Double-bassist on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The double bass (), also known simply as the bass () (or by other names), is the largest and lowest-pitched
, Andrew Hugill with the Philharmonia Orchestra as well as the
"Chamber music in the Vienna Double Bass Archive"
, September 1996, translated by James Barket The bass is used in a range of other genres, such as
 The double bass stands around from scroll to endpin.''Double Bass Sizing FAQ''
The double bass stands around from scroll to endpin.''Double Bass Sizing FAQ''
Bob Gollihur However, other sizes are available, such as a or , which serve to accommodate a player's height and hand size. These sizes do not reflect the size relative to a full size, or bass; a bass is not half the length of a bass, but is only about 15% smaller. It is typically constructed from several types of wood, including maple for the back, spruce for the top, and ebony for the fingerboard. It is uncertain whether the instrument is a descendant of the
 Classical players perform both bowed and pizz notes using
Classical players perform both bowed and pizz notes using
Jacob Head Before the 20th century many double basses had only three strings, in contrast to the five to six strings typical of instruments in the viol family or the four strings of instruments in the violin family. The double bass's proportions are dissimilar to those of the violin and cello; for example, it is deeper (the distance from front to back is proportionally much greater than the violin). In addition, while the violin has bulging shoulders, most double basses have shoulders carved with a more acute slope, like members of the viol family. Many very old double basses have had their shoulders cut or sloped to aid playing with modern techniques. Before these modifications, the design of their shoulders was closer to instruments of the violin family. The double bass is the only modern bowed string instrument that is tuned in fourths (like a viol), rather than fifths (see Tuning below). The instrument's exact lineage is still a matter of some debate, and the supposition that the double bass is a direct descendant of the
 A person who plays this instrument is called a "bassist", "double bassist", "double bass player", "contrabassist", "contrabass player" or "bass player". The names contrabass and double bass refer to the instrument's range and use one
A person who plays this instrument is called a "bassist", "double bassist", "double bass player", "contrabassist", "contrabass player" or "bass player". The names contrabass and double bass refer to the instrument's range and use one

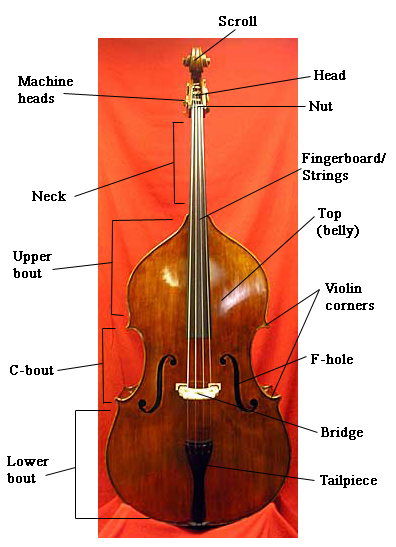 In general, there are two major approaches to the design outline shape of the double bass: the ''violin form'' (shown in the labelled picture in the construction section); and the ''viola da gamba'' form (shown in the header picture of this article). A third less common design, called the ''busetto'' shape, can also be found, as can the even more rare ''guitar'' or ''pear'' shape. The back of the instrument can vary from being a round, carved back similar to that of the violin, to a flat and angled back similar to the viol family.
The double bass features many parts that are similar to members of the violin family, including a wooden, carved
In general, there are two major approaches to the design outline shape of the double bass: the ''violin form'' (shown in the labelled picture in the construction section); and the ''viola da gamba'' form (shown in the header picture of this article). A third less common design, called the ''busetto'' shape, can also be found, as can the even more rare ''guitar'' or ''pear'' shape. The back of the instrument can vary from being a round, carved back similar to that of the violin, to a flat and angled back similar to the viol family.
The double bass features many parts that are similar to members of the violin family, including a wooden, carved
 Laminated (plywood) basses, which are widely used in music schools,
Laminated (plywood) basses, which are widely used in music schools,

 The history of the double bass is tightly coupled to the development of string technology, as it was the advent of overwound gut strings, which first rendered the instrument more generally practicable, as wound or overwound strings attain low notes within a smaller overall string diameter than non-wound strings. Professor
The history of the double bass is tightly coupled to the development of string technology, as it was the advent of overwound gut strings, which first rendered the instrument more generally practicable, as wound or overwound strings attain low notes within a smaller overall string diameter than non-wound strings. Professor
Gut strings are also more vulnerable to changes of humidity and temperature, and break more easily than steel strings. Gut strings are nowadays mostly used by bassists who perform in baroque ensembles,
 These two bows provide different ways of moving the arm and distributing force and weight on the strings. Proponents of the French bow argue that it is more maneuverable, due to the angle at which the player holds the bow. Advocates of the German bow claim that it allows the player to apply more arm weight on the strings. The differences between the two, however, are minute for a proficient player, and modern players in major orchestras use both bows.
These two bows provide different ways of moving the arm and distributing force and weight on the strings. Proponents of the French bow argue that it is more maneuverable, due to the angle at which the player holds the bow. Advocates of the German bow claim that it allows the player to apply more arm weight on the strings. The differences between the two, however, are minute for a proficient player, and modern players in major orchestras use both bows.
 The German bow (sometimes called the Butler bow) is the older of the two designs. The design of the bow and the manner of holding it descend from the older viol instrument family. With older viols, before
The German bow (sometimes called the Butler bow) is the older of the two designs. The design of the bow and the manner of holding it descend from the older viol instrument family. With older viols, before
 The French bow was not widely popular until its adoption by 19th-century virtuoso
The French bow was not widely popular until its adoption by 19th-century virtuoso 
 String players apply
String players apply
 The lowest note of a double bass is an E1 (on standard four-string basses) at approximately 41 Hz or a C1 (≈33 Hz), or sometimes B0 (≈31 Hz), when five strings are used. This is within about an octave above the lowest frequency that the average human ear can perceive as a distinctive pitch. The top of the instrument's fingerboard range is typically near D5, two octaves and a fifth above the open pitch of the G string (G2), as shown in the range illustration found at the head of this article. Playing beyond the end of the fingerboard can be accomplished by pulling the string slightly to the side.
Double bass symphony parts sometimes indicate that the performer should play
The lowest note of a double bass is an E1 (on standard four-string basses) at approximately 41 Hz or a C1 (≈33 Hz), or sometimes B0 (≈31 Hz), when five strings are used. This is within about an octave above the lowest frequency that the average human ear can perceive as a distinctive pitch. The top of the instrument's fingerboard range is typically near D5, two octaves and a fifth above the open pitch of the G string (G2), as shown in the range illustration found at the head of this article. Playing beyond the end of the fingerboard can be accomplished by pulling the string slightly to the side.
Double bass symphony parts sometimes indicate that the performer should play
 Most professional orchestral players use four-string double basses with a ''C extension''. This is an extra section of fingerboard mounted on the head of the bass. It extends the fingerboard under the lowest string and gives an additional four semitones of downward range. The lowest string is typically tuned down to C1, an octave below the lowest note on the cello (as it is quite common for a bass part to double the cello part an octave lower). More rarely this string may be tuned to a low B0, as a few works in the orchestral repertoire call for such a B, such as
Most professional orchestral players use four-string double basses with a ''C extension''. This is an extra section of fingerboard mounted on the head of the bass. It extends the fingerboard under the lowest string and gives an additional four semitones of downward range. The lowest string is typically tuned down to C1, an octave below the lowest note on the cello (as it is quite common for a bass part to double the cello part an octave lower). More rarely this string may be tuned to a low B0, as a few works in the orchestral repertoire call for such a B, such as
Jan Alm
Bernhard Alt, Norman Ludwin,
Ludus Gravis
founded by Daniele Roccato and
Music Interludes by London Double Bass Ensemble
on Bruton Music records, Brno Double Bass Orchestra (14 members) founded by the double bass professor at
 Jazz bass players are expected to improvise an accompaniment line or solo for a given chord progression. They are also expected to know the rhythmic patterns that are appropriate for different styles (e.g., Afro-Cuban). Bassists playing in a big band must also be able to read written-out bass lines, as some arrangements have written bass parts.
Many upright bass players have contributed to the evolution of jazz. Examples include swing era players such as
Jazz bass players are expected to improvise an accompaniment line or solo for a given chord progression. They are also expected to know the rhythmic patterns that are appropriate for different styles (e.g., Afro-Cuban). Bassists playing in a big band must also be able to read written-out bass lines, as some arrangements have written bass parts.
Many upright bass players have contributed to the evolution of jazz. Examples include swing era players such as
 Early pre-bluegrass traditional music was often accompanied by the cello. The cellist Natalie Haas points out that in the US, you can find "...old photographs, and even old recordings, of American string bands with cello". However, "The cello dropped out of sight in folk music, and became associated with the orchestra." The cello did not reappear in bluegrass until the 1990s and first decade of the 21st century. Some contemporary bluegrass bands favor the electric bass, because it is easier to transport than the large and somewhat fragile upright bass. However, the bass guitar has a different musical sound. Many musicians feel the slower attack and percussive, woody tone of the upright bass gives it a more "earthy" or "natural" sound than an electric bass, particularly when gut strings are used.
Common rhythms in bluegrass bass playing involve (with some exceptions) plucking on beats 1 and 3 in time; beats 1 and 2 in time, and on the downbeat in time (waltz time). Bluegrass bass lines are usually simple, typically staying on the root and fifth of each chord throughout most of a song. There are two main exceptions to this rule. Bluegrass bassists often do a diatonic ''walkup'' or ''
Early pre-bluegrass traditional music was often accompanied by the cello. The cellist Natalie Haas points out that in the US, you can find "...old photographs, and even old recordings, of American string bands with cello". However, "The cello dropped out of sight in folk music, and became associated with the orchestra." The cello did not reappear in bluegrass until the 1990s and first decade of the 21st century. Some contemporary bluegrass bands favor the electric bass, because it is easier to transport than the large and somewhat fragile upright bass. However, the bass guitar has a different musical sound. Many musicians feel the slower attack and percussive, woody tone of the upright bass gives it a more "earthy" or "natural" sound than an electric bass, particularly when gut strings are used.
Common rhythms in bluegrass bass playing involve (with some exceptions) plucking on beats 1 and 3 in time; beats 1 and 2 in time, and on the downbeat in time (waltz time). Bluegrass bass lines are usually simple, typically staying on the root and fifth of each chord throughout most of a song. There are two main exceptions to this rule. Bluegrass bassists often do a diatonic ''walkup'' or '' An early bluegrass bassist to rise to prominence was Howard Watts (also known as Cedric Rainwater), who played with
An early bluegrass bassist to rise to prominence was Howard Watts (also known as Cedric Rainwater), who played with
Stewart Evans The classical bassist
Special Collections and Archives Department, Missouri State University The upright bass remained an integral part of pop lineups throughout the 1950s, as the new genre of
, Monica M. Smith The electric bass was easily amplified with its built-in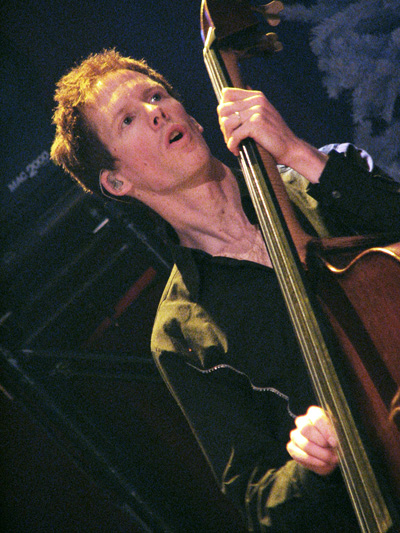
 In popular music genres, the instrument is usually played with amplification and almost exclusively played with the fingers, ''
In popular music genres, the instrument is usually played with amplification and almost exclusively played with the fingers, ''
 Some of the most influential contemporary classical double bass players are known as much for their contributions to pedagogy as for their performing skills, such as US bassist
Some of the most influential contemporary classical double bass players are known as much for their contributions to pedagogy as for their performing skills, such as US bassist
 The experimental post 1960s era, and free jazz and jazz-rock fusion, produced several influential bassists.
The experimental post 1960s era, and free jazz and jazz-rock fusion, produced several influential bassists.
 Of all of the genres, classical and jazz have the most established and comprehensive systems of instruction and training. In the classical milieu, children can begin taking private lessons on the instrument and performing in children's or youth orchestras. Teens who aspire to becoming professional classical bassists can continue their studies in a variety of formal training settings, including colleges, conservatories, and universities. Colleges offer certificates and diplomas in bass performance.
Conservatories, which are the standard musical training system in France and in Quebec (Canada) provide lessons and amateur orchestral experience for double bass players. Universities offer a range of double bass programs, including bachelor's degrees, Master of Music degrees, and
Of all of the genres, classical and jazz have the most established and comprehensive systems of instruction and training. In the classical milieu, children can begin taking private lessons on the instrument and performing in children's or youth orchestras. Teens who aspire to becoming professional classical bassists can continue their studies in a variety of formal training settings, including colleges, conservatories, and universities. Colleges offer certificates and diplomas in bass performance.
Conservatories, which are the standard musical training system in France and in Quebec (Canada) provide lessons and amateur orchestral experience for double bass players. Universities offer a range of double bass programs, including bachelor's degrees, Master of Music degrees, and  Doctor of Musical Arts (referred to as D.M.A., DMA, D.Mus.A. or A.Mus.D.) degrees in double bass performance provide an opportunity for advanced study at the highest artistic and pedagogical level, requiring usually an additional 54+ credit hours beyond a master's degree (which is about 30+ credits beyond a bachelor's degree). For this reason, admission is highly selective. Examinations in music history, music theory, ear training/dictation, and an entrance examination-recital, are required. Students perform a number of recitals (around six), including a lecture-recital with an accompanying doctoral dissertation, advanced coursework, and a minimum B average are other typical requirements of a D.M.A. program.
Throughout the early history of jazz, double bass players either learned the instrument informally, or from getting classical training early on, as in the case of Ron Carter and Charles Mingus. In the 1980s and 1990s, colleges and universities began to introduce diplomas and degrees in jazz performance. Students in jazz diploma or Bachelor of Music programs take individual bass lessons, get experience in small jazz combos with coaching from an experienced player, and play in jazz big bands. As with classical training programs, jazz programs also include classroom courses in music history and music theory. In a jazz program, these courses focus on the different eras of jazz history. such as Swing, Bebop, and fusion. The theory courses focus on the musical skills used in jazz improvisation and in jazz comping (accompanying) and the composition of jazz tunes. There are also jazz summer camps and training festivals/seminars, which offer students the chance to learn new skills and styles.
Doctor of Musical Arts (referred to as D.M.A., DMA, D.Mus.A. or A.Mus.D.) degrees in double bass performance provide an opportunity for advanced study at the highest artistic and pedagogical level, requiring usually an additional 54+ credit hours beyond a master's degree (which is about 30+ credits beyond a bachelor's degree). For this reason, admission is highly selective. Examinations in music history, music theory, ear training/dictation, and an entrance examination-recital, are required. Students perform a number of recitals (around six), including a lecture-recital with an accompanying doctoral dissertation, advanced coursework, and a minimum B average are other typical requirements of a D.M.A. program.
Throughout the early history of jazz, double bass players either learned the instrument informally, or from getting classical training early on, as in the case of Ron Carter and Charles Mingus. In the 1980s and 1990s, colleges and universities began to introduce diplomas and degrees in jazz performance. Students in jazz diploma or Bachelor of Music programs take individual bass lessons, get experience in small jazz combos with coaching from an experienced player, and play in jazz big bands. As with classical training programs, jazz programs also include classroom courses in music history and music theory. In a jazz program, these courses focus on the different eras of jazz history. such as Swing, Bebop, and fusion. The theory courses focus on the musical skills used in jazz improvisation and in jazz comping (accompanying) and the composition of jazz tunes. There are also jazz summer camps and training festivals/seminars, which offer students the chance to learn new skills and styles.

EarlyBass.com by Jerry Fuller
Polish folk music double basses
bowed
Bowed string instruments are a subcategory of string instruments that are played by a bow rubbing the strings. The bow rubbing the string causes vibration which the instrument emits as sound.
Despite the numerous specialist studies devoted to t ...
(or plucked) string instrument in the modern symphony orchestra
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families.
There are typically four main sections of instruments:
* bowed string instruments, such as the violin, viola, ...
(excluding unorthodox additions such as the octobass
The octobass is an extremely large and rare bowed string instrument that was first built around 1850 in Paris by the French luthier Jean-Baptiste Vuillaume (1798–1875). It has three strings and is essentially a larger version of the double ba ...
). Similar in structure to the cello, it has four, although occasionally five, strings.
The bass is a standard member of the orchestra's string section, along with violins, viola, and cello, ''The Orchestra: A User's Manual'', Andrew Hugill with the Philharmonia Orchestra as well as the
concert band
A concert band, also called a wind band, wind ensemble, wind symphony, wind orchestra, symphonic band, the symphonic winds, or symphonic wind ensemble, is a performing ensemble consisting of members of the woodwind, brass, and percussion famil ...
, and is featured in concertos
A concerto (; plural ''concertos'', or ''concerti'' from the Italian plural) is, from the late Baroque era, mostly understood as an instrumental composition, written for one or more soloists accompanied by an orchestra or other ensemble. The typ ...
, solo, and chamber music
Chamber music is a form of classical music that is composed for a small group of instruments—traditionally a group that could fit in a palace chamber or a large room. Most broadly, it includes any art music that is performed by a small num ...
in Western classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical music, as the term "classical music" ...
.Alfred Planyavsky
Alfred Planyavsky (22 January 1924 – 18 June 2013) was an Austrian double-bassist and music historian.
Born in Vienna, Planyavsky was a member of the boys choir Wiener Sängerknaben between 1933 and 1938. In 1946, he began studying as a tenor a ...
"Chamber music in the Vienna Double Bass Archive"
, September 1996, translated by James Barket The bass is used in a range of other genres, such as
jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a majo ...
, 1950s-style blues, rock and roll
Rock and roll (often written as rock & roll, rock 'n' roll, or rock 'n roll) is a genre of popular music that evolved in the United States during the late 1940s and early 1950s. It originated from African-American music such as jazz, rhythm an ...
, rockabilly
Rockabilly is one of the earliest styles of rock and roll music. It dates back to the early 1950s in the United States, especially the Southern United States, South. As a genre it blends the sound of Western music (North America), Western music ...
, psychobilly
Psychobilly is a rock music fusion genre that fuses elements of rockabilly and punk rock. It's been defined as "loud frantic rockabilly music", it has also been said that it "takes the traditional countrified rock style known as rockabilly, ram ...
, traditional country music
Country (also called country and western) is a genre of popular music that originated in the Southern and Southwestern United States in the early 1920s. It primarily derives from blues, church music such as Southern gospel and spirituals, o ...
, bluegrass, tango
Tango is a partner dance and social dance that originated in the 1880s along the Río de la Plata, the natural border between Argentina and Uruguay. The tango was born in the impoverished port areas of these countries as the result of a combina ...
and folk music
Folk music is a music genre that includes traditional folk music and the contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be called world music. Traditional folk music has ...
.
The bass is a transposing instrument
A transposing instrument is a musical instrument for which music notation is not written at concert pitch (concert pitch is the pitch on a non-transposing instrument such as the piano). For example, playing a written middle C on a transposing ...
and is typically notated one octave
In music, an octave ( la, octavus: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is the interval between one musical pitch and another with double its frequency. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been refer ...
higher than tuned to avoid excessive ledger lines below the staff. The double bass is the only modern bowed string instrument that is tuned in fourths (like a bass guitar
The bass guitar, electric bass or simply bass (), is the lowest-pitched member of the string family. It is a plucked string instrument similar in appearance and construction to an electric or an acoustic guitar, but with a longer neck and s ...
or viol
The viol (), viola da gamba (), or informally gamba, is any one of a family of bowed, fretted, and stringed instruments with hollow wooden bodies and pegboxes where the tension on the strings can be increased or decreased to adjust the pitc ...
), rather than fifths, with strings usually tuned to E1, A1, D2 and G2.
The instrument's exact lineage is still a matter of some debate, with scholars divided on whether the bass is derived from the viol or the violin family
The violin family of musical instruments was developed in Italy in the 16th century. At the time the name of this family of instruments was viole da braccio which was used to distinguish them from the viol family (viole ''da gamba''). The standa ...
.
The double bass is played with a bow (arco), or by plucking the strings (pizzicato
Pizzicato (, ; translated as "pinched", and sometimes roughly as "plucked") is a playing technique that involves plucking the strings of a string instrument. The exact technique varies somewhat depending on the type of instrument :
* On bowe ...
), or via a variety of extended techniques
In music, extended technique is unconventional, unorthodox, or non-traditional methods of singing or of playing musical instruments employed to obtain unusual sounds or timbres.Burtner, Matthew (2005).Making Noise: Extended Techniques after Exper ...
. In orchestral repertoire and tango music, both arco and pizzicato are employed. In jazz, blues, and rockabilly, pizzicato is the norm. Classical music and jazz use the natural sound produced acoustically by the instrument, as does traditional bluegrass
Traditional bluegrass, as the name implies, emphasizes the traditional elements of bluegrass music, and stands in contrast to progressive bluegrass. Traditional bluegrass musicians play folk songs, tunes with simple traditional chord progressio ...
. In funk, blues, reggae, and related genres, the double bass is often amplified.
Description
 The double bass stands around from scroll to endpin.''Double Bass Sizing FAQ''
The double bass stands around from scroll to endpin.''Double Bass Sizing FAQ''Bob Gollihur However, other sizes are available, such as a or , which serve to accommodate a player's height and hand size. These sizes do not reflect the size relative to a full size, or bass; a bass is not half the length of a bass, but is only about 15% smaller. It is typically constructed from several types of wood, including maple for the back, spruce for the top, and ebony for the fingerboard. It is uncertain whether the instrument is a descendant of the
viola da gamba
The viol (), viola da gamba (), or informally gamba, is any one of a family of bowed, fretted, and stringed instruments with hollow wooden bodies and pegboxes where the tension on the strings can be increased or decreased to adjust the pitch ...
or of the violin, but it is traditionally aligned with the violin family. While the double bass is nearly identical in construction to other violin family instruments, it also embodies features found in the older viol
The viol (), viola da gamba (), or informally gamba, is any one of a family of bowed, fretted, and stringed instruments with hollow wooden bodies and pegboxes where the tension on the strings can be increased or decreased to adjust the pitc ...
family.
The notes of the open strings are E1, A1, D2, and G2, the same as an acoustic or electric bass guitar
The bass guitar, electric bass or simply bass (), is the lowest-pitched member of the string family. It is a plucked string instrument similar in appearance and construction to an electric or an acoustic guitar, but with a longer neck and s ...
. However, the resonance of the wood, combined with the violin-like construction and long scale length gives the double bass a much richer tone than the bass guitar, in addition to the ability to use a bow, while the fretless fingerboard accommodates smooth glissando
In music, a glissando (; plural: ''glissandi'', abbreviated ''gliss.'') is a glide from one pitch to another (). It is an Italianized musical term derived from the French ''glisser'', "to glide". In some contexts, it is distinguished from the ...
s and legato
In music performance and notation, legato (; Italian for "tied together"; French ''lié''; German ''gebunden'') indicates that musical notes are played or sung smoothly and connected. That is, the player makes a transition from note to note w ...
s.
Playing style
Like other violin and viol-family string instruments, the double bass is played either with a bow (arco) or by plucking the strings (pizzicato
Pizzicato (, ; translated as "pinched", and sometimes roughly as "plucked") is a playing technique that involves plucking the strings of a string instrument. The exact technique varies somewhat depending on the type of instrument :
* On bowe ...
). When employing a bow, the player can either use it traditionally or strike the wood of the bow against the string. In orchestral repertoire and tango music, both arco and pizzicato are employed. In jazz, blues, and rockabilly, pizzicato is the norm, except for some solos and occasional written parts in modern jazz
Bebop or bop is a style of jazz developed in the early-to-mid-1940s in the United States. The style features compositions characterized by a fast tempo, complex chord progressions with rapid chord changes and numerous changes of key, instrumen ...
that call for bowing.
In classical pedagogy, almost all of the focus is on performing with the bow and producing a good bowed tone; there is little work done on developing significant pizzicato skills. Bowed notes in the lowest register of the instrument produce a dark, heavy, mighty, or even menacing effect, when played with a fortissimo dynamic; however, the same low pitches played with a delicate pianissimo can create a sonorous, mellow accompaniment line. Classical bass students learn all of the different bow articulations used by other string section players (e.g., violin
The violin, sometimes known as a ''fiddle'', is a wooden chordophone (string instrument) in the violin family. Most violins have a hollow wooden body. It is the smallest and thus highest-pitched instrument (soprano) in the family in regular ...
and cello
The cello ( ; plural ''celli'' or ''cellos'') or violoncello ( ; ) is a Bow (music), bowed (sometimes pizzicato, plucked and occasionally col legno, hit) string instrument of the violin family. Its four strings are usually intonation (music), t ...
), such as détaché, legato
In music performance and notation, legato (; Italian for "tied together"; French ''lié''; German ''gebunden'') indicates that musical notes are played or sung smoothly and connected. That is, the player makes a transition from note to note w ...
, staccato
Staccato (; Italian for "detached") is a form of musical articulation. In modern notation, it signifies a note of shortened duration, separated from the note that may follow by silence. It has been described by theorists and has appeared in music ...
, sforzato, martelé ("hammered"-style), sul ponticello
A variety of musical terms are likely to be encountered in printed scores, music reviews, and program notes. Most of the terms are Italian, in accordance with the Italian origins of many European musical conventions. Sometimes, the special mu ...
, sul tasto
A variety of musical terms are likely to be encountered in printed scores, music reviews, and program notes. Most of the terms are Italian, in accordance with the Italian origins of many European musical conventions. Sometimes, the special mu ...
, tremolo
In music, ''tremolo'' (), or ''tremolando'' (), is a trembling effect. There are two types of tremolo.
The first is a rapid reiteration:
* Of a single note, particularly used on bowed string instruments, by rapidly moving the bow back and fo ...
, spiccato
Spiccato is a bowing technique for string instruments in which the bow appears to bounce lightly upon the string. The term comes from the past participle of the Italian verb ''spiccare'', meaning "to separate". The terms '' martelé'', '' saltan ...
and sautillé
Playing the violin entails holding the instrument between the jaw and the collar bone (see below for variations of this posture). The strings are sounded either by drawing the bow across them (''arco''), or by plucking them ('' pizzicato''). The ...
. Some of these articulations can be combined; for example, the combination of sul ponticello and tremolo can produce eerie, ghostly sounds. Classical bass players do play pizzicato parts in orchestra, but these parts generally require simple notes (quarter notes, half notes, whole notes), rather than rapid passages.
 Classical players perform both bowed and pizz notes using
Classical players perform both bowed and pizz notes using vibrato
Vibrato (Italian, from past participle of " vibrare", to vibrate) is a musical effect consisting of a regular, pulsating change of pitch. It is used to add expression to vocal and instrumental music. Vibrato is typically characterised in terms o ...
, an effect created by rocking or quivering the left hand finger that is contacting the string, which then transfers an undulation in pitch to the tone. Vibrato is used to add expression to string playing. In general, very loud, low-register passages are played with little or no vibrato, as the main goal with low pitches is to provide a clear fundamental bass
In music theory, the concept of root is the idea that a chord can be represented and named by one of its notes. It is linked to harmonic thinking—the idea that vertical aggregates of notes can form a single unit, a chord. It is in this sense ...
for the string section. Mid- and higher-register melodies are typically played with more vibrato. The speed and intensity of the vibrato is varied by the performer for an emotional and musical effect.
In jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a majo ...
, rockabilly
Rockabilly is one of the earliest styles of rock and roll music. It dates back to the early 1950s in the United States, especially the Southern United States, South. As a genre it blends the sound of Western music (North America), Western music ...
and other related genres, much or all of the focus is on playing pizzicato. In jazz and jump blues
Jump blues is an up-tempo style of blues, usually played by small groups and featuring horn instruments. It was popular in the 1940s and was a precursor of rhythm and blues and rock and roll. Appreciation of jump blues was renewed in the 1990s a ...
, bassists are required to play rapid pizzicato walking bass
Bassline (also known as a bass line or bass part) is the term used in many styles of music, such as blues, jazz, funk, dub and electronic, traditional, or classical music for the low-pitched instrumental part or line played (in jazz and so ...
lines for extended periods. Jazz and rockabilly bassists develop virtuoso pizzicato techniques that enable them to play rapid solos that incorporate fast-moving triplet and sixteenth note figures. Pizzicato basslines performed by leading jazz professionals are much more difficult than the pizzicato basslines that classical bassists encounter in the standard orchestral literature, which are typically whole notes, half notes, quarter notes, and occasional eighth note passages. In jazz and related styles, bassists often add semi-percussive "ghost note
In music, a ghost note is a musical note with a rhythmic value, but no discernible pitch when played. In musical notation, this is represented by an "X" for a note head instead of an oval, or parentheses around the note head. It should not be c ...
s" into basslines, to add to the rhythmic feel and to add fills to a bassline.
The double bass player stands, or sits on a high stool, and leans the instrument against their body, turned slightly inward to put the strings comfortably in reach. This stance is a key reason for the bass's sloped shoulders, which mark it apart from the other members of the violin family—the narrower shoulders facilitate playing the strings in their higher registers.
History
The double bass is generally regarded as a modern descendant of the string family of instruments that originated in Europe in the 15th century, and as such has been described as a ''bass Violin.''''The Double Bass''Jacob Head Before the 20th century many double basses had only three strings, in contrast to the five to six strings typical of instruments in the viol family or the four strings of instruments in the violin family. The double bass's proportions are dissimilar to those of the violin and cello; for example, it is deeper (the distance from front to back is proportionally much greater than the violin). In addition, while the violin has bulging shoulders, most double basses have shoulders carved with a more acute slope, like members of the viol family. Many very old double basses have had their shoulders cut or sloped to aid playing with modern techniques. Before these modifications, the design of their shoulders was closer to instruments of the violin family. The double bass is the only modern bowed string instrument that is tuned in fourths (like a viol), rather than fifths (see Tuning below). The instrument's exact lineage is still a matter of some debate, and the supposition that the double bass is a direct descendant of the
viol
The viol (), viola da gamba (), or informally gamba, is any one of a family of bowed, fretted, and stringed instruments with hollow wooden bodies and pegboxes where the tension on the strings can be increased or decreased to adjust the pitc ...
family is one that has not been entirely resolved.
In his ''A New History of the Double Bass'', Paul Brun asserts that the double bass has origins as the true bass of the violin family
The violin family of musical instruments was developed in Italy in the 16th century. At the time the name of this family of instruments was viole da braccio which was used to distinguish them from the viol family (viole ''da gamba''). The standa ...
. He states that, while the exterior of the double bass may resemble the viola da gamba, the internal construction of the double bass is nearly identical to instruments in the violin family
The violin family of musical instruments was developed in Italy in the 16th century. At the time the name of this family of instruments was viole da braccio which was used to distinguish them from the viol family (viole ''da gamba''). The standa ...
, and very different from the internal structure of viols.
Double bass professor Larry Hurst
Larry is a masculine given name in English, derived from Lawrence or Laurence. It can be a shortened form of those names.
Larry may refer to the following:
People Arts and entertainment
* Larry D. Alexander, American artist/writer
*Larry Boon ...
argues that the "modern double bass is not a true member of either the violin or viol families". He says that "most likely its first general shape was that of a violone, the largest member of the viol family. Some of the earliest basses extant are violones, (including C-shaped sound holes) that have been fitted with modern trappings." Some existing instruments, such as those by Gasparo da Salò
Gasparo da Salò (20 May 154214 April 1609) is the name given to Gasparo Bertolotti, one of the earliest violin makers and an expert double bass player. Around 80 of his instruments are known to have survived to the present day: violins (small ...
, were converted from 16th-century six-string contrabass violoni.
Terminology
octave
In music, an octave ( la, octavus: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is the interval between one musical pitch and another with double its frequency. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been refer ...
lower than the cello (i.e. doubling on cello). The terms for the instrument among classical performers are contrabass (which comes from the instrument's Italian name, contrabbasso), string bass (to distinguish it from brass bass instruments in a concert band
A concert band, also called a wind band, wind ensemble, wind symphony, wind orchestra, symphonic band, the symphonic winds, or symphonic wind ensemble, is a performing ensemble consisting of members of the woodwind, brass, and percussion famil ...
, such as tuba
The tuba (; ) is the lowest-pitched musical instrument in the brass instrument, brass family. As with all brass instruments, the sound is produced by lip vibrationa buzzinto a mouthpiece (brass), mouthpiece. It first appeared in the mid-19th&n ...
s), or simply bass.
In jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a majo ...
, blues, rockabilly
Rockabilly is one of the earliest styles of rock and roll music. It dates back to the early 1950s in the United States, especially the Southern United States, South. As a genre it blends the sound of Western music (North America), Western music ...
and other genres outside of classical music, this instrument is commonly called the upright bass, standup bass or acoustic bass to distinguish it from the (usually electric) bass guitar
The bass guitar, electric bass or simply bass (), is the lowest-pitched member of the string family. It is a plucked string instrument similar in appearance and construction to an electric or an acoustic guitar, but with a longer neck and s ...
. In folk
Folk or Folks may refer to:
Sociology
*Nation
*People
* Folklore
** Folk art
** Folk dance
** Folk hero
** Folk music
*** Folk metal
*** Folk punk
*** Folk rock
** Folk religion
* Folk taxonomy
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Folk Plus or Fol ...
and bluegrass music
Bluegrass music is a genre of American roots music that developed in the 1940s in the Appalachian region of the United States. The genre derives its name from the band Bill Monroe and the Blue Grass Boys. Like mainstream country music, it la ...
, the instrument is also referred to as a "bass fiddle" or "bass violin" (or more rarely as "doghouse bass" or "bull fiddle"
). As a member of the violin-family of instruments, the construction of the upright bass is quite different from that of the acoustic bass guitar
The acoustic bass guitar (sometimes shortened to acoustic bass or initialized ABG) is a bass instrument with a hollow wooden body similar to, though usually larger than a steel-string acoustic guitar. Like the traditional electric bass guitar an ...
, as the latter is a derivative of the electric bass guitar, and usually built like a larger and sturdier variant of an acoustic guitar
An acoustic guitar is a musical instrument in the string family. When a string is plucked its vibration is transmitted from the bridge, resonating throughout the top of the guitar. It is also transmitted to the side and back of the instrument, ...
.
The double bass is sometimes confusingly called the violone
The term violone (; literally "large viol" in Italian, " -one" being the augmentative suffix) can refer to several distinct large, bowed musical instruments which belong to either the viol or violin family. The violone is sometimes a fretted i ...
, bass violin
Bass violin is the modern term for various 16th- and 17th-century bass instruments of the violin (i.e. ''viola da braccio'') family. They were the direct ancestor of the modern cello. Bass violins were usually somewhat larger than the modern cel ...
or bass viol
The viol (), viola da gamba (), or informally gamba, is any one of a family of bowed, fretted, and stringed instruments with hollow wooden bodies and pegboxes where the tension on the strings can be increased or decreased to adjust the pitch ...
. Other colourful names or nicknames are found in other languages. In Hungarian, the double bass is called ''nagybőgő'', which roughly translates as "big crier", referring to its large voice.
Design

 In general, there are two major approaches to the design outline shape of the double bass: the ''violin form'' (shown in the labelled picture in the construction section); and the ''viola da gamba'' form (shown in the header picture of this article). A third less common design, called the ''busetto'' shape, can also be found, as can the even more rare ''guitar'' or ''pear'' shape. The back of the instrument can vary from being a round, carved back similar to that of the violin, to a flat and angled back similar to the viol family.
The double bass features many parts that are similar to members of the violin family, including a wooden, carved
In general, there are two major approaches to the design outline shape of the double bass: the ''violin form'' (shown in the labelled picture in the construction section); and the ''viola da gamba'' form (shown in the header picture of this article). A third less common design, called the ''busetto'' shape, can also be found, as can the even more rare ''guitar'' or ''pear'' shape. The back of the instrument can vary from being a round, carved back similar to that of the violin, to a flat and angled back similar to the viol family.
The double bass features many parts that are similar to members of the violin family, including a wooden, carved bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually somethi ...
to support the strings, two f-hole
A sound hole is an opening in the body of a stringed musical instrument, usually the upper sound board.
Sound holes have different shapes:
* round in flat-top guitars and traditional bowl-back mandolins;
* F-holes in instruments from the vi ...
s, a tailpiece
A tailpiece is a component on many stringed musical instruments that anchors one end of the strings, usually opposite the end with the tuning mechanism (the scroll, headstock, peghead, etc.).
Function and construction
The tailpiece anchors ...
into which the ball ends of the strings are inserted (with the tailpiece anchored around the endpin mount), an ornamental scroll
A scroll (from the Old French ''escroe'' or ''escroue''), also known as a roll, is a roll of papyrus, parchment, or paper containing writing.
Structure
A scroll is usually partitioned into pages, which are sometimes separate sheets of papyrus ...
near the pegbox, a nut with grooves for each string at the junction of the fingerboard and the pegbox and a sturdy, thick sound post
In a string instrument, the sound post or soundpost is a dowel inside the instrument under the treble end of the bridge, spanning the space between the top and back plates and held in place by friction. It serves as a structural support for an ar ...
, which transmits the vibrations from the top of the instrument to the hollow body and supports the pressure of the string tension. Unlike the rest of the violin family, the double bass still reflects influences from, and can be considered partly derived, from the viol
The viol (), viola da gamba (), or informally gamba, is any one of a family of bowed, fretted, and stringed instruments with hollow wooden bodies and pegboxes where the tension on the strings can be increased or decreased to adjust the pitc ...
family of instruments, in particular the violone
The term violone (; literally "large viol" in Italian, " -one" being the augmentative suffix) can refer to several distinct large, bowed musical instruments which belong to either the viol or violin family. The violone is sometimes a fretted i ...
, the lowest-pitched and largest bass member of the viol family. For example, the bass is tuned in fourths, like a viol, rather than in fifths, which is the standard in the violin group. Also, notice that the 'shoulders' meet the neck in a curve, rather than the sharp angle seen among violins. As with the other violin and viol family instruments that are played with a bow (and unlike mainly plucked or picked instruments like guitar), the double bass's bridge has an arc-like, curved shape. This is done because with bowed instruments, the player must be able to play individual strings. If the double bass were to have a flat bridge, it would be impossible to bow the A and D strings individually.
The double bass also differs from members of the violin family in that the shoulders are typically sloped and the back is often angled (both to allow easier access to the instrument, particularly in the upper range). Machine tuners are always fitted, in contrast to the rest of the violin family, where traditional wooden friction pegs are still the primary means of tuning. Lack of standardization in design means that one double bass can sound and look very different from another.
Construction
The double bass is closest in construction to violins, but has some notable similarities to the violone ("large viol"), the largest and lowest-pitched member of the viol family. Unlike the violone, however, the fingerboard of the double bass is unfretted, and the double bass has fewer strings (the violone, like most viols, generally had six strings, although some specimens had five or four). The fingerboard is made ofebony
Ebony is a dense black/brown hardwood, coming from several species in the genus '' Diospyros'', which also contains the persimmons. Unlike most woods, ebony is dense enough to sink in water. It is finely textured and has a mirror finish when ...
on high-quality instruments; on less expensive student instruments, other woods may be used and then painted or stained black (a process called "ebonizing"). The fingerboard is radiused using a curve, for the same reason that the bridge is curved: if the fingerboard and bridge were to be flat, then a bassist would not be able to bow the inner two strings individually. By using a curved bridge and a curved fingerboard, the bassist can align the bow with any of the four strings and play them individually. Unlike the violin and viola, but like the cello, the bass fingerboard is somewhat flattened out underneath the E string (the C string on cello), this is commonly known as a Romberg bevel. The vast majority of fingerboards cannot be adjusted by the performer; any adjustments must be made by a luthier. A very small number of expensive basses for professionals have adjustable fingerboards, in which a screw mechanism can be used to raise or lower the fingerboard height.
An important distinction between the double bass and other members of the violin family is the construction of the pegbox
A variety of methods are used to tune different stringed instruments. Most change the pitch produced when the string is played by adjusting the tension of the strings.
A tuning peg in a pegbox is perhaps the most common system. A peg has ...
and the tuning mechanism. While the violin, viola
; german: Bratsche
, alt=Viola shown from the front and the side
, image=Bratsche.jpg
, caption=
, background=string
, hornbostel_sachs=321.322-71
, hornbostel_sachs_desc=Composite chordophone sounded by a bow
, range=
, related=
*Violin family ...
, and cello all use friction pegs for tuning adjustments (tightening and loosening the string tension to raise or lower the string's pitch), the double bass has metal machine head
A machine head (also referred to as a tuning machine, tuner, or gear head) is a geared apparatus for tuning stringed musical instruments by adjusting string tension. Machine heads are used on mandolins, guitars, double basses and others, and ar ...
s and gears. One of the challenges with tuning pegs is that the friction between the wood peg and the peg hole may become insufficient to hold the peg in place, particularly if the peg hole become worn and enlarged. The key on the tuning machine of a double bass turns a metal ''worm'', which drives a worm gear
A worm drive is a gear arrangement in which a worm (which is a gear in the form of a screw) meshes with a worm wheel (which is similar in appearance to a spur gear). The two elements are also called the worm screw and worm gear. The terminolo ...
that winds the string. Turning the key in one direction tightens the string (thus raising its pitch); turning the key the opposite direction reduces the tension on the string (thus lowering its pitch). While this development makes fine tuners on the tailpiece (important for violin, viola and cello players, as their instruments use friction pegs for major pitch adjustments) unnecessary, a very small number of bassists use them nevertheless. One rationale for using fine tuners on bass is that for instruments with the low C extension, the pulley system for the long string may not effectively transfer turns of the key into changes of string tension/pitch. At the base of the double bass is a metal rod with a spiked or rubberized end called the endpin, which rests on the floor. This endpin
The endpin is the component of a cello or double bass that makes contact with the floor to support the instrument's weight. It is made of metal, carbon fiber, or, occasionally, wood, and is typically extensible from the bottom of the instrument, s ...
is generally thicker and more robust than that of a cello, because of the greater mass of the instrument.
The materials most often used in double bass construction for fully carved basses (the type used by professional orchestra bassists and soloists) are maple
''Acer'' () is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated since ht ...
(back, neck, ribs), spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' (), a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal ( taiga) regions of the Earth. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the sub ...
(top), and ebony
Ebony is a dense black/brown hardwood, coming from several species in the genus '' Diospyros'', which also contains the persimmons. Unlike most woods, ebony is dense enough to sink in water. It is finely textured and has a mirror finish when ...
(fingerboard, tailpiece). The tailpiece may be made from other types of wood or non-wood materials. Less expensive basses are typically constructed with laminate
Lamination is the technique/process of manufacturing a material in multiple layers, so that the composite material achieves improved strength, stability, sound insulation, appearance, or other properties from the use of the differing materi ...
d ( plywood) tops, backs, and ribs, or are hybrid models produced with laminated backs and sides and carved solid wood tops. Some 2010-era lower- to mid-priced basses are made of willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist ...
, student models constructed of Fiberglass
Fiberglass (American English) or fibreglass (Commonwealth English) is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass cl ...
were produced in the mid-20th century, and some (typically fairly expensive) basses have been constructed of carbon fiber
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (American English), carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers (Commonwealth English), carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon-fiber reinforced-thermoplastic (CFRP, CRP, CFRTP), also known as carbon fiber, carbon compo ...
.
 Laminated (plywood) basses, which are widely used in music schools,
Laminated (plywood) basses, which are widely used in music schools, youth orchestra
A youth orchestra is an orchestra made of Youth, young musicians, typically ranging from pre-teens or teenagers to those of Music school, conservatory age. Depending on the age range and selectiveness, they may serve different purposes. Orchest ...
s, and in popular and folk music settings (including rockabilly
Rockabilly is one of the earliest styles of rock and roll music. It dates back to the early 1950s in the United States, especially the Southern United States, South. As a genre it blends the sound of Western music (North America), Western music ...
, psychobilly
Psychobilly is a rock music fusion genre that fuses elements of rockabilly and punk rock. It's been defined as "loud frantic rockabilly music", it has also been said that it "takes the traditional countrified rock style known as rockabilly, ram ...
, blues, etc.), are very resistant to humidity and heat, as well to the physical abuse they are apt to encounter in a school environment (or, for blues and folk musicians, to the hazards of touring and performing in bars). Another option is the hybrid body bass, which has a laminated back and a carved or solid wood top. It is less costly and somewhat less fragile (at least regarding its back) than a fully carved bass.
The soundpost
In a string instrument, the sound post or soundpost is a dowel inside the instrument under the treble end of the bridge, spanning the space between the top and back plates and held in place by friction. It serves as a structural support for an arc ...
and bass bar
In a string instrument, the bass bar is a brace running from the foot of the neck to a position under the bridge, which bears much of the tension of the strings. Bass bars are used:
* In the members of the violin family;
* In the members of th ...
are components of the internal construction. All the parts of a double bass are glued together, except the soundpost, bridge, and tailpiece, which are held in place by string tension (although the soundpost usually remains in place when the instrument's strings are loosened or removed, as long as the bass is kept on its back. Some luthiers recommend changing only one string at a time to reduce the risk of the soundpost falling). If the soundpost falls, a luthier is needed to put the soundpost back into position, as this must be done with tools inserted into the f-holes; moreover, the exact placement of the soundpost under the bridge is essential for the instrument to sound its best. Basic bridges are carved from a single piece of wood, which is customized to match the shape of the top of each instrument. The least expensive bridges on student instruments may be customized just by sanding the feet to match the shape of the instrument's top. A bridge on a professional bassist's instrument may be ornately carved by a luthier.
Professional bassists are more likely to have adjustable bridges, which have a metal screw mechanism. This enables the bassist to raise or lower the height of the strings to accommodate changing humidity or temperature conditions. The metal tuning machines are attached to the sides of the pegbox with metal screws. While tuning mechanisms generally differ from the higher-pitched orchestral stringed instruments, some basses have non-functional, ornamental tuning peg
A variety of methods are used to tune different stringed instruments. Most change the pitch produced when the string is played by adjusting the tension of the strings.
A tuning peg in a pegbox is perhaps the most common system. A peg has ...
s projecting from the side of the pegbox, in imitation of the tuning pegs on a cello or violin.
Famous double bass makers come from around the world and often represent varied national characteristics. The most highly sought (and expensive) instruments come from Italy and include basses made by Giovanni Paolo Maggini
Giovanni Paolo Maggini (c. 1580 - c. 1630), was a luthier born in Botticino (Brescia), Italy. Maggini was a pupil of the most important violin maker of the Brescian school, Gasparo da Salò.
Maggini's early instruments are now considered very de ...
, Gasparo da Salò
Gasparo da Salò (20 May 154214 April 1609) is the name given to Gasparo Bertolotti, one of the earliest violin makers and an expert double bass player. Around 80 of his instruments are known to have survived to the present day: violins (small ...
, the Testore Testore is an Italian surname
A name in the Italian language consists of a given name ( it, nome), and a surname (); in most contexts, the given name is written before the surname. (In official documents, the Western surname may be written befor ...
family (Carlo Antonio, Carlo Giuseppe, Gennaro, Giovanni, Paulo Antonio), Celestino Puolotti Celestino is both a surname and a given name. Notable people with the name include:
*Anthony Celestino, the touring bassist for the ''Blink-182'' side project, Box Car Racer
*Celestino Alfonso (1916–1944), Spanish republican and volunteer in the ...
, and Matteo Goffriller
Matteo Goffriller (1659–1742) was a Venetian luthier, particularly noted for the quality of his cellos. He was active between 1685–1735 and was the founder of the " Venetian School" of luthiers, during a time when Venice was one of the most imp ...
. French and English basses from famous makers are also sought out by players.
Travel instruments
Several manufacturers make travel instruments, which are double basses that have features which reduce the size of the instrument so that the instrument will meet airline travel requirements. Travel basses are designed for touring musicians. One type of travel bass has a much smaller body than normal, while still retaining all of the features needed for playing. While these smaller-body instruments appear similar toelectric upright bass
The electric upright bass (EUB) is an instrument that can perform the musical function of a double bass.
It requires only a minimal or 'skeleton' body to produce sound because it uses a pickup and electronic amplifier and loudspeaker. Therefore, ...
es, the difference is that small-body travel basses still have a fairly large hollow acoustic sound chamber, while many EUBs are solid body, or only have a small hollow chamber. A second type of travel bass has a hinged or removable neck and a regular sized body. The hinged or removable neck makes the instrument smaller when it is packed for transportation.
Strings
 The history of the double bass is tightly coupled to the development of string technology, as it was the advent of overwound gut strings, which first rendered the instrument more generally practicable, as wound or overwound strings attain low notes within a smaller overall string diameter than non-wound strings. Professor
The history of the double bass is tightly coupled to the development of string technology, as it was the advent of overwound gut strings, which first rendered the instrument more generally practicable, as wound or overwound strings attain low notes within a smaller overall string diameter than non-wound strings. Professor Larry Hurst
Larry is a masculine given name in English, derived from Lawrence or Laurence. It can be a shortened form of those names.
Larry may refer to the following:
People Arts and entertainment
* Larry D. Alexander, American artist/writer
*Larry Boon ...
argues that had "it not been for the appearance of the overwound gut string in the 1650s, the double bass would surely have become extinct", because thicknesses needed for regular gut strings made the lower-pitched strings almost unplayable and hindered the development of fluid, rapid playing in the lower register.
Prior to the 20th century, double bass strings were usually made of catgut
Catgut (also known as gut) is a type of cord that is prepared from the natural fiber found in the walls of animal intestines. Catgut makers usually use sheep or goat intestines, but occasionally use the intestines of cattle, hogs, horses, mules, ...
; however, steel has largely replaced it, because steel strings hold their pitch better and yield more volume when played with the bow.Article on bass strings by the Double Bass WorkshopGut strings are also more vulnerable to changes of humidity and temperature, and break more easily than steel strings. Gut strings are nowadays mostly used by bassists who perform in baroque ensembles,
rockabilly
Rockabilly is one of the earliest styles of rock and roll music. It dates back to the early 1950s in the United States, especially the Southern United States, South. As a genre it blends the sound of Western music (North America), Western music ...
bands, traditional blues bands, and bluegrass bands. In some cases, the low E and A are wound in silver, to give them added mass. Gut strings provide the dark, "thumpy" sound heard on 1940s and 1950s recordings. The late Jeff Sarli, a blues upright bassist, said that "Starting in the 1950s, they began to reset the necks on basses for steel strings." Rockabilly and bluegrass bassists also prefer gut because it is much easier to perform the "slapping
Slap or slapping may refer to:
* Slapping (strike), a method of striking with the palm of the hand
* Slapping (music), a musical technique used with stringed instruments
* Slap tonguing, a musical technique used on wind instruments
* ''Slap'' ( ...
" upright bass style (in which the strings are percussively slapped and clicked against the fingerboard) with gut strings than with steel strings, because gut does not hurt the plucking fingers as much. A less expensive alternative to gut strings is nylon strings; the higher strings are pure nylon, and the lower strings are nylon wrapped in wire, to add more mass to the string, slowing the vibration, and thus facilitating lower pitches.
The change from gut to steel has also affected the instrument's playing technique over the last hundred years. Steel strings can be set up closer to the fingerboard and, additionally, strings can be played in higher positions on the lower strings and still produce clear tone. The classic 19th century Franz Simandl
Franz Simandl (August 1, 1840 – December 15, 1912) was a Czech double-bassist and pedagogue most remembered for his book ''New Method for the Double Bass,'' known as the "Simandl book", which is to this day used as a standard study of double ...
method does not use the low E string in higher positions because older gut strings, set up high over the fingerboard, could not produce clear tone in these higher positions. However, with modern steel strings, bassists can play with clear tone in higher positions on the low E and A strings, particularly when they use modern lighter-gauge, lower-tension steel strings.
Bows
The double bassbow
Bow often refers to:
* Bow and arrow, a weapon
* Bowing, bending the upper body as a social gesture
* An ornamental knot made of ribbon
Bow may also refer to:
* Bow (watercraft), the foremost part of a ship or boat
* Bow (position), the rower ...
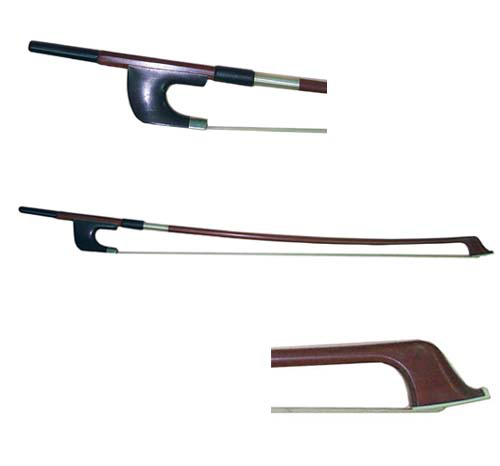
comes in two distinct forms (shown below). The "French" or "overhand" bow is similar in shape and implementation to the bow used on the other members of the orchestral string instrument family, while the "German" or "Butler" bow is typically broader and shorter, and is held in a "hand shake" (or "hacksaw") position.
 These two bows provide different ways of moving the arm and distributing force and weight on the strings. Proponents of the French bow argue that it is more maneuverable, due to the angle at which the player holds the bow. Advocates of the German bow claim that it allows the player to apply more arm weight on the strings. The differences between the two, however, are minute for a proficient player, and modern players in major orchestras use both bows.
These two bows provide different ways of moving the arm and distributing force and weight on the strings. Proponents of the French bow argue that it is more maneuverable, due to the angle at which the player holds the bow. Advocates of the German bow claim that it allows the player to apply more arm weight on the strings. The differences between the two, however, are minute for a proficient player, and modern players in major orchestras use both bows.
German bow
 The German bow (sometimes called the Butler bow) is the older of the two designs. The design of the bow and the manner of holding it descend from the older viol instrument family. With older viols, before
The German bow (sometimes called the Butler bow) is the older of the two designs. The design of the bow and the manner of holding it descend from the older viol instrument family. With older viols, before frogs
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" ''Triadobatrachus'' is ...
had screw threads to tighten the bow, players held the bow with two fingers between the stick and the hair to maintain tension of the hair. Proponents of the use of German bow claim that the German bow is easier to use for heavy strokes that require a lot of power.
Compared to the French bow, the German bow has a taller frog, and the player holds it with the palm angled upwards, as with the upright members of the viol
The viol (), viola da gamba (), or informally gamba, is any one of a family of bowed, fretted, and stringed instruments with hollow wooden bodies and pegboxes where the tension on the strings can be increased or decreased to adjust the pitc ...
family. When held in the traditionally correct manner, the thumb applies the necessary power to generate the desired sound. The index finger meets the bow at the point where the frog meets the stick. The index finger also applies an upward torque to the frog when tilting the bow. The little finger (or "pinky") supports the frog from underneath, while the ring finger and middle finger rest in the space between the hair and the shaft.
French bow
 The French bow was not widely popular until its adoption by 19th-century virtuoso
The French bow was not widely popular until its adoption by 19th-century virtuoso Giovanni Bottesini
Giovanni Bottesini (22 December 1821 – 7 July 1889) was an Italian Romantic composer, conductor, and a double bass virtuoso.
Biography
Born in Crema, Lombardy, he was taught the rudiments of music by his father, an accomplished clarinetist ...
. This style is more similar to the traditional bows of the smaller string family instruments. It is held as if the hand is resting by the side of the performer with the palm facing toward the bass. The thumb rests on the shaft of the bow, next to the frog while the other fingers drape on the other side of the bow. Various styles dictate the curve of the fingers and thumb, as do the style of piece; a more pronounced curve and lighter hold on the bow is used for virtuoso or more delicate pieces, while a flatter curve and sturdier grip on the bow sacrifices some power for easier control in strokes such as detaché, spiccato, and staccato.

Bow construction and materials
Double bass bows vary in length, ranging from . In general, a bass bow is shorter and heavier than a cello bow.Pernambuco
Pernambuco () is a state of Brazil, located in the Northeast region of the country. With an estimated population of 9.6 million people as of 2020, making it seventh-most populous state of Brazil and with around 98,148 km², being the ...
, also known as Brazilwood, is regarded as an excellent quality stick material, but due to its scarcity and expense, other materials are increasingly being used. Inexpensive student bows may be constructed of solid fiberglass
Fiberglass (American English) or fibreglass (Commonwealth English) is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass cl ...
, which makes the bow much lighter than a wooden bow (even too light to produce a good tone, in some cases). Student bows may also be made of the less valuable varieties of brazilwood. Snakewood Snakewood is a common name of several different plants:
* ''Acacia'' species (family Fabaceae) in Australia, '' Acacia eremaea'', '' Acacia intorta'', ''Acacia xiphophylla'
* '' Brosimum guianense'' (= ''Piratinera guianensis'') (family Moraceae) ...
and carbon fiber
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (American English), carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers (Commonwealth English), carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon-fiber reinforced-thermoplastic (CFRP, CRP, CFRTP), also known as carbon fiber, carbon compo ...
are also used in bows of a variety of different qualities. The frog of the double bass bow is usually made out of ebony
Ebony is a dense black/brown hardwood, coming from several species in the genus '' Diospyros'', which also contains the persimmons. Unlike most woods, ebony is dense enough to sink in water. It is finely textured and has a mirror finish when ...
, although snakewood and buffalo
Buffalo most commonly refers to:
* Bubalina, including most "Old World" buffalo, such as water buffalo
* Bison, including the American buffalo
* Buffalo, New York
Buffalo or buffaloes may also refer to:
Animals
* Bubalina, a subtribe of the tr ...
horn are used by some luthiers
A luthier ( ; AmE also ) is a craftsperson who builds or repairs string instruments that have a neck and a sound box. The word "luthier" is originally French and comes from the French word for lute. The term was originally used for makers of ...
. The frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" '' Triadobatrachus'' is ...
is movable, as it can be tightened or loosened with a knob (like all violin family bows). The bow is loosened at the end of a practice session or performance. The bow is tightened before playing, until it reaches a tautness that is preferred by the player. The frog on a quality bow is decorated with mother of pearl
Nacre ( , ), also known as mother of pearl, is an organicinorganic composite material produced by some molluscs as an inner shell layer; it is also the material of which pearls are composed. It is strong, resilient, and iridescent.
Nacre is ...
inlay.
Bows have a leather wrapping on the wooden part of the bow near the frog. Along with the leather wrapping, there is also a wire wrapping, made of gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
or silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
in quality bows. The hair is usually horsehair
Horsehair is the long hair growing on the manes and tails of horses. It is used for various purposes, including upholstery, brushes, the bows of musical instruments, a hard-wearing fabric called haircloth, and for horsehair plaster, a wa ...
. Part of the regular maintenance of a bow is having the bow "rehaired" by a luthier
A luthier ( ; AmE also ) is a craftsperson who builds or repairs string instruments that have a neck and a sound box. The word "luthier" is originally French and comes from the French word for lute. The term was originally used for makers of ...
with fresh horsehair and having the leather and wire wrapping replaced. The double bass bow is strung with either white or black horsehair, or a combination of the two (known as "salt and pepper"), as opposed to the customary white horsehair used on the bows of other string instruments. Some bassists argue that the slightly rougher black hair "grabs" the heavier, lower strings better. As well, some bassists and luthiers believe that it is easier to produce a smoother sound with the white variety. Red hair (chestnut) is also used by some bassists. Some of the lowest-quality, lowest cost student bows are made with synthetic hair. Synthetic hair does not have the tiny "barbs" that real horsehair has, so it does not "grip" the string well or take rosin well.
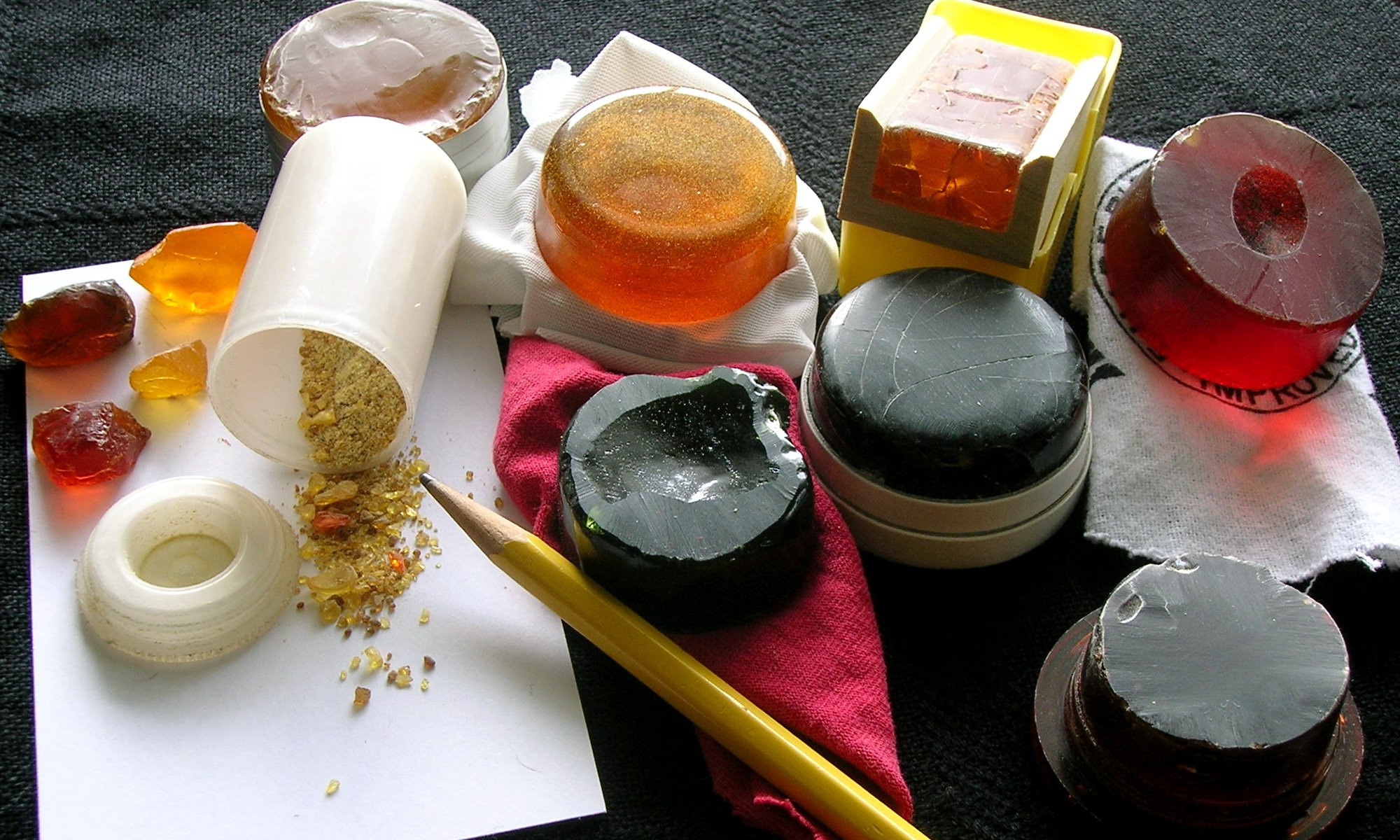
Rosin
rosin
Rosin (), also called colophony or Greek pitch ( la, links=no, pix graeca), is a solid form of resin obtained from pines and some other plants, mostly conifers, produced by heating fresh liquid resin to vaporize the volatile liquid terpene com ...
to the bow hair so it "grips" the string and makes it vibrate. Double bass rosin is generally softer and stickier than violin rosin to allow the hair to grab the thicker strings better, but players use a wide variety of rosins that vary from quite hard (like violin rosin) to quite soft, depending on the weather, the humidity, and the preference of the player. The amount used generally depends on the type of music being performed as well as the personal preferences of the player. Bassists may apply more rosin in works for large orchestra (e.g., Brahms symphonies) than for delicate chamber works. Some brands of rosin, such as Wiedoeft or Pop's double bass rosin, are softer and more prone to melting in hot weather. Other brands, such as Carlsson or Nyman Harts double bass rosin, are harder and less prone to melting.
Mechanism of sound production
Owing to their relatively small diameters, the strings themselves do not move much air and therefore cannot produce much sound on their own. The vibrational energy of the strings must somehow be transferred to the surrounding air. To do this, the strings vibrate the bridge and this in turn vibrates the top surface. Very small amplitude but relatively large force variations (due to the cyclically varying tension in the vibrating string) at the bridge are transformed to larger amplitude ones by combination of bridge and body of the bass. The bridge transforms the high force, small amplitude vibrations to lower force higher amplitude vibrations on the top of the bass body. The top is connected to the back by means of a sound post, so the back also vibrates. Both the front and back transmit the vibrations to the air and act to match the impedance of the vibrating string to theacoustic impedance
Acoustic impedance and specific acoustic impedance are measures of the opposition that a system presents to the acoustic flow resulting from an acoustic pressure applied to the system. The SI unit of acoustic impedance is the pascal-second per c ...
of the air.
Specific sound and tone production mechanism
Because the acoustic bass is a non-fretted instrument, any string vibration due to plucking or bowing will cause an audible sound due to the strings vibrating against the fingerboard near to the fingered position. This busing sound gives the note its character.Pitch
harmonics
A harmonic is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the '' fundamental frequency'', the frequency of the original periodic signal, such as a sinusoidal wave. The original signal is also called the ''1st harmonic'', ...
(also called flageolet tone
A harmonic is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'', the frequency of the original periodic signal, such as a sinusoidal wave. The original signal is also called the ''1st harmonic'', the ...
s), in which the bassist lightly touches the string–without pressing it onto the fingerboard in the usual fashion–in the location of a note and then plucks or bows the note. Bowed harmonics are used in contemporary music for their "glassy" sound. Both natural harmonics
A harmonic is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the '' fundamental frequency'', the frequency of the original periodic signal, such as a sinusoidal wave. The original signal is also called the ''1st harmonic'', ...
and artificial harmonic
Playing a string harmonic (a flageolet) is a string instrument technique that uses the nodes of natural harmonics of a musical string to isolate overtones. Playing string harmonics produces high pitched tones, often compared in timbre to a wh ...
s, where the thumb stops the note and the octave or other harmonic is activated by lightly touching the string at the relative node point, extend the instrument's range considerably. Natural and artificial harmonics are used in plenty of virtuoso concertos for the double bass.
Orchestral parts from the standard Classical repertoire
In European art music, the common-practice period is the era of the tonal system. Most of its features persisted from the mid- Baroque period through the Classical and Romantic periods, roughly from 1650 to 1900. There was much stylistic evolution ...
rarely demand the double bass exceed a two-octave and a minor third range, from E1 to G3, with occasional A3s appearing in the standard repertoire (an exception to this rule is Orff's ''Carmina Burana
''Carmina Burana'' (, Latin for "Songs from Benediktbeuern" 'Buria'' in Latin is a manuscript of 254 poems and dramatic texts mostly from the 11th or 12th century, although some are from the 13th century. The pieces are mostly bawdy, irreveren ...
'', which calls for three octaves and a perfect fourth). The upper limit of this range is extended a great deal for 20th- and 21st-century orchestral parts (e.g., Prokofiev
Sergei Sergeyevich Prokofiev; alternative transliterations of his name include ''Sergey'' or ''Serge'', and ''Prokofief'', ''Prokofieff'', or ''Prokofyev''., group=n (27 April .S. 15 April1891 – 5 March 1953) was a Russian composer, p ...
's ''Lieutenant Kijé Suite
A lieutenant ( , ; abbreviated Lt., Lt, LT, Lieut and similar) is a commissioned officer rank in the armed forces of many nations.
The meaning of lieutenant differs in different militaries (see comparative military ranks), but it is often su ...
'' (1933) bass solo, which calls for notes as high as D4 and E4). The upper range a virtuoso
A virtuoso (from Italian ''virtuoso'' or , "virtuous", Late Latin ''virtuosus'', Latin ''virtus'', "virtue", "excellence" or "skill") is an individual who possesses outstanding talent and technical ability in a particular art or field such as ...
solo player can achieve using natural and artificial harmonics is hard to define, as it depends on the skill of the particular player. The high harmonic in the range illustration found at the head of this article may be taken as representative rather than normative.
Five-string instruments have an additional string, typically tuned to a low B below the E string (B0). On rare occasions, a higher string is added instead, tuned to the C above the G string (C3). Four-string instruments may feature the C extension extending the range of the E string downwards to C1 (sometimes B0).
Traditionally, the double bass is a transposing instrument
A transposing instrument is a musical instrument for which music notation is not written at concert pitch (concert pitch is the pitch on a non-transposing instrument such as the piano). For example, playing a written middle C on a transposing ...
. Since much of the double bass's range lies below the standard bass clef
A clef (from French: 'key') is a musical symbol used to indicate which notes are represented by the lines and spaces on a musical stave. Placing a clef on a stave assigns a particular pitch to one of the five lines, which defines the pit ...
, it is notated an octave higher than it sounds to avoid having to use excessive ledger lines below the staff. Thus, when double bass players and cellists are playing from a combined bass-cello part, as used in many Mozart and Haydn symphonies, they will play in octaves, with the basses one octave below the cellos. This transposition applies even when bass players are reading the tenor
A tenor is a type of classical male singing voice whose vocal range lies between the countertenor and baritone voice types. It is the highest male chest voice type. The tenor's vocal range extends up to C5. The low extreme for tenors i ...
and treble clef
A clef (from French: 'key') is a musical symbol used to indicate which notes are represented by the lines and spaces on a musical stave. Placing a clef on a stave assigns a particular pitch to one of the five lines, which defines the pitc ...
(which are used in solo playing and some orchestral parts). The tenor clef is also used by composers for cello and low brass parts. The use of tenor or treble clef avoids excessive ledger lines above the staff when notating the instrument's upper range. Other notation traditions exist. Italian solo music is typically written at the sounding pitch, and the "old" German method sounded an octave below where notation except in the treble clef, where the music was written at pitch.
Tuning
Regular tuning
The double bass is generally tuned in fourths, in contrast to other members of the orchestral string family, which are tuned in fifths (for example, the violin's four strings are, from lowest-pitched to highest-pitched: G–D–A–E). The standard tuning (lowest-pitched to highest-pitched) for bass is E–A–D–G, starting from E below second low C (concert pitch
Concert pitch is the pitch reference to which a group of musical instruments are tuned for a performance. Concert pitch may vary from ensemble to ensemble, and has varied widely over music history. The most common modern tuning standard uses ...
). This is the same as the standard tuning of a bass guitar and is one octave
In music, an octave ( la, octavus: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is the interval between one musical pitch and another with double its frequency. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been refer ...
lower than the four lowest-pitched strings of standard guitar tuning. Prior to the 19th-century, many double basses had only three strings; "Giovanni Bottesini (1821–1889) favored the three-stringed instrument popular in Italy at the time", because "the three-stringed instrument as viewed as
As, AS, A. S., A/S or similar may refer to:
Art, entertainment, and media
* A. S. Byatt (born 1936), English critic, novelist, poet and short story writer
* "As" (song), by Stevie Wonder
* , a Spanish sports newspaper
* , an academic male voice ...
being more sonorous". Many cobla
The cobla (, plural ''cobles'') is a traditional music ensemble of Catalonia, and in Northern Catalonia in France. It is generally used to accompany the Sardana, a traditional Catalan folk dance, danced in a circle.
Structure
The modern Cobla no ...
bands in Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
still have players using traditional three-string double basses tuned A–D–G.
Throughout classical
Classical may refer to:
European antiquity
*Classical antiquity, a period of history from roughly the 7th or 8th century B.C.E. to the 5th century C.E. centered on the Mediterranean Sea
*Classical architecture, architecture derived from Greek and ...
repertoire, there are notes that fall below the range of a standard double bass. Notes below low E appear regularly in the double bass parts found in later arrangements and interpretations of Baroque music. In the Classical
Classical may refer to:
European antiquity
*Classical antiquity, a period of history from roughly the 7th or 8th century B.C.E. to the 5th century C.E. centered on the Mediterranean Sea
*Classical architecture, architecture derived from Greek and ...
era, the double bass typically doubled the cello part an octave below, occasionally requiring descent to C below the E of the four-string double bass. In the Romantic
Romantic may refer to:
Genres and eras
* The Romantic era, an artistic, literary, musical and intellectual movement of the 18th and 19th centuries
** Romantic music, of that era
** Romantic poetry, of that era
** Romanticism in science, of that e ...
era and the 20th century, composers such as Wagner
Wilhelm Richard Wagner ( ; ; 22 May 181313 February 1883) was a German composer, theatre director, polemicist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas (or, as some of his mature works were later known, "music dramas"). Unlike most op ...
, Mahler
Gustav Mahler (; 7 July 1860 – 18 May 1911) was an Austro-Bohemian Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th-century Austro-German tradition and the modernism o ...
, Busoni
Ferruccio Busoni (1 April 1866 – 27 July 1924) was an Italian composer, pianist, conductor, editor, writer, and teacher. His international career and reputation led him to work closely with many of the leading musicians, artists and literary ...
and Prokofiev
Sergei Sergeyevich Prokofiev; alternative transliterations of his name include ''Sergey'' or ''Serge'', and ''Prokofief'', ''Prokofieff'', or ''Prokofyev''., group=n (27 April .S. 15 April1891 – 5 March 1953) was a Russian composer, p ...
also requested notes below the low E.
There are several methods for making these notes available to the player. Players with standard double basses (E–A–D–G) may play the notes below "E" an octave higher or if this sounds awkward, the entire passage may be transposed up an octave. The player may tune the low E string down to the lowest note required in the piece: D or C. Four-string basses may be fitted with a "low-C extension" ( see below). Or the player may employ a five-string instrument, with the additional lower string tuned to C, or (more commonly in modern times) B, three octave
In music, an octave ( la, octavus: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is the interval between one musical pitch and another with double its frequency. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been refer ...
s and a semitone
A semitone, also called a half step or a half tone, is the smallest musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most dissonant when sounded harmonically.
It is defined as the interval between two adjacent no ...
below middle C
C or Do is the first note and semitone of the C major scale, the third note of the A minor scale (the relative minor of C major), and the fourth note (G, A, B, C) of the Guidonian hand, commonly pitched around 261.63 Hz. The actual fre ...
. Several major European orchestras use basses with a fifth string.
C extension
 Most professional orchestral players use four-string double basses with a ''C extension''. This is an extra section of fingerboard mounted on the head of the bass. It extends the fingerboard under the lowest string and gives an additional four semitones of downward range. The lowest string is typically tuned down to C1, an octave below the lowest note on the cello (as it is quite common for a bass part to double the cello part an octave lower). More rarely this string may be tuned to a low B0, as a few works in the orchestral repertoire call for such a B, such as
Most professional orchestral players use four-string double basses with a ''C extension''. This is an extra section of fingerboard mounted on the head of the bass. It extends the fingerboard under the lowest string and gives an additional four semitones of downward range. The lowest string is typically tuned down to C1, an octave below the lowest note on the cello (as it is quite common for a bass part to double the cello part an octave lower). More rarely this string may be tuned to a low B0, as a few works in the orchestral repertoire call for such a B, such as Respighi
Ottorino Respighi ( , , ; 9 July 187918 April 1936) was an Italian composer, violinist, teacher, and musicologist and one of the leading Italian composers of the early 20th century. List of compositions by Ottorino Respighi, His compositions r ...
's ''The Pines of Rome''. In rare cases, some players have a low B extension, which has B as its lowest note. There are several varieties of extensions:
In the simplest mechanical extensions, there are no mechanical aids attached to the fingerboard extension except a locking nut or "gate" for the E note. To play the extension notes, the player reaches back over the area under the scroll to press the string to the fingerboard. The advantage of this "fingered" extension is that the player can adjust the intonation of all of the stopped note
On string instruments, a stopped note is a note whose pitch has been altered from the pitch of the open string by the player's left hand pressing (stopping) the string against the fingerboard.
Bowed strings
On bowed string instruments, a stop ...
s on the extension, and there are no mechanical noises from metal keys and levers. The disadvantage of the "fingered" extension is that it can be hard to perform rapid alternations between low notes on the extension and notes on the regular fingerboard, such as a bassline that quickly alternates between G1 and D1.
The simplest type of mechanical aid is the use of wooden "fingers" or "gates" that can be closed to press the string down and fret the C, D, E, or E notes. This system is particularly useful for basslines that have a repeating pedal point
In music, a pedal point (also pedal note, organ point, pedal tone, or pedal) is a sustained tone, typically in the bass, during which at least one foreign (i.e. dissonant) harmony is sounded in the other parts. A pedal point sometimes functions ...
such as a low D because once the note is locked in place with the mechanical finger the lowest string sounds a different note when played open.
The most complicated mechanical aid for use with extensions is the mechanical lever system nicknamed the ''machine''. This lever system, which superficially resembles the keying mechanism of reed instruments such as the bassoon, mounts levers beside the regular fingerboard (near the nut, on the E-string side), which remotely activate metal "fingers" on the extension fingerboard. The most expensive metal lever systems also give the player the ability to "lock" down notes on the extension fingerboard, as with the wooden "finger" system. One criticism of these devices is that they may lead to unwanted metallic clicking noises.
Once a mechanical "finger" of the wooden "finger" extension or the metal "finger" machine extension is locked down or depressed, it is not easy to make microtonal pitch adjustments or glissando
In music, a glissando (; plural: ''glissandi'', abbreviated ''gliss.'') is a glide from one pitch to another (). It is an Italianized musical term derived from the French ''glisser'', "to glide". In some contexts, it is distinguished from the ...
effects, as is possible with a hand-fingered extension.
Five-string basses, in which the lowest string is normally B0, may use either a two semitone extension, providing a low A, or the very rare low G extension.
Other tuning variations
A small number of bass players tune their strings in fifths, like a cello but an octave lower (C1–G1–D2–A2 low to high). This tuning was used by the jazz playerRed Mitchell
Keith Moore "Red" Mitchell (September 20, 1927 – November 8, 1992) was an American jazz double-bassist, composer, lyricist, and poet.
Biography
Mitchell was born in New York City. His younger brother, Whitey Mitchell, also became a jazz ...
and is used by some classical players, notably the Canadian bassist Joel Quarrington
Joel Quarrington (born January 15, 1955) is a Canadian double bass player, soloist and teacher. He is the former Principal Double Bass of the London Symphony Orchestra.
Career
He was born in Toronto, Ontario, and began playing the double bass at ...
. Advocates of tuning the bass in fifths point out that all of the other orchestral strings are tuned in fifths (violin, viola, and cello), so this puts the bass in the same tuning approach. Fifth tuning provides a bassist with a wider range of pitch than a standard E–A–D–G bass, as it ranges (without an extension) from C1 to A2. Some players who use fifths tuning who play a five-string bass use an additional high E3 string (thus, from lowest to highest: C–G–D–A–E). Some fifth tuning bassists who only have a four string instrument and who are mainly performing soloistic works use the G–D–A–E tuning, thus omitting the low C string but gaining a high E. Some fifth tuning bassists who use a five-string use a smaller scale instrument, thus making fingering somewhat easier. The Berlioz–Strauss Treatise on Instrumentation
A treatise is a formal and systematic written discourse on some subject, generally longer and treating it in greater depth than an essay, and more concerned with investigating or exposing the principles of the subject and its conclusions."Treat ...
(first published in 1844) states that "A good orchestra should have several four-string double-basses, some of them tuned in fifths and thirds." The book then shows a tuning of E1–G1–D2–A2) from bottom to top string. "Together with the other double-basses tuned in fourths, a combination of open strings would be available, which would greatly increase the sonority of the orchestra."
In classical solo playing the double bass is usually tuned a whole tone higher (F1–B1–E2–A2). This higher tuning is called "solo tuning", whereas the regular tuning is known as "orchestral tuning". Solo tuning strings are generally thinner than regular strings. String tension differs so much between solo and orchestral tuning that a different set of strings is often employed that has a lighter gauge. Strings are always labelled for either solo or orchestral tuning and published solo music is arranged for either solo or orchestral tuning. Some popular solos and concerti, such as the ''Koussevitsky Concerto Koussvitzky is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Moshe Koussevitzky (1889–1966), Belarusian-born cantor
* Sergei Koussevitzky (1874–1951), Russian-born conductor
{{Short pages monitor
Miguel is a given name and surname, the Portuguese and Spanish form of the Hebrew name Michael. It may refer to:
Places
* Pedro Miguel, a parish in the municipality of Horta and the island of Faial in the Azores Islands
* São Miguel (disa ...
(''Nostalgica'' for string quartet and bass), Darius Milhaud
Darius Milhaud (; 4 September 1892 – 22 June 1974) was a French composer, conductor, and teacher. He was a member of Les Six—also known as ''The Group of Six''—and one of the most prolific composers of the 20th century. His compositions ...
, Luigi Boccherini
Ridolfo Luigi Boccherini (, also , ; 19 February 1743 – 28 May 1805) was an Italian composer and cellist of the Classical era whose music retained a courtly and '' galante'' style even while he matured somewhat apart from the major Eur ...
(3 quintets), Harold Shapero
Harold Samuel Shapero (April 29, 1920 – May 17, 2013) was an American composer.
Early years
Shapero was born in Lynn, Massachusetts, on April 29, 1920. He and his family later moved to nearby Newton. He learned to play the piano as a chi ...
, and Paul Hindemith
Paul Hindemith (; 16 November 189528 December 1963) was a German composer, music theorist, teacher, violist and conductor. He founded the Amar Quartet in 1921, touring extensively in Europe. As a composer, he became a major advocate of the '' ...
. Another example is Alistair Hinton's String Quintet (1969–77), which also includes a major part for solo soprano; at almost 170 minutes in duration, it is almost certainly the largest such work in the repertoire.
Slightly smaller string works with the double bass include six string sonatas by Gioachino Rossini
Gioachino Antonio Rossini (29 February 1792 – 13 November 1868) was an Italian composer who gained fame for his 39 operas, although he also wrote many songs, some chamber music and piano pieces, and some sacred music. He set new standards f ...
, for two violins, cello, and double bass written at the age of twelve over the course of three days in 1804. These remain his most famous instrumental works and have also been adapted for wind quartet. Franz Anton Hoffmeister
Franz Anton Hoffmeister (12 May 1754 – 9 February 1812) was an Austrian composer and music publisher.
Early years
Franz Anton Hoffmeister was born in Rottenburg am Neckar (Further Austria) on 12 May 1754. At the age of fourteen he went ...
wrote four String Quartets for Solo Double Bass, Violin, Viola, and Cello in D Major. Frank Proto
Frank Proto (born July 18, 1941 in Brooklyn, New York) is an American composer and bassist. He was a double bass student of Fred Zimmermann and David Walter. He is a graduate of the Manhattan School of Music in 1966 with a Master of Music. A se ...
has written a Trio for Violin, Viola and Double Bass (1974), 2 Duos for Violin and Double Bass (1967 and 2005), and ''The Games of October'' for Oboe/English Horn and Double Bass (1991).
Larger works that incorporate the double bass include Beethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 177026 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. Beethoven remains one of the most admired composers in the history of Western music; his works rank amongst the most performed of the classic ...
's Septet in E major, Op. 20, one of his most famous pieces during his lifetime, which consists of clarinet, horn, bassoon, violin, viola, cello, and bass. When the clarinetist Ferdinand Troyer
Count Ferdinand Troyer (February 1, 1780 – July 23, 1851) was an Austrian noble, philanthropist
Philanthropy is a form of altruism that consists of "private initiatives, for the Public good (economics), public good, focusing on quality of l ...
commissioned a work from Franz Schubert
Franz Peter Schubert (; 31 January 179719 November 1828) was an Austrian composer of the late Classical and early Romantic eras. Despite his short lifetime, Schubert left behind a vast ''oeuvre'', including more than 600 secular vocal wor ...
for similar forces, he added one more violin for his Octet in F major, D.803. Paul Hindemith
Paul Hindemith (; 16 November 189528 December 1963) was a German composer, music theorist, teacher, violist and conductor. He founded the Amar Quartet in 1921, touring extensively in Europe. As a composer, he became a major advocate of the '' ...
used the same instrumentation as Schubert for his own Octet. In the realm of even larger works, Mozart included the double bass in addition to 12 wind instruments for his "Gran Partita
The Serenade No. 10 for winds in B-flat major, K. 361/370a, is a serenade by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart scored for thirteen instruments: twelve winds and string bass. The piece was probably composed in 1781 or 1782 and is often known by the sub ...
" Serenade, K.361 and Martinů used the double bass in his nonet
Nonet may refer to:
*nonet (music), a composition which requires nine musicians for a performance
**Nonet (Farrenc) (1849) by Louise Farrenc
**Nonet (Lachner) (1875) by Franz Lachner
**Nonet (Villa-Lobos) (1923) by Heitor Villa-Libos
**Wind Nonet ...
for wind quintet, violin, viola, cello and double bass.
Other examples of chamber works that use the double bass in mixed ensembles include Sergei Prokofiev
Sergei Sergeyevich Prokofiev; alternative transliterations of his name include ''Sergey'' or ''Serge'', and ''Prokofief'', ''Prokofieff'', or ''Prokofyev''., group=n (27 April .S. 15 April1891 – 5 March 1953) was a Russian composer, p ...
's Quintet in G minor, Op. 39 for oboe, clarinet, violin, viola, and double bass; Miguel del Aguila
-->
Miguel is a given name and surname, the Portuguese and Spanish form of the Hebrew name Michael. It may refer to:
Places
* Pedro Miguel, a parish in the municipality of Horta and the island of Faial in the Azores Islands
* São Miguel (disa ...
's ''Malambo'' for bass flute and piano and for string quartet, bass and bassoon; Erwin Schulhoff
Erwin Schulhoff ( cs, Ervín Šulhov; 8 June 189418 August 1942) was an Austro-Czech composer and pianist. He was one of the figures in the generation of European musicians whose successful careers were prematurely terminated by the rise of the ...
's Concertino for flute/piccolo, viola, and double bass; Frank Proto
Frank Proto (born July 18, 1941 in Brooklyn, New York) is an American composer and bassist. He was a double bass student of Fred Zimmermann and David Walter. He is a graduate of the Manhattan School of Music in 1966 with a Master of Music. A se ...
's ''Afro-American Fragments'' for bass clarinet, cello, double bass and narrator and Sextet for clarinet and strings; Fred Lerdahl
Alfred Whitford (Fred) Lerdahl (born March 10, 1943, in Madison, Wisconsin) is the Fritz Reiner Professor Emeritus of Musical Composition at Columbia University, and a composer and music theorist best known for his work on musical grammar and c ...
's Waltzes for violin, viola, cello, and double bass; Mohammed Fairouz
Mohammed Fairouz (born November 1, 1985) is an American composer.
He is one of the most frequently performed composers of his generation and has been described by Daniel J. Wakin of ''The New York Times'' as an "important new artistic voice".
Fa ...
's Litany for double bass and wind quartet; Mario Davidovsky
Mario Davidovsky (March 4, 1934 – August 23, 2019) was an Argentine-American composer. Born in Argentina, he emigrated in 1960 to the United States, where he lived for the remainder of his life. He is best known for his series of compositions ca ...
's Festino for guitar, viola, cello, and double bass; and Iannis Xenakis
Giannis Klearchou Xenakis (also spelled for professional purposes as Yannis or Iannis Xenakis; el, Γιάννης "Ιωάννης" Κλέαρχου Ξενάκης, ; 29 May 1922 – 4 February 2001) was a Romanian-born Greek-French avant-garde ...
's Morsima-Amorsima for piano, violin, cello, and double bass. There are also new music ensembles that utilize the double bass such as Time for Three and PROJECT Trio
PROJECT Trio is a chamber music ensemble based in Brooklyn, New York. It consists of Greg Pattillo ( flute), Eric Stephenson (cello), and Peter Seymour (double bass). Their extensive repertoire consists of original compositions and arrangements ...
.
Orchestral passages and solos
In the baroque and classical periods, composers typically had the double bass double the cello part in orchestral passages. A notable exception is Haydn, who composed solo passages for the double bass in his Symphonies No. 6 ''Le Matin'', No. 7 ''Le midi'', No. 8 ''Le Soir'', No. 31 ''Horn Signal'', and No. 45 ''Farewell''—but who otherwise grouped bass and cello parts together. Beethoven paved the way for separate double bass parts, which became more common in the romantic era. Thescherzo
A scherzo (, , ; plural scherzos or scherzi), in western classical music, is a short composition – sometimes a movement from a larger work such as a symphony or a sonata. The precise definition has varied over the years, but scherzo often ...
and trio from Beethoven's Fifth Symphony
The Symphony No. 5 in C minor of Ludwig van Beethoven, Op. 67, was written between 1804 and 1808. It is one of the best-known compositions in classical music and one of the most frequently played symphonies, and it is widely considered one of ...
are famous orchestral excerpts, as is the recitative at the beginning of the fourth movement of Beethoven's Ninth Symphony
The Symphony No. 9 in D minor, Op. 125, is a choral symphony, the final complete symphony by Ludwig van Beethoven, composed between 1822 and 1824. It was first performed in Vienna on 7 May 1824. The symphony is regarded by many critics and music ...
. In many nineteenth century symphonies and concertos, the typical impact of separate bass and cello parts was that bass parts became simpler and cello parts got the melodic lines and rapid passage work.
A double bass section of a modern orchestra
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families.
There are typically four main sections of instruments:
* bowed string instruments, such as the violin, viola, c ...
typically uses eight double bassists, usually in unison
In music, unison is two or more musical parts that sound either the same pitch or pitches separated by intervals of one or more octaves, usually at the same time. ''Rhythmic unison'' is another term for homorhythm.
Definition
Unison or pe ...
. Smaller orchestras may have four double basses, and in exceptional cases, bass sections may have as many as ten members. If some double bassists have low C extensions, and some have regular (low E) basses, those with the low C extensions may play some passages an octave below the regular double basses. Also, some composers write divided (divisi) parts for the basses, where upper and lower parts in the music are often assigned to "outside" (nearer the audience) and "inside" players. Composers writing divisi parts for bass often write perfect interval
In music theory, an interval is a difference in pitch between two sounds.
An interval may be described as horizontal, linear, or melodic if it refers to successively sounding tones, such as two adjacent pitches in a melody, and vertical or ha ...
s, such as octaves and fifths, but in some cases use thirds and sixths.
Where a composition calls for a solo bass part, the principal bass invariably plays that part. The section leader (or principal) also determines the bowings, often based on bowings set out by the concertmaster. In some cases, the principal bass may use a slightly different bowing than the concertmaster, to accommodate the requirements of playing bass. The principal bass also leads entrances for the bass section, typically by lifting the bow or plucking hand before the entrance or indicating the entrance with the head, to ensure the section starts together. Major professional orchestras typically have an assistant principal bass player, who plays solos and leads the bass section if the principal is absent.
While orchestral bass solos are somewhat rare, there are some notable examples. Johannes Brahms
Johannes Brahms (; 7 May 1833 – 3 April 1897) was a German composer, pianist, and conductor of the mid- Romantic period. Born in Hamburg into a Lutheran family, he spent much of his professional life in Vienna. He is sometimes grouped wit ...
, whose father was a double bass player, wrote many difficult and prominent parts for the double bass in his symphonies. Richard Strauss
Richard Georg Strauss (; 11 June 1864 – 8 September 1949) was a German composer, conductor, pianist, and violinist. Considered a leading composer of the late Romantic music, Romantic and early Modernism (music), modern eras, he has been descr ...
assigned the double bass daring parts, and his symphonic poems and operas stretch the instrument to its limits. "The Elephant" from Camille Saint-Saëns
Charles-Camille Saint-Saëns (; 9 October 183516 December 1921) was a French composer, organist, conductor and pianist of the Romantic era. His best-known works include Introduction and Rondo Capriccioso (1863), the Second Piano Concerto ...
' ''The Carnival of the Animals
''The Carnival of the Animals'' (''Le Carnaval des animaux'') is a humorous musical suite of fourteen movements, including " The Swan", by the French composer Camille Saint-Saëns. The work, about 25 minutes in duration, was written for priva ...
'' is a satirical portrait of the double bass, and American virtuoso Gary Karr
Gary Michael Karr (born November 20, 1941 in Los Angeles) is an American classical double bass virtuoso and teacher; he is considered one of the best bassists of the 20th and 21st centuries.
Biography
Although he comes from several generations ...
made his televised debut playing "The Swan" (originally written for the cello) with the New York Philharmonic
The New York Philharmonic, officially the Philharmonic-Symphony Society of New York, Inc., globally known as New York Philharmonic Orchestra (NYPO) or New York Philharmonic-Symphony Orchestra, is a symphony orchestra based in New York City. It is ...
conducted by Leonard Bernstein
Leonard Bernstein ( ; August 25, 1918 – October 14, 1990) was an American conductor, composer, pianist, music educator, author, and humanitarian. Considered to be one of the most important conductors of his time, he was the first America ...
. The third movement of Gustav Mahler's first symphony features a solo for the double bass that quotes the children's song ''Frere Jacques'', transposed into a minor key. Sergei Prokofiev
Sergei Sergeyevich Prokofiev; alternative transliterations of his name include ''Sergey'' or ''Serge'', and ''Prokofief'', ''Prokofieff'', or ''Prokofyev''., group=n (27 April .S. 15 April1891 – 5 March 1953) was a Russian composer, p ...
's ''Lieutenant Kijé
Lieutenant Kijé or Kizhe (russian: Пору́чик Киже́, translit. Poruchik Kizhe), originally Kizh (Киж), is a fictional character in an anecdote about the reign of Emperor Paul I of Russia, in which the cover up of a transcripti ...
Suite'' features a difficult and very high double bass solo in the "Romance" movement. Benjamin Britten
Edward Benjamin Britten, Baron Britten (22 November 1913 – 4 December 1976, aged 63) was an English composer, conductor, and pianist. He was a central figure of 20th-century British music, with a range of works including opera, other ...
's ''The Young Person's Guide to the Orchestra
''The Young Person's Guide to the Orchestra'', Op. 34, is a 1945 musical composition by Benjamin Britten with a subtitle ''Variations and Fugue on a Theme of Purcell''. It was based on the second movement, "Rondeau", of the '' Abdelazer'' sui ...
'' contains a prominent passage for the double bass section.
Double bass ensembles
Ensembles made up entirely of double basses, though relatively rare, also exist, and several composers have written or arranged for such ensembles. Compositions for four double basses exist byGunther Schuller
Gunther Alexander Schuller (November 22, 1925June 21, 2015) was an American composer, conductor, horn player, author, historian, educator, publisher, and jazz musician.
Biography and works
Early years
Schuller was born in Queens, New York City ...
, Jacob Druckman
Jacob Raphael Druckman (June 26, 1928 – May 24, 1996) was an American composer born in Philadelphia.
Life
A graduate of the Juilliard School in 1956, Druckman studied with Vincent Persichetti, Peter Mennin, and Bernard Wagenaar. In 1949 and ...
, James Tenney
James Tenney (August 10, 1934 – August 24, 2006) was an American composer and music theorist. He made significant early musical contributions to plunderphonics, sound synthesis, algorithmic composition, process music, spectral music, microto ...
, Claus Kühnl
Claus Kühnl (born in Arnstein, Lower Franconia, 17 November 1957) is a German composer and teacher.
Life
Kühnl is the eldest child of Gudrun Kühnl (''née'' Schmitt) from Lower Franconia and Wilhelm Kühnl who comes from the Sudetenland.
...
, Robert CeelyJan Alm
Bernhard Alt, Norman Ludwin,
Frank Proto
Frank Proto (born July 18, 1941 in Brooklyn, New York) is an American composer and bassist. He was a double bass student of Fred Zimmermann and David Walter. He is a graduate of the Manhattan School of Music in 1966 with a Master of Music. A se ...
, Joseph Lauber, Erich Hartmann
Erich Alfred Hartmann (19 April 1922 – 20 September 1993) was a German fighter pilot during World War II and the most successful fighter ace in the history of aerial warfare. He flew 1,404 combat missions and participated in aerial comb ...
, Colin Brumby
Colin James Brumby (18 June 1933 – 3 January 2018) was an Australian composer and conductor.
Biography
Brumby was born in Melbourne and educated at the Glen Iris State School, Spring Road Central School, and Melbourne Boys' High School. He s ...
, Miloslav Gajdos and Theodore Albin Findeisen. David A. Jaffe
David Aaron Jaffe (born April 29, 1955) is an American composer who has written over ninety works for orchestra, chorus, chamber ensembles, and electronics. He is best known for his use of technology as an electronic-music or computer-music c ...
's "Who's on First?", commissioned by the Russian National Orchestra is scored for five double basses. Bertold Hummel
Bertold Hummel (27 November 1925 – 9 August 2002) was a German composer of modern classical music.
Life
Bertold Hummel was born in Hüfingen, Baden. He studied at the Academy of Music in Freiburg from 1947 to 1954, taking composition with Ha ...
wrote a ''Sinfonia piccola'' for eight double basses. Larger ensemble works include Galina Ustvolskaya
Galina Ivanovna Ustvolskaya (russian: Гали́на Ива́новна Уство́льская , 17 June 1919 – 22 December 2006), was a Russian composer of classical music.
Early years
Born in Petrograd, Ustvolskaya studied from 1937 to 1 ...
's Composition No. 2, "Dies Irae" (1973), for eight double basses, piano, and wooden cube, José Serebrier
José Serebrier (born 3 December 1938) is a Uruguayan conductor and composer. He is one of the most recorded conductors of his generation.
Early life
Serebrier was born in Montevideo to Russian and Polish parents of Jewish extraction. He fi ...
's "George and Muriel" (1986), for solo bass, double bass ensemble, and chorus, and Gerhard Samuel's ''What of my music!'' (1979), for soprano, percussion, and 30 double basses.
Double bass ensembles include L'Orchestre de Contrebasses (6 members), Bass Instinct (6 members), Bassiona Amorosa (6 members), the Chicago Bass Ensemble (4+ members)Ludus Gravis
founded by Daniele Roccato and
Stefano Scodanibbio
Stefano Scodanibbio (18 June 1956 – 8 January 2012) was an Italian musician who reached international prominence as a double bassist and composer.
Biography
Scodanibbio was born in Macerata. He studied double bass with Fernando Grillo and c ...
, The Bass Gang (4 members), the London Double Bass Ensemble The London Double Bass Ensemble (6 members) was established by members of the Philharmonia Orchestra of London in 1981. The ensemble has performed on television and radio and at venues including the South Bank and Wigmore Hall, giving many first per ...
(6 members) founded by members of the Philharmonia Orchestra of London who produced the LMusic Interludes by London Double Bass Ensemble
on Bruton Music records, Brno Double Bass Orchestra (14 members) founded by the double bass professor at
Janáček Academy of Music and Performing Arts
The Janáček Academy of Music and Performing Arts ( cs, Janáčkova akademie múzických umění v Brně; abbreviation in Czech: JAMU) is a public university with an artistic focus in Brno, Czech Republic. It was established in 1947 and consis ...
and principal double bass player at Brno Philharmonic Orchestra
The Brno Philharmonic (Czech: ''Filharmonie Brno'') is a Czech orchestra based in Brno, the Czech Republic. Its principal concert venue in Brno is the ''Besední dům''. The orchestra also performs regularly in the Janáček Opera House in Brno ...
– Miloslav Jelinek, and the ensembles of Ball State University (12 members), Shenandoah University
Shenandoah University is a private university in Winchester, Virginia. It has an enrollment of approximately 4,000 students across more than 200 areas of study in six schools: College of Arts & Sciences (including the Division of Education and ...
, and the Hartt School of Music
The Hartt School is the comprehensive performing arts conservatory of the University of Hartford located in West Hartford, Connecticut, United States, that offers degree programs in music, dance, and theatre. Founded in 1920 by Julius Hartt and ...
. The Amarillo Bass Base of Amarillo, Texas
Amarillo ( ; Spanish for " yellow") is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the seat of Potter County. It is the 14th-most populous city in Texas and the largest city in the Texas Panhandle. A portion of the city extends into Randall Co ...
once featured 52 double bassists, and The London Double Bass Sound, who have released a CD on Cala Records, have 10 players.
In addition, the double bass sections of some orchestras perform as an ensemble, such as the Chicago Symphony Orchestra
The Chicago Symphony Orchestra (CSO) was founded by Theodore Thomas in 1891. The ensemble makes its home at Orchestra Hall in Chicago and plays a summer season at the Ravinia Festival. The music director is Riccardo Muti, who began his tenu ...
's Lower Wacker Consort. There is an increasing number of published compositions and arrangements for double bass ensembles, and the International Society of Bassists The International Society of Bassists (ISB) is a 501(C)(3) not-for-profit organization for anybody who enjoys the double bass. The society was founded in 1967 by Gary Karr as the International Institute for String Bass (IISB). After a two-year hiat ...
regularly features double bass ensembles (both smaller ensembles as well as very large "mass bass" ensembles) at its conferences, and sponsors the biennial David Walter Composition Competition, which includes a division for double bass ensemble works.
Use in jazz
Beginning around 1890, the early New Orleansjazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a majo ...
ensemble (which played a mixture of marches, ragtime
Ragtime, also spelled rag-time or rag time, is a musical style that flourished from the 1890s to 1910s. Its cardinal trait is its syncopated or "ragged" rhythm. Ragtime was popularized during the early 20th century by composers such as Scott ...
, and Dixieland
Dixieland jazz, also referred to as traditional jazz, hot jazz, or simply Dixieland, is a style of jazz based on the music that developed in New Orleans at the start of the 20th century. The 1917 recordings by the Original Dixieland Jass Band ...
) was initially a marching band with a tuba
The tuba (; ) is the lowest-pitched musical instrument in the brass instrument, brass family. As with all brass instruments, the sound is produced by lip vibrationa buzzinto a mouthpiece (brass), mouthpiece. It first appeared in the mid-19th&n ...
or sousaphone
The sousaphone ( ) is a brass instrument in the tuba family. Created around 1893 by J. W. Pepper at the direction of American bandleader John Philip Sousa (after whom the instrument was then named), it was designed to be easier to play than t ...
(or occasionally bass saxophone
The bass saxophone is one of the lowest-pitched members of the saxophone family—larger and lower than the more common baritone saxophone. It was likely the first type of saxophone built by Adolphe Sax, as first observed by Berlioz in 1842. I ...
) supplying the bass line. As the music moved into bars and brothels, the upright bass gradually replaced these wind instruments around the 1920s. Many early bassists doubled on both the ''brass bass (tuba
The tuba (; ) is the lowest-pitched musical instrument in the brass instrument, brass family. As with all brass instruments, the sound is produced by lip vibrationa buzzinto a mouthpiece (brass), mouthpiece. It first appeared in the mid-19th&n ...
)'' and ''string bass'', as the instruments were then often referred to. Bassists played improvised "walking" bass lines—scale- and arpeggio-based lines that outlined the chord progression
In a musical composition, a chord progression or harmonic progression (informally chord changes, used as a plural) is a succession of chords. Chord progressions are the foundation of harmony in Western musical tradition from the common practice ...
.
Because an unamplified upright bass is generally the quietest instrument in a jazz band, many players of the 1920s and 1930s used the ''slap style'', slapping and pulling the strings to produce a rhythmic "slap" sound against the fingerboard. The slap style cuts through the sound of a band better than simply plucking the strings, and made the bass more easily heard on early sound recordings, as the recording equipment of that time did not favor low frequencies. For more about the slap style, see ''Modern playing styles'', below.
 Jazz bass players are expected to improvise an accompaniment line or solo for a given chord progression. They are also expected to know the rhythmic patterns that are appropriate for different styles (e.g., Afro-Cuban). Bassists playing in a big band must also be able to read written-out bass lines, as some arrangements have written bass parts.
Many upright bass players have contributed to the evolution of jazz. Examples include swing era players such as
Jazz bass players are expected to improvise an accompaniment line or solo for a given chord progression. They are also expected to know the rhythmic patterns that are appropriate for different styles (e.g., Afro-Cuban). Bassists playing in a big band must also be able to read written-out bass lines, as some arrangements have written bass parts.
Many upright bass players have contributed to the evolution of jazz. Examples include swing era players such as Jimmy Blanton
James Blanton (October 5, 1918 – July 30, 1942) was an American jazz double bassist. Blanton is credited with being the originator of more complex pizzicato and arco bass solos in a jazz context than previous bassists. Nicknamed "Jimmie," Bla ...
, who played with Duke Ellington
Edward Kennedy "Duke" Ellington (April 29, 1899 – May 24, 1974) was an American jazz pianist, composer, and leader of his eponymous jazz orchestra from 1923 through the rest of his life. Born and raised in Washington, D.C., Ellington was ba ...
, and Oscar Pettiford
Oscar Pettiford (September 30, 1922 – September 8, 1960) was an American jazz double bassist, cellist and composer. He was one of the earliest musicians to work in the bebop idiom.
Biography
Pettiford was born in Okmulgee, Oklahoma, United ...
, who pioneered the instrument's use in bebop
Bebop or bop is a style of jazz developed in the early-to-mid-1940s in the United States. The style features compositions characterized by a fast tempo, complex chord progressions with rapid chord changes and numerous changes of key, instrum ...
. Paul Chambers
Paul Laurence Dunbar Chambers Jr. (April 22, 1935 – January 4, 1969) was an American jazz double bassist. A fixture of rhythm sections during the 1950s and 1960s, he has become one of the most widely-known jazz bassists of the hard bop era. H ...
(who worked with Miles Davis
Miles Dewey Davis III (May 26, 1926September 28, 1991) was an American trumpeter, bandleader, and composer. He is among the most influential and acclaimed figures in the history of jazz and 20th-century music. Davis adopted a variety of musi ...
on the famous ''Kind of Blue
''Kind of Blue'' is a studio album by American jazz trumpeter, composer, and bandleader Miles Davis. It was recorded on March 2 and April 22, 1959, at Columbia's 30th Street Studio in New York City, and released on August 17 of that year by C ...
'' album) achieved renown for being one of the first jazz bassists to play bebop solos with the bow. Terry Plumeri
Jon Terryl "Terry" Plumeri (November 28, 1944 – March 31, 2016) was an American musician, classical composer, orchestra conductor, double bassist, lecturer, teacher, producer, and film score composer.
Early life
Plumeri was born in Greensb ...
furthered the development of arco (bowed) solos, achieving horn-like technical freedom and a clear, vocal bowed tone, while Charlie Haden
Charles Edward Haden (August 6, 1937 – July 11, 2014) was an American jazz double bass player, bandleader, composer and educator whose career spanned more than 50 years. In the late 1950s, he was an original member of the ground-breaking ...
, best known for his work with Ornette Coleman
Randolph Denard Ornette Coleman (March 9, 1930 – June 11, 2015) was an American jazz saxophonist, violinist, trumpeter, and composer known as a principal founder of the free jazz genre, a term derived from his 1960 album '' Free Jazz: A Col ...
, defined the role of the bass in Free Jazz
Free jazz is an experimental approach to jazz improvisation that developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s when musicians attempted to change or break down jazz conventions, such as regular tempos, tones, and chord changes. Musicians dur ...
.
A number of other bassists, such as Ray Brown, Slam Stewart
Leroy Eliot "Slam" Stewart (September 21, 1914December 10, 1987) was an American jazz double bass player, whose trademark style was his ability to bow the bass (arco) and simultaneously hum or sing an octave higher. He was a violinist before swi ...
and Niels-Henning Ørsted Pedersen
Niels-Henning Ørsted Pedersen (, 27 May 1946 – 19 April 2005), also known by his abbreviated nickname NHØP, was a Danish jazz double bassist.
Biography
Pedersen was born in Osted, near Roskilde, on the Danish island of Zealand, the son of ...
, were central to the history of jazz. Stewart, who was popular with the beboppers, played his solos with a bow combined with octave humming. Notably, Charles Mingus
Charles Mingus Jr. (April 22, 1922 – January 5, 1979) was an American jazz upright bassist, pianist, composer, bandleader, and author. A major proponent of collective improvisation, he is considered to be one of the greatest jazz musicians an ...
was a highly regarded composer as well as a bassist noted for his technical virtuosity and powerful sound. Scott LaFaro
Rocco Scott LaFaro (April 3, 1936 – July 6, 1961) was an American jazz double bassist known for his work with the Bill Evans Trio. LaFaro broke new ground on the instrument, developing a countermelodic style of accompaniment rather than playin ...
influenced a generation of musicians by liberating the bass from contrapuntal "walking" behind soloists instead favoring interactive, conversational melodies. Since the commercial availability of bass amplifier
A bass amplifier (also abbreviated to bass amp) is a musical instrument electronic device that uses electrical power to make lower-pitched instruments such as the bass guitar or double bass loud enough to be heard by the performers and audien ...
s in the 1950s, jazz bassists have used amplification to augment the natural volume of the instrument.
While the electric bass guitar was used intermittently in jazz as early as 1951, beginning in the 1970s bassist Bob Cranshaw
Melbourne Robert Cranshaw (December 3, 1932 – November 2, 2016) was an American jazz bassist. His career spanned the heyday of Blue Note Records to his recent involvement with the Musicians Union. He is perhaps best known for his long associa ...
, playing with saxophonist Sonny Rollins
Walter Theodore "Sonny" Rollins (born September 7, 1930) is an American jazz tenor saxophonist who is widely recognized as one of the most important and influential jazz musicians. In a seven-decade career, he has recorded over sixty albums as ...
, and fusion pioneers Jaco Pastorius
John Francis Anthony "Jaco" Pastorius III (; December 1, 1951 – September 21, 1987) was an American jazz bassist, composer and producer. He recorded albums as a solo artist and band leader and was a member of Weather Report from 1976 to 1981. ...
and Stanley Clarke
Stanley Clarke (born June 30, 1951) is an American bassist, film composer and founding member of Return to Forever, one of the first jazz fusion bands. Clarke gave the bass guitar a prominence it lacked in jazz-related music. He is the first jaz ...
began to commonly substitute the bass guitar for the upright bass. Apart from the jazz styles of jazz fusion and Latin-influenced jazz however, the upright bass is still the dominant bass instrument in jazz. The sound and tone of the plucked upright bass is distinct from that of the fretted bass guitar. The upright bass produces a different sound than the bass guitar, because its strings are not stopped by metal fret
A fret is any of the thin strips of material, usually metal wire, inserted laterally at specific positions along the neck or fretboard of a stringed instrument. Frets usually extend across the full width of the neck. On some historical instru ...
s, instead having a continuous tonal range on the uninterrupted fingerboard. As well, bass guitars usually have a solid wood body, which means that their sound is produced by electronic amplification of the vibration of the strings, instead of the upright bass's acoustic reverberation.
Demonstrative examples of the sound of a solo double bass and its technical use in jazz can be heard on the solo recordings ''Emerald Tears
''Emerald Tears'' is a solo album by bassist Dave Holland recorded in 1977 and released on the ECM label.Dave Holland
David “Dave” Holland (born 1 October 1946) is an English jazz double bassist, composer and bandleader who has been performing and recording for five decades. He has lived in the United States for over 40 years.
His extensive discography r ...
or ''Emergence
In philosophy, systems theory, science, and art, emergence occurs when an entity is observed to have properties its parts do not have on their own, properties or behaviors that emerge only when the parts interact in a wider whole.
Emergen ...
'' (1986) by Miroslav Vitous Miroslav may refer to:
* Miroslav (given name), a Slavic masculine given name
* ''Young America'' (clipper) or ''Miroslav'', an Austrian clipper ship in the Transatlantic case oil trade
* Miroslav (Znojmo District), a town in the Czech Republic
S ...
. Holland also recorded an album with the representative title ''Music from Two Basses
''Music from Two Basses'' is an album by bassists Dave Holland and Barre Phillips recorded in 1971 and released on the ECM label.
'' (1971) on which he plays with Barre Phillips
Barre Phillips (born October 27, 1934, in San Francisco, California, United States) is an American jazz bassist. A professional musician since 1960, he moved to New York City in 1962, then to Europe in 1967. Since 1972, he has been based in south ...
while he sometimes switches to cello.
Use in bluegrass and country
The string bass is the most commonly used bass instrument inbluegrass music
Bluegrass music is a genre of American roots music that developed in the 1940s in the Appalachian region of the United States. The genre derives its name from the band Bill Monroe and the Blue Grass Boys. Like mainstream country music, it la ...
and is almost always plucked, though some modern bluegrass bassists have also used a bow. The bluegrass bassist is part of the rhythm section, and is responsible for keeping a steady beat, whether fast, slow, in , or time. The bass also maintains the chord progression and harmony. The Engelhardt-Link (formerly Kay
The name Kay is found both as a surname (see Kay (surname)) and as a given name. In English-speaking countries, it is usually a feminine name, often a short form of Katherine or one of its variants; but it is also used as a first name in its own ...
) brands of plywood laminate basses have long been popular choices for bluegrass bassists. Most bluegrass bassists use the size bass, but the full-size and size basses are also used.
 Early pre-bluegrass traditional music was often accompanied by the cello. The cellist Natalie Haas points out that in the US, you can find "...old photographs, and even old recordings, of American string bands with cello". However, "The cello dropped out of sight in folk music, and became associated with the orchestra." The cello did not reappear in bluegrass until the 1990s and first decade of the 21st century. Some contemporary bluegrass bands favor the electric bass, because it is easier to transport than the large and somewhat fragile upright bass. However, the bass guitar has a different musical sound. Many musicians feel the slower attack and percussive, woody tone of the upright bass gives it a more "earthy" or "natural" sound than an electric bass, particularly when gut strings are used.
Common rhythms in bluegrass bass playing involve (with some exceptions) plucking on beats 1 and 3 in time; beats 1 and 2 in time, and on the downbeat in time (waltz time). Bluegrass bass lines are usually simple, typically staying on the root and fifth of each chord throughout most of a song. There are two main exceptions to this rule. Bluegrass bassists often do a diatonic ''walkup'' or ''
Early pre-bluegrass traditional music was often accompanied by the cello. The cellist Natalie Haas points out that in the US, you can find "...old photographs, and even old recordings, of American string bands with cello". However, "The cello dropped out of sight in folk music, and became associated with the orchestra." The cello did not reappear in bluegrass until the 1990s and first decade of the 21st century. Some contemporary bluegrass bands favor the electric bass, because it is easier to transport than the large and somewhat fragile upright bass. However, the bass guitar has a different musical sound. Many musicians feel the slower attack and percussive, woody tone of the upright bass gives it a more "earthy" or "natural" sound than an electric bass, particularly when gut strings are used.
Common rhythms in bluegrass bass playing involve (with some exceptions) plucking on beats 1 and 3 in time; beats 1 and 2 in time, and on the downbeat in time (waltz time). Bluegrass bass lines are usually simple, typically staying on the root and fifth of each chord throughout most of a song. There are two main exceptions to this rule. Bluegrass bassists often do a diatonic ''walkup'' or ''walkdown
In country music, walkdown is a bassline which connects two root position chords whose roots are a third apart, often featuring an inverted chord to go between the root notes of the first two chords. See: slash chord. A walkup would be the con ...
,'' in which they play every beat of a bar for one or two bars, typically when there is a chord change. In addition, if a bass player is given a solo, they may play a walking bass
Bassline (also known as a bass line or bass part) is the term used in many styles of music, such as blues, jazz, funk, dub and electronic, traditional, or classical music for the low-pitched instrumental part or line played (in jazz and so ...
line with a note on every beat or play a pentatonic scale-influenced bassline.
 An early bluegrass bassist to rise to prominence was Howard Watts (also known as Cedric Rainwater), who played with
An early bluegrass bassist to rise to prominence was Howard Watts (also known as Cedric Rainwater), who played with Bill Monroe
William Smith "Bill" Monroe (; September 13, 1911 – September 9, 1996) was an American mandolinist, singer, and songwriter, who created the bluegrass music genre. Because of this, he is often called the " Father of Bluegrass".
The genre take ...
's Blue Grass Boys beginning in 1944.''Howard "Cedric Rainwater" Watts''Stewart Evans The classical bassist
Edgar Meyer
Edgar Meyer (born November 24, 1960) is an American bassist and composer. His styles include classical, bluegrass, newgrass, and jazz. He has won five Grammy Awards and been nominated seven times.
Meyer is a member of the Telluride Bluegras ...
has frequently branched out into newgrass
Bluegrass music is a genre of American roots music that developed in the 1940s in the Appalachian region of the United States. The genre derives its name from the band Bill Monroe and the Blue Grass Boys. Like mainstream country music, it lar ...
, old-time, jazz, and other genres.
"My all-time favorite is Todd Phillips
Todd Phillips (né Bunzl, born December 20, 1970) is an American film director, producer, and screenwriter. He began his career in 1993 and directed films in the 2000s such as ''Road Trip'', '' Old School'', '' Starsky & Hutch'', and '' School ...
", proclaimed Union Station bassist Barry Bales in April 2005. "He brought a completely different way of thinking about and playing bluegrass.
An upright bass was the standard bass instrument in traditional country western music
Country (also called country and western) is a genre of popular music that originated in the Southern United States, Southern and Southwestern United States in the early 1920s. It primarily derives from blues, church music such as Southern gosp ...
. While the upright bass is still occasionally used in country music
Country (also called country and western) is a genre of popular music that originated in the Southern and Southwestern United States in the early 1920s. It primarily derives from blues, church music such as Southern gospel and spirituals, o ...
, the electric bass has largely replaced its bigger cousin in country music, especially in the more pop-infused country styles of the 1990s and 2000s, such as new country.
Slap-style bass
Slap-style bass is sometimes used in bluegrass bass playing. When bluegrass bass players slap the string by pulling it until it hits the fingerboard or hit the strings against the fingerboard, it adds the high-pitched percussive "clack" or "slap" sound to the low-pitched bass notes, sounding much like the clacks of a tap dancer. Slapping is a subject of minor controversy in the bluegrass scene. Even slapping experts such asMike Bub
The Del McCoury Band is a Grammy award-winning American bluegrass band.
History
Originally the band was called Del McCoury and the Dixie Pals with Del on guitar and his brother Jerry on bass. The band went through a number of changes in personn ...
say, "Don't slap on every gig", or in songs where it is not appropriate. As well, bluegrass bassists who play slap-style on live shows often slap less on records. Bub and his mentor Jerry McCoury
The Del McCoury Band is a Grammy award-winning American bluegrass band.
History
Originally the band was called Del McCoury and the Dixie Pals with Del on guitar and his brother Jerry on bass. The band went through a number of changes in person ...
rarely do slap bass on recordings. While bassists such as Jack Cook slap bass on the occasional faster "Clinch Mountain Boys song", bassists such as Gene Libbea, Missy Raines
Missy Raines (born April 6, 1962) is an American bassist, singer, teacher, and songwriter. She has won 10 International Bluegrass Music Awards for Bass Player of the Year. Missy Raines was the first woman to win IBMA Bass Player of the Year a ...
, Jenny Keel, and Barry Bales
Barry Turner Bales (born August 23, 1969 in Kingsport, Tennessee, United States) is an American musician best known as the long time bass player and harmony vocalist for Alison Krauss and Union Station. He has been in the band for around 25 years ...
arelyslap bass.
Bluegrass bassist Mark Schatz, who teaches slap bass in his ''Intermediate Bluegrass Bass'' DVD acknowledges that slap bass "...has not been stylistically very predominant in the music I have recorded". He notes that "Even in traditional bluegrass slap bass only appears sporadically and most of what I've done has been on the more contemporary side of that (Tony Rice, Tim O'Brien)." Schatz states that he would be "... more likely to use it lap
A lap is a surface (usually horizontal) created between the knee and hips of a biped when it is in a seated or lying down position. The lap of a parent or loved one is seen as a physically and psychologically comfortable place for a child to sit ...
in a live situation than on a recording—for a solo or to punctuate a particular place in a song or tune where I wouldn't be obliterating someone's solo". Another bluegrass method, ''Learn to Play Bluegrass Bass'', by Earl Gately, also teaches bluegrass slap bass technique. German bassist Didi Beck
Didi Beck is a German electric bass and double bass player. He plays in the rockabilly band, the Boppin'B. An accomplished upright bass slap bass
Slapping and popping are ways to produce percussive sounds on a stringed instrument. It is p ...
plays rapid triplet slaps, as demonstrated in this video.
Use in popular music
In the early 1950s, the upright bass was the standard bass instrument in the emerging style ofrock and roll
Rock and roll (often written as rock & roll, rock 'n' roll, or rock 'n roll) is a genre of popular music that evolved in the United States during the late 1940s and early 1950s. It originated from African-American music such as jazz, rhythm an ...
music, Marshall Lytle
Marshall Edward Lytle (September 1, 1933 – May 25, 2013) was an American rock and roll Double bass, bassist, best known for his work with the groups Bill Haley & His Comets and The Jodimars in the 1950s. He played upright slap bass on the icon ...
of Bill Haley & His Comets
Bill Haley & His Comets were an American rock and roll band founded in 1947 that continued until Haley's death in 1981. The band was also known as Bill Haley and the Comets and Bill Haley's Comets. From late 1954 to late 1956, the group record ...
being but one example. In the 1940s, a new style of dance music called rhythm and blues
Rhythm and blues, frequently abbreviated as R&B or R'n'B, is a Music genre, genre of popular music that originated in African-American communities in the 1940s. The term was originally used by record companies to describe recordings marketed p ...
developed, incorporating elements of the earlier styles of blues and swing. Louis Jordan
Louis Thomas Jordan (July 8, 1908 – February 4, 1975) was an American saxophonist, multi-instrumentalist, songwriter and bandleader who was popular from the late 1930s to the early 1950s. Known as " the King of the Jukebox", he earned his high ...
, the first innovator of this style, featured an upright bass in his group, the Tympany Five
Tympany Five was a successful and influential American rhythm and blues and jazz dance band founded by Louis Jordan in 1938. The group was composed of a horn section of three to five different pieces and also drums, double bass, guitar and pi ...
.''Dallas Bartley – Small town Boy: Playing in the bands''Special Collections and Archives Department, Missouri State University The upright bass remained an integral part of pop lineups throughout the 1950s, as the new genre of
rock and roll
Rock and roll (often written as rock & roll, rock 'n' roll, or rock 'n roll) is a genre of popular music that evolved in the United States during the late 1940s and early 1950s. It originated from African-American music such as jazz, rhythm an ...
was built largely upon the model of rhythm and blues, with strong elements also derived from jazz, country, and bluegrass. However, upright bass players using their instruments in these contexts faced inherent problems. They were forced to compete with louder horn instruments (and later amplified electric guitar
An electric guitar is a guitar that requires external amplification in order to be heard at typical performance volumes, unlike a standard acoustic guitar (however combinations of the two - a semi-acoustic guitar and an electric acoustic gu ...
s), making bass parts difficult to hear. The upright bass is difficult to amplify in loud concert venue settings, because it can be prone to feedback
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause-and-effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handled ...
''howls''. As well, the upright bass is large and awkward to transport, which also created transportation problems for touring bands. In some groups, the slap bass was utilized as band percussion in lieu of a drummer; such was the case with Bill Haley & His Saddlemen (the forerunner group to the Comets), which did not use drummers on recordings and live performances until late 1952; prior to this the slap bass was relied on for percussion, including on recordings such as Haley's versions of "Rock the Joint
"Rock the Joint", also known as "We're Gonna Rock This Joint Tonight", is a 1949 boogie song recorded by various proto- rock and roll singers, notably Jimmy Preston and early rock and roll singers, most notably Bill Haley in 1952. Preston's ver ...
" and "Rocket 88
"Rocket 88" (originally stylized as Rocket "88") is a song that was first recorded in Memphis, Tennessee, in March 1951. The recording was credited to " Jackie Brenston and his Delta Cats", who were actually Ike Turner and his Kings of Rhythm. Th ...
".
In 1951, Leo Fender
Clarence Leonidas Fender (August 10, 1909 – March 21, 1991) was an American inventor known for designing the Fender Stratocaster. He also founded the Fender Musical Instruments Corporation. In January 1965, he sold Fender to CBS, and later foun ...
released his Precision Bass
The Fender Precision Bass (often shortened to "P-Bass") is a model of electric bass guitar manufactured by Fender Musical Instruments Corporation. In its standard, post-1957 configuration, the Precision Bass is a solid body, four-stringed instrume ...
, the first commercially successful electric bass
The bass guitar, electric bass or simply bass (), is the lowest-pitched member of the string family. It is a plucked string instrument similar in appearance and construction to an electric or an acoustic guitar, but with a longer neck and ...
guitar.''The Electric Guitar: How We Got From Andrés Segovia To Kurt Cobain'', Monica M. Smith The electric bass was easily amplified with its built-in
magnetic pickup
A pickup is a transducer that captures or senses mechanical vibrations produced by musical instruments, particularly stringed instruments such as the electric guitar, and converts these to an electrical signal that is amplified using an instru ...
s, easily portable (less than a foot longer than an electric guitar), and easier to play in tune than an upright bass, thanks to the metal frets. In the 1960s and 1970s bands were playing at louder volumes and performing in larger venues. The electric bass was able to provide the huge, highly amplified stadium-filling bass tone that the pop and rock music of this era demanded, and the upright bass receded from the limelight of the popular music scene.
The upright bass began making a comeback in popular music in the mid-1980s, in part due to a renewed interest in earlier forms of folk and country music, as part of the roots rock
Roots rock is a genre of rock music that looks back to rock's origins in folk, blues and country music. It is particularly associated with the creation of hybrid subgenres from the later 1960s, including blues rock, country rock, Southern roc ...
and Americana
Americana may refer to:
*Americana (music), a genre or style of American music
*Americana (culture), artifacts of the culture of the United States
Film, radio and television
* ''Americana'' (1992 TV series), a documentary series presented by J ...
trends. In the 1990s, improvements in pickups and amplifier designs for electro-acoustic horizontal and upright basses made it easier for bassists to get a good, clear amplified tone from an acoustic instrument. Some popular bands decided to anchor their sound with an upright bass instead of an electric bass, such as the Barenaked Ladie
Barenaked Ladies is a Canadian rock band formed in 1988 in Scarborough, Ontario. The band developed a following in Canada, with their self-titled 1991 cassette becoming the first independent release to be certified gold in Canada. They reached ...
s. A trend for "unplugged" performances on MTV
MTV (Originally an initialism of Music Television) is an American cable channel that launched on August 1, 1981. Based in New York City, it serves as the flagship property of the MTV Entertainment Group, part of Paramount Media Networks, a di ...
, in which rock bands performed with solely acoustic instruments, further helped to enhance the public's interest in the upright bass and acoustic bass guitar
The acoustic bass guitar (sometimes shortened to acoustic bass or initialized ABG) is a bass instrument with a hollow wooden body similar to, though usually larger than a steel-string acoustic guitar. Like the traditional electric bass guitar an ...
s.
Jim Creeggan
James Raymond Creeggan (born February 12, 1970) is the bassist for Canadian alternative rock band Barenaked Ladies. Early life
Creeggan was born in Scarborough, Ontario. His mother taught piano lessons to neighborhood children, which Creeggan cre ...
of Barenaked Ladies
Barenaked Ladies is a Canadian rock band formed in 1988 in Scarborough, Ontario. The band developed a following in Canada, with their Barenaked Ladies (EP), self-titled 1991 cassette becoming the first independent release to be certified gold i ...
primarily plays upright bass, although he has increasingly played bass guitar throughout the band's career. Chris Wyse
Chris Wyse (born 15 July 1969) is an American bassist and vocalist. He is best known for his performances with Hollywood Vampires (band), Hollywood Vampires, Ace Frehley, The Cult and Ozzy Osbourne. He is the vocalist and bassist for Owl, a band ...
of alternative rock group Owl
Owls are birds from the order Strigiformes (), which includes over 200 species of mostly solitary and nocturnal birds of prey typified by an upright stance, a large, broad head, binocular vision, binaural hearing, sharp talons, and feathers a ...
uses a combination of electric and double bass. Athol Guy
Athol George Guy (born 5 January 1940) is a member of the Australian pop music group the Seekers, for whom he plays double bass and sings. He is easily recognisable by his black-framed "Buddy Holly" style glasses, and, during live performance ...
of the Australian folk/pop group The Seekers
The Seekers were an Australian folk-influenced pop quartet, originally formed in Melbourne in 1962. They were the first Australian pop music group to achieve major chart and sales success in the United Kingdom and the United States. They were ...
plays an upright bass. Shannon Birchall
Shannon Birchall is an Australian born musician, probably best known as the bassist for jam band the John Butler Trio. Birchall is often labeled a virtuoso by different music experts. He is also known for composing and conducting the string s ...
, of the Australian folk-rock group The John Butler Trio
The John Butler Trio are an Australian roots/ rock band led by guitarist and vocalist John Butler, an APRA and ARIA-award-winning musician. They formed in Fremantle in 1998 with Jason McGann on drums, Gavin Shoesmith on bass and John Butler on ...
, makes extensive use of upright basses, performing extended live solos in songs such as Betterman. On the 2008 album ''In Ear Park
''In Ear Park'' is the second album by Department of Eagles. It was released by 4AD on October 7, 2008. The inspiration for the album is noted to come from Daniel Rossen's childhood experiences, most notably memories of those related to his fat ...
'' by the indie/pop band Department of Eagles
Department of Eagles is an American duo formed in New York in 2000, consisting of Daniel Rossen and Fred Nicolaus.
History
The band was formed in 2000 by Rossen and Nicolaus, who were friends and New York University (NYU) roommates. They create ...
, a bowed upright bass is featured quite prominently on the songs "Teenagers" and "In Ear Park". Norwegian ompa-rock band Kaizers Orchestra
Kaizers Orchestra is a Norwegian alternative rock band formed on 1 January 2000. They are notable for being among the first non-black metal Norwegian artists singing in their native language to become popular beyond Scandinavia.
In 2012, the g ...
use the upright bass exclusively both live and on their recordings.
French contemporary pop duet "What a day" uses double bass extended pizzicato technique with vocals and type writer
Hank Williams III
Shelton Hank Williams (born December 12, 1972), known as Hank Williams III, is an American musician, singer and multi-instrumentalist, known for his unique fusion of traditional country music, rockabilly, heavy metal and punk rock. He was the ...
's bass players (Jason Brown, Joe Buck
Joseph Francis Buck (born April 25, 1969) is an American sportscaster.
The son of sportscaster Jack Buck, he worked for Fox Sports from its 1994 inception through 2022, including roles as lead play-by-play announcer for the network's Nation ...
and Zach Shedd, most notably) have used upright basses for recording as well as during the country and Hellbilly sets of Hank III's live performances before switching to electric bass for the Assjack
Assjack is an American heavy metal band led by Hank Williams III and Garrett Bremer. The band is one of the three incarnations of Williams' live show.
Career
For Assjack's long-anticipated 2009 self-titled studio debut, only Williams sang and p ...
set.
The late 1970s rockabilly-punk genre of psychobilly
Psychobilly is a rock music fusion genre that fuses elements of rockabilly and punk rock. It's been defined as "loud frantic rockabilly music", it has also been said that it "takes the traditional countrified rock style known as rockabilly, ram ...
continued and expanded upon the rockabilly tradition of slap bass. Bassists such as Kim Nekroman
Kim Nekroman is the bassist and lead singer for the psychobilly band Nekromantix and the lead guitarist of HorrorPops. He is from Denmark, and worked for the Danish Navy as a submarine radio operator for eight years before beginning his music c ...
and Geoff Kresge
Geoff Kresge is a songwriter, guitarist, bassist, and record producer. He played with the punk rock/horror punk band AFI for most of their early career, from 1992 through 1997, and co-wrote the majority of their early material alongside front ...
have developed the ability to play rapid slap bass that in effect turns the bass into a percussion instrument.
Modern playing styles
 In popular music genres, the instrument is usually played with amplification and almost exclusively played with the fingers, ''
In popular music genres, the instrument is usually played with amplification and almost exclusively played with the fingers, ''pizzicato
Pizzicato (, ; translated as "pinched", and sometimes roughly as "plucked") is a playing technique that involves plucking the strings of a string instrument. The exact technique varies somewhat depending on the type of instrument :
* On bowe ...
'' style. The pizzicato style varies between different players and genres. Some players perform with the sides of one, two, or three fingers, especially for walking basslines and slow tempo ballads, because this is purported to create a stronger and more solid tone. Some players use the more nimble tips of the fingers to play fast-moving solo passages or to pluck lightly for quiet tunes. The use of amplification allows the player to have more control over the tone of the instrument, because amplifiers have equalization controls that allow the bassist to accentuate certain frequencies (often the bass frequencies) while de-accentuating some frequencies (often the high frequencies, so that there is less finger noise).
An unamplified acoustic bass's tone is limited by the frequency responsiveness of the instrument's hollow body, which means that the very low pitches may not be as loud as the higher pitches. With an amplifier and equalization devices, a bass player can boost the low frequencies, which changes the frequency response. In addition, the use of an amplifier can increase the sustain of the instrument, which is particularly useful for accompaniment during ballads and for melodic solos with held notes.
In traditional jazz, swing
Swing or swinging may refer to:
Apparatus
* Swing (seat), a hanging seat that swings back and forth
* Pendulum, an object that swings
* Russian swing, a swing-like circus apparatus
* Sex swing, a type of harness for sexual intercourse
* Swing rid ...
, polka, rockabilly, and psychobilly music, it is sometimes played in the '' slap style''. This is a vigorous version of pizzicato where the strings are "slapped" against the fingerboard between the main notes of the bass line, producing a snare drum
The snare (or side drum) is a percussion instrument that produces a sharp staccato sound when the head is struck with a drum stick, due to the use of a series of stiff wires held under tension against the lower skin. Snare drums are often used i ...
-like percussive sound. The main notes are either played normally or by pulling the string away from the fingerboard and releasing it so that it bounces off the fingerboard, producing a distinctive percussive attack in addition to the expected pitch. Notable slap style bass players, whose use of the technique was often highly syncopated and virtuosic, sometimes interpolated two, three, four, or more slaps in between notes of the bass line.
"Slap style" may have influenced electric bass guitar players who, from the mid-sixties (particularly Larry Graham of Sly and the Family Stone), developed a technique called ''slap and pop
Slapping and popping are ways to produce percussive sounds on a stringed instrument. It is primarily used on the double bass or bass guitar. Slapping on bass guitar involves using the edge of one's knuckle, where it is particularly bony, to ...
'' that used the thumb of the plucking hand to hit the string, making a slapping sound but still letting the note ring, and the index or middle finger of the plucking hand to pull the string back so it hits the fretboard, achieving the pop sound described above. Motown
Motown Records is an American record label owned by the Universal Music Group. It was founded by Berry Gordy Jr. as Tamla Records on June 7, 1958, and incorporated as Motown Record Corporation on April 14, 1960. Its name, a portmanteau of ''mot ...
bass player James Jamerson
James Lee Jamerson (January 29, 1936 – August 2, 1983) was an American bass player. He was the uncredited bassist on most of the Motown Records hits in the 1960s and early 1970s (Motown did not list session musician credits on their releases ...
routinely used a double bass for enhancement of the electric bass in post-production ("sweetening") of recorded tracks and vice versa in many instances.
Double bassists
Historical
*Domenico Dragonetti
Domenico Carlo Maria Dragonetti (7 April 1763 – 16 April 1846) was an Italian double bass virtuoso and composer with a 3 string double bass. He stayed for thirty years in his hometown of Venice, Italy and worked at the Opera Buffa, at the Cha ...
(1763–1846) Virtuoso
A virtuoso (from Italian ''virtuoso'' or , "virtuous", Late Latin ''virtuosus'', Latin ''virtus'', "virtue", "excellence" or "skill") is an individual who possesses outstanding talent and technical ability in a particular art or field such as ...
, composer, conductor
* Giovanni Bottesini
Giovanni Bottesini (22 December 1821 – 7 July 1889) was an Italian Romantic composer, conductor, and a double bass virtuoso.
Biography
Born in Crema, Lombardy, he was taught the rudiments of music by his father, an accomplished clarinetist ...
(1821–1889) Virtuoso, composer, conductor
* Franz Simandl
Franz Simandl (August 1, 1840 – December 15, 1912) was a Czech double-bassist and pedagogue most remembered for his book ''New Method for the Double Bass,'' known as the "Simandl book", which is to this day used as a standard study of double ...
(1840–1912) Virtuoso, composer, pedagogue
Pedagogy (), most commonly understood as the approach to teaching, is the theory and practice of learning, and how this process influences, and is influenced by, the social, political and psychological development of learners. Pedagogy, taken ...
* Edouard Nanny (1872–1943) Virtuoso, composer
* Serge Koussevitzky
Sergei Alexandrovich KoussevitzkyKoussevitzky's original Russian forename is usually transliterated into English as either "Sergei" or "Sergey"; however, he himself adopted the French spelling " Serge", using it in his signature. (SeThe Koussevi ...
(1874–1951) Virtuoso, composer, conductor
Modern
*François Rabbath
François Rabbath (born 1931 in Aleppo, Syria) is a contemporary French double-bass virtuoso, soloist, and composer.
Career
He was born into a Syrian family of musicians but his only instruction came from a book written by a Parisian bassist E ...
(1931–) Virtuoso, composer
* Gary Karr
Gary Michael Karr (born November 20, 1941 in Los Angeles) is an American classical double bass virtuoso and teacher; he is considered one of the best bassists of the 20th and 21st centuries.
Biography
Although he comes from several generations ...
(1941– ) Virtuoso
* Edgar Meyer
Edgar Meyer (born November 24, 1960) is an American bassist and composer. His styles include classical, bluegrass, newgrass, and jazz. He has won five Grammy Awards and been nominated seven times.
Meyer is a member of the Telluride Bluegras ...
(1960– ) Virtuoso, composer, teacher
Contemporary (1900s)
Classical
 Some of the most influential contemporary classical double bass players are known as much for their contributions to pedagogy as for their performing skills, such as US bassist
Some of the most influential contemporary classical double bass players are known as much for their contributions to pedagogy as for their performing skills, such as US bassist Oscar G. Zimmerman
Oscar G. Zimmerman (September 21, 1910 – April 2, 1987) was an American musician, teacher and double-bass player.
Life and career
Born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania in 1910, Oscar Zimmerman was the double bassist with the Rochester Philhar ...
(1910–1987), known for his teaching at the Eastman School of Music
The Eastman School of Music is the music school of the University of Rochester, a private research university in Rochester, New York. It was established in 1921 by industrialist and philanthropist George Eastman.
It offers Bachelor of Music ...
and, for 44 summers at the Interlochen
Interlochen ( ') is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Grand Traverse County in the U.S. state of Michigan. At the 2020 census, the population was 694, up from 583 at the 2010 census. The community is located with ...
National Music Camp in Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
and French bassist François Rabbath
François Rabbath (born 1931 in Aleppo, Syria) is a contemporary French double-bass virtuoso, soloist, and composer.
Career
He was born into a Syrian family of musicians but his only instruction came from a book written by a Parisian bassist E ...
(b. 1931) who developed a new bass method that divided the entire fingerboard into six positions. Bassists noted for their virtuoso solo skills include American pedagogue and performer Gary Karr
Gary Michael Karr (born November 20, 1941 in Los Angeles) is an American classical double bass virtuoso and teacher; he is considered one of the best bassists of the 20th and 21st centuries.
Biography
Although he comes from several generations ...
(b. 1941), Finnish composer Teppo Hauta-Aho (b. 1941), Italian composer Fernando Grillo, and US player-composer Edgar Meyer
Edgar Meyer (born November 24, 1960) is an American bassist and composer. His styles include classical, bluegrass, newgrass, and jazz. He has won five Grammy Awards and been nominated seven times.
Meyer is a member of the Telluride Bluegras ...
. For a longer list, see the ''List of contemporary classical double bass players
Contemporary classical double bass players are performers who play the double bass, the largest and lowest-pitched Bow (music), bowed string instrument. They perform European art music ranging from Baroque music, Baroque Suite (music), suites and W ...
''.
Jazz
Notable jazz bassists from the 1940s to the 1950s included bassistJimmy Blanton
James Blanton (October 5, 1918 – July 30, 1942) was an American jazz double bassist. Blanton is credited with being the originator of more complex pizzicato and arco bass solos in a jazz context than previous bassists. Nicknamed "Jimmie," Bla ...
(1918–1942) whose short tenure in the Duke Ellington
Edward Kennedy "Duke" Ellington (April 29, 1899 – May 24, 1974) was an American jazz pianist, composer, and leader of his eponymous jazz orchestra from 1923 through the rest of his life. Born and raised in Washington, D.C., Ellington was ba ...
Swing band (cut short by his death from tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in w ...
) introduced new melodic and harmonic solo ideas for the instrument; bassist Ray Brown (1926–2002), known for backing Beboppers Dizzy Gillespie, Oscar Peterson
Oscar Emmanuel Peterson (August 15, 1925 – December 23, 2007) was a Canadian virtuoso jazz pianist and composer. Considered one of the greatest jazz pianists of all time, Peterson released more than 200 recordings, won seven Grammy Awards, ...
, Art Tatum
Arthur Tatum Jr. (, October 13, 1909 – November 5, 1956) was an American jazz pianist who is widely regarded as one of the greatest in his field. From early in his career, Tatum's technical ability was regarded by fellow musicians as extraord ...
and Charlie Parker
Charles Parker Jr. (August 29, 1920 – March 12, 1955), nicknamed "Bird" or "Yardbird", was an American jazz saxophonist, band leader and composer. Parker was a highly influential soloist and leading figure in the development of bebop, a form ...
, and forming the Modern Jazz Quartet
The Modern Jazz Quartet (MJQ) was a jazz combo established in 1952 that played music influenced by classical, cool jazz, blues and bebop. For most of its history the Quartet consisted of John Lewis (piano), Milt Jackson (vibraphone), Percy H ...
; hard bop
Hard bop is a subgenre of jazz that is an extension of bebop (or "bop") music. Journalists and record companies began using the term in the mid-1950s to describe a new current within jazz that incorporated influences from rhythm and blues, gosp ...
bassist Ron Carter
Ronald Levin Carter (born May 4, 1937) is an American jazz double bassist. His appearances on 2,221 recording sessions make him the most-recorded jazz bassist in history. He has won three Grammy awards, and is also a cellist who has recorded n ...
(born 1937), who has appeared on 3,500 albums make him one of the most-recorded bassists in jazz history, including LPs by Thelonious Monk
Thelonious Sphere Monk (, October 10, 1917 – February 17, 1982) was an American jazz pianist and composer. He had a unique improvisational style and made numerous contributions to the standard jazz repertoire, including " 'Round Midnight", ...
and Wes Montgomery
John Leslie "Wes" Montgomery (March 6, 1923 – June 15, 1968) was an American jazz guitarist. Montgomery was known for an unusual technique of plucking the strings with the side of his thumb and his extensive use of octaves, which gave him a dist ...
and many Blue Note Records
Blue Note Records is an American jazz record label owned by Universal Music Group and operated under Capitol Music Group. Established in 1939 by Alfred Lion and Max Margulis, it derived its name from the blue notes of jazz and the blues. Or ...
artists; and Paul Chambers
Paul Laurence Dunbar Chambers Jr. (April 22, 1935 – January 4, 1969) was an American jazz double bassist. A fixture of rhythm sections during the 1950s and 1960s, he has become one of the most widely-known jazz bassists of the hard bop era. H ...
(1935–1969), a member of the Miles Davis Quintet
The Miles Davis Quintet was an American jazz band from 1955 to early 1969 led by Miles Davis. The quintet underwent frequent personnel changes toward its metamorphosis into a different ensemble in 1969. Most references pertain to two distinct and ...
(including the landmark modal jazz recording ''Kind of Blue
''Kind of Blue'' is a studio album by American jazz trumpeter, composer, and bandleader Miles Davis. It was recorded on March 2 and April 22, 1959, at Columbia's 30th Street Studio in New York City, and released on August 17 of that year by C ...
'') and many other 1950s and 1960s rhythm sections, was known for his virtuosic improvisation
Improvisation is the activity of making or doing something not planned beforehand, using whatever can be found. Improvisation in the performing arts is a very spontaneous performance without specific or scripted preparation. The skills of impr ...
s.
 The experimental post 1960s era, and free jazz and jazz-rock fusion, produced several influential bassists.
The experimental post 1960s era, and free jazz and jazz-rock fusion, produced several influential bassists. Charles Mingus
Charles Mingus Jr. (April 22, 1922 – January 5, 1979) was an American jazz upright bassist, pianist, composer, bandleader, and author. A major proponent of collective improvisation, he is considered to be one of the greatest jazz musicians an ...
(1922–1979), who was also a composer and bandleader
A bandleader is the leader of a music group such as a rock or pop band or jazz quartet. The term is most commonly used with a group that plays popular music as a small combo or a big band, such as one which plays jazz, blues, rhythm and blues o ...
, produced music that fused hard bop
Hard bop is a subgenre of jazz that is an extension of bebop (or "bop") music. Journalists and record companies began using the term in the mid-1950s to describe a new current within jazz that incorporated influences from rhythm and blues, gosp ...
with black gospel music, free jazz
Free jazz is an experimental approach to jazz improvisation that developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s when musicians attempted to change or break down jazz conventions, such as regular tempos, tones, and chord changes. Musicians dur ...
, and classical music. Free jazz
Free jazz is an experimental approach to jazz improvisation that developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s when musicians attempted to change or break down jazz conventions, such as regular tempos, tones, and chord changes. Musicians dur ...
and post-bop bassist Charlie Haden
Charles Edward Haden (August 6, 1937 – July 11, 2014) was an American jazz double bass player, bandleader, composer and educator whose career spanned more than 50 years. In the late 1950s, he was an original member of the ground-breaking ...
(1937–2014) is best known for his long association with saxophonist Ornette Coleman
Randolph Denard Ornette Coleman (March 9, 1930 – June 11, 2015) was an American jazz saxophonist, violinist, trumpeter, and composer known as a principal founder of the free jazz genre, a term derived from his 1960 album '' Free Jazz: A Col ...
, and for his role in the 1970s-era Liberation Music Orchestra
Charles Edward Haden (August 6, 1937 – July 11, 2014) was an American jazz double bass player, bandleader, composer and educator whose career spanned more than 50 years. In the late 1950s, he was an original member of the ground-breaking ...
, an experimental group. Eddie Gómez
Edgar Gómez (born October 4, 1944) is a Puerto Rican jazz double bassist, known for his work with the Bill Evans Trio from 1966 to 1977.
Biography
Gómez moved with his family from Puerto Rico at a young age to New York, where he was raised. ...
and George Mraz
George Mraz (born Jiří Mráz; 9 September 1944 – 16 September 2021) was a Czech-born American jazz bassist and alto saxophonist. He was a member of Oscar Peterson's group, and worked with Pepper Adams, Stan Getz, Michel Petrucciani, Ste ...
, who played with Bill Evans
William John Evans (August 16, 1929 – September 15, 1980) was an American jazz pianist and composer who worked primarily as the leader of his trio. His use of impressionist harmony, interpretation of traditional jazz repertoire, block ch ...
and Oscar Peterson
Oscar Emmanuel Peterson (August 15, 1925 – December 23, 2007) was a Canadian virtuoso jazz pianist and composer. Considered one of the greatest jazz pianists of all time, Peterson released more than 200 recordings, won seven Grammy Awards, ...
, respectively, and are both acknowledged to have furthered expectations of pizzicato fluency and melodic phrasing. Fusion
Fusion, or synthesis, is the process of combining two or more distinct entities into a new whole.
Fusion may also refer to:
Science and technology Physics
*Nuclear fusion, multiple atomic nuclei combining to form one or more different atomic nucl ...
virtuoso Stanley Clarke
Stanley Clarke (born June 30, 1951) is an American bassist, film composer and founding member of Return to Forever, one of the first jazz fusion bands. Clarke gave the bass guitar a prominence it lacked in jazz-related music. He is the first jaz ...
(born 1951) is notable for his dexterity on both the upright bass and the electric bass. Terry Plumeri
Jon Terryl "Terry" Plumeri (November 28, 1944 – March 31, 2016) was an American musician, classical composer, orchestra conductor, double bassist, lecturer, teacher, producer, and film score composer.
Early life
Plumeri was born in Greensb ...
is noted for his horn-like arco fluency and vocal-sounding tone.
In the 1990s and first decade of the 21st century, one of the new "young lions" was Christian McBride
Christian McBride (born May 31, 1972) is an American jazz bassist, composer and arranger. He has appeared on more than 300 recordings as a sideman, and is an eight-time Grammy Award winner.
McBride has performed and recorded with a number of j ...
(born 1972), who has performed with a range of veterans ranging from McCoy Tyner
Alfred McCoy Tyner (December 11, 1938March 6, 2020) was an American jazz pianist and composer known for his work with the John Coltrane Quartet (from 1960 to 1965) and his long solo career afterwards. He was an NEA Jazz Master and five-time Gr ...
to fusion gurus Herbie Hancock
Herbert Jeffrey Hancock (born April 12, 1940) is an American jazz pianist, keyboardist, bandleader, and composer. Hancock started his career with trumpeter Donald Byrd's group. He shortly thereafter joined the Miles Davis Quintet, where he hel ...
and Chick Corea
Armando Anthony "Chick" Corea (June 12, 1941 – February 9, 2021) was an American jazz composer, pianist, keyboardist, bandleader, and occasional percussionist. His compositions "Spain", "500 Miles High", "La Fiesta", "Armando's Rhumba", and " ...
, and who has released albums such as 2003's ''Vertical Vision
''Vertical Vision'' is an album by bassist Christian McBride's sextet that was released in 2003 by Warner Bros. Records. This album was his only release on that record label.
Reception
Christian McBride of '' Jazz Review'' stated "For several y ...
''. Another young bassist of note is Esperanza Spalding
Esperanza Emily Spalding (born October 18, 1984) is an American bassist, singer, songwriter, and composer. Her accolades include five Grammy Awards, a Boston Music Award, and a Soul Train Music Award.
A native of Portland, Oregon, Spalding be ...
(born 1984) who, at 27 years of age, had already won a Grammy
The Grammy Awards (stylized as GRAMMY), or simply known as the Grammys, are awards presented by the Recording Academy of the United States to recognize "outstanding" achievements in the music industry. They are regarded by many as the most pres ...
for Best New Artist.
Other popular genres
In addition to being a noted classical player,Edgar Meyer
Edgar Meyer (born November 24, 1960) is an American bassist and composer. His styles include classical, bluegrass, newgrass, and jazz. He has won five Grammy Awards and been nominated seven times.
Meyer is a member of the Telluride Bluegras ...
is well known in bluegrass and newgrass
Bluegrass music is a genre of American roots music that developed in the 1940s in the Appalachian region of the United States. The genre derives its name from the band Bill Monroe and the Blue Grass Boys. Like mainstream country music, it lar ...
circles. Todd Phillips
Todd Phillips (né Bunzl, born December 20, 1970) is an American film director, producer, and screenwriter. He began his career in 1993 and directed films in the 2000s such as ''Road Trip'', '' Old School'', '' Starsky & Hutch'', and '' School ...
is another prominent bluegrass player. Well-known rockabilly
Rockabilly is one of the earliest styles of rock and roll music. It dates back to the early 1950s in the United States, especially the Southern United States, South. As a genre it blends the sound of Western music (North America), Western music ...
bassists include Bill Black
William Patton Black Jr. (September 17, 1926 – October 21, 1965) was an American musician and bandleader who is noted as one of the pioneers of rock and roll. He played in Elvis Presley's early trio. Black later formed Bill Black's Combo.
Ear ...
, Marshall Lytle
Marshall Edward Lytle (September 1, 1933 – May 25, 2013) was an American rock and roll Double bass, bassist, best known for his work with the groups Bill Haley & His Comets and The Jodimars in the 1950s. He played upright slap bass on the icon ...
(with Bill Haley & His Comets
Bill Haley & His Comets were an American rock and roll band founded in 1947 that continued until Haley's death in 1981. The band was also known as Bill Haley and the Comets and Bill Haley's Comets. From late 1954 to late 1956, the group record ...
) and Lee Rocker
Lee Rocker (born Leon Drucker, August 3, 1961) is an American musician. He is a member of the rockabilly revival band Stray Cats.
He is the son of the classical clarinetists Stanley Drucker, the late former principal clarinetist of the New Yo ...
(with 1980s-era rockabilly revivalists the Stray Cats
Stray Cats are an American rockabilly band formed in 1979 by guitarist and vocalist Brian Setzer, double bassist Lee Rocker, and drummer Slim Jim Phantom in the Long Island town of Massapequa, New York. The group had numerous hit singles ...
).
Notable rockabilly revivalists and psychobilly
Psychobilly is a rock music fusion genre that fuses elements of rockabilly and punk rock. It's been defined as "loud frantic rockabilly music", it has also been said that it "takes the traditional countrified rock style known as rockabilly, ram ...
performers from the 1990s and first decade of the 21st century include Scott Owen
Scott may refer to:
Places Canada
* Scott, Quebec, municipality in the Nouvelle-Beauce regional municipality in Quebec
* Scott, Saskatchewan, a town in the Rural Municipality of Tramping Lake No. 380
* Rural Municipality of Scott No. 98, Saska ...
(from the Australian band The Living End
The Living End are an Australian punk rockabilly band from Melbourne, formed in 1994. Since 2002, the line-up consists of Chris Cheney (vocals, guitar), Scott Owen (double bass, vocals), and Andy Strachan (drums). The band rose to fame in 199 ...
), Jimbo Wallace
Jimbo Wallace is an upright and electric bass player, vocalist, and songwriter in the psychobilly and rockabilly genres. He has played bass in the Reverend Horton Heat band since 1989. He is the most-tattooed member of the band.
He plays using the ...
(from the US band Reverend Horton Heat
The Reverend Horton Heat is the stage name of American musician James C. Heath (born 1959) as well as the name of his Dallas, Texas-based psychobilly trio. Heath is a singer, songwriter and guitarist. A ''Prick'' magazine reviewer called Heath ...
), Kim Nekroman
Kim Nekroman is the bassist and lead singer for the psychobilly band Nekromantix and the lead guitarist of HorrorPops. He is from Denmark, and worked for the Danish Navy as a submarine radio operator for eight years before beginning his music c ...
(Nekromantix
The Nekromantix is a Danish-American psychobilly band founded in Copenhagen in 1989. Their lyrics are generally structured around monster and horror themes. A central icon of the band's image is founder and frontman Kim Nekroman's "coffinbass", ...
), Patricia Day
Patricia Day is a Danish musician best known as the lead singer and bass player of the rockabilly/psychobilly band HorrorPops.
Early life
Patricia Day was born in Copenhagen, Denmark.
Career Bands
Patricia Day began her musical career performi ...
(HorrorPops
HorrorPops are a Danish punk band that formed in 1996. The band's sound is rooted in psychobilly, rockabilly, and punk rock.
History
1996–1999: Formation
Band founders Patricia Day and Kim Nekroman first met when Day's now-defunct b ...
), Geoff Kresge
Geoff Kresge is a songwriter, guitarist, bassist, and record producer. He played with the punk rock/horror punk band AFI for most of their early career, from 1992 through 1997, and co-wrote the majority of their early material alongside front ...
(Tiger Army
Tiger Army is an American psychobilly band based in Los Angeles, California. The group was formed in 1996 in Berkeley, California, and its only constant member is singer, guitarist, and lead songwriter Nick 13. The band has released six studi ...
, ex- AFI). Willie Dixon (1915–1992) was one of the most notable figures in the history of rhythm and blues
Rhythm and blues, frequently abbreviated as R&B or R'n'B, is a Music genre, genre of popular music that originated in African-American communities in the 1940s. The term was originally used by record companies to describe recordings marketed p ...
. In addition to being an upright bassist, he wrote dozens of R&B hits and worked as a producer. He also plays bass on numerous Chuck Berry
Charles Edward Anderson Berry (October 18, 1926 – March 18, 2017) was an American singer, songwriter and guitarist who pioneered rock and roll. Nicknamed the "Honorific nicknames in popular music, Father of Rock and Roll", he refined a ...
's rock and roll hits. Many other rockabilly
Rockabilly is one of the earliest styles of rock and roll music. It dates back to the early 1950s in the United States, especially the Southern United States, South. As a genre it blends the sound of Western music (North America), Western music ...
bands like El Rio Trio (from the Netherlands) also use this instrument in their work. See also the List of double bassists in popular music
This list of double bassists in popular music includes double bass performers from a range of genres, including rockabilly, psychobilly, country, blues, folk, bluegrass, and other styles. In these styles, the instrument is often referred to as an ...
.
Pedagogy and training
The pedagogy and training for the double bass varies widely by genre and country. Classical double bass has a history of pedagogy dating back several centuries, including teaching manuals, studies, and progressive exercises that help students to develop the endurance and accuracy of the left hand, and control for the bowing hand. Classical training methods vary by country: many of the major European countries are associated with specific methods (e.g., the Edouard Nanny method in France or theFranz Simandl
Franz Simandl (August 1, 1840 – December 15, 1912) was a Czech double-bassist and pedagogue most remembered for his book ''New Method for the Double Bass,'' known as the "Simandl book", which is to this day used as a standard study of double ...
method in Germany). In classical training, the majority of the instruction for the right hand focuses on the production of bowing tone; little time is spent studying the varieties of pizzicato tone.
In contrast, in genres that mainly or exclusively use pizzicato (plucking), such as jazz and blues, a great deal of time and effort is focused on learning the varieties of different pizzicato styles used for music of different styles of tempi. For example, in jazz, aspiring bassists have to learn how to perform a wide range of pizzicato tones, including using the sides of the fingers to create a full, deep sound for ballads, using the tips of the fingers for fast walking basslines or solos, and performing a variety of percussive ''ghost notes'' by raking muted or partially muted strings.
Formal training
 Of all of the genres, classical and jazz have the most established and comprehensive systems of instruction and training. In the classical milieu, children can begin taking private lessons on the instrument and performing in children's or youth orchestras. Teens who aspire to becoming professional classical bassists can continue their studies in a variety of formal training settings, including colleges, conservatories, and universities. Colleges offer certificates and diplomas in bass performance.
Conservatories, which are the standard musical training system in France and in Quebec (Canada) provide lessons and amateur orchestral experience for double bass players. Universities offer a range of double bass programs, including bachelor's degrees, Master of Music degrees, and
Of all of the genres, classical and jazz have the most established and comprehensive systems of instruction and training. In the classical milieu, children can begin taking private lessons on the instrument and performing in children's or youth orchestras. Teens who aspire to becoming professional classical bassists can continue their studies in a variety of formal training settings, including colleges, conservatories, and universities. Colleges offer certificates and diplomas in bass performance.
Conservatories, which are the standard musical training system in France and in Quebec (Canada) provide lessons and amateur orchestral experience for double bass players. Universities offer a range of double bass programs, including bachelor's degrees, Master of Music degrees, and Doctor of Musical Arts
The Doctor of Musical Arts (DMA) is a doctoral academic degree in music. The DMA combines advanced studies in an applied area of specialization (usually music performance, music composition, or conducting) with graduate-level academic study ...
degrees. As well, there are a variety of other training programs such as classical summer camps and orchestral, opera, or chamber music training festivals, which give students the opportunity to play a wide range of music.
Bachelor's degrees in bass performance (referred to as B.Mus.
Bachelor of Music (BM or BMus) is an academic degree awarded by a college, university, or conservatory upon completion of a program of study in music. In the United States, it is a professional degree, and the majority of work consists of presc ...
or B.M.) are four-year programs that include individual bass lessons, amateur orchestra experience, and a sequence of courses in music history, music theory, and liberal arts courses (e.g., English literature), which give the student a more well-rounded education. Usually, bass performance students perform several recitals of solo double bass music, such as concertos, sonatas, and Baroque suites.
Master of music degrees ( M.mus.) in double bass performance consist of private lessons, ensemble experience, coaching in playing orchestral double bass parts, and graduate courses in music history and music theory, along with one or two solo recitals. A Master's degree in music (referred to as an M.Mus. or M.M.) is often a required credential for people who wish to become a professor of double bass at a university or conservatory.
 Doctor of Musical Arts (referred to as D.M.A., DMA, D.Mus.A. or A.Mus.D.) degrees in double bass performance provide an opportunity for advanced study at the highest artistic and pedagogical level, requiring usually an additional 54+ credit hours beyond a master's degree (which is about 30+ credits beyond a bachelor's degree). For this reason, admission is highly selective. Examinations in music history, music theory, ear training/dictation, and an entrance examination-recital, are required. Students perform a number of recitals (around six), including a lecture-recital with an accompanying doctoral dissertation, advanced coursework, and a minimum B average are other typical requirements of a D.M.A. program.
Throughout the early history of jazz, double bass players either learned the instrument informally, or from getting classical training early on, as in the case of Ron Carter and Charles Mingus. In the 1980s and 1990s, colleges and universities began to introduce diplomas and degrees in jazz performance. Students in jazz diploma or Bachelor of Music programs take individual bass lessons, get experience in small jazz combos with coaching from an experienced player, and play in jazz big bands. As with classical training programs, jazz programs also include classroom courses in music history and music theory. In a jazz program, these courses focus on the different eras of jazz history. such as Swing, Bebop, and fusion. The theory courses focus on the musical skills used in jazz improvisation and in jazz comping (accompanying) and the composition of jazz tunes. There are also jazz summer camps and training festivals/seminars, which offer students the chance to learn new skills and styles.
Doctor of Musical Arts (referred to as D.M.A., DMA, D.Mus.A. or A.Mus.D.) degrees in double bass performance provide an opportunity for advanced study at the highest artistic and pedagogical level, requiring usually an additional 54+ credit hours beyond a master's degree (which is about 30+ credits beyond a bachelor's degree). For this reason, admission is highly selective. Examinations in music history, music theory, ear training/dictation, and an entrance examination-recital, are required. Students perform a number of recitals (around six), including a lecture-recital with an accompanying doctoral dissertation, advanced coursework, and a minimum B average are other typical requirements of a D.M.A. program.
Throughout the early history of jazz, double bass players either learned the instrument informally, or from getting classical training early on, as in the case of Ron Carter and Charles Mingus. In the 1980s and 1990s, colleges and universities began to introduce diplomas and degrees in jazz performance. Students in jazz diploma or Bachelor of Music programs take individual bass lessons, get experience in small jazz combos with coaching from an experienced player, and play in jazz big bands. As with classical training programs, jazz programs also include classroom courses in music history and music theory. In a jazz program, these courses focus on the different eras of jazz history. such as Swing, Bebop, and fusion. The theory courses focus on the musical skills used in jazz improvisation and in jazz comping (accompanying) and the composition of jazz tunes. There are also jazz summer camps and training festivals/seminars, which offer students the chance to learn new skills and styles.
Informal training
In other genres, such as blues, rockabilly, and psychobilly, the pedagogical systems and training sequences are not as formalized and institutionalized. There are not degrees in blues bass performance, or conservatories offering multiple-year diplomas in rockabilly bass. However, there are a range of books, playing methods, and, since the 1990s, instructional DVDs (e.g., on how to play rockabilly-style slap bass). As such, performers in these other genres tend to come from a variety of routes, including informal learning by using bass method books or DVDs, taking private lessons and coaching, and learning from records and CDs. In some cases, blues or rockabilly bassists may have obtained some initial training through the classical or jazz pedagogy systems (e.g., youth orchestra or high school big band). In genres such as tango, which use a lot of bowed passages and jazz-style pizzicato lines, the bassists tend to come from classical or jazz training routes.Careers
Careers in double bass vary widely by genre and by region or country. Most bassists earn their living from a mixture of performance and teaching jobs. The first step to getting most performance jobs is by playing at anaudition
An audition is a sample performance by an actor, singer, musician, dancer or other performer. It typically involves the performer displaying their talent through a previously memorized and rehearsed solo piece or by performing a work or piece ...
. In some styles of music, such as jazz-oriented stage bands, bassists may be asked to sight read
In music, sight-reading, also called ''a prima vista'' (Italian meaning "at first sight"), is the practice of reading and performing of a piece in a music notation that the performer has not seen or learned before. Sight-singing is used to descri ...
printed music or perform standard pieces (e.g., a jazz standard
Jazz standards are musical compositions that are an important part of the musical repertoire of jazz musicians, in that they are widely known, performed, and recorded by jazz musicians, and widely known by listeners. There is no definitive l ...
such as ''Now's the Time'') with an ensemble. Similarly, in a rock or blues band, auditionees may be asked to play various rock or blues standards. An upright bassist auditioning for a blues band might be asked to play in a Swing-style walking bassline, a rockabilly-style "slapping" bassline (in which the strings are percussively struck against the fingerboard) and a 1950s ballad with long held notes. A person auditioning for a role as a bassist in some styles of pop or rock music may be expected to demonstrate the ability to perform harmony vocals
Vocal harmony is a style of vocal music in which a consonant note or notes are simultaneously sung as a main melody in a predominantly homophonic texture. Vocal harmonies are used in many subgenres of European art music, including Classical ...
as a backup singer
A backing vocalist is a singer who provides vocal harmony with the lead vocalist or other backing vocalists. A backing vocalist may also sing alone as a lead-in to the main vocalist's entry or to sing a counter-melody. Backing vocalists are used ...
. In some pop and rock groups, the bassist may be asked to play other instruments from time to time, such as electric bass, keyboards or acoustic guitar. The ability to play electric bass is widely expected in country groups, in case the band is performing a classic rock
Classic rock is a US radio format which developed from the album-oriented rock (AOR) format in the early 1980s. In the United States, the classic rock format comprises rock music ranging generally from the mid-1960s through the mid 1990s, prim ...
or new country song.

Classical music
In classical music, bassists audition for playing jobs in orchestras and for admission into university or Conservatory programs or degrees. At a classical bass audition, the performer typically plays a movement from a J.S. Bach suite for solo cello or a movement from a bass concerto and a variety of excerpts from the orchestral literature. The excerpts are typically the most technically challenging parts of bass parts and bass solos from the orchestral literature. Some of the most commonly requested orchestral excerpts at bass auditions are fromBeethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 177026 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. Beethoven remains one of the most admired composers in the history of Western music; his works rank amongst the most performed of the classic ...
's Symphonies Nos. 5, 7 and 9; Strauss
Strauss, Strauß or Straus is a common Germanic surname. Outside Germany and Austria ''Strauß'' is always spelled ''Strauss'' (the letter " ß" is not used in the German-speaking part of Switzerland). In classical music, "Strauss" usually r ...
's ''Ein Heldenleben
''Ein Heldenleben'' (''A Hero's Life''), Op. 40, is a tone poem by Richard Strauss. The work was completed in 1898. It was his eighth work in the genre, and exceeded any of its predecessors in its orchestral demands. Generally agreed to be au ...
'' and ''Don Juan''; Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 17565 December 1791), baptised as Joannes Chrysostomus Wolfgangus Theophilus Mozart, was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition r ...
's Symphonies Nos. 35, 39 and 40; Brahms
Johannes Brahms (; 7 May 1833 – 3 April 1897) was a German composer, pianist, and conductor of the mid- Romantic period. Born in Hamburg into a Lutheran family, he spent much of his professional life in Vienna. He is sometimes grouped wit ...
' Symphonies Nos. 1 and 2; Stravinsky
Igor Fyodorovich Stravinsky (6 April 1971) was a Russian composer, pianist and conductor, later of French (from 1934) and American (from 1945) citizenship. He is widely considered one of the most important and influential composers of the ...
's Pulcinella; Shostakovich
Dmitri Dmitriyevich Shostakovich, , group=n (9 August 1975) was a Soviet-era Russian composer and pianist who became internationally known after the premiere of his First Symphony in 1926 and was regarded throughout his life as a major compo ...
's Symphony No. 5; Ginastera
Alberto Evaristo Ginastera (; April 11, 1916June 25, 1983) was an Argentinian composer of classical music. He is considered to be one of the most important 20th-century classical composers of the Americas.
Biography
Ginastera was born in Bue ...
's ''Variaciones Concertante''; Tchaikovsky
Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky , group=n ( ; 7 May 1840 – 6 November 1893) was a Russian composer of the Romantic period. He was the first Russian composer whose music would make a lasting impression internationally. He wrote some of the most pop ...
's Symphony No. 4; Mahler
Gustav Mahler (; 7 July 1860 – 18 May 1911) was an Austro-Bohemian Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th-century Austro-German tradition and the modernism o ...
's Symphony No. 2; J. S. Bach's Suite No. 2 in B; Berlioz's ''Symphonie Fantastique'', Mendelssohn's Symphony No. 4; and the bass solos from Verdi's opera ''Otello'', Mahler
Gustav Mahler (; 7 July 1860 – 18 May 1911) was an Austro-Bohemian Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th-century Austro-German tradition and the modernism o ...
's Symphony No. 1, Britten's ''The Young Person's Guide to the Orchestra
''The Young Person's Guide to the Orchestra'', Op. 34, is a 1945 musical composition by Benjamin Britten with a subtitle ''Variations and Fugue on a Theme of Purcell''. It was based on the second movement, "Rondeau", of the '' Abdelazer'' sui ...
'' and Prokofiev
Sergei Sergeyevich Prokofiev; alternative transliterations of his name include ''Sergey'' or ''Serge'', and ''Prokofief'', ''Prokofieff'', or ''Prokofyev''., group=n (27 April .S. 15 April1891 – 5 March 1953) was a Russian composer, p ...
's ''Lieutenant Kije Suite''.
See also
* ''Bach: Unaccompanied Cello Suites Performed on Double Bass'' * Bogdon Box Bass * Double bass concerto * Electric upright bass * List of historical classical double bass players * Octobass * Piccolo bass * Tololoche * Triple contrabass violReferences
External links
*EarlyBass.com by Jerry Fuller
Polish folk music double basses
Further reading
General
*Grodner, Murray, ''Comprehensive Catalog of books, recordings and videos for the double bass''. Bloomington IN, Murray Grodner, 2000. *Praetorius, Michael, ''Syntagma Musicum, Band II'', Kassel, Bärenreiter, 2001. (Reprint of the first edition of 1619). ISBN 978-3-76181527-4.History
*Billė, Isaia, ''Gli strumenti ad arco e i loro culturi.'' Rome, Ausonia. 1928. Pdf available at: https://www.vitoliuzzi.com/news-for-a-new-and-authentic-history-of-the-classic-bass/. *Boyden, David B., et al, ''The Violin Family'', The New Grove Musical Instruments Series, London, Macmillan, 1989. . *Brun, Paul, ''A New History of the Double Bass'', Seillons source d'Argens, Paul Brun Productions, 2018. . *Elgar, Raymond, ''Introduction to the Double Bass'', published by the author, St Leonards on Sea, 1960. *Elgar, Raymond, ''More About the Double Bass'', published by the author, St Leonards on Sea, 1963. *Elgar, Raymomd, ''Looking at the Double Bass'', published by the author, St Leonards on Sea, 1967. *Lohse, Jonas, ''Das Kontrabass-Buch'', Friedberg, Jonas Lohse Verlag, 2020. . *Martin, Thomas, Martin Lawrence and George Martin, ''The English Double Bass ''. Banbury, Arpeggio Publishing, 2018. *Palmer, Fiona M. (1997). ''Domenico Dragonetti in England (1794-1846) : the career of a double bass virtuoso''. Oxford, Clarendon Press, 1997. ISBN 0-19-816591-9. *Alfred Planyavsky, Planyavsky, Alfred, ''Geschichte des Kontrabasses'', Tutzing, Verlag Hans Schneider, 1984. *Stanton, David H., ''The String (Double) Bass''. Evanston IL, The Instrumentalist Company, 1982. *West, Chris, "The Paganini of the Double Bass - Bottesini in Britain." Independently published, 2021. ISBN 979-8747194595.Instruction methods and performance
* Billè, Isaia, ''Nuovo metodo per contrabbasso''. Milan: Ricordi, 1922 * Bradetich, Jeff, ''Double Bass: The Ultimate Challenge''. Denton, TX: Music for All to Hear, 2016. * Cruft, Eugene, ''The Eugene Cruft School of Double Bass Playing: A Method with a Repertoire''. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1966. * Goïlav, Yoan, ''La contrebasse: Une philosophie du jeu, histoire, pédagogie, technique / The Double Bass: A Philosophy of Playing, History, Pedagogy, Technique.'' Lévis, Quebec: Doberman-Yppan, 2003. * Goldsby, John, ''The Jazz Bass Book: Technique and Tradition''. San Francisco: Backbeat Books, 2002. * O'Brien, Orin. ''Double-Bass Notebook: Ideas, Tips, and Pointers for the Complete Professional.'' New York: Carl Fisher, 2016. . * Simandl, Franz, ''New Method for the Double Bass''. Carl Fischer, 1984. * Tambroni, Peter, ''An Introduction to Double Bass Playing''. Oak Park IL, www.MostlyBass.com, 2014. * Trebbi, Alfredo, "Il Contrabbasso - novissimo manuale semiserio." Milan: Casa Musicale Sonzogno, 2007. ISBN 978-88-87318-40-1. * Turetzky, Bertram. ''The Contemporary Contrabass''. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1989. {{Authority control Double basses, Bass (sound) Contrabass instruments C instruments Rhythm section Rockabilly instruments Blues instruments Amplified instruments Folk music instruments String section Basso continuo instruments Jazz instruments