service using that infrastructure). Public utilities are subject to forms of public control and ...
engaging in the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity in West Texas and southern New Mexico. The fourth publicly traded company is Western Refining Logistics, also traded in the NYSE. It is a Western Refining subsidiary, which owns, operates, develops, and acquires terminals, storage tanks, pipelines, and other logistics assets.
More than 70 ''Fortune'' 500 companies have offices in El Paso, including AT&T
AT&T Inc., an abbreviation for its predecessor's former name, the American Telephone and Telegraph Company, is an American multinational telecommunications holding company headquartered at Whitacre Tower in Downtown Dallas, Texas. It is the w ...
, ADP, Boeing
The Boeing Company, or simply Boeing (), is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product support s ...
, Charles Schwab, Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), was an ancient sacred precinct and the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient Classical antiquity, classical world. The A ...
, Dish Network
DISH Network L.L.C., often referred to as DISH, an abbreviation for Digital Sky Highway, is an American provider of satellite television and IPTV services and wholly owned subsidiary of EchoStar Corporation.
The company was originally establ ...
, Eureka, Hoover, Raytheon
Raytheon is a business unit of RTX Corporation and is a major U.S. defense contractor and industrial corporation with manufacturing concentrations in weapons and military and commercial electronics. Founded in 1922, it merged in 2020 with Unite ...
, USAA
The United Services Automobile Association (USAA) is an American financial services company providing insurance and banking products exclusively to members of the military, veterans and their families. It was founded in 1922 in San Antonio, Texas ...
and Verizon Wireless. Hispanic Business Magazine included 28 El Paso companies in its list of the 500 largest Hispanic owned businesses in the United States. El Paso's 28 companies are second only to Miami's 57. The list of the largest Hispanic owned businesses includes companies like Fred Loya Insurance, a Hispanic 500 company and the 18th largest Hispanic business in the nation. Other companies on the list are Dos Lunas Spirits, Dynatec Labs, Spira Footwear, DATAMARK, Inc. and El Taco Tote. El Paso was home to El Paso Corporation formerly known as El Paso Natural Gas Company.
The city also has a large military presence with Fort Bliss, William Beaumont Army Medical Center, and Biggs Army Airfield
Biggs Army Airfield (formerly Biggs Air Force Base) is a United States Army military airbase located on the Fort Bliss military base in El Paso, Texas.
History Biggs Field/Biggs Army Airfield (1916–47)
On 15 June 1919, following an attack ...
. The defense industry in El Paso employs over 41,000 and provides a $6 billion annual impact to the city's economy. In 2013, Fort Bliss was chosen as the newly configured U.S. Air Force Security Forces Regional Training Center which added 8,000 to 10,000 Air Force personnel annually.
In addition to the military, the federal government has a strong presence in El Paso to manage its status and unique issues as an important border region. Operations headquartered in El Paso include the DEA Domestic Field Division 7, El Paso Intelligence Center, Joint Task Force North, U.S. Border Patrol El Paso Sector, and U.S. Border Patrol Special Operations Group.
Call-center operations employ more than 10,000 people in the area. Automatic Data Processing
Automatic Data Processing, Inc. (ADP) is an American provider of human resources management software and services, headquartered in Roseland, New Jersey.
History
In 1949, Henry Taub founded Automatic Payrolls, Inc. as a manual payroll processin ...
has an office in West El Paso, employing about 1,100 people with expansion plans to reach 2,200 by 2020.
Tourism is another major industry in El Paso, bringing in $1.5 billion and over 2.3 million visitors annually due to the city's sunny weather, natural beauty, rich cultural history, and many outdoor attractions.
Education is also a driving force in El Paso's economy. El Paso's three large school districts are among the largest employers in the area, employing more than 20,000 people among them. UTEP has an annual budget of nearly $418 million and employs nearly 4,800 people. A 2010 study by the university's Institute for Policy and Economic Development stated the university's impact on local businesses is $417 million annually.
Arts and culture
The culture of El Paso, Texas is influenced heavily by the mixing of American and Mexican cultures, due to the city's position on the U.S. Mexico border, its large Chicano population, and its history as part of Hispanic America and Mexico.
Annual cultural events and festivals
The Amigo Airsho is one of El Paso's premier events, and is ranked as one of the top-10 air shows in the country, filled with air entertainment and ground activities. Acts include the Franklin's Flying Circus, where performers walk on the wings of an airborne plane. Ground activities include a jet-powered school bus. After 31 years of being held at Biggs Army Airfield, the show was moved to Dona Ana Airport in 2014.
The KLAQ Great River Raft Race is an annual event celebrated on the second to last Saturday of June. Participants are encouraged to ride the river and float the Rio Grande with family and friends. The organizers encourage the building of unique rafts that get down the river, with prizes and trophies awarded for the most points earned, best-looking crew, and best-decorated raft. The race starts at the Vinton Bridge and ends 3 miles downstream at the Canutillo Bridge.
The Southwestern International PRCA Rodeo is the 17th-oldest rodeo in the nation and El Paso's longest-running sporting event. Consistently ranked as one of the top 50 shows in the country by the Professional Rodeo Cowboys Association
The Professional Rodeo Cowboys Association (PRCA) is the largest rodeo organization in the world. It sanctions events in the United States, Canada, and Mexico, with members from said countries, as well as others. Its championship event is the N ...
, this charitable event is a true celebration of western culture and heritage.
 La Fiesta de las Flores is one of the oldest Hispanic festivals in the Southwest. The three-day fiesta is held each year during the Labor Day weekend and emphasizes El Paso's Hispanic heritage and culture. The festival attracts 20,000 to 30,000 visitors from El Paso County, New Mexico, West Texas, and the State of Chihuahua, Mexico. Activities included in the fiesta are crowning of the queen, a Fiesta Parade, Senior Appreciation Dance, Military Appreciation Day, and live entertainment. The fiesta is also well known for the authentic regional cuisine, arts and crafts, games, and services available for the enjoyment of all attendees. Over 80 booths, sponsored by local vendors and nonprofit organizations, create the Hispanic ambience and culture.
The El Paso Balloonfest is an annual event celebrated on Memorial Day weekend and is self described as "3 days of hot air balloons filling the El Paso skies, 3 afternoons of concerts and fun in the sun at Wet N' Wild Waterworld in Anthony, Texas". Over 60 balloons take to the air from TFCU launch field, which is adjacent to the water park. After the balloons launch, visitors have a weekend of water rides, swimming, concerts, and grilling. The concert aspect of the event features local bands, starting at noon, and different headlining artists in the afternoon. Overnight camping has been added for 2014.
The El Paso Sun City Pride is the largest annual
La Fiesta de las Flores is one of the oldest Hispanic festivals in the Southwest. The three-day fiesta is held each year during the Labor Day weekend and emphasizes El Paso's Hispanic heritage and culture. The festival attracts 20,000 to 30,000 visitors from El Paso County, New Mexico, West Texas, and the State of Chihuahua, Mexico. Activities included in the fiesta are crowning of the queen, a Fiesta Parade, Senior Appreciation Dance, Military Appreciation Day, and live entertainment. The fiesta is also well known for the authentic regional cuisine, arts and crafts, games, and services available for the enjoyment of all attendees. Over 80 booths, sponsored by local vendors and nonprofit organizations, create the Hispanic ambience and culture.
The El Paso Balloonfest is an annual event celebrated on Memorial Day weekend and is self described as "3 days of hot air balloons filling the El Paso skies, 3 afternoons of concerts and fun in the sun at Wet N' Wild Waterworld in Anthony, Texas". Over 60 balloons take to the air from TFCU launch field, which is adjacent to the water park. After the balloons launch, visitors have a weekend of water rides, swimming, concerts, and grilling. The concert aspect of the event features local bands, starting at noon, and different headlining artists in the afternoon. Overnight camping has been added for 2014.
The El Paso Sun City Pride is the largest annual LGBT
LGBTQ people are individuals who are lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, or questioning. Many variants of the initialism are used; LGBTQIA+ people incorporates intersex, asexual, aromantic, agender, and other individuals. The gro ...
event in the region, attracting thousands every June. The event was established in 2007.
Music festivals
The annual El Paso Downtown Street Festival is held during the last weekend of June in downtown El Paso near the El Paso Convention Center. It is the oldest musical festival in the city and brings local, regional, and nationally known acts.
The annual Neon Desert Music Festival is a two-day event usually held on the last Saturday and Sunday of May on five stages in downtown El Paso, stretching from San Jacinto Plaza to Cleveland Square. The festival brings over 30 acts from the worlds of indie rock, Latin, and electronic dance music.
The outdoor concert series, started in 1983, is held annually at the Chamizal National Memorial and draws over 60,000 attendees. It features local and international performers with wide-ranging musical genres: Classical, Country, Tejano, rock and others. The evening concerts are showcased every Sunday afternoon and start in early June and end in the middle of August.
The only El Paso musical festival not held downtown, instead it is held at Ascarate Park. The Sun City Music Festival is a two-day event dubbed as the largest electronic dance music festival in Texas.
The Texas Showdown Festival is an annual event celebrating musicians and tattoo artists under one roof. Dubbed as the world's largest tattoo and musical festival, the event is held usually the last weekend of July at the El Paso County Coliseum.
Comedy festivals
The ChucoTown Comedy Festival is the first comedy festival established in the El Paso region, bringing together comedy enthusiasts to celebrate in downtown El Paso. Launched in 2024, the festival showcases a diverse lineup of local comedians and headlining acts from across the country. Founded by ChucoTown Comedy, the festival is the culmination of a year-round production of comedy shows, building anticipation and support within the local and regional comedy community.
Performing arts
 The outdoor musical extravaganza '' Viva! El Paso'' is performed in the McKelligon Canyon Amphitheatre. It is locally produced and chronicles the 400-year history and cultural evolution of the El Paso region. The show is performed each Friday and Saturday night in June, July, and August. It has entertained local residents and out-of-town visitors for over 35 years.
The El Paso Symphony was established in the 1930s, and is the oldest performing-arts organization in El Paso and the longest continuously running symphony orchestra in Texas. It has received both national and international recognition as a result of its very successful tours of Germany in 1996 and Turkey in 2000, and continues to represent the El Paso region with pride and distinction.
The El Paso Symphony Orchestra Association season is anchored by 12 classical concerts. Special events serve as outreach toward new audiences.
Ballet was largely nonexistent in El Paso until the arrival of Ingeborg Heuser, a professional ballerina from Germany, in the 1950s. Heuser taught ballet at UTEP for 47 years and founded the city's first professional ballet company, firstly known as Texas Western Civic Ballet and eventually as ''Ballet El Paso''. The company dissipated due to financial trouble in 1997 and Heuser retired from UTEP soon after. The El Paso Youth Ballet was founded in 2009 by Heuser's student, Marta Katz, following Heuser's departure from the university. With students from the youth ballet, Heuser staged her last ''Nutcracker'' in 2006. The youth company continues to perform the ''Nutcracker'' and other preprofessional pieces in and around the El Paso area. The company provides the only platform for young ballet dancers to train and perform at such a level within the city since the folding of Ballet El Paso.
El Paso City Ballet is a current professional ballet company in El Paso, providing local employment for professional dancers in the field of ballet. The company performs a variety of classical and contemporary works choreographed by Artistic Director Lisa Skaf and artists from the US and Latin America. It has been active since 2005, performing yearly productions.
The outdoor musical extravaganza '' Viva! El Paso'' is performed in the McKelligon Canyon Amphitheatre. It is locally produced and chronicles the 400-year history and cultural evolution of the El Paso region. The show is performed each Friday and Saturday night in June, July, and August. It has entertained local residents and out-of-town visitors for over 35 years.
The El Paso Symphony was established in the 1930s, and is the oldest performing-arts organization in El Paso and the longest continuously running symphony orchestra in Texas. It has received both national and international recognition as a result of its very successful tours of Germany in 1996 and Turkey in 2000, and continues to represent the El Paso region with pride and distinction.
The El Paso Symphony Orchestra Association season is anchored by 12 classical concerts. Special events serve as outreach toward new audiences.
Ballet was largely nonexistent in El Paso until the arrival of Ingeborg Heuser, a professional ballerina from Germany, in the 1950s. Heuser taught ballet at UTEP for 47 years and founded the city's first professional ballet company, firstly known as Texas Western Civic Ballet and eventually as ''Ballet El Paso''. The company dissipated due to financial trouble in 1997 and Heuser retired from UTEP soon after. The El Paso Youth Ballet was founded in 2009 by Heuser's student, Marta Katz, following Heuser's departure from the university. With students from the youth ballet, Heuser staged her last ''Nutcracker'' in 2006. The youth company continues to perform the ''Nutcracker'' and other preprofessional pieces in and around the El Paso area. The company provides the only platform for young ballet dancers to train and perform at such a level within the city since the folding of Ballet El Paso.
El Paso City Ballet is a current professional ballet company in El Paso, providing local employment for professional dancers in the field of ballet. The company performs a variety of classical and contemporary works choreographed by Artistic Director Lisa Skaf and artists from the US and Latin America. It has been active since 2005, performing yearly productions.
Theaters
 The Plaza Theatre is a National Historic Building of Significance built in 1930.
The Plaza Theatre is a National Historic Building of Significance built in 1930.concert hall
A concert hall is a cultural building with a stage (theatre), stage that serves as a performance venue and an auditorium filled with seats.
This list does not include other venues such as sports stadia, dramatic theatres or convention ...
adjacent to the Williams Convention Center. Its exterior resembles a '' sombrero'' and features a three-story glass main entrance. The theatre is named after Maestro Abraham Chavez, who was the longtime conductor of the El Paso Symphony. Inside, the theatre has a lobby and a 40-by-56-ft stage, as well as 14 dressing rooms. The theater's seating is in three levels. Also, a meeting room is adjacent to the theater.concerts
A concert, often known informally as a gig or show, is a live performance of music in front of an audience. The performance may be carried by a single musician, in which case it is sometimes called a recital, or by a musical ensemble such as an ...
, Broadway shows, graduation
A graduation is the awarding of a diploma by an educational institution. It may also refer to the ceremony that is associated with it, which can also be called Commencement speech, commencement, Congregation (university), congregation, Convocat ...
ceremonies, performances of the El Paso Symphony Orchestra, and other special events.
McKelligon Canyon is a park, located in the Franklin Mountains, open to hikers and picnickers. In the canyon, McKelligon Canyon Amphitheatre is surrounded on three sides by canyon walls; the 1,500-seat amphitheater is used for concerts and special events, such as ''Viva! El Paso''.
The El Paso Playhouse, a community theatre, provides entertainment and educational experiences to a diverse multicultural population through the high-quality production of plays and theatrical events. The playhouse provides a venue for artists, technicians, patrons, and community members to participate in the arts through regularly scheduled season productions and holiday performances. The theater is affiliated with Kids-N-Co, a theater for child actors to children's performances .
The University of Texas, El Paso Dinner Theatre located inside the University of Texas, El Paso campus, and was founded in 1983 and is entirely produced, designed and directed by students. The theatre presents 4 fully staged musicals each season and a fully staged student produced musical.
Area museums
 The Centennial Museum and Chihuahuan Desert Gardens, located on the grounds of UTEP, includes a comprehensive collection of El Paso Brown, Native American pottery, as well as educational exhibits for students.
The El Paso Museum of Archaeology is located on the eastern slope of North Franklin Mountain, west of Gateway South Blvd. on TransMountain Rd. Its grounds include native plants of the American Southwest, as well samples of Native American shelters, in an unspoiled location. The museum includes
The Centennial Museum and Chihuahuan Desert Gardens, located on the grounds of UTEP, includes a comprehensive collection of El Paso Brown, Native American pottery, as well as educational exhibits for students.
The El Paso Museum of Archaeology is located on the eastern slope of North Franklin Mountain, west of Gateway South Blvd. on TransMountain Rd. Its grounds include native plants of the American Southwest, as well samples of Native American shelters, in an unspoiled location. The museum includes diorama
A diorama is a replica of a scene, typically a three-dimensional model either full-sized or miniature. Sometimes dioramas are enclosed in a glass showcase at a museum. Dioramas are often built by hobbyists as part of related hobbies like mili ...
s for school children that illustrate the culture and geology of the American Southwest, such as Hueco Tanks in El Paso County. One diorama (see image to the right) is of the Cueva de la Olla (cave of the pot) which is located in the Sierra Madre of Chihuahua, an example of the Paquimé culture.
The El Paso Museum of Art is located next to the Plaza Theater adjacent to San Jacinto Plaza, the public square downtown. It contains works of Southwestern artists such as Tom Lea.
Other area museums include:
* El Paso Holocaust Museum and Study Center
* International Museum of Art El Paso
* El Paso Museum of History
* Fort Bliss Museums and Study Center
* Insights El Paso Science Museum
* The Magoffin Homestead, dating from 1875, is now a state historic site.
* The National Border Patrol Museum is located adjacent to the El Paso Museum of Archaeology.
* Railroad and Transportation Museum of El Paso
* The Gene Roddenberry Planetarium
* Lynx Exhibits
Sites within the city limits
 * Ysleta Mission is recognized as the oldest continuously operated parish in the State of Texas.
* Cathedral of Saint Patrick erected in 1916 is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of El Paso.
* Chamizal National Memorial
* El Paso Zoo – a facility housing 220 species.
* Magoffin Home State Historic Site
* Plaza Hotel
* Union Depot
*
* Ysleta Mission is recognized as the oldest continuously operated parish in the State of Texas.
* Cathedral of Saint Patrick erected in 1916 is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of El Paso.
* Chamizal National Memorial
* El Paso Zoo – a facility housing 220 species.
* Magoffin Home State Historic Site
* Plaza Hotel
* Union Depot
* El Paso High School
El Paso High School is the oldest operating high school in El Paso, Texas, and is part of the El Paso Independent School District. It serves the west-central section of the city, roughly south and west of the Franklin Mountains and north of Int ...
* University of Texas at El Paso
The University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP) is a public university, public research university in El Paso, Texas, United States. Founded in 1913 as the State School of Mines and Metallurgy, it is the third oldest academic component of the Univers ...
The university's distinctive style is a type of fortress architecture, Dzong, found in the present and former Buddhist mountain kingdoms of the Himalayas, Bhutan and Tibet.
Sports

 El Paso is home to the Sun Bowl,
El Paso is home to the Sun Bowl,El Paso Chihuahuas
The El Paso Chihuahuas are a Minor League Baseball team based in El Paso, Texas. The Chihuahuas compete in the Pacific Coast League (PCL) as the Triple-A (baseball), Triple-A affiliate of the San Diego Padres. The team plays its home games at Sou ...
Triple-A team (San Diego Padres
The San Diego Padres are an American professional baseball team based in San Diego. The Padres compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (baseball), National League (NL) National League West, West Division. ...
affiliate); it opened in 2014. The team was purchased by Mountainstar Sports Group of El Paso. City Hall was demolished on April 14, 2013.
The El Paso Marathon takes place annually since 2007. The El Paso Locomotive FC soccer team began playing in 2019 in the USL Championship
The USL Championship (USLC) is a men's professional association football, soccer league in the second tier of the United States soccer league system#Men's leagues, United States league system. It is organized by the United Soccer League (USL) a ...
. They play their home matches at the Southwest University Park.
Parks and recreation
El Paso is home to the largest urban park in the nation. The Franklin Mountains State Park, with its more than , is completely located within the city limits. It is considered a small range (23 miles long, wide) that extends from the city north into New Mexico
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also ...
. It is home to the highest peak in the county North Franklin Mountain at 7,192 feet.The park is open year-round for recreation including hiking, mountain biking, picnicking, scenic driving and views of the city. Scenic Drive runs along the mountain range, and is designated as a city park to allow better vandalism
Vandalism is the action involving deliberate destruction of or damage to public or private property.
The term includes property damage, such as graffiti and defacement directed towards any property without permission of the owner. The t ...
control and cleanup, Roads are closed to vehicles on certain Sundays to allow walking, running, cycling, and skating. The road offers views of El Paso, as well as nearby Ciudad Juárez
Ciudad Juárez ( , ; "Juárez City"), commonly referred to as just Juárez (Lipan language, Lipan: ''Tsé Táhú'ayá''), is the most populous city in the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. It was k ...
, across the Mexico–United States border
The international border separating Mexico and the United States extends from the Pacific Ocean in the west to the Gulf of Mexico in the east. The border traverses a variety of terrains, ranging from urban areas to deserts. It is the List of ...
.
 The Wyler Aerial Tramway is operated by the
The Wyler Aerial Tramway is operated by the Texas Parks and Wildlife Department
The Texas Parks & Wildlife Department (TPWD) is a Texas state agency that oversees and protects wildlife and their habitat (ecology), habitats. In addition, the agency is responsible for managing the state park, state's parks and historical ar ...
and is in the Franklin Mountains State Park. The tramway complex covers on the east side of the Franklin Mountains. The gondolas travel along two -diameter steel cables to Ranger Peak, above sea level. The trip takes about four minutes and lifts riders above the boarding area.The tramway was built in 1959 by KTSM radio to aid in the construction of a transmitter tower. Karl O. Wyler managed the project. First opening to the public as the El Paso Aerial Tramway, the facility provided rides from 1960 to 1986, when high liability insurance costs forced the tram to stop public operations. The tram was only used to service the transmitter towers. Wyler donated the tramway for public use in his will. The Texas Parks and Wildlife Department accepted the donation in 1997 and renovated and re-opened the tramway to the public in 2001. The tramway was closed indefinitely on September 18, 2020.
 Hueco Tanks State Historic Site is a Texas historic site in the Hueco Tanks area, approximately northeast of downtown El Paso and just west of the Hueco Mountains. The park is popular for recreation such as birdwatching and bouldering, and is culturally and spiritually significant to many Native Americans. This significance is partially manifested in the
Hueco Tanks State Historic Site is a Texas historic site in the Hueco Tanks area, approximately northeast of downtown El Paso and just west of the Hueco Mountains. The park is popular for recreation such as birdwatching and bouldering, and is culturally and spiritually significant to many Native Americans. This significance is partially manifested in the pictographs
A pictogram (also pictogramme, pictograph, or simply picto) is a graphical symbol that conveys meaning through its visual resemblance to a physical object. Pictograms are used in systems of writing and visual communication. A pictography is a wri ...
(rock paintings) that can be found throughout the region, many of which are thousands of years old. Hueco Tanks is also widely regarded as one of the best areas in the world for bouldering
Bouldering is a form of rock climbing that is performed on small rock formations or Climbing wall, artificial rock walls without the use of ropes or Climbing harness, harnesses. While bouldering can be done without any equipment, most climbers ...
(rock climbing
Rock climbing is a climbing sports discipline that involves ascending climbing routes, routes consisting of natural rock in an outdoor environment, or on artificial resin climbing walls in a mostly indoor environment. Routes are documented in c ...
, low enough to attempt without ropes for protection), unique for its rock type, the concentration and quality of the climbing, and after which the Hueco bouldering grades are named. In any given climbing season, which generally lasts from October through March, it is common for climbers from across Europe, Asia, and Australia to visit the park. Since implementation of the Public Use Plan, following a brief closure of the entire park due to the park service's inability to manage the growing crowds of international climbers, volunteer or commercial guides are required to access more than 2/3 of the park's area. Only North Mountain is accessible without guides, and then only for about 70 people at any given time. The park offers camping and showers for a small fee a day or, as is most popular for climbers, the nearby Hueco Rock Ranch offers camping where climbers can relax and socialize.
Located in downtown El Paso, San Jacinto Plaza is a historical park notable for its alligator statues in the middle of the area. Known as "Alligator Plaza", it used to have a pond that held live alligators that the community can interact with starting in 1962. They were removed and relocated to the El Paso Zoo in 1974. The area around the park is typically used to hold major events such as "Chalk the Block Arts Festival" and "Winterfest".
The Chamizal National Memorial is a 54.90-acre (22.22 ha) memorial park that serves primarily as a cultural center and contains art galleries, a theater, and an amphitheatre. A museum detailing the history of the Mexico–U.S. border is located inside the visitor center.
The city is also home to 242 municipal parks.
Botanical gardens
 * The Chihuahuan Desert Gardens (CDG) display the flora of the Chihuahuan Desert and adjacent regions in the United States and Mexico. The Gardens were formally dedicated in September 1999 and contain over 625 different species of plants, comprising one of the largest captive assemblages of Chihuahuan Desert flora in the world.
* The El Paso Municipal Rose Garden (officially named the All-American Rose Selection (AARS) public garden) is one of over 100 certified gardens within the United States. There are over 1,900 rosebushes with 500 varieties. The wrought-iron fenced garden has wide walkways with handicap accessibility, raised beds, a waterfall, and trees and shrubs. Several new rose varieties are planted each year, and after two years the highest-rated are named and receive the AARS symbol.
* Feather Lake is a wildlife sanctuary based on a wetland built by the City of El Paso in 1969 as a stormwater-
* The Chihuahuan Desert Gardens (CDG) display the flora of the Chihuahuan Desert and adjacent regions in the United States and Mexico. The Gardens were formally dedicated in September 1999 and contain over 625 different species of plants, comprising one of the largest captive assemblages of Chihuahuan Desert flora in the world.
* The El Paso Municipal Rose Garden (officially named the All-American Rose Selection (AARS) public garden) is one of over 100 certified gardens within the United States. There are over 1,900 rosebushes with 500 varieties. The wrought-iron fenced garden has wide walkways with handicap accessibility, raised beds, a waterfall, and trees and shrubs. Several new rose varieties are planted each year, and after two years the highest-rated are named and receive the AARS symbol.
* Feather Lake is a wildlife sanctuary based on a wetland built by the City of El Paso in 1969 as a stormwater-retention basin
A retention basin, sometimes called a retention pond, wet detention basin, or storm water management pond (SWMP), is an artificial pond with vegetation around the perimeter and a permanent pool of water in its design. It is used to manage ...
. Since 1976, the El Paso/Trans-Pecos Audubon Society has leased this land from the city and managed it for wildlife. Over 200 different species of birds, especially those associated with water, have been observed at the sanctuary. Fauna residing there include muskrats, spiny softshell turtle
The spiny softshell turtle (''Apalone spinifera'') is a species of softshell turtle, one of the largest freshwater turtle species in North America. Both the common name, spiny softshell, and the Specific name (zoology), specific name, ''spinifer ...
s, pond sliders, and Trans-Pecos striped whiptail lizards.
* Keystone Heritage Park comprises an Archaic-period archaeological site, wetlands, and a desert botanical garden. The 4,500-year-old site is one of the oldest villages in the United States. The wetlands are home to many birds, and over 200 species have been spotted there on their seasonal migrations. The botanical garden features a variety of native plants, and includes a pavilion and a replica of an Archaic period brush hut. The newest component, The Chihuahuan Desert Experience, is a work in progress that will allow visitors to stroll the length of desert over a recreation of the plant indigenous life.
* Rio Bosque Wetlands is a city park, managed by the Center for Environmental Resource Management of the University of Texas at El Paso
The University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP) is a public university, public research university in El Paso, Texas, United States. Founded in 1913 as the State School of Mines and Metallurgy, it is the third oldest academic component of the Univers ...
, which began restoration efforts in 1998. In the fall and winter, water flows through the park along the route of the river before it was confined within levees in the 1930s. Many animals and birds have returned to the area as the restoration proceeds, and over 200 species of birds have been sighted.
Golf courses
The metro area has 16 golf courses including Butterfield Trail Golf Club, the only public premium daily fee Tom Fazio designed golf course in the state of Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
. It was ranked No. 1 in Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
and No. 3 in the Nation on '' Golfweeks 2013 Best Municipal Golf Courses. Other golf courses found in the county include:
* Ascarate Golf Course
* Coronado Country Club
* El Paso Country Club
* Horizon City Golf Course
* Lone Star Golf Club
* Painted Dunes Desert Golf Club
* Underwood Golf Complex
Government
City
The city government is officially nonpartisan. Mayors and city council members are elected for four year terms and may not serve more than two full terms or for more than ten years total in their respective offices. Municipal elections were held in May in odd-numbered years until a voter-approved charter amendment changed this to November in even-numbered years, beginning in 2018.
The city operates under a council–manager form of government. Power is concentrated in the eight-member elected city council and mayor, who hire a manager to carry out its directives and oversee the delivery of public services. The current city manager is Dionne Mack, and the current mayor of El Paso is Renard Johnson, who was elected to the office in 2024.
The terms of Johnson, Acevedo, Maldonado-Rocha, Boyar Trejo, and Limon will end in January 2029. The terms of Chavez, Canales, Fierro, and Nino will end in January 2027. Canales and Fierro have been on the council since 2023; Acevedo since 2024, and Maldonado-Rocha, Boyar Trejo, and Nino since 2025. Limon previously served from 2013 to 2017, and begins a new term in 2025. Due to the term limits clause of the city charter, Limon will be ineligible to run for another term. All other councilors are eligible for reelection.
County
The El Paso County Judge is Ricardo Samaniego, and the County Commissioners are Jackie Arroyo Butler (Precinct 1), David Stout (Precinct 2), Iliana Holguin (Precinct 3), and Sergio Coronado (Precinct 4). The commissioners and the county judge are Democrats.
Stout was first elected to his position in 2014, and was re-elected in 2018 and 2022. Samaniego was first elected in 2018, and was re-elected unopposed in 2022. Holguin was first elected to her position in 2020 and re-elected unopposed in 2024. Coronado was first elected to his position in 2022. Arroyo Butler was first elected to her position in 2024.
State
The El Paso metropolitan area is represented in the Texas State House by Democrats Eddie Morales, Mary Gonzalez, Joe Moody, Claudia Ordaz, and Vincent Perez, and in the State Senate by Cesar Blanco (D-El Paso).
The Texas Department of Criminal Justice operates the El Paso I District Parole Office in the city. The El Paso II District Parole Office is in an unincorporated area
An unincorporated area is a parcel of land that is not governed by a local general-purpose municipal corporation. (At p. 178.) They may be governed or serviced by an encompassing unit (such as a county) or another branch of the state (such as th ...
east of Horizon City.
Federal
El Paso City and County vote overwhelmingly Democratic, like most of the Texas–Mexico border area and urban Texas.
In the United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is a chamber of the Bicameralism, bicameral United States Congress; it is the lower house, with the U.S. Senate being the upper house. Together, the House and Senate have the authority under Artic ...
, most of El Paso is part of represented by Democrat Veronica Escobar. A small sliver in the eastern part of the city is part of , represented by Republican Tony Gonzales. The current U.S. senators for Texas are Ted Cruz
Rafael Edward Cruz (; born December 22, 1970) is an American politician and attorney serving as the junior United States senator from Texas since 2013. A member of the Republican Party, Cruz was the solicitor general of Texas from 2003 ...
(R-Texas) and John Cornyn
John Cornyn III ( ; born February 2, 1952) is an American politician, attorney, and former jurist serving as the Seniority in the United States Senate, senior United States Senate, United States senator from Texas, a seat he has held since 2002. ...
(R-Texas).
Education

 El Paso is home to the
El Paso is home to the University of Texas at El Paso
The University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP) is a public university, public research university in El Paso, Texas, United States. Founded in 1913 as the State School of Mines and Metallurgy, it is the third oldest academic component of the Univers ...
, a Tier 1 doctoral research university and the largest public university in the region. UTEP was ranked as the 7th best university in Washington Monthly's 2013 National University Rankings, just behind Stanford and ahead of Harvard. Also, the university's School of Engineering is the nation's top producer of Hispanic engineers with M.S. and Ph.D. degrees.
El Paso is also home to Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center at El Paso, Paul L. Foster School of Medicine, Texas Tech College of Architecture at El Paso, Brightwood College, Park University, Southwest University, Webster University and the University of Phoenix
University of Phoenix (UoPX) is a Private university, private For-profit higher education in the United States, for-profit university headquartered in Phoenix, Arizona. Founded in 1976, the university confers certificates and degrees at the Ac ...
. Also due to its proximity, many El Paso students attend New Mexico State University
New Mexico State University (NMSU or NM State) is a public, land-grant, research university in Las Cruces, New Mexico, United States. Founded in 1888, it is the state's oldest public institution of higher education, and was the original land-g ...
where the school offers in-state tuition to El Paso County residents.
The El Paso Community College's boundary includes all of El Paso County. There are several technical schools and for profit schools. El Pasoans also have access to the Doña Ana Community College with campuses in Sunland Park, Anthony and Chaparral, New Mexico: This community college is a part of the New Mexico State University
New Mexico State University (NMSU or NM State) is a public, land-grant, research university in Las Cruces, New Mexico, United States. Founded in 1888, it is the state's oldest public institution of higher education, and was the original land-g ...
system.
El Paso area students attend public schools in four school districts that cover portions of the city limits: El Paso Independent School District
The El Paso Independent School District (or EPISD) is the largest school district serving El Paso, Texas, El Paso, Texas (United States, USA). Originally organized in 1883, it is currently the largest district in the Texas Education Agency's E ...
, Ysleta Independent School District
Ysleta Independent School District is a school district based in El Paso, Texas, El Paso, Texas (United States, USA). Ysleta ISD is the third largest school district in the city of El Paso. All of the district area covers sections of El Paso.
...
, Socorro Independent School District and Canutillo Independent School District; there are nine independent school districts in the county. Numerous accredited private preparatory schools also serve El Paso students. These include various pre-high school religious (Christian, Jewish) affiliates and Montessori schools, Cathedral High School, Loretto Academy, Father Yermo High School, Lydia Patterson Institute, Faith Christian Academy, El Paso Jewish Academy, Rose of Sharon Christian Academy, Zion Lutheran Day School and Radford School. The University of El Paso offers the country's only bilingual M.F.A. creative writing program.
El Paso is home to bi-national economic development groups; the Hub of Human Innovation and Technology Hub. The industry groups' tertiary vocational programs, give workforce training in automation, robotics and AI technology.
Public libraries
The El Paso Public Library serves the needs of the public in El Paso. It consists of 12 branches, a bookmobile, a mobile computer classroom and a mobile outreach unit (Kidsmobile). It also has multiple outreach services available.
Media
Newspapers
The main newspapers are the English-language daily ''El Paso Times
The ''El Paso Times'' is the newspaper for the US city of El Paso, Texas. The paper is the only English-language daily in El Paso (after the ''El Paso Herald-Post'', an afternoon paper, closed in 1997), but often competes with the Spanish-languag ...
'', founded in 1881; the Spanish-language daily ''El Diario de El Paso
The ''El Diario de El Paso'' is the primary Spanish-language newspaper for the U.S. city of El Paso, Texas. The paper was founded on May 16, 2005, by '' El Diario de Juárez''. It originally started out as a Mexican newspaper circulated through ...
'', and the online newspaper '' El Paso Herald-Post'' started in 2015. The original and defunct ''El Paso Herald Post'' was also founded in 1881 as the ''El Paso Herald'', which then merged with the ''El Paso Post'' in 1931. The paper was shut down in 1997. ''El Paso Matters'', a non-profit online newspaper, was founded in 2019.
Weekly and niche magazines:
* ''El Paso Inc''
* ''El Paso Scene''
* ''La Polaka''
* ''Jrznoticias''
* ''The City Magazine''
* ''The Prospector'', published by the University of Texas at El Paso
* ''Tejano Tribune'', published by El Paso Community College
Radio stations
Radio stations from Las Cruces, New Mexico
Las Cruces (; ; lit. 'the crosses') is the List of municipalities in New Mexico, second-most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico and the county seat, seat of Doña Ana County, New Mexico, Doña Ana County. As of the 2020 United States ce ...
, and Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua, can also be heard within the El Paso market.
Television
El Paso was the largest city in the United States without a PBS television station within the city limits until 1978, when KCOS-TV was founded. El Paso viewers had to watch channel 22, KRWG, from Las Cruces until 1978. In fact, the city had only three English-speaking channels and two Spanish-language channels (channel 2 and channel 5) from Juarez, and cable TV subscribers in the 1970s and 1980s could receive four Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
independent channels: KTLA
KTLA (channel 5) is a television station in Los Angeles, California, United States, serving as the West Coast flagship station of The CW. It is the largest directly owned property of the network's majority owner, Nexstar Media Group, and is ...
, KHJ, KTTV
KTTV (channel 11) is a television station in Los Angeles, California, United States, serving as the West Coast of the United States, West Coast flagship (broadcasting), flagship station of the Fox Broadcasting Company, Fox network. It is owned a ...
and KCOP
KCOP-TV (channel 13), branded Fox 11 Plus, is a television station in Los Angeles, California, United States, serving as the West Coast of the United States, West Coast flagship (broadcasting), flagship station of MyNetworkTV. It is owned and op ...
as well as Spanish-language stations KMEX of Los Angeles and KWEX of San Antonio
San Antonio ( ; Spanish for " Saint Anthony") is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the most populous city in Greater San Antonio. San Antonio is the third-largest metropolitan area in Texas and the 24th-largest metropolitan area in the ...
usually sharing the same cable channel slot. Over time, as more television stations signed on, more cable channels were added and those stations added network affiliations, the Los Angeles and San Antonio stations disappeared from the lineup. The last to be removed was KTLA in the fall of 2006 as a consequence of the WB-UPN merger into The CW
The CW Network, LLC (commonly referred to as The CW or simply CW) is an American commercial broadcast television network which is controlled by Nexstar Media Group through a 75% ownership interest. The network's name is derived from the firs ...
, when KVIA-TV launched a digital subchannel with the network's programming.
In 2019, KCOS was absorbed and moved to Lubbock as part of Texas Tech Public Media in order to keep the station on air after years of financial struggles. KCOS still focuses on broadcasting to the El Paso community.
Infrastructure
Healthcare
El Paso is the medical hub of West Texas
West Texas is a loosely defined region in the U.S. state of Texas, generally encompassing the desert climate, arid and semiarid climate, semiarid lands west of a line drawn between the cities of Wichita Falls, Texas, Wichita Falls, Abilene, Texa ...
and Southern New Mexico
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also ...
, hosting numerous state-of-the-art medical centers. Some of the city's top hospitals include University Medical Center, William Beaumont Army Medical Center, Sierra Medical Center, Las Palmas Medical Center, Del Sol Medical Center, Sierra Providence East Medical Center, El Paso Children's Hospital, and Providence Memorial Hospital. University Medical Center is the only level I trauma center
A trauma center, or trauma centre, is a hospital equipped and staffed to provide care for patients suffering from major trauma, major traumatic injuries such as Falling (accident), falls, motor vehicle collisions, or gunshot wounds. The term "tra ...
in the region. William Beaumont Army Medical Center will be replaced by a new state of the art $1.2 billion Fort Bliss Replacement Hospital expected to open in 2020. El Paso's newest hospital, The Hospitals of Providence Transmountain Campus opened in Northwest El Paso on January 27, 2017. The 106-bed teaching hospital is a collaboration between Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center El Paso and The Hospitals of Providence. The hospitals were strained during the COVID-19 pandemic in Texas, and 10 refrigerated morgue trailers were installed to handle increased mortality.
El Paso is also home to the Medical Center of the Americas, an integrated complex of medical facilities anchored by Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center at El Paso, Paul L. Foster School of Medicine, University Medical Center, the El Paso Psychiatric Center and by the El Paso Children's Hospital. It is also the site to the Cardwell Collaborative biomedical research building, the Gayle Greve Hunt School of Nursing, and the Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences. The Woody L. Hunt School of Dental Medicine is expected to open in 2021 in the MCA area as well.
Transportation
El Paso is served by El Paso International Airport and Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, Trade name, doing business as Amtrak (; ), is the national Passenger train, passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates intercity rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous United Stat ...
via the historic Union Depot.
Several roads and highways connect El Paso, including I-10, US 54 (known locally as "54", the "North-South Freeway" or officially as the Patriot Freeway), Spur 601 (Liberty Expressway), US 180 and US 62 (Montana Avenue), US Highway 85 (Paisano Drive), Loop 375, Loop 478 (Copia Street-Pershing Drive-Dyer Street), numerous Texas Farm-to-Market roads (a class of state highway commonly abbreviated to FM) and the city's original thoroughfare, SH 20, the eastern portion of which is known locally as Alameda Avenue (formerly US 80). SH 20 also includes portions of Texas Avenue in Central El Paso, Mesa Street from Downtown
''Downtown'' is a term primarily used in American and Canadian English to refer to a city's sometimes commercial, cultural and often the historical, political, and geographic heart. It is often synonymous with its central business district ( ...
to the West Side, and Doniphan Drive on the West Side. Northeast El Paso is connected to West El Paso by Transmountain Road (Loop 375). The city also shares four international bridges and one railbridge with Ciudad Juárez, Mexico. In 2009, El Paso was home to number 52, number 98, and number 100 of the 100 most congested roads in Texas, which are, respectively: North Zaragoza Road between Sun Fire Boulevard and I-10; Lee Trevino Drive between Montana Avenue and I-10; and I-10 between the Patriot Freeway and Loop 375.
In 2009, 79.8% of El Paso (city) commuters drive to work alone. The 2009 mode share for El Paso (city) commuters are 10.3% for carpooling, 2.4% for transit, 2.5% for walking, and .2% for cycling. In 2016, Walk Score
Walk Score, a subsidiary of Redfin, provides walkability analysis and apartment search tools. Its flagship product is a large-scale, public access walkability index that assigns a numerical walkability score to any address in the United States, U ...
ranked El Paso as the 32nd most walkable of the 50 largest U.S. cities, rating it "car-dependent". The city of El Paso has a slightly lower than average percentage of households without a car. In 2015, 7.4 percent of El Paso households lacked a car, and increased to 8.4 percent in 2016. The national average was 8.7 percent in 2016. El Paso averaged 1.82 cars per household in 2016, compared to a national average of 1.8.
Airports
 * El Paso International Airport, a public airport four miles (6 km) northeast of downtown El Paso. It is the largest commercial airport in
* El Paso International Airport, a public airport four miles (6 km) northeast of downtown El Paso. It is the largest commercial airport in West Texas
West Texas is a loosely defined region in the U.S. state of Texas, generally encompassing the desert climate, arid and semiarid climate, semiarid lands west of a line drawn between the cities of Wichita Falls, Texas, Wichita Falls, Abilene, Texa ...
, handling 3,260,556 passengers in 2018. The El Paso International Airport serves the El Paso-Las Cruces Combined Statistical area.
*Biggs Army Airfield
Biggs Army Airfield (formerly Biggs Air Force Base) is a United States Army military airbase located on the Fort Bliss military base in El Paso, Texas.
History Biggs Field/Biggs Army Airfield (1916–47)
On 15 June 1919, following an attack ...
, a military airbase serving Fort Bliss
Fort Bliss is a United States Army post in New Mexico and Texas, with its headquarters in El Paso, Texas. Established in 1848, the fort was renamed in 1854 to honor William Wallace Smith Bliss, Bvt.Lieut.Colonel William W.S. Bliss (1815–1853 ...
.
Railroad
*Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, Trade name, doing business as Amtrak (; ), is the national Passenger train, passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates intercity rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous United Stat ...
, the national passenger rail system, serves El Paso at the Union Depot, operating its Sunset Limited
The ''Sunset Limited'' is a long-distance passenger train run by Amtrak, operating on a route between New Orleans and Los Angeles. Major stops include Houston, San Antonio and El Paso in Texas, as well as Tucson, Arizona. Opening in 1894 thr ...
/ Texas Eagle three times weekly between Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
and New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
via San Antonio
San Antonio ( ; Spanish for " Saint Anthony") is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the most populous city in Greater San Antonio. San Antonio is the third-largest metropolitan area in Texas and the 24th-largest metropolitan area in the ...
and Houston
Houston ( ) is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in the U.S. state of Texas and in the Southern United States. Located in Southeast Texas near Galveston Bay and the Gulf of Mexico, it is the county seat, seat of ...
and between Los Angeles and Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
via San Antonio and Fort Worth
Fort Worth is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the county seat of Tarrant County, Texas, Tarrant County, covering nearly into Denton County, Texas, Denton, Johnson County, Texas, Johnson, Parker County, Texas, Parker, and Wise County, Te ...
.
*Freight service is provided by BNSF and Union Pacific
The Union Pacific Railroad is a Class I freight-hauling railroad that operates 8,300 locomotives over routes in 23 U.S. states west of Chicago and New Orleans. Union Pacific is the second largest railroad in the United States after BNSF, ...
.
Major highways
* I-10: The primary thoroughfare through the city, connecting the city with other major U.S. cities such as Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
, Phoenix, Tucson
Tucson (; ; ) is a city in Pima County, Arizona, United States, and its county seat. It is the second-most populous city in Arizona, behind Phoenix, Arizona, Phoenix, with a population of 542,630 in the 2020 United States census. The Tucson ...
, San Antonio
San Antonio ( ; Spanish for " Saint Anthony") is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the most populous city in Greater San Antonio. San Antonio is the third-largest metropolitan area in Texas and the 24th-largest metropolitan area in the ...
, Houston
Houston ( ) is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in the U.S. state of Texas and in the Southern United States. Located in Southeast Texas near Galveston Bay and the Gulf of Mexico, it is the county seat, seat of ...
, Baton Rouge
Baton Rouge ( ; , ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of Louisiana. It had a population of 227,470 at the 2020 United States census, making it List of municipalities in Louisiana, Louisiana's second-m ...
, New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
, Gulfport and Mobile, with the east end located in Jacksonville
Jacksonville ( ) is the most populous city proper in the U.S. state of Florida, located on the Atlantic coast of North Florida, northeastern Florida. It is the county seat of Duval County, Florida, Duval County, with which the City of Jacksonv ...
. I-10 is also a connector to I-25, which connects with the cities of Albuquerque, Santa Fe, Colorado Springs
Colorado Springs is the most populous city in El Paso County, Colorado, United States, and its county seat. The city had a population of 478,961 at the 2020 census, a 15.02% increase since 2010. Colorado Springs is the second-most populous c ...
, Denver
Denver ( ) is a List of municipalities in Colorado#Consolidated city and county, consolidated city and county, the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Colorado, most populous city of the U.S. state of ...
, Fort Collins, Cheyenne
The Cheyenne ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. The Cheyenne comprise two Native American tribes, the Só'taeo'o or Só'taétaneo'o (more commonly spelled as Suhtai or Sutaio) and the (also spelled Tsitsistas, The term for th ...
, Casper, and north to the interchange with I-90, located in Buffalo, Wyoming
Buffalo is a city in and the county seat of Johnson County, Wyoming, United States. The population was 4,415 at the 2020 census, down from 4,585 at the 2010 census. The city had experienced an economic boom due to methane production from the C ...
.
* I-110: I-110 is a spur of I-10 providing access to the Bridge of the Americas over the Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( or ) in the United States or the Río Bravo (del Norte) in Mexico (), also known as Tó Ba'áadi in Navajo language, Navajo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the Southwestern United States a ...
to connect with Avenida Abraham Lincoln in Ciudad Juárez, Mexico.
* US 54: Officially called the Patriot Freeway, it is also known as the North-South Freeway. A business route runs along Dyer Street, the former US 54, from the freeway near Fort Bliss to the Texas–New Mexico state line, where it again rejoins the expressway. The original US 54 was a transcontinental route connecting El Paso with Chicago.
US 54: Officially called the Patriot Freeway, it is also known as the North-South Freeway. A business route runs along Dyer Street, the former US 54, from the freeway near Fort Bliss to the Texas–New Mexico state line, where it again rejoins the expressway. The original US 54 was a transcontinental route connecting El Paso with Chicago.
 *
* US 62: Santa Fe Street south of Paisano Drive concurrently runs with US 85, Paisano Drive east of Santa Fe Street to Montana Avenue, then Montana Avenue concurrently with US 180.
*
US 62: Santa Fe Street south of Paisano Drive concurrently runs with US 85, Paisano Drive east of Santa Fe Street to Montana Avenue, then Montana Avenue concurrently with US 180.
* US 85: Santa Fe Street south of Paisano Drive concurrently runs with US 62 and Paisano Drive west of Santa Fe Street to I-10.
*
US 85: Santa Fe Street south of Paisano Drive concurrently runs with US 62 and Paisano Drive west of Santa Fe Street to I-10.
* US 180: Montana Avenue is a bypass route to the Dallas-Fort Worth Metroplex to the east, and
US 180: Montana Avenue is a bypass route to the Dallas-Fort Worth Metroplex to the east, and Flagstaff, Arizona
Flagstaff ( ), known locally as Flag, is the county seat of Coconino County, Arizona, in the southwestern United States. As of the 2020 United States census, the city's population was 76,831.
Flagstaff is the principal city of the Coconino Cou ...
to the west.
* SH 20: Alameda Avenue (formerly US 80), Texas Avenue, Mesa Street and Doniphan Drive
*
SH 20: Alameda Avenue (formerly US 80), Texas Avenue, Mesa Street and Doniphan Drive
* SH 178: Artcraft Road in Northwest El Paso extends from I-10 west to the New Mexico state line, at which point it becomes NM 136, the Pete V. Domenici International Highway.
*
SH 178: Artcraft Road in Northwest El Paso extends from I-10 west to the New Mexico state line, at which point it becomes NM 136, the Pete V. Domenici International Highway.
* Loop 375: Loop 375 encircles the city of El Paso. Between I-10 and Fort Bliss, including the stretch that crosses the Franklin Mountains via Smuggler's Pass, it is Transmountain Road. In the Fort Bliss Military Reservation between northeast and east El Paso, it is officially the Purple Heart Memorial Highway. In East El Paso, the north- and south-bound sections are known as Joe Battle Boulevard, or simply as "the Loop". South of I-10, in the east and westbound portion, it is known as the Cesar Chavez Border Highway, a four-lane expressway which is located along the Mexican border between Downtown El Paso and the Ysleta area. The newest section of Loop 375 is the Border West Expressway, which takes the highway from the Ysleta area and downtown through a narrow gap between UTEP and the Mexican border. Loop 375 continues north back to I-10 with the New Mexico state line 13 miles away.
*
Loop 375: Loop 375 encircles the city of El Paso. Between I-10 and Fort Bliss, including the stretch that crosses the Franklin Mountains via Smuggler's Pass, it is Transmountain Road. In the Fort Bliss Military Reservation between northeast and east El Paso, it is officially the Purple Heart Memorial Highway. In East El Paso, the north- and south-bound sections are known as Joe Battle Boulevard, or simply as "the Loop". South of I-10, in the east and westbound portion, it is known as the Cesar Chavez Border Highway, a four-lane expressway which is located along the Mexican border between Downtown El Paso and the Ysleta area. The newest section of Loop 375 is the Border West Expressway, which takes the highway from the Ysleta area and downtown through a narrow gap between UTEP and the Mexican border. Loop 375 continues north back to I-10 with the New Mexico state line 13 miles away.
* Spur 601: Once known as the Inner Loop, it was officially named the Liberty Expressway by the El Paso City Council in April 2010 at the request of then Fort Bliss commander Maj. Gen. Howard Bromberg. It was fully completed on April 27, 2011; it connects the Patriot Freeway ( US 54) and
Spur 601: Once known as the Inner Loop, it was officially named the Liberty Expressway by the El Paso City Council in April 2010 at the request of then Fort Bliss commander Maj. Gen. Howard Bromberg. It was fully completed on April 27, 2011; it connects the Patriot Freeway ( US 54) and Biggs Army Airfield
Biggs Army Airfield (formerly Biggs Air Force Base) is a United States Army military airbase located on the Fort Bliss military base in El Paso, Texas.
History Biggs Field/Biggs Army Airfield (1916–47)
On 15 June 1919, following an attack ...
to the Purple Heart Memorial Highway ( Loop 375).
* North Loop Road, as well as Delta Drive between North Loop Road and Alameda Avenue (Texas Highway 20)
*
North Loop Road, as well as Delta Drive between North Loop Road and Alameda Avenue (Texas Highway 20)
* Zaragoza Road, running more or less north from the Ysleta International Bridge to US 62–180 (Montana Avenue), it lies mostly in east El Paso.
*
Zaragoza Road, running more or less north from the Ysleta International Bridge to US 62–180 (Montana Avenue), it lies mostly in east El Paso.
* Texas Farm-to-Market Road 3255 runs north from US 54 to the New Mexico state line in Northeast El Paso and bears the city street name Martin Luther King Boulevard.
Texas Farm-to-Market Road 3255 runs north from US 54 to the New Mexico state line in Northeast El Paso and bears the city street name Martin Luther King Boulevard.
Mass transit
The Sun Metro Mass Transit System operates a system of medium- to large-capacity natural gas-powered buses all around the city of El Paso. In 2011, Sun Metro was named the most outstanding public transit system of the year in all of North America for a mid-size transit system by the American Public Transportation Association.
El Paso County Transit makes trips with small-capacity buses mainly in the eastern El Paso area. South Central Regional Transit District operates two routes from El Paso to Sunland Park, New Mexico and Anthony, New Mexico.
On September 1, 2009, NMDOT Park and Ride began operating commuter bus service to and from Las Cruces, New Mexico
Las Cruces (; ; lit. 'the crosses') is the List of municipalities in New Mexico, second-most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico and the county seat, seat of Doña Ana County, New Mexico, Doña Ana County. As of the 2020 United States ce ...
.
Historically, El Paso and Ciudad Juarez had a shared streetcar
A tram (also known as a streetcar or trolley in Canada and the United States) is an urban rail transit in which vehicles, whether individual railcars or multiple-unit trains, run on tramway tracks on urban public streets; some include s ...
system with a peak electrified route mileage of in 1920. The first electrified line across the Rio Grande, which opened on January 11, 1902, was preceded by a network that relied on animal labor. The system quickly spread into residential and industrial areas of El Paso. In 1913, a interurban
The interurban (or radial railway in Canada) is a type of electric railway, with tram-like electric self-propelled railcars which run within and between cities or towns. The term "interurban" is usually used in North America, with other terms u ...
line was built to Ysleta. At the close of 1943, the holding company El Paso Electric sold its subsidiary, the El Paso Electric Railway Company and its Mexican counterpart, to one of National City Lines' subsidiaries. This resulted in the formation of El Paso City Lines, whose domestic streetcar lines were replaced by buses in 1947. The international streetcar line which crossed the border via the Stanton Street Bridge continued to operate until 1973. In 1977, El Paso City Lines and two other bus companies were bought by the municipality and merged to form Sun City Area Transit (SCAT). In 1987, SCAT restyled itself Sun Metro.
Streetcar
 The El Paso Streetcar is a
The El Paso Streetcar is a streetcar
A tram (also known as a streetcar or trolley in Canada and the United States) is an urban rail transit in which vehicles, whether individual railcars or multiple-unit trains, run on tramway tracks on urban public streets; some include s ...
system that opened for service on November 9, 2018, and uses a fleet of restored PCC streetcars that had served the city's previous system until its closure in 1974.University of Texas at El Paso
The University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP) is a public university, public research university in El Paso, Texas, United States. Founded in 1913 as the State School of Mines and Metallurgy, it is the third oldest academic component of the Univers ...
. The system was constructed under the authority of the Camino Real Regional Mobility Authority, but when the major construction was completed, around spring 2018, it was transferred to Sun Metro, for operation and maintenance.
International border crossings
The first bridge to cross the Rio Grande at El Paso del Norte was built in the time of Nueva España, over 250 years ago, from wood hauled in from Santa Fe. This bridge is honored by the modern Santa Fe Street Bridge, and Santa Fe Street in downtown El Paso.
Several bridges serve the El Paso–Ciudad Juárez area:
* Bridge of the Americas, also known as the Cordova Bridge.
* Good Neighbor International Bridge, also known as the Stanton Street Bridge
* Paso del Norte International Bridge, also known as the Santa Fe Street Bridge.
* Ysleta–Zaragoza International Bridge, also known as the Zaragoza Bridge.
The city collects tolls at its international bridges, except for the Bridge of the Americas, which is free. All bridges are open year-round.
Water
The Kay Bailey Hutchison
Kay Bailey Hutchison (born Kathryn Ann Bailey; July 22, 1943) is an American attorney, television correspondent, politician, diplomat, and was the 22nd United States Permanent Representative to NATO from 2017 until 2021. A member of the Republic ...
Desalination Plant takes in brackish groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
from an aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing material, consisting of permeability (Earth sciences), permeable or fractured rock, or of unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Aquifers vary greatly in their characteristics. The s ...
that is too salty for human consumption and treats it through reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water purification process that uses a partially permeable membrane, semi-permeable membrane to separate water molecules from other substances. RO applies pressure to overcome osmotic pressure that favors even distribu ...
. A joint study by Fort Bliss
Fort Bliss is a United States Army post in New Mexico and Texas, with its headquarters in El Paso, Texas. Established in 1848, the fort was renamed in 1854 to honor William Wallace Smith Bliss, Bvt.Lieut.Colonel William W.S. Bliss (1815–1853 ...
and El Paso-area city governments found that desalination was a viable method for increasing El Paso's water supply by 25%. The plant on Fort Bliss property desalinates the groundwater of the Hueco Bolson for use by El Paso and Fort Bliss.
Sister cities
* Ciudad Juárez, MexicoLas Cruces, New Mexico
Las Cruces (; ; lit. 'the crosses') is the List of municipalities in New Mexico, second-most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico and the county seat, seat of Doña Ana County, New Mexico, Doña Ana County. As of the 2020 United States ce ...
See also
* List of museums in West Texas
* List of people from El Paso, Texas
* National Register of Historic Places listings in El Paso County, Texas
* El Paso in popular culture
Notes
Footnotes
Source notes
References
*
*
*
*
*
*
=MASH
TV Show, year=1983, Season 11 episode 2 , location = Korea,
External links
City of El Paso WebsiteChamber of Commerce Website
*
* El Paso �
from '' Vanity Fair'', March 2009.
''Forty years at El Paso, 1858–1898; recollections of war, politics, adventure, events, narratives, sketches, etc.''
by W. W. Mills, hosted by th
Portal to Texas History
El Paso TX ZIP Code Map
{{Authority control
Cities in El Paso County, Texas
County seats in Texas
Mexico–United States border crossings
Populated places established in 1659
1659 establishments in New Spain
San Antonio–El Paso Road
Spanish mission settlements in North America
Special economic zones of the United States
Cities in Texas
Texas populated places on the Rio Grande
Hispanic and Latino American culture in Texas
 During the
During the  After the Civil War's conclusion, the town's population began to grow as white Texans continued to move into the villages and soon became the majority. El Paso itself, incorporated in 1873, encompassed the small area of communities that had developed along the river. In the 1870s, a population of 23 non-Hispanic Whites and 150 Hispanics was reported. With the arrival of the Southern Pacific, Texas and Pacific, and Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe railroads in 1881, the population boomed to 10,000 by the 1890 census, with many Anglo-Americans, recent immigrants, old Hispanic settlers, and recent arrivals from Mexico. The location of El Paso and the arrival of these more wild newcomers caused the city to become a violent and wild
After the Civil War's conclusion, the town's population began to grow as white Texans continued to move into the villages and soon became the majority. El Paso itself, incorporated in 1873, encompassed the small area of communities that had developed along the river. In the 1870s, a population of 23 non-Hispanic Whites and 150 Hispanics was reported. With the arrival of the Southern Pacific, Texas and Pacific, and Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe railroads in 1881, the population boomed to 10,000 by the 1890 census, with many Anglo-Americans, recent immigrants, old Hispanic settlers, and recent arrivals from Mexico. The location of El Paso and the arrival of these more wild newcomers caused the city to become a violent and wild 
 In 1909, the El Paso Chamber of Commerce hosted U.S. President
In 1909, the El Paso Chamber of Commerce hosted U.S. President 
 El Paso's second-tallest building, the Wells Fargo Plaza, was built in the early 1970s as State National Plaza. The black-windowed, building is famous for its 13 white horizontal lights (18 lights per row on the east and west sides of the building, and seven bulbs per row on the north and south sides) that were lit at night. The tower did use a design of the United States flag during the
El Paso's second-tallest building, the Wells Fargo Plaza, was built in the early 1970s as State National Plaza. The black-windowed, building is famous for its 13 white horizontal lights (18 lights per row on the east and west sides of the building, and seven bulbs per row on the north and south sides) that were lit at night. The tower did use a design of the United States flag during the  This part of town contains some of the city's oldest and most historic neighborhoods. Located in the heart of the city, it is home to about 44,993 people. Development of the area started in 1827 with the first resident, Juan Maria Ponce de Leon, a wealthy merchant from Paso del Norte (present-day Ciudad Juárez), who built the region's first structure establishing Rancho Ponce within the vicinity of S. El Paso Street and Paisano Dr. when the city was barely beginning. Today, central El Paso has grown into the center of the city's economy and a thriving urban community. It contains numerous historic sites and landmarks, many in the Sunset Heights district. Other historic districts in this area include the Rio Grade Avenue Historic District, Segundo Barrio Historic District, and the Magoffin Historic District. It is close to the El Paso International Airport, the international border, and Fort Bliss. It is part of the
This part of town contains some of the city's oldest and most historic neighborhoods. Located in the heart of the city, it is home to about 44,993 people. Development of the area started in 1827 with the first resident, Juan Maria Ponce de Leon, a wealthy merchant from Paso del Norte (present-day Ciudad Juárez), who built the region's first structure establishing Rancho Ponce within the vicinity of S. El Paso Street and Paisano Dr. when the city was barely beginning. Today, central El Paso has grown into the center of the city's economy and a thriving urban community. It contains numerous historic sites and landmarks, many in the Sunset Heights district. Other historic districts in this area include the Rio Grade Avenue Historic District, Segundo Barrio Historic District, and the Magoffin Historic District. It is close to the El Paso International Airport, the international border, and Fort Bliss. It is part of the  Dr. James Day, an El Paso historian, said that downtown's main business area was originally centered between Second Avenue (now Paisano Drive) and San Francisco Avenue. At a later point, the main business area was centered around Stanton Street and Santa Fe Street. In the late 1800s, most of the
Dr. James Day, an El Paso historian, said that downtown's main business area was originally centered between Second Avenue (now Paisano Drive) and San Francisco Avenue. At a later point, the main business area was centered around Stanton Street and Santa Fe Street. In the late 1800s, most of the  West-central El Paso is located north of Interstate 10 and west of the Franklin Mountains. The University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP) and the Cincinnati Entertainment district are located in the heart of the area. Historic districts Kern Place and Sunset Heights are in this part of town.
Kern Place was founded in 1914 by Peter E. Kern, for whom the neighborhood was named. The homes of Kern Place are unique in architecture and some were built by residents themselves. One of the better known homes is the Paul Luckett Home located at 1201 Cincinnati Ave. above Madeline Park, and is made of local rock. It is known as "The Castle" due to its round walls and a crenelated rooftop.
Kern Place is extremely popular with college and university students. The area is known for its glitzy entertainment district, restaurants and coffee shops that cater to both business patrons and university students. After UTEP's basketball and football games, UTEP fans pack the Kern Place area for food and entertainment at Cincinnati Street, a small bar district. This bar scene has grown over the years and has attracted thousands to its annual Mardi Gras
West-central El Paso is located north of Interstate 10 and west of the Franklin Mountains. The University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP) and the Cincinnati Entertainment district are located in the heart of the area. Historic districts Kern Place and Sunset Heights are in this part of town.
Kern Place was founded in 1914 by Peter E. Kern, for whom the neighborhood was named. The homes of Kern Place are unique in architecture and some were built by residents themselves. One of the better known homes is the Paul Luckett Home located at 1201 Cincinnati Ave. above Madeline Park, and is made of local rock. It is known as "The Castle" due to its round walls and a crenelated rooftop.
Kern Place is extremely popular with college and university students. The area is known for its glitzy entertainment district, restaurants and coffee shops that cater to both business patrons and university students. After UTEP's basketball and football games, UTEP fans pack the Kern Place area for food and entertainment at Cincinnati Street, a small bar district. This bar scene has grown over the years and has attracted thousands to its annual Mardi Gras  This part of town is located north of central El Paso and east of the Franklin Mountains. Development of the area was extensive during the 1950s and 1960s. It is one of the more ethnically diverse areas in the city due to the concentration of military families. The Northeast has not developed as rapidly as other areas, such as east El Paso and northwest El Paso, but its development is steadily increasing. The population is expected to grow more rapidly as a result of the troop increase at Ft. Bliss in the coming years. The area has also gained recognition throughout the city for the outstanding high-school athletic programs at Andress High School, Parkland High School, Irvin High School, and Chapin High School.
In May 2021 a major developer announced plans for a Master Planned Community in the Northeast modeled after Scarborough's Sunfield Master Planned Community in Buda, Texas. The first phase of the development is to include about 2,500 homes, 10-acre park, walking trails, a four-acre resort-like area with a lazy river, kiddy splash pad, pool, grass areas, and a food truck area, the developers reported. Jessica Herrera, director of the city of El Paso Economic and International Development Department, in a statement released by the developers, said Campo del Sol will generate hundreds of millions of dollars in tax revenues, "which will stimulate other growth and development on the north side of town".
This part of town is located north of central El Paso and east of the Franklin Mountains. Development of the area was extensive during the 1950s and 1960s. It is one of the more ethnically diverse areas in the city due to the concentration of military families. The Northeast has not developed as rapidly as other areas, such as east El Paso and northwest El Paso, but its development is steadily increasing. The population is expected to grow more rapidly as a result of the troop increase at Ft. Bliss in the coming years. The area has also gained recognition throughout the city for the outstanding high-school athletic programs at Andress High School, Parkland High School, Irvin High School, and Chapin High School.
In May 2021 a major developer announced plans for a Master Planned Community in the Northeast modeled after Scarborough's Sunfield Master Planned Community in Buda, Texas. The first phase of the development is to include about 2,500 homes, 10-acre park, walking trails, a four-acre resort-like area with a lazy river, kiddy splash pad, pool, grass areas, and a food truck area, the developers reported. Jessica Herrera, director of the city of El Paso Economic and International Development Department, in a statement released by the developers, said Campo del Sol will generate hundreds of millions of dollars in tax revenues, "which will stimulate other growth and development on the north side of town".
 El Paso has a
El Paso has a  El Paso and the nearby mountains also receive snow. Weather systems have produced over of snow on several occasions. In the 1982–1983 winter season, three major snowstorms produced record seasonal snowfall. On December 25–26, 1982, of snow fell, producing a white Christmas for the city. This was followed by another on December 30–31, 1982. On April 4–7, 1983, of snow fell on El Paso, bringing the seasonal total to nearly . On December 13–14, 1987, a record storm dumped over of snow on El Paso, and two weeks later (December 25–26), another fell, bringing the monthly total for December 1987 to an all-time record high of of snow.
The average annual snowfall for the city varies widely between different neighborhoods at different elevations, but is at the airport (but with a median of 0, meaning most years see no snow at all). Snow is most rare around Ysleta and the eastern valley area, which usually include large numbers of palm trees; in the higher neighborhoods, palm trees are more vulnerable to snow and cold snaps and are often seen with brown, frost-damaged fronds.
El Paso and the nearby mountains also receive snow. Weather systems have produced over of snow on several occasions. In the 1982–1983 winter season, three major snowstorms produced record seasonal snowfall. On December 25–26, 1982, of snow fell, producing a white Christmas for the city. This was followed by another on December 30–31, 1982. On April 4–7, 1983, of snow fell on El Paso, bringing the seasonal total to nearly . On December 13–14, 1987, a record storm dumped over of snow on El Paso, and two weeks later (December 25–26), another fell, bringing the monthly total for December 1987 to an all-time record high of of snow.
The average annual snowfall for the city varies widely between different neighborhoods at different elevations, but is at the airport (but with a median of 0, meaning most years see no snow at all). Snow is most rare around Ysleta and the eastern valley area, which usually include large numbers of palm trees; in the higher neighborhoods, palm trees are more vulnerable to snow and cold snaps and are often seen with brown, frost-damaged fronds.
 One example of El Paso's varying climate at its most extreme was the damaging winter storm of early February 2011, which caused closures of schools, businesses, and City Hall. The snow, which was light, stopped after about a day, but during the ensuing cold episode, municipal utilities went into a crisis. The high temperature on February 2, 2011, was , the lowest daily maximum on record. In addition, the low temperature on February 3 was , breaking the monthly record low set during the cold wave of 1899. Loss of desert vegetation, such as Mexican/California palm trees, oleanders, and iceplants to the cold weather was one of the results. Two local power plants failed, forcing El Paso Electric to institute
One example of El Paso's varying climate at its most extreme was the damaging winter storm of early February 2011, which caused closures of schools, businesses, and City Hall. The snow, which was light, stopped after about a day, but during the ensuing cold episode, municipal utilities went into a crisis. The high temperature on February 2, 2011, was , the lowest daily maximum on record. In addition, the low temperature on February 3 was , breaking the monthly record low set during the cold wave of 1899. Loss of desert vegetation, such as Mexican/California palm trees, oleanders, and iceplants to the cold weather was one of the results. Two local power plants failed, forcing El Paso Electric to institute  Although the average annual rainfall is only about 8.8 in (225 mm), many parts of El Paso are subject to occasional flooding during intense summer monsoonal thunderstorms. In late July and early August 2006, up to of rain fell in a week, the flood-control reservoirs overflowed and caused major flooding citywide. The city staff estimated damage to public infrastructure at $21 million, and to private property (residential and commercial) at $77 million. Much of the damage was associated with development in recent decades in arroyos protected by flood-control dams and reservoirs, and the absence of any storm drain utility in the city to handle the flow of rain water.
Although the average annual rainfall is only about 8.8 in (225 mm), many parts of El Paso are subject to occasional flooding during intense summer monsoonal thunderstorms. In late July and early August 2006, up to of rain fell in a week, the flood-control reservoirs overflowed and caused major flooding citywide. The city staff estimated damage to public infrastructure at $21 million, and to private property (residential and commercial) at $77 million. Much of the damage was associated with development in recent decades in arroyos protected by flood-control dams and reservoirs, and the absence of any storm drain utility in the city to handle the flow of rain water.
 El Paso has a diversified economy focused primarily within
El Paso has a diversified economy focused primarily within  La Fiesta de las Flores is one of the oldest Hispanic festivals in the Southwest. The three-day fiesta is held each year during the Labor Day weekend and emphasizes El Paso's Hispanic heritage and culture. The festival attracts 20,000 to 30,000 visitors from El Paso County, New Mexico, West Texas, and the State of Chihuahua, Mexico. Activities included in the fiesta are crowning of the queen, a Fiesta Parade, Senior Appreciation Dance, Military Appreciation Day, and live entertainment. The fiesta is also well known for the authentic regional cuisine, arts and crafts, games, and services available for the enjoyment of all attendees. Over 80 booths, sponsored by local vendors and nonprofit organizations, create the Hispanic ambience and culture.
The El Paso Balloonfest is an annual event celebrated on Memorial Day weekend and is self described as "3 days of hot air balloons filling the El Paso skies, 3 afternoons of concerts and fun in the sun at Wet N' Wild Waterworld in Anthony, Texas". Over 60 balloons take to the air from TFCU launch field, which is adjacent to the water park. After the balloons launch, visitors have a weekend of water rides, swimming, concerts, and grilling. The concert aspect of the event features local bands, starting at noon, and different headlining artists in the afternoon. Overnight camping has been added for 2014.
The El Paso Sun City Pride is the largest annual
La Fiesta de las Flores is one of the oldest Hispanic festivals in the Southwest. The three-day fiesta is held each year during the Labor Day weekend and emphasizes El Paso's Hispanic heritage and culture. The festival attracts 20,000 to 30,000 visitors from El Paso County, New Mexico, West Texas, and the State of Chihuahua, Mexico. Activities included in the fiesta are crowning of the queen, a Fiesta Parade, Senior Appreciation Dance, Military Appreciation Day, and live entertainment. The fiesta is also well known for the authentic regional cuisine, arts and crafts, games, and services available for the enjoyment of all attendees. Over 80 booths, sponsored by local vendors and nonprofit organizations, create the Hispanic ambience and culture.
The El Paso Balloonfest is an annual event celebrated on Memorial Day weekend and is self described as "3 days of hot air balloons filling the El Paso skies, 3 afternoons of concerts and fun in the sun at Wet N' Wild Waterworld in Anthony, Texas". Over 60 balloons take to the air from TFCU launch field, which is adjacent to the water park. After the balloons launch, visitors have a weekend of water rides, swimming, concerts, and grilling. The concert aspect of the event features local bands, starting at noon, and different headlining artists in the afternoon. Overnight camping has been added for 2014.
The El Paso Sun City Pride is the largest annual  The outdoor musical extravaganza '' Viva! El Paso'' is performed in the McKelligon Canyon Amphitheatre. It is locally produced and chronicles the 400-year history and cultural evolution of the El Paso region. The show is performed each Friday and Saturday night in June, July, and August. It has entertained local residents and out-of-town visitors for over 35 years.
The El Paso Symphony was established in the 1930s, and is the oldest performing-arts organization in El Paso and the longest continuously running symphony orchestra in Texas. It has received both national and international recognition as a result of its very successful tours of Germany in 1996 and Turkey in 2000, and continues to represent the El Paso region with pride and distinction.
The El Paso Symphony Orchestra Association season is anchored by 12 classical concerts. Special events serve as outreach toward new audiences.
Ballet was largely nonexistent in El Paso until the arrival of Ingeborg Heuser, a professional ballerina from Germany, in the 1950s. Heuser taught ballet at UTEP for 47 years and founded the city's first professional ballet company, firstly known as Texas Western Civic Ballet and eventually as ''Ballet El Paso''. The company dissipated due to financial trouble in 1997 and Heuser retired from UTEP soon after. The El Paso Youth Ballet was founded in 2009 by Heuser's student, Marta Katz, following Heuser's departure from the university. With students from the youth ballet, Heuser staged her last ''Nutcracker'' in 2006. The youth company continues to perform the ''Nutcracker'' and other preprofessional pieces in and around the El Paso area. The company provides the only platform for young ballet dancers to train and perform at such a level within the city since the folding of Ballet El Paso.
El Paso City Ballet is a current professional ballet company in El Paso, providing local employment for professional dancers in the field of ballet. The company performs a variety of classical and contemporary works choreographed by Artistic Director Lisa Skaf and artists from the US and Latin America. It has been active since 2005, performing yearly productions.
The outdoor musical extravaganza '' Viva! El Paso'' is performed in the McKelligon Canyon Amphitheatre. It is locally produced and chronicles the 400-year history and cultural evolution of the El Paso region. The show is performed each Friday and Saturday night in June, July, and August. It has entertained local residents and out-of-town visitors for over 35 years.
The El Paso Symphony was established in the 1930s, and is the oldest performing-arts organization in El Paso and the longest continuously running symphony orchestra in Texas. It has received both national and international recognition as a result of its very successful tours of Germany in 1996 and Turkey in 2000, and continues to represent the El Paso region with pride and distinction.
The El Paso Symphony Orchestra Association season is anchored by 12 classical concerts. Special events serve as outreach toward new audiences.
Ballet was largely nonexistent in El Paso until the arrival of Ingeborg Heuser, a professional ballerina from Germany, in the 1950s. Heuser taught ballet at UTEP for 47 years and founded the city's first professional ballet company, firstly known as Texas Western Civic Ballet and eventually as ''Ballet El Paso''. The company dissipated due to financial trouble in 1997 and Heuser retired from UTEP soon after. The El Paso Youth Ballet was founded in 2009 by Heuser's student, Marta Katz, following Heuser's departure from the university. With students from the youth ballet, Heuser staged her last ''Nutcracker'' in 2006. The youth company continues to perform the ''Nutcracker'' and other preprofessional pieces in and around the El Paso area. The company provides the only platform for young ballet dancers to train and perform at such a level within the city since the folding of Ballet El Paso.
El Paso City Ballet is a current professional ballet company in El Paso, providing local employment for professional dancers in the field of ballet. The company performs a variety of classical and contemporary works choreographed by Artistic Director Lisa Skaf and artists from the US and Latin America. It has been active since 2005, performing yearly productions.
 The Plaza Theatre is a National Historic Building of Significance built in 1930. It features the 2,050-seat Kendall Kidd Performance Hall, and the smaller 200-seat Philanthropy Theatre. It hosts Broadway productions, musical concerts, individual performers, and the annual Plaza Classic Film Festival.
The Abraham Chavez Theatre is a 2,500-seat
The Plaza Theatre is a National Historic Building of Significance built in 1930. It features the 2,050-seat Kendall Kidd Performance Hall, and the smaller 200-seat Philanthropy Theatre. It hosts Broadway productions, musical concerts, individual performers, and the annual Plaza Classic Film Festival.
The Abraham Chavez Theatre is a 2,500-seat  The Centennial Museum and Chihuahuan Desert Gardens, located on the grounds of UTEP, includes a comprehensive collection of El Paso Brown, Native American pottery, as well as educational exhibits for students.
The El Paso Museum of Archaeology is located on the eastern slope of North Franklin Mountain, west of Gateway South Blvd. on TransMountain Rd. Its grounds include native plants of the American Southwest, as well samples of Native American shelters, in an unspoiled location. The museum includes
The Centennial Museum and Chihuahuan Desert Gardens, located on the grounds of UTEP, includes a comprehensive collection of El Paso Brown, Native American pottery, as well as educational exhibits for students.
The El Paso Museum of Archaeology is located on the eastern slope of North Franklin Mountain, west of Gateway South Blvd. on TransMountain Rd. Its grounds include native plants of the American Southwest, as well samples of Native American shelters, in an unspoiled location. The museum includes  * Ysleta Mission is recognized as the oldest continuously operated parish in the State of Texas.
* Cathedral of Saint Patrick erected in 1916 is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of El Paso.
* Chamizal National Memorial
* El Paso Zoo – a facility housing 220 species.
* Magoffin Home State Historic Site
* Plaza Hotel
* Union Depot
*
* Ysleta Mission is recognized as the oldest continuously operated parish in the State of Texas.
* Cathedral of Saint Patrick erected in 1916 is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of El Paso.
* Chamizal National Memorial
* El Paso Zoo – a facility housing 220 species.
* Magoffin Home State Historic Site
* Plaza Hotel
* Union Depot
* 
 El Paso is home to the Sun Bowl, the second-oldest consecutive college football contest (after the Rose Bowl). Its first game was held in 1935.
On September 18, 2012, the city council voted to approve the demolition of its city hall to make way for Southwest University Park, the new home of the
El Paso is home to the Sun Bowl, the second-oldest consecutive college football contest (after the Rose Bowl). Its first game was held in 1935.
On September 18, 2012, the city council voted to approve the demolition of its city hall to make way for Southwest University Park, the new home of the  The Wyler Aerial Tramway is operated by the
The Wyler Aerial Tramway is operated by the  Hueco Tanks State Historic Site is a Texas historic site in the Hueco Tanks area, approximately northeast of downtown El Paso and just west of the Hueco Mountains. The park is popular for recreation such as birdwatching and bouldering, and is culturally and spiritually significant to many Native Americans. This significance is partially manifested in the
Hueco Tanks State Historic Site is a Texas historic site in the Hueco Tanks area, approximately northeast of downtown El Paso and just west of the Hueco Mountains. The park is popular for recreation such as birdwatching and bouldering, and is culturally and spiritually significant to many Native Americans. This significance is partially manifested in the  * The Chihuahuan Desert Gardens (CDG) display the flora of the Chihuahuan Desert and adjacent regions in the United States and Mexico. The Gardens were formally dedicated in September 1999 and contain over 625 different species of plants, comprising one of the largest captive assemblages of Chihuahuan Desert flora in the world.
* The El Paso Municipal Rose Garden (officially named the All-American Rose Selection (AARS) public garden) is one of over 100 certified gardens within the United States. There are over 1,900 rosebushes with 500 varieties. The wrought-iron fenced garden has wide walkways with handicap accessibility, raised beds, a waterfall, and trees and shrubs. Several new rose varieties are planted each year, and after two years the highest-rated are named and receive the AARS symbol.
* Feather Lake is a wildlife sanctuary based on a wetland built by the City of El Paso in 1969 as a stormwater-
* The Chihuahuan Desert Gardens (CDG) display the flora of the Chihuahuan Desert and adjacent regions in the United States and Mexico. The Gardens were formally dedicated in September 1999 and contain over 625 different species of plants, comprising one of the largest captive assemblages of Chihuahuan Desert flora in the world.
* The El Paso Municipal Rose Garden (officially named the All-American Rose Selection (AARS) public garden) is one of over 100 certified gardens within the United States. There are over 1,900 rosebushes with 500 varieties. The wrought-iron fenced garden has wide walkways with handicap accessibility, raised beds, a waterfall, and trees and shrubs. Several new rose varieties are planted each year, and after two years the highest-rated are named and receive the AARS symbol.
* Feather Lake is a wildlife sanctuary based on a wetland built by the City of El Paso in 1969 as a stormwater-
 El Paso is home to the
El Paso is home to the  *
* The El Paso Streetcar is a
The El Paso Streetcar is a