Droughts And Famines In Russia And The Soviet Union on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Throughout Russian history
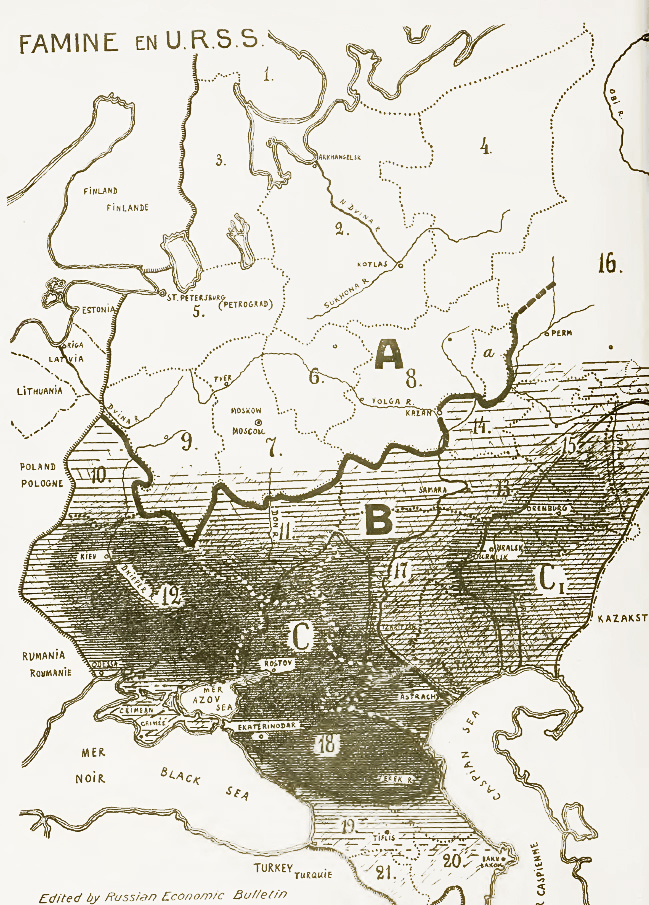 The second major Soviet famine happened during the initial push for collectivization during the 30s. Major
The second major Soviet famine happened during the initial push for collectivization during the 30s. Major
Art and photographs from the Great Famine
The Years of Hunger: Soviet Agriculture, 1931–1933
{{DEFAULTSORT:Droughts And Famines In Russia And The Soviet Union Economic crises in Europe
famines
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accompan ...
and droughts
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
have been a common feature, often resulting in humanitarian crises traceable to political or economic instability, poor policy, environmental issues and war. Droughts and famines in the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
tended to occur fairly regularly, with famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
occurring every 10–13 years and drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
s every five to seven years. Golubev and Dronin distinguish three types of drought according to productive areas vulnerable to droughts: Central (the Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the List of rivers of Europe#Rivers of Europe by length, longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Cas ...
basin, North Caucasus
The North Caucasus, ( ady, Темыр Къафкъас, Temır Qafqas; kbd, Ишхъэрэ Къаукъаз, İṩxhərə Qauqaz; ce, Къилбаседа Кавказ, Q̇ilbaseda Kavkaz; , os, Цӕгат Кавказ, Cægat Kavkaz, inh, ...
and the Central Chernozem Region), Southern (Volga and Volga- Vyatka area, the Ural
Ural may refer to:
*Ural (region), in Russia and Kazakhstan
*Ural Mountains, in Russia and Kazakhstan
*Ural (river), in Russia and Kazakhstan
* Ual (tool), a mortar tool used by the Bodo people of India
*Ural Federal District, in Russia
*Ural econ ...
region, and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
), and Eastern (steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslands, ...
and forest-steppe belts in Western and Eastern Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
, and Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
).
Pre-1900 droughts and famines
In the 17th century, Russia experienced the famine of 1601–1603, as a proportion of the population, believed to be its worst as it may have killed 2 million people (1/3 of the population). Other major famines include theGreat Famine of 1315–17
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements
* Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size
* Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent
People
* List of people known as "the Great"
*Artel Great (born ...
, which affected much of Europe including part of Russia as well as the Baltic states. The Nikonian chronicle, written between 1127 and 1303, recorded no less than eleven famine years during that period. One of the most serious crises before 1900 was the famine of 1891–1892, which killed between 375,000 and 500,000 people, mainly due to famine-related diseases. Causes included a large Autumn drought resulting in crop failures. Attempts by the government to alleviate the situation generally failed which may have contributed to a lack of faith in the Czarist regime and later political instability. In 1899, the Volga area, especially Samara, suffered starvation, typhus and scurvy, which depleted Red Cross aid.
List of post-1900 droughts and famines
The Golubev and Dronin report gives the following table of the major droughts in Russia between 1900 and 2000. Mass famines were reported in years of drought in the 1920s and 1930s, and the last one occurred in 1946. * Central: 1920, 1924, 1936, 1946, 1984. * Southern: 1901, 1906, 1921, 1939, 1948, 1995. * Eastern: 1911, 1931.1900s
There was a famine in Russia in 1901-1902 (in which 49governorate
A governorate is an administrative division of a state. It is headed by a governor. As English-speaking nations tend to call regions administered by governors either State (administrative division), states or province, provinces, the term ''govern ...
s, or gubernias, were starving) and in 1906-1908 (starved from 19 to 29 governorates)
1910s
During theRussian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and ad ...
and following civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
there was a decline in total agricultural output. Measured in millions of tons the 1920 grain harvest was only 46.1, compared to 80.1 in 1913. By 1926 it had almost returned to pre-war levels reaching 76.8.
1920s
The early 1920s saw a series of famines. The first famine in the USSR happened in 1921–1923 and garnered wide international attention. The most affected area being the Southeastern areas ofEuropean Russia
European Russia (russian: Европейская Россия, russian: европейская часть России, label=none) is the western and most populated part of Russia. It is geographically situated in Europe, as opposed to the cou ...
(including Volga region
The Volga Region (russian: Поволжье, ''Povolzhye'', literally: "along the Volga") is a historical region in Russia that encompasses the drainage basin of the Volga River, the longest river in Europe, in central and southern European Russ ...
, especially national republics of Idel-Ural
Idel-Ural ( tt-Cyrl, Идел-Урал, translit=Idel-Üral, russian: Идель-Урал), literally Volga-Ural, is a historical region in Eastern Europe, in what is today Russia. The name literally means ''Volga-Urals'' in the Tatar language. T ...
, see 1921–22 famine in Tatarstan) and . An estimated 16 million people may have been affected and up to 5 million died. Fridtjof Nansen
Fridtjof Wedel-Jarlsberg Nansen (; 10 October 186113 May 1930) was a Norwegian polymath and Nobel Peace Prize laureate. He gained prominence at various points in his life as an explorer, scientist, diplomat, and humanitarian. He led the team t ...
was honored with the 1922 Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Swedish industrialist, inventor and armaments (military weapons and equipment) manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Nobel Prize in Chemistry, Chemi ...
, in part for his work as High Commissioner for Relief In Russia. Other organizations that helped to combat the Soviet famine were International Save the Children Union The International Save the Children Union (french: L’Union Internationale de Secours aux Enfants) was a Geneva-based international organisation of children's welfare organisations founded in 1920 by Eglantyne Jebb and her sister Dorothy Buxton, wh ...
and the International Committee of the Red Cross
The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC; french: Comité international de la Croix-Rouge) is a humanitarian organization which is based in Geneva, Switzerland, and it is also a three-time Nobel Prize Laureate. State parties (signato ...
.
When the Russian famine of 1921
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
broke out, the American Relief Administration
American Relief Administration (ARA) was an American relief mission to Europe and later post-revolutionary Russia after World War I. Herbert Hoover, future president of the United States, was the program director.
The ARA's immediate predeces ...
's director in Europe, Walter Lyman Brown, began negotiating with Soviet deputy People's Commissar
Commissar (or sometimes ''Kommissar'') is an English transliteration of the Russian (''komissar''), which means 'commissary'. In English, the transliteration ''commissar'' often refers specifically to the political commissars of Soviet and Eas ...
for Foreign Affairs, Maxim Litvinov
Maxim Maximovich Litvinov (; born Meir Henoch Wallach; 17 July 1876 – 31 December 1951) was a Russian revolutionary and prominent Soviet statesman and diplomat.
A strong advocate of diplomatic agreements leading towards disarmament, Litvinov wa ...
, in Riga
Riga (; lv, Rīga , liv, Rīgõ) is the capital and largest city of Latvia and is home to 605,802 inhabitants which is a third of Latvia's population. The city lies on the Gulf of Riga at the mouth of the Daugava river where it meets the Ba ...
, Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
. An agreement was reached on August 21, 1921, and an additional implementation agreement was signed by Brown and People's Commisar for Foreign Trade Leonid Krasin
Leonid Borisovich Krasin (russian: Леони́д Бори́сович Кра́син; 15 July 1870 – 24 November 1926) was a Russian Soviet politician, engineer, social entrepreneur, Bolshevik revolutionary politician and a Soviet diplomat. In 1 ...
on December 30, 1921. The U.S. Congress appropriated $20,000,000 for relief under the Russian Famine Relief Act
The Russian Famine Relief Act of 1921 authorized the expenditure of $20,000,000 for the purchase of American foodstuffs to send to post-Russian Revolution, revolutionary Russia for relief of the Russian famine of 1921–22.
The Act was overseen by ...
of late 1921.
At its peak, the ARA employed 300 Americans, more than 120,000 Russians and fed 10.5 million people daily. Its Russian operations were headed by Col. William N. Haskell
Lieutenant General William Nafew Haskell Jr. (13 August 1878, in Albany, New York – 13 August 1952, in Greenwich, Connecticut) was a U.S. military officer. He was a 1901 graduate of the United States Military Academy.
After graduation from Wes ...
. The Medical Division of the ARA functioned from November 1921 to June 1923 and helped overcome the typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposure.
...
epidemic then ravaging Russia. The ARA's famine relief operations ran in parallel with much smaller Mennonite
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the Radic ...
, Jewish and Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belie ...
famine relief operations in Russia. The ARA's operations in Russia were shut down on June 15, 1923, after it was discovered that Russia renewed the export of grain.
While the Moscow government recognized the famine in Russia, authorities paid no attention to the famine's impact in Ukraine. Moreover, Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 19 ...
ordered to move trains full of grain from Ukraine to the Volga region, Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
, and Petrograd
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
, to combat starvation there. 1,127 trains were sent between fall 1921 and August 1922.
Soviet famine of 1932–1933
 The second major Soviet famine happened during the initial push for collectivization during the 30s. Major
The second major Soviet famine happened during the initial push for collectivization during the 30s. Major causes Causes, or causality, is the relationship between one event and another. It may also refer to:
* Causes (band), an indie band based in the Netherlands
* Causes (company)
Causes.com is a civic-technology app and website that enables users to orga ...
include the 1932–33 confiscations of grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legum ...
and other food by the Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
authorities which contributed to the famine and affected more than forty million people, especially in the south on the Don
Don, don or DON and variants may refer to:
Places
*County Donegal, Ireland, Chapman code DON
*Don (river), a river in European Russia
*Don River (disambiguation), several other rivers with the name
*Don, Benin, a town in Benin
*Don, Dang, a vill ...
and Kuban
Kuban (Russian language, Russian and Ukrainian language, Ukrainian: Кубань; ady, Пшызэ) is a historical and geographical region of Southern Russia surrounding the Kuban River, on the Black Sea between the Pontic–Caspian steppe, ...
areas and in Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
, where by various estimates millions starved to death or died due to famine related illness (the event known as ''Holodomor
The Holodomor ( uk, Голодомо́р, Holodomor, ; derived from uk, морити голодом, lit=to kill by starvation, translit=moryty holodom, label=none), also known as the Terror-Famine or the Great Famine, was a man-made famin ...
''). The famine was perhaps most severe in Kazakhstan where the semi-nomadic pastoralists' traditional way of life was most disturbed by Soviet agricultural ambitions.Gráda, C. Ó. (2010). ''Famine: a short history''. Princeton University Press.
Demographic impact
The demographic impact of the famine of 1932–1933 was multifold. In addition to direct and indirect deaths associated with the famine, there were significant internal migrations of Soviet citizens, often fleeing famine-ridden regions. A sudden decline in birthrates permanently "scarred" the long-term population growth of the Soviet Union in a way similar to, although not as severe, as that of World War 2. Estimates of Soviet deaths attributable to the 1932–1933 famine vary wildly, but are typically given in the range of millions. Vallin et al. estimated that the disasters of the decade culminated in a dramatic fall in fertility and a rise in mortality. Their estimates suggest that total losses can be put at about 4.6 million, 0.9 million of which was due to forced migration, 1 million to a deficit in births, and 2.6 million to exceptional mortality. The long-term demographic consequences of collectivization and the Second World War meant that the Soviet Union's 1989 population was 288 million rather than 315 million, 9% lower than it otherwise would have been. In addition to the deaths, the famine resulted in massive population movements, as about 300,000 Kazakhnomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the popu ...
s fled to China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
and Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
during the famine. A 2020 ''Journal of Genocide Research
The ''Journal of Genocide Research'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal covering studies of genocide. Established in 1999, for the first six years it was not peer-reviewed. Since December 2005, it is the official journal of the Internat ...
'' article by Oleh Wolowyna estimated 8.7 million deaths across the entire Soviet Union including 3.9 million in Ukraine, 3.3 million in Russia, and 1.3 million in Kazakhstan, plus a lower number of dead in other republics.
Although famines were taking place in various parts of the USSR in 1932–1933, for example in Kazakhstan, parts of Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
and the Volga German Republic
The Volga German Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (german: Autonome Sozialistische Sowjetrepublik der Wolgadeutschen; russian: Автономная Советская Социалистическая Республика Немцев По� ...
, the name ''Holodomor'' is specifically applied to the events that took place in territories populated by Ukrainians and also North Caucasian Kazakhs.
Legacy
The legacy of Holodomor remains a sensitive and controversial issue in contemporary Ukraine where it is regarded as an act of genocide by the government and is generally remembered as one of the greatest tragedies in the nation's history. The issue of Holodomor being an intentional act of genocide or not has often been a subject of dispute between the Russian Federation and Ukrainian government. The modern Russian government has generally attempted to disassociate and downplay any links between itself and the famine. There is still debate over whether or not Holodomor was a massive failure of policy or a deliberate act of genocide.Robert Conquest
George Robert Acworth Conquest (15 July 1917 – 3 August 2015) was a British historian and poet.
A long-time research fellow at Stanford University's Hoover Institution, Conquest was most notable for his work on the Soviet Union. His books ...
held the view that the famine was not intentionally inflicted by Stalin, but "with resulting famine imminent, he could have prevented it, but put “Soviet interest” other than feeding the starving first—thus consciously abetting it". Michael Ellman's analysis of the famine found that "there is some evidence that in 1930-33 ... Stalin also used starvation in his war against the peasants", which he calls a "conscious policy of starvation", but concludes that there were several factors, primarily focusing on the leadership's culpability in continuing to prioritize collectivization and industrialization over preventing mass death, due to their Leninist stance of regarding starvation "as a necessary cost of the progressive policies of industrialisation and the building of socialism", and thus did not "perceive the famine as a humanitarian catastrophe requiring a major effort to relieve distress and hence made only limited relief efforts."
1940s
During theSiege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad (russian: links=no, translit=Blokada Leningrada, Блокада Ленинграда; german: links=no, Leningrader Blockade; ) was a prolonged military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet city of L ...
by Nazi Germany, as many as one million people died while many more went hungry or starved but survived. Germans tried to starve out Leningrad in order to break its resistance. Starvation was one of the primary causes of death as the food supply was cut off and strict rationing was enforced. Animals in the city were slaughtered and eaten. Instances of cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, b ...
were reported.
The last major famine in the USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
happened mainly in 1947 as a cumulative effect of consequences of collectivization, war damage, the severe drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
in 1946 in over 50 percent of the grain-productive zone of the country and government social policy and mismanagement of grain reserves. The regions primarily affected were Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a Landlocked country, landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The List of states ...
and . In Ukraine, between 100,000 and one million people may have perished. In Moldova, according to Soviet officials, the famine claimed the lives of more than 150,000 people, while historians estimate that this figure reaches at least 250,000-300,000 people.
1947–1991
After 1947 there were no known famines. The drought of 1963 caused panic slaughtering of livestock, but there was no risk of famine. After that year the Soviet Union started importing feedgrains
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legume ...
for its livestock in increasing amounts.
Post-Soviet Russia
Since the collapse of the Soviet Union, there have been occasional issues with hunger and food insecurity in Russia. Both Russia and Ukraine were subject to a series of severe droughts from July 2010 to 2015. The 2010 drought saw wheat production fall by 20% in Russia and subsequently resulted in a temporary ban on grain exports.See also
*1921–1922 famine in Tatarstan
The 1921–1922 famine in Tatarstan was a period of mass starvation and drought that took place in the Tatar ASSR as a result of the Russian Civil War, in which 500,000 to 2,000,000 peasants died. The event was part of the greater Russian famine ...
* Kazakh famine of 1930–1933
The Kazakh famine of 1930–1933, also known the Goloshchyokin Genocide, or Asharshylyk (Kazakh language, Kazakh: Ашаршылық, meaning 'famine' or 'hunger') was a famine during which approximately 1.5 million people died in the Kazakh A ...
* Holodomor
The Holodomor ( uk, Голодомо́р, Holodomor, ; derived from uk, морити голодом, lit=to kill by starvation, translit=moryty holodom, label=none), also known as the Terror-Famine or the Great Famine, was a man-made famin ...
* Hunger Plan
The Hunger Plan (german: der Hungerplan; der Backe-Plan) was a partially implemented plan developed by Nazi bureaucrats during World War II to seize food from the Soviet Union and give it to German soldiers and civilians. The plan entailed the gen ...
* List of famines
This is a list of famines.
List
See also
Main article lists
* Bengal famine
* Droughts and famines in Russia and the Soviet Union
* Famine in India
* Famines in Czechia
* Famines in Ethiopia
* Great Bengal famine of 1770
* Great Fam ...
* Russian famine of 1921–1922
The Russian famine of 1921–1922, also known as the Povolzhye famine, was a severe famine in the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic which began early in the spring of 1921 and lasted through 1922. The famine resulted from the combined ...
* Siege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad (russian: links=no, translit=Blokada Leningrada, Блокада Ленинграда; german: links=no, Leningrader Blockade; ) was a prolonged military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet city of L ...
* Soviet famine of 1930–1933
* Soviet famine of 1946–1947
The Soviet famine of 1946–1947 was a major famine in the Soviet Union that lasted from mid-1946 to the winter of 1947 to 1948.
The estimates of victim numbers vary, ranging from several hundred thousand to 2 million. Recent estimates from histo ...
* Trofim Lysenko
Trofim Denisovich Lysenko (russian: Трофим Денисович Лысенко, uk, Трохи́м Дени́сович Лисе́нко, ; 20 November 1976) was a Soviet agronomist and Pseudoscience, pseudo-scientist.''An ill-educated agro ...
Notable victims
*Aleksey Shakhmatov
Alexei Alexandrovich Shakhmatov (russian: link=no, Алексе́й Алекса́ндрович Ша́хматов, – 16 August 1920) was a Russian Imperial philologist and historian credited with laying foundations for the science of tex ...
* Alexander Blok
Alexander Alexandrovich Blok ( rus, Алекса́ндр Алекса́ндрович Бло́к, p=ɐlʲɪˈksandr ɐlʲɪˈksandrəvʲɪtɕ ˈblok, a=Ru-Alyeksandr Alyeksandrovich Blok.oga; 7 August 1921) was a Russian lyrical poet, writer, publ ...
References
Footnotes
Notations
* * *External links
*Art and photographs from the Great Famine
The Years of Hunger: Soviet Agriculture, 1931–1933
{{DEFAULTSORT:Droughts And Famines In Russia And The Soviet Union Economic crises in Europe
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
Disasters in the Soviet Union
Disasters in Russia
Agriculture in the Soviet Union
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...