EIDAS on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The eIDAS Regulation (for "electronic IDentification, Authentication and trust Services") is an EU regulation with the stated purpose of governing " electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions". It passed in 2014 and its provisions came into effect between 2016 and 2018.
The eIDAS Regulation was fundamentally amended by Regulation (EU) 2024/1183 of the
 The eIDAS-Regulation oversees electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the European Union's
The eIDAS-Regulation oversees electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the European Union's
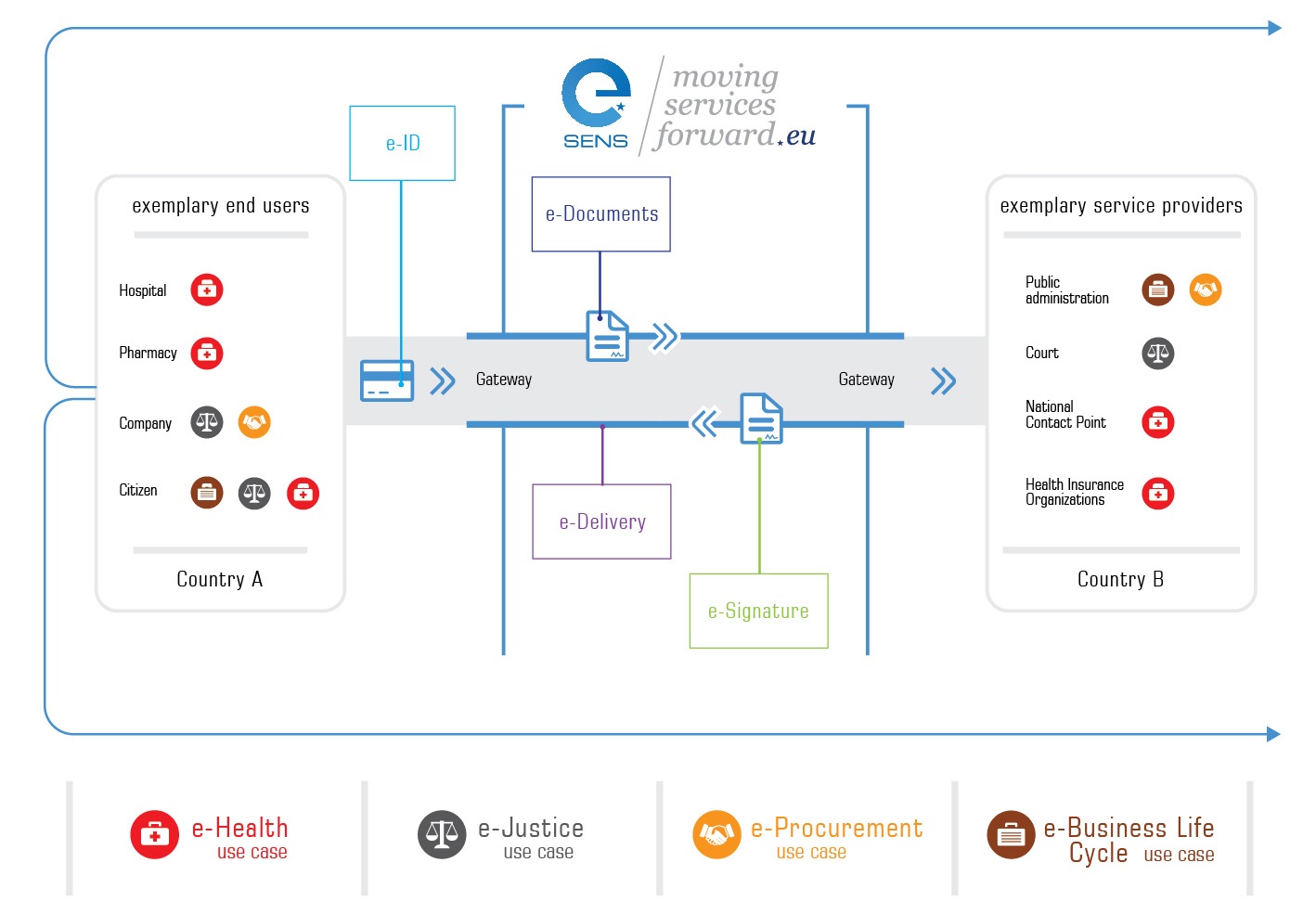 The Regulation provides the regulatory environment for the following important aspects related to electronic transactions:
*
The Regulation provides the regulatory environment for the following important aspects related to electronic transactions:
*
Regulation (EU) No 910/2014 of 23 July 2014 on electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the internal market
on
Regulation (EU) 2024/1183 of 11 April 2024 amending Regulation (EU) No 910/2014 as regards establishing the European Digital Identity Framework
on EUR-Lex
European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the two legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it ...
and of the Council
A council is a group of people who come together to consult, deliberate, or make decisions. A council may function as a legislature, especially at a town, city or county/shire level, but most legislative bodies at the state/provincial or natio ...
of 11 April 2024. The main purpose of the amendment is to introduce a voluntary digital wallet (European Digital Identity) that member states
A member state is a state that is a member of an international organization or of a federation or confederation.
Since the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) include some members that are not sovereign states ...
must issue at the request of EU citizens
The European Union citizenship is a legal status afforded to all nationals of member states of the European Union (EU). It was formally created with the adoption of the 1992 Maastricht Treaty, at the same time as the creation of the EU. EU ...
.
Description
 The eIDAS-Regulation oversees electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the European Union's
The eIDAS-Regulation oversees electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the European Union's internal market
The European single market, also known as the European internal market or the European common market, is the single market comprising mainly the member states of the European Union (EU). With certain exceptions, it also comprises Iceland, ...
. It regulates electronic signature
An electronic signature, or e-signature, is data that is logically associated with other data and which is used by the signatory to sign the associated data. This type of signature has the same legal standing as a handwritten signature as long as ...
s, electronic transactions, involved bodies, and their embedding processes to provide a safe way for users to conduct business online like electronic funds transfer
Electronic funds transfer (EFT) is the transfer of money from one bank account to another, either within a single financial institution or across multiple institutions, via computer-based systems.
The funds transfer process generally consists ...
or transactions with public services
A public service or service of general (economic) interest is any service (economics), service intended to address the needs of aggregate members of a community, whether provided directly by a public sector agency, via public financing availab ...
. Both the signatory and the recipient can have more convenience and security
Security is protection from, or resilience against, potential harm (or other unwanted coercion). Beneficiaries (technically referents) of security may be persons and social groups, objects and institutions, ecosystems, or any other entity or ...
. Instead of relying on traditional methods, such as mail or facsimile
A facsimile (from Latin ''fac simile'', "to make alike") is a copy or reproduction of an old book, manuscript, map, art print, or other item of historical value that is as true to the original source as possible. It differs from other forms of r ...
, or appearing in person to submit paper-based documents, they may now perform transactions across borders, like " 1-Click" technology.
eIDAS has created standards for which electronic signatures, qualified digital certificates, electronic seals, timestamp
A timestamp is a sequence of characters or encoded information identifying when a certain event occurred, usually giving date and time of day, sometimes accurate to a small fraction of a second. Timestamps do not have to be based on some absolu ...
s, and other proof for authentication
Authentication (from ''authentikos'', "real, genuine", from αὐθέντης ''authentes'', "author") is the act of proving an Logical assertion, assertion, such as the Digital identity, identity of a computer system user. In contrast with iden ...
mechanisms enable electronic transactions, with the same legal standing as transactions that are performed on paper.
The regulation came into effect in July 2015, as a means to facilitate secure and seamless electronic transactions within the European Union. Member states are required to recognise electronic signatures that meet the standards of eIDAS.
Timeline
The law was established in EU Regulation 910/2014 of 23 July 2014 on electronic identification and repealed 1999/93/EC from 13 December 1999. It entered into force on 17 September 2014 and applies from 1 July 2016 except for certain articles, which are listed in its Article 52. All organizations delivering public digital services in an EU member state must recognize electronic identification from all EU member states from September 29, 2018. It applied to all countries in theEuropean Single Market
The European single market, also known as the European internal market or the European common market, is the single market comprising mainly the member states of the European Union (EU). With certain exceptions, it also comprises Iceland, ...
.
In July 2024, the first eIDAS-Testbed was launched by the go.eIDAS-Association with a number of German tech firms and foundations to issue PID-Credentials to Architecture and Reference Framework (ARF)-compliant wallets.
eIDAS is a result of the European Commission's focus on Europe's Digital Agenda. With the commission's oversight, eIDAS was implemented to spur digital growth within the EU.
The intent of eIDAS is to drive innovation. By adhering to the guidelines set for technology under eIDAS, organisations are pushed towards using higher levels of information security
Information security is the practice of protecting information by mitigating information risks. It is part of information risk management. It typically involves preventing or reducing the probability of unauthorized or inappropriate access to data ...
and innovation
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or service (economics), services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a n ...
. Additionally, eIDAS focuses on the following:
*''Interoperability
Interoperability is a characteristic of a product or system to work with other products or systems. While the term was initially defined for information technology or systems engineering services to allow for information exchange, a broader de ...
'': Member states are required to create a common framework that will recognize eIDs from other member states and ensure its authenticity and security. That makes it easy for users to conduct business across borders.
*'' Transparency'': eIDAS provides a clear and accessible list of trusted services that may be used within the centralised signing framework. That allows security stakeholders the ability to engage in dialogue about the best technologies and tools for securing digital signatures.
Regulated aspects in electronic transactions
 The Regulation provides the regulatory environment for the following important aspects related to electronic transactions:
*
The Regulation provides the regulatory environment for the following important aspects related to electronic transactions:
*Digital identity
A digital identity is data stored on Computer, computer systems relating to an individual, organization, application, or device. For individuals, it involves the collection of personal data that is essential for facilitating automated access to ...
: a European-wide framework (European Digital Identity Wallet, EDIW) for digital authentication of citizens, with legal validity. Nine principles of ''European digital identity'' have been defined: user choice, privacy, Interoperability and security, trust, convenience, user consent and control proportionality, counterpart knowledge and global scalability.
*''Advanced electronic signature
An advanced electronic signature (AES or AdES) is an electronic signature that has met the requirements set forth under EU Regulation No 910/2014 ( eIDAS-regulation) on electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in t ...
'' (AdES): An electronic signature is considered advanced if it meets certain requirements:
**It provides unique identifying information that links it to its signatory.
**The signatory has sole control of the data used to create the electronic signature.
**It must be capable of identifying if the data accompanying the message has been tampered with after being signed. If the signed data has changed, the signature is marked invalid.
**There is a certificate for electronic signature, electronic proof that confirms the identity of the signatory and links the electronic signature validation data to that person.
**Advanced electronic signatures can be technically implemented, following the XAdES, PAdES, CAdES or ASiC Baseline Profile ( Associated Signature Containers) standard for digital signatures, specified by the ETSI
The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) is an independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization operating in the field of Information and communications technology, information and communications. ETSI supports the de ...
.
*'' Qualified electronic signature'', an advanced electronic signature that is created by a qualified electronic signature creation device based on a qualified certificate for electronic signatures.
*'' Qualified digital certificate for electronic signature'', a certificate that attests to a qualified electronic signature's authenticity that has been issued by a qualified trust service provider.
*'' Qualified website authentication certificate'', a qualified digital certificate under the trust services defined in the eIDAS Regulation.
*'' Trust service'', an electronic service that creates, validates, and verifies electronic signature
An electronic signature, or e-signature, is data that is logically associated with other data and which is used by the signatory to sign the associated data. This type of signature has the same legal standing as a handwritten signature as long as ...
s, time stamps, seals, and certificates. Also, a trust service may provide website authentication and preservation of created electronic signatures, certificates, and seals. It is handled by a trust service provider
A trust service provider (TSP) is a person or legal entity providing and preserving digital certificates to create and validate electronic signatures and to authenticate their signatories as well as websites in general. Trust service providers are ...
.
* '' European Union Trusted Lists ( EUTL)''
Evolution and legal implications
The eIDAS Regulation evolved from Directive 1999/93/EC, which set a goal that EU member states were expected to achieve in regards to electronic signing. Smaller European countries were among the first to start adopting digital signatures and identification, for example the first Estonian digital signature was given in 2002 and the first Latvian digital signature was given in 2006. Their experience has been used to develop a now EU-wideregulation
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. Fo ...
, that became binding as law throughout the EU since the first of July, 2016. Directive 1999/93/EC made EU member states
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated population of over 449million as of 2024. The EU is often de ...
responsible for creating laws that would allow them to meet the goal of creating an electronic signing system within the EU. The directive also allowed each member state to interpret the law and impose restrictions, thus preventing real interoperability, and leading toward a fragmented scenario. In contrast with the 1999 directive, eIDAS ensures mutual recognition of the eID for authentication among member states, thus achieving the goal of the Digital Single Market.
eIDAS provides a tiered approach of legal value. It requires that no electronic signature can be denied legal effect or admissibility in court solely for not being an advanced or qualified electronic signature. Qualified electronic signatures must be given the same legal effect as handwritten signatures.
For electronic seals (legal entities' version of signatures), probative value is explicitly addressed, as seals should enjoy the presumption of integrity and the correctness of the origin of the attached data.
In June 2021, the Commission proposed an amendment and published a recommendation.
Controversy
In 2023, a proposed change to the law was scrutinized as it would potentially enable EU governments to performman-in-the-middle attack
In cryptography and computer security, a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack, or on-path attack, is a cyberattack where the attacker secretly relays and possibly alters the communications between two parties who believe that they are directly communi ...
s, including encrypted communications. The proposal was condemned by groups of cyber security researchers, NGOs, and civil society, as a threat to human rights, privacy, and dignity. The proposal worked via the same mechanism as a 2019 attempt at mass surveillance in Kazakhstan.
At the core of this controversy is the second paragraph of the amendment to the article 45, which states: Critics claimed that allowing certification authorities (CA) to issue certificates without going through auditing and vetting procedures put in place by browser vendors can jeopardize the security of the Internet as a whole and open the door for man-in-the-middle attacks. This would possibly allow government mandated CAs to issue certificates for any domain name and use it for impersonation, and most critically, without browsers being able to remove them as trustworthy. This is considered particularly concerning in countries with weaker rule of law, where state and state-connected actors would be able to use the law to spy on their own citizens for political repression and personal gain. There was additional concern that this allow private actors with state connections to gain access to and misuse the power for their own purposes.
In the final draft, however, provisions were made to enable browser vendors to continue to implement security provisions that in practice would make this type of interception difficult to perform without being discovered. Specifically, the final draft text states that:
which has been interpreted as allowing browser vendors to continue to use mechanisms such as certificate transparency to maintain browser security. The statement of the European Commission on amendment of the article 45 clarifies this statement and denotes that through an agreement with browser vendors, no restriction are imposed on browsers' "own security policies".
Design requirements
Database information has to be linked to some kind of identity number. To certify that a person has the right to access some personal information involves several steps. *Connecting a person to a number, which can be done through methods developed in one country, such asdigital certificate
In cryptography, a public key certificate, also known as a digital certificate or identity certificate, is an electronic document used to prove the validity of a public key. The certificate includes the public key and information about it, informa ...
s.
*Connecting a number to specific information, done in databases.
*For eIDAS it is needed to connect the number used by a country having information, to the number used by the country issuing the digital certificates.
eIDAS has as minimum identity concept, the name and birth date. But in order to access more sensitive information, some kind of certification is needed that identity numbers issued by two countries refer to the same person.
Vulnerabilities
In October 2019, two security flaws in ''eIDAS-Node'' (a sample implementation of the eID eIDAS Profile provided by the European Commission) were discovered by security researchers; both vulnerabilities were patched for version 2.3.1 of eIDAS-Node.European Self-Sovereign Identity Framework
The European Union started creating an eIDAS compatible European Self-Sovereign Identity Framework (ESSIF), but in many countries, users need to be Google or Apple customers to use eIDAS services.EUTL
The European Union Trusted Lists (EUTL) is a public list of over 200 active and legacy Trust Service Providers (TSPs) that are specifically accredited to deliver the highest levels of compliance with the EU eIDAS electronic signature regulation.External links
Regulation (EU) No 910/2014 of 23 July 2014 on electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the internal market
on
EUR-Lex
EUR-Lex is the official online database of European Union law and other public documents of the European Union (EU), published in 24 official Languages of the European Union, languages of the EU. The Official Journal of the European Union, Offici ...
Regulation (EU) 2024/1183 of 11 April 2024 amending Regulation (EU) No 910/2014 as regards establishing the European Digital Identity Framework
on EUR-Lex
See also
* USA:Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act
The Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act (ESIGN, , ) is a United States federal law, passed by the U.S. Congress to facilitate the use of electronic records and electronic signatures in interstate and foreign commerce. T ...
and Uniform Electronic Transactions Act
The Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA) is one of the several United States Uniform Acts proposed by the National Conference of Commissioners on Uniform State Laws (NCCUSL). Forty-nine states, the District of Columbia, and the U.S. Virgin ...
( UETA)
* China: China RealDID
* AdES and Long-term validation (LTV)
* PAdES
* Multi-factor authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA; two-factor authentication, or 2FA) is an electronic authentication method in which a user is granted access to a website or application only after successfully presenting two or more distinct types of evidence ...
* Single Digital Gateway
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:eIDAS 2014 in law 2014 in the European Union European Union regulations Information technology organizations based in Europe Authentication methods Computer law Cryptography standards Electronic identification Signature