440 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Year 440 ( CDXL) was a
Year 440 ( CDXL) was a
 Year 440 ( CDXL) was a
Year 440 ( CDXL) was a leap year starting on Monday
A leap year starting on Monday is any year with 366 days (i.e. it includes February 29, 29 February) that begins on Monday, 1 January, and ends on Leap year starting on Tuesday, Tuesday, 31 December. Its dominical letters hence are GF. The most rec ...
of the Julian calendar
The Julian calendar is a solar calendar of 365 days in every year with an additional leap day every fourth year (without exception). The Julian calendar is still used as a religious calendar in parts of the Eastern Orthodox Church and in parts ...
. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Valentinianus and Anatolius (or, less frequently, year 1193 ''Ab urbe condita
''Ab urbe condita'' (; 'from the founding of Rome, founding of the City'), or (; 'in the year since the city's founding'), abbreviated as AUC or AVC, expresses a date in years since 753 BC, 753 BC, the traditional founding of Rome. It is ...
''). The denomination 440 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used when designating years in the Gregorian calendar, Gregorian and Julian calendar, Julian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means "in the year of the Lord" but is often presented using "o ...
calendar era
A calendar era is the period of time elapsed since one '' epoch'' of a calendar and, if it exists, before the next one. For example, the current year is numbered in the Gregorian calendar, which numbers its years in the Western Christian era ...
became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Events
By place
Europe
*Flavius Aetius
Flavius Aetius (also spelled Aëtius; ; 390 – 21 September 454) was a Roman Empire, Roman general and statesman of the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, closing period of the Western Roman Empire. He was a military commander and the most inf ...
, Roman general (''magister militum
(Latin for "master of soldiers"; : ) was a top-level military command used in the late Roman Empire, dating from the reign of Constantine the Great. The term referred to the senior military officer (equivalent to a war theatre commander, the e ...
''), returns as '' triumphator'' back to Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
, after several years' fighting the Burgundians
The Burgundians were an early Germanic peoples, Germanic tribe or group of tribes. They appeared east in the middle Rhine region in the third century AD, and were later moved west into the Roman Empire, in Roman Gaul, Gaul. In the first and seco ...
and Visigoths
The Visigoths (; ) were a Germanic people united under the rule of a king and living within the Roman Empire during late antiquity. The Visigoths first appeared in the Balkans, as a Roman-allied Barbarian kingdoms, barbarian military group unite ...
in Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . Ac ...
. He is honoured by a statue
A statue is a free-standing sculpture in which the realistic, full-length figures of persons or animals are carved or Casting (metalworking), cast in a durable material such as wood, metal or stone. Typical statues are life-sized or close to ...
erected by the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
, and by order of Emperor Valentinian III
Valentinian III (; 2 July 41916 March 455) was Roman emperor in the Western Roman Empire, West from 425 to 455. Starting in childhood, his reign over the Roman Empire was one of the longest, but was dominated by civil wars among powerful general ...
.
* The Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
under Attila
Attila ( or ; ), frequently called Attila the Hun, was the ruler of the Huns from 434 until his death in early 453. He was also the leader of an empire consisting of Huns, Ostrogoths, Alans, and Gepids, among others, in Central Europe, C ...
reappear in force, along the frontier of the Western Roman Empire
In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. ...
. They attack merchant
A merchant is a person who trades in goods produced by other people, especially one who trades with foreign countries. Merchants have been known for as long as humans have engaged in trade and commerce. Merchants and merchant networks operated i ...
s on the north bank of the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
and cities in Illyricum, including (according to Priscus) Viminacium, city of Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballi ...
.
Africa
* AVandal
The Vandals were a Germanic people who were first reported in the written records as inhabitants of what is now Poland, during the period of the Roman Empire. Much later, in the fifth century, a group of Vandals led by kings established Vandal ...
fleet and their allies (Alans
The Alans () were an ancient and medieval Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, nomadic pastoral people who migrated to what is today North Caucasus – while some continued on to Europe and later North Africa. They are generally regarded ...
, Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is ...
and Moors
The term Moor is an Endonym and exonym, exonym used in European languages to designate the Muslims, Muslim populations of North Africa (the Maghreb) and the Iberian Peninsula (particularly al-Andalus) during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a s ...
) set out from Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
for Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
, the principal supplier of oil and grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached husk, hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and ...
to Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
after the loss of North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
. They loot all the coastal towns and besiege Palermo
Palermo ( ; ; , locally also or ) is a city in southern Italy, the capital (political), capital of both the autonomous area, autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan province. The ...
. Heavily laden ships return to the court of King Genseric.
Asia
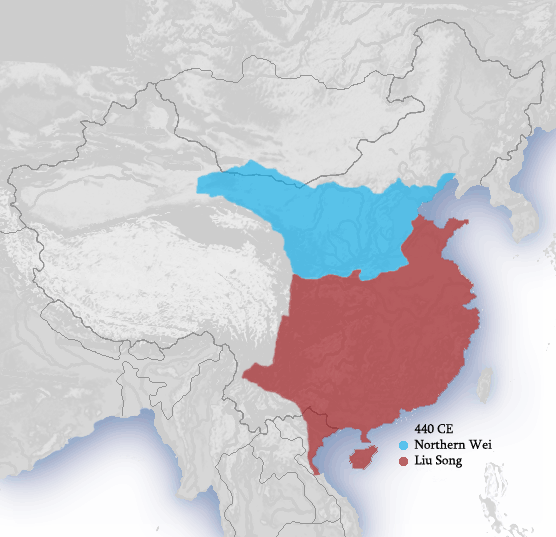
*Northern and Southern dynasties
The Northern and Southern dynasties () was a period of political division in the history of China that lasted from 420 to 589, following the tumultuous era of the Sixteen Kingdoms and the Eastern Jin dynasty. It is sometimes considered a ...
: Northern China
Northern China () and Southern China () are two approximate regions that display certain differences in terms of their geography, demographics, economy, and culture.
Extent
The Qinling, Qinling–Daba Mountains serve as the transition zone ...
is unified by the Northern Wei dynasty
Wei (), known in historiography as the Northern Wei ( zh, c=北魏, p=Běi Wèi), Tuoba Wei ( zh, c=拓跋魏, p=Tuòbá Wèi), Yuan Wei ( zh, c=元魏, p=Yuán Wèi) and Later Wei ( zh, t=後魏, p=Hòu Wèi), was an imperial dynasty of Chi ...
. The South is still under the control of the Song (or Liu Song
Song, known as Liu Song (), Former Song (前宋) or Song of (the) Southern dynasties (南朝宋) in historiography, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and the first of the four Northern and Southern dynasties#Southern dynasti ...
) dynasty.
* A center of Buddhist studies is established at Nalanda in Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
on the plains of the Ganges River
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
(India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
).
Persia
* TheHephthalites
The Hephthalites (), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian languages, Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit and Prakrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during the 5th to ...
(White Huns) move south from the Altai Mountains
The Altai Mountains (), also spelled Altay Mountains, are a mountain range in Central Asia, Central and East Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan converge, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob River, Ob have their headwaters. The ...
region into Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (, now called the Amu Darya) is the Latin name for the region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
, Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian language, Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization in Central Asia based in the area south of the Oxus River (modern Amu Darya) and north of the mountains of the Hindu Kush, an area ...
, Khorasan and eastern Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
.
By topic
Art
* '' The Parting of Lot and Abraham'', mosaic in the nave arcade, Church of Santa Maria Maggiore (Rome), is made.Ancient Games
*Chaturanga
Chaturanga (, , ) is an Traditional games of India, ancient Indian Strategy game, strategy board game. It is first known from India around the seventh century AD.
While there is some uncertainty, the prevailing view among chess historians is t ...
, Indian war game and an ancestor of chess
Chess is a board game for two players. It is an abstract strategy game that involves Perfect information, no hidden information and no elements of game of chance, chance. It is played on a square chessboard, board consisting of 64 squares arran ...
through the Persian game of Shatranj (or ''Chatrang''), evolves in the Indus Valley on the Indian subcontinent (approximate date).
Religion
* August 18 – Pope Sixtus III dies after an 8-year reign in which he has resistedheresy
Heresy is any belief or theory that is strongly at variance with established beliefs or customs, particularly the accepted beliefs or religious law of a religious organization. A heretic is a proponent of heresy.
Heresy in Heresy in Christian ...
and sponsored major construction programs in Rome. He is succeeded by Leo I as the 45th pope
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
.
* September 29 – Leo I begins to formulate Orthodoxy
Orthodoxy () is adherence to a purported "correct" or otherwise mainstream- or classically-accepted creed, especially in religion.
Orthodoxy within Christianity refers to acceptance of the doctrines defined by various creeds and ecumenical co ...
and condemns Eutychianism, an extreme form of monophysitism which holds that the human nature of Christ
Jesus ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Christianity, central figure of Christianity, the M ...
is absorbed by His divine nature.
* Winter – Leo I sends a letter to Valentinian III stating, "by the Holy Spirit's inspiration the emperor needs no human instruction and is incapable of doctrinal error".
Births
* Bodhidharma, semi-legendaryBuddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
monk
A monk (; from , ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a man who is a member of a religious order and lives in a monastery. A monk usually lives his life in prayer and contemplation. The concept is ancient and can be seen in many reli ...
(approximate date)
* Euric, Visigothic
The Visigoths (; ) were a Germanic people united under the rule of a king and living within the Roman Empire during late antiquity. The Visigoths first appeared in the Balkans, as a Roman-allied barbarian military group united under the comman ...
king and son of Theodoric I (d. 484)
* Gaudentius, son of Flavius Aetius
Flavius Aetius (also spelled Aëtius; ; 390 – 21 September 454) was a Roman Empire, Roman general and statesman of the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, closing period of the Western Roman Empire. He was a military commander and the most inf ...
(approximate date)
* Qi Wudi, Chinese emperor of the Southern Qi dynasty (d. 493)
* Tonantius Ferreolus, Gallo-Roman
Gallo-Roman culture was a consequence of the Romanization (cultural), Romanization of Gauls under the rule of the Roman Empire in Roman Gaul. It was characterized by the Gaulish adoption or adaptation of Roman culture, Roman culture, language ...
senator and prefect of Gaul
* Vakhtang I, king of Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, compri ...
(modern Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
) (approximate date)
* Wen Cheng Di, emperor of the Northern Wei dynasty
Wei (), known in historiography as the Northern Wei ( zh, c=北魏, p=Běi Wèi), Tuoba Wei ( zh, c=拓跋魏, p=Tuòbá Wèi), Yuan Wei ( zh, c=元魏, p=Yuán Wèi) and Later Wei ( zh, t=後魏, p=Hòu Wèi), was an imperial dynasty of Chi ...
(d. 465)
Deaths
*February 17
Events Pre-1600
* 1370 – Northern Crusades: Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Teutonic Knights meet in the Battle of Rudau.
* 1411 – Following the successful campaigns during the Ottoman Interregnum, Musa Çelebi, one of the sons ...
– Mesrob, Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian diaspora, Armenian communities around the ...
monk
A monk (; from , ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a man who is a member of a religious order and lives in a monastery. A monk usually lives his life in prayer and contemplation. The concept is ancient and can be seen in many reli ...
and linguist
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds ...
(b. 362)
* August 18 – Pope Sixtus III (b. 390
__NOTOC__
Year 390 (Roman numerals, CCCXC) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Valentinian II, Augustus and Neoterius (or, less frequently, year 1143 ''Ab ur ...
)
* Amalgaid mac Fiachrae, king of Connacht
Connacht or Connaught ( ; or ), is the smallest of the four provinces of Ireland, situated in the west of Ireland. Until the ninth century it consisted of several independent major Gaelic kingdoms (Uí Fiachrach, Uí Briúin, Uí Maine, C ...
(Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
)
* Yuan Qigui, empress and wife of Wen of Liu Song (b. 405)
See also
* 4-4-0, a steam locomotive, known by its wheel arrangement & for opening up North America in 1800-1850References
{{DEFAULTSORT:440