Echiurus echiurus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Echiurus echiurus'' is a
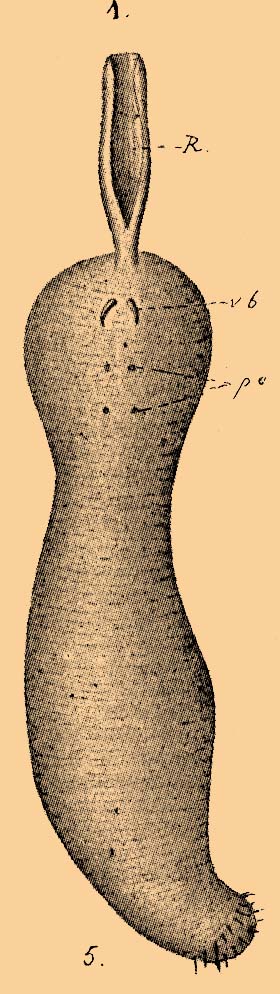 ''Echiurus echiurus'' has a
''Echiurus echiurus'' has a
species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
of spoon worm in the family Echiuridae. It is found in the North Atlantic Ocean and a subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morpholog ...
is found in Alaska. It burrows into soft sediment and under boulders and stones in muddy places.
Description
This spoon worm has a roughly cylindrical trunk between long. At the anterior end of the trunk, just beside the mouth, a scoop-shapedproboscis
A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a pr ...
about long extends forward. The trunk has about 22 rings of papillae, a ring of larger papillae alternating with several rings of smaller papillae. A pair of hooked chaeta
A chaeta or cheta (; ) is a chitinous bristle or seta found on annelid worms, although the term is also frequently used to describe similar structures in other invertebrates such as arthropods. Polychaete annelids (''polychaeta'' literally me ...
e (chitinous bristles) is borne just behind the mouth on the underside of the worm and there are two rings of chaetae on the posterior end of the trunk, near the anus. Internally, the rectum is partially obscured by two long anal diverticula
In medicine or biology, a diverticulum is an outpouching of a hollow (or a fluid-filled) structure in the body. Depending upon which layers of the structure are involved, diverticula are described as being either true or false.
In medicine, t ...
with ciliated funnels. Externally, the trunk is greyish-brown while the proboscis is orange with brownish streaks.
Distribution
 ''Echiurus echiurus'' has a
''Echiurus echiurus'' has a holarctic
The Holarctic realm is a biogeographic realm that comprises the majority of habitats found throughout the continents in the Northern Hemisphere. It corresponds to the floristic Boreal Kingdom. It includes both the Nearctic zoogeographical reg ...
distribution, extending southwards in the Atlantic Ocean as far as the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ...
and the Kattegat
The Kattegat (; ; ) is a sea area bounded by the peninsula of Jutland in the west, the Danish straits islands of Denmark and the Baltic Sea to the south and the Swedish provinces of Bohuslän, Västergötland, Halland and Scania in Swede ...
, burrowing into soft sediment, often at considerable depths. A subspecies ''Echiurus echiurus alaskanus'' occurs in southeastern Alaska, its range extending from Point Barrow
Point Barrow or Nuvuk is a headland on the Arctic coast in the U.S. state of Alaska, northeast of Utqiagvik (formerly Barrow). It is the northernmost point of all the territory of the United States, at , south of the North Pole. (The northe ...
, Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
to Puget Sound
Puget Sound ( ; ) is a complex estuary, estuarine system of interconnected Marine habitat, marine waterways and basins located on the northwest coast of the U.S. state of Washington (state), Washington. As a part of the Salish Sea, the sound ...
, Washington. This subspecies inhabits muddy deposits that accumulate around boulders and pebbles in the lower intertidal zone
The intertidal zone or foreshore is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide; in other words, it is the part of the littoral zone within the tidal range. This area can include several types of habitats with various ...
and the shallow subtidal zone.
Ecology
When burrowing, the proboscis is raised and folded backwards and plays no part in the digging process. The front of the trunk is shaped into a wedge and pushed forward, with the two anterior chaetae being driven into the sediment. Next the rear end of the trunk is drawn forward and the posterior chaetae anchor it in place. These manoeuvres are repeated and the worm slowly digs its way forwards and downwards. It takes about forty minutes for the worm to disappear from view. The burrow descends diagonally and then flattens out, and it may be a metre or so long before ascending vertically to the surface. Here, the worm unfolds its proboscis and extends it along the surface of the sediment to feed, retreating into its burrow when the tide goes out.References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q2338159 Echiurans Annelids of the Atlantic Ocean Annelids of the Pacific Ocean Annelids described in 1766 Taxa named by Peter Simon Pallas