Eion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Eion (, ''Ēiṓn''), ancient Chrysopolis, was an
Eion (, ''Ēiṓn''), ancient Chrysopolis, was an 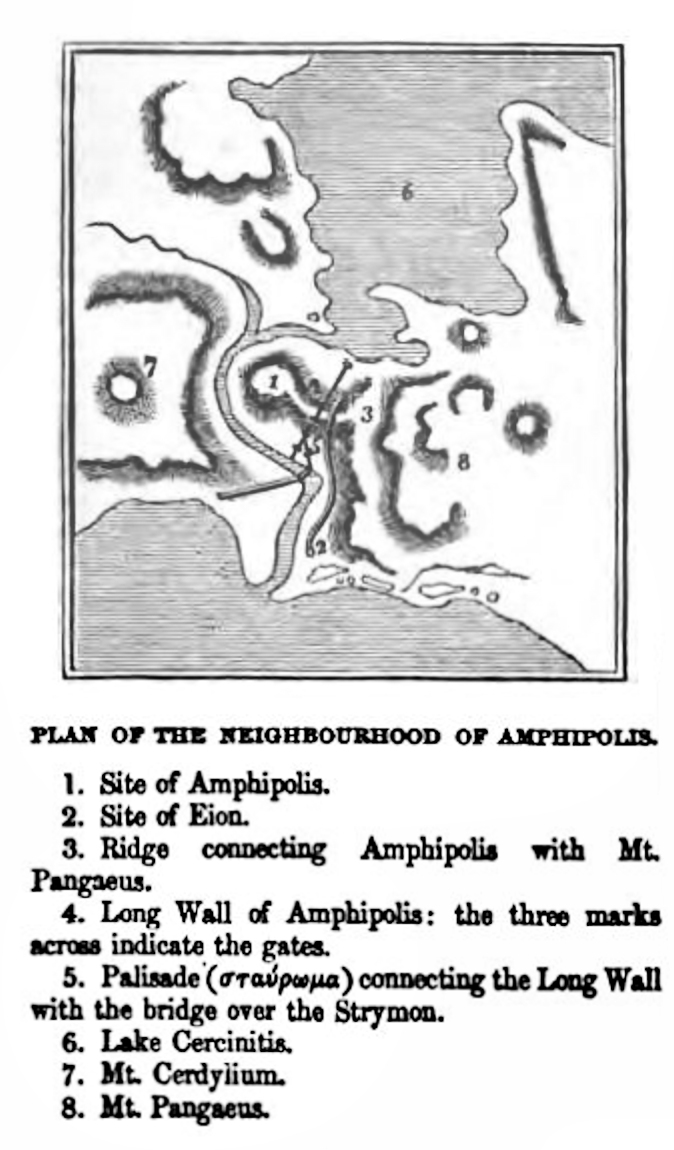 The nearby Athenian colony of
The nearby Athenian colony of
 Eion (, ''Ēiṓn''), ancient Chrysopolis, was an
Eion (, ''Ēiṓn''), ancient Chrysopolis, was an ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
Eretria
Eretria (; , , , , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th century BC, mentioned by many famous writers ...
n colony in Thracian Macedonia specifically in the region of Edonis. It sat at the mouth of the Strymon River
The Struma or Strymonas (, ; , ) is a river in Bulgaria and Greece. Its Ancient Greek, ancient name was Strymon (, ). Its drainage area is , of which in Bulgaria, in Greece and the remaining in North Macedonia and Serbia. It takes its source fr ...
which flows into the Aegean from the interior of Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
. It is referred to in Thucydides
Thucydides ( ; ; BC) was an Classical Athens, Athenian historian and general. His ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts Peloponnesian War, the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been d ...
' ''History of the Peloponnesian War
The ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' () is a historical account of the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), which was fought between the Peloponnesian League (led by Sparta) and the Delian League (led by Classical Athens, Athens). The account, ...
'' as a place of considerable strategic importance to the Athenians
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
during the Peloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancien ...
.
Athenians for the first time attempted to capture Eion in 497 BC during the Ionian Revolt
The Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris (Asia Minor), Doris, Ancient history of Cyprus, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Achaemenid Empire, Persian rule, lasting from 499 ...
, which was unsuccessful as the revolt ended with Persians
Persians ( ), or the Persian people (), are an Iranian ethnic group from West Asia that came from an earlier group called the Proto-Iranians, which likely split from the Indo-Iranians in 1800 BCE from either Afghanistan or Central Asia. They ...
re-establishing control over the Thrace, including Eion, and a Persian fortress meant for permanent stay was built there, probably in 492 BC. Eion functioned as one of the main Achaemenid cities in Thrace where food was stored for the Persian king Xerxes I
Xerxes I ( – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was a List of monarchs of Persia, Persian ruler who served as the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 486 BC until his assassination in 465 BC. He was ...
and his great armies. Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
and Diodorus
Diodorus Siculus or Diodorus of Sicily (; 1st century BC) was an ancient Greek historian from Sicily. He is known for writing the monumental universal history '' Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which survive intact, b ...
speak of Persian garrisons, of which the one at Eion was amongst them, which meant that its senior commander was apparently ethnically Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
. Xerxes had recalled most of the Persian troops from the area in the winter of 480/479 BC. It was then captured by the Delian League
The Delian League was a confederacy of Polis, Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, founded in 478 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Classical Athens, Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Achaemenid Empire, Persian ...
in 476 BC under the leadership of the Athenian general Cimon
Cimon or Kimon (; – 450BC) was an Athenian '' strategos'' (general and admiral) and politician.
He was the son of Miltiades, also an Athenian ''strategos''. Cimon rose to prominence for his bravery fighting in the naval Battle of Salamis ...
, the son of Miltiades the Younger
Miltiades (; ; c. 550 – 489 BC), also known as Miltiades the Younger, was a Ancient Greece, Greek Classical Athens, Athenian Politician, statesman known mostly for his role in the Battle of Marathon, as well as for his downfall afterwards. He ...
, who started a siege on the city. Refusing Cimon's offer of an honorable withdrawal, the Persian commander Boges destroyed the treasure, killed his family, and committed suicide as the food ran out. Cimon turned the course of the River Strymon so that it flowed against the city walls, causing the mud brick fortifications to dissolve. The inhabitants were enslaved. The capture of Eion was the beginning of a military campaign undertaken by the newly formed Delian League, whose objective was to clear the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some . In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn con ...
of Persian fleets and pirates
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and valuable goods, or taking hostages. Those who conduct acts of piracy are call ...
in order to facilitate Athenian access to the Hellespont
The Dardanelles ( ; ; ), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli (after the Gallipoli peninsula) and in classical antiquity as the Hellespont ( ; ), is a narrow, natural strait and internationally significant waterway in northwestern Turkey t ...
.
 The nearby Athenian colony of
The nearby Athenian colony of Amphipolis
Amphipolis (; ) was an important ancient Greek polis (city), and later a Roman city, whose large remains can still be seen. It gave its name to the modern municipality of Amphipoli, in the Serres regional unit of northern Greece.
Amphipol ...
was founded in 437 BC three miles up the Strymon River. The settlers, led by Hagnon, used Eion as their initial base of operations; and Eion functioned as the harbour of Amphipolis.
In 424 BC, during the Peloponnesian War, Eion was the site where the Athenian commander Aristides intercepted a Persian messenger named Artaphernes. The message, which was on its way to Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas rive ...
, was a letter from the Persian king addressing previous requests made to him by the Spartans.
Later in the war, in the winter of 424/423 BC, the Spartan general Brasidas
Brasidas (, died 422 BC) was the most distinguished Spartan officer during the first decade of the Peloponnesian War. He died during the Second Battle of Amphipolis while winning one of his most spectacular victories.
Biography
Brasidas was ...
captured Amphipolis with his Thracian
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared between north-eastern Greece, ...
allies. When he moved against Eion, however, he was unable to overcome the Athenian defenders, who were led by Thucydides
Thucydides ( ; ; BC) was an Classical Athens, Athenian historian and general. His ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts Peloponnesian War, the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been d ...
, who had come from Thasos
Thasos or Thassos (, ''Thásos'') is a Greek island in the North Aegean Sea. It is the northernmost major Greek island, and 12th largest by area.
The island has an area of 380 km2 and a population of about 13,000. It forms a separate regiona ...
with his squadron in time to save it. Although he held Eion, Thucydides was subsequently ostracized by the Athenians for his failure to defend the more pivotal city of Amphipolis.
Eion was known in the early 19th century as Rendina, hence the earlier name Gulf of Rendina for the Strymonian Gulf The Strymonian or Strymonic Gulf (), also known as the Orfano Gulf (), is a branch of the Thracian Sea—itself part of the Aegean Sea—lying east of the Chalcidice peninsula and south of the Serres regional unit. It was formerly known as the Gul ...
. Whether its site was also that of Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
Chrysopolis (Χρυσούπολης) is disputed.
The location has been recovered since at least the 19th century, as William Martin Leake
William Martin Leake FRS (14 January 17776 January 1860) was an English soldier, spy, topographer, diplomat, antiquarian, writer, and Fellow of the Royal Society. He served in the British Army, spending much of his career in the Mediterrane ...
reported finding there extensive ruins of thick walls, constructed of small stones and mortar, among which appear many squared blocks in the Hellenic style, on the left bank of the Strymon. However, those ruins belong to the Byzantine period, and have been attributed to a town of the Lower Empire, Komitisse (Κομιτίσση), which the Italians converted into Contessa, siting on the site of Eion.
References
Attribution
External links
{{coord, 40.788754, N, 23.89065, E, display=title, format=dms, source:http://dare.ht.lu.se/places/22032.html Populated places in ancient Macedonia Populated places in ancient Thrace Former populated places in Greece Greek colonies in East Macedonia Geography of ancient Thrace Delian League Eretrian colonies Achaemenid cities Achaemenid Macedon Achaemenid Thrace