Donough MacCarty, 1st Earl Of Clancarty on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sir Donough MacCarty, 1st Earl of Clancarty (1594–1665), was an Irish soldier and politician. He succeeded his father as 2nd Viscount Muskerry in 1641. He rebelled against the government and joined the Irish Catholic Confederation, demanding religious freedom as a Catholic and defending the rights of the Gaelic nobility. Later, he supported the King against his Parliamentarian enemies during the

 The Munster insurgents then attacked the castles of Sir Philip Perceval. In the summer of 1642 Muskerry took Annagh Castle,
The Munster insurgents then attacked the castles of Sir Philip Perceval. In the summer of 1642 Muskerry took Annagh Castle,

 In April 1650, Muskerry lost Macroom Castle. An Irish force raised by Fermoy and Boetius MacEgan, Catholic Bishop of Ross, tried to relieve the Siege of Clonmel. Led by Colonel David Roche and the bishop, this force passed by Macroom and camped in the castle's park. Macroom's garrison burned the castle and joined Roche's force, Cromwell sent Broghill to intercept the Irish, which were routed in the Battle of Macroom on 10 April. Clonmel surrendered to Cromwell in May. Cromwell had to hurry away to counter a threat from Scotland and passed the Irish command to
In April 1650, Muskerry lost Macroom Castle. An Irish force raised by Fermoy and Boetius MacEgan, Catholic Bishop of Ross, tried to relieve the Siege of Clonmel. Led by Colonel David Roche and the bishop, this force passed by Macroom and camped in the castle's park. Macroom's garrison burned the castle and joined Roche's force, Cromwell sent Broghill to intercept the Irish, which were routed in the Battle of Macroom on 10 April. Clonmel surrendered to Cromwell in May. Cromwell had to hurry away to counter a threat from Scotland and passed the Irish command to  Edmund Ludlow besieged Muskerry in Ross Castle, on the shore of Lough Leane. The defenders were supplied by boat over the lake. Ludlow brought boats of his own whereupon Muskerry surrendered on 27 June 1652 after a siege of three weeks. The terms took a possible prosecution into account. Muskerry gave two hostages to guarantee his compliance with the terms: one of his sons and "Daniel O'Brien". Daniel O'Brien. This son probably was Callaghan, whereas the Daniel O'Brien probably was the future 3rd Viscount Clare, about 30 at the time, rather than the future 1st Viscount, who was about 70. Muskerry disbanded his 5,000-strong army. He was excluded from pardon of life and estate in the Commonwealth's Act of Settlement on 12 August and therefore lost his estates. His surrender was one of the last, but Clanricarde, 28 June, and Philip O'Reilly, 27 April 1653, surrendered later.
Edmund Ludlow besieged Muskerry in Ross Castle, on the shore of Lough Leane. The defenders were supplied by boat over the lake. Ludlow brought boats of his own whereupon Muskerry surrendered on 27 June 1652 after a siege of three weeks. The terms took a possible prosecution into account. Muskerry gave two hostages to guarantee his compliance with the terms: one of his sons and "Daniel O'Brien". Daniel O'Brien. This son probably was Callaghan, whereas the Daniel O'Brien probably was the future 3rd Viscount Clare, about 30 at the time, rather than the future 1st Viscount, who was about 70. Muskerry disbanded his 5,000-strong army. He was excluded from pardon of life and estate in the Commonwealth's Act of Settlement on 12 August and therefore lost his estates. His surrender was one of the last, but Clanricarde, 28 June, and Philip O'Reilly, 27 April 1653, surrendered later.
/> Charles left an infant son, called Charles James, who became the new heir apparent. Only one and a half months later, on 4 or 5 August 1665, Clancarty died at Ormond's house at Moor Park, Hertfordshire. Ormond, despite being a Protestant, called in a Catholic priest for the last rites of his friend. The Catholic political pamphlet ''The Unkinde Deserter of Loyall Men and True Frinds'' claims that in his last hour Clancarty expressed regret at having trusted Ormond. Charles's infant son Charles James succeeded his grandfather as the 2nd Earl of Clancarty but died a year later. The succession then reverted to the 1st Earl's second son, Callaghan, who succeeded as the 3rd Earl of Clancarty.
Portrait
at the Hunt Museum, Limerick
Biography of Donough MacCarthy, Viscount Muskerry
online at the British Civil War Project {{DEFAULTSORT:MacCarty, Donough, 1st Earl of Clancarty 1594 births 1665 deaths Earls of Clancarty Irish generals MacCarty, Donough Irish Roman Catholic Confederates MacCarthy dynasty Members of the Parliament of Ireland (pre-1801) for County Cork constituencies MacCarthy Military personnel from County Cork
Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
The Cromwellian conquest of Ireland (1649–1653) was the re-conquest of Ireland by the Commonwealth of England, initially led by Oliver Cromwell. It forms part of the 1641 to 1652 Irish Confederate Wars, and wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of the Three ...
.
He sat in the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of ...
of the Irish parliaments of 1634–1635 and 1640–1649 where he opposed Strafford, King Charles I's authoritarian viceroy. In 1642, he sided with the Irish Rebellion when it reached his estates in Munster
Munster ( or ) is the largest of the four provinces of Ireland, located in the south west of the island. In early Ireland, the Kingdom of Munster was one of the kingdoms of Gaelic Ireland ruled by a "king of over-kings" (). Following the Nor ...
. He fought for the insurgents at the Siege of Limerick and the Battle of Liscarroll. He joined the Irish Catholic Confederates and sat on their Supreme Council. Having fought in the Irish Confederate Wars
The Irish Confederate Wars, took place from 1641 to 1653. It was the Irish theatre of the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, a series of civil wars in Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, all then ...
, he negotiated the Cessation of 1643, a cease-fire between the Confederates and the King. He tried to transform this cease-fire into a permanent peace and was the leader of the Confederates' peace party, which opposed the clerical faction led by Rinuccini, the papal nuncio. Together with President Mountgarret, he negotiated the Glamorgan Peace in 1645, which was disavowed by the King. In 1646 he captured Bunratty Castle from the Parliamentarians and negotiated the First Ormond Peace, which was rejected by Rinuccini, who excommunicating him. During the Cromwellian conquest, he lost the Battle of Knocknaclashy in 1651 but held on until 1652, defending Ross Castle against Edmund Ludlow. He was one of the last to surrender.
In 1653 during the Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the 15th century. Originally a phrase (the common-wealth ...
he stood trial for war crimes but was acquitted. In exile on the continent, Charles II created him Earl of Clancarty. He recovered his lands at the restoration of the monarchy in 1660.
Birth and origins
Donough MacCarty was born in 1594 inCounty Cork
County Cork () is the largest and the southernmost Counties of Ireland, county of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, named after the city of Cork (city), Cork, the state's second-largest city. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster ...
, most likely at Blarney Castle or Macroom Castle, residences of his parents. He was the second but eldest surviving son of Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English language, English and French language, French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic, Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''* ...
(alias Cormac Oge) MacCarthy and his first wife Margaret O'Brien. His father was at that time known as Sir Charles MacCarthy while his paternal grandfather, Cormac MacDermot MacCarthy, held the title as 16th Lord of Muskerry and owned the ancestral land covering large parts of central County Cork. His father's family were the MacCarthys of Muskerry, a Gaelic Irish dynasty that had branched from the MacCarthy-Mor line in the 14th century when a younger son received Muskerry as appanage
An appanage, or apanage (; ), is the grant of an estate, title, office or other thing of value to a younger child of a monarch, who would otherwise have no inheritance under the system of primogeniture (where only the eldest inherits). It was ...
.
Donough's mother was the eldest daughter of Donogh O'Brien, 4th Earl of Thomond. Donough was named for this grandfather (there were no Donoughs in the line of the MacCarthy of Muskerry). The name is an anglicised, shortened form of the Gaelic first name Donnchadh. Her family, the O'Briens, were another Gaelic Irish dynasty that descended from Brian Boru
Brian Boru (; modern ; 23 April 1014) was the High King of Ireland from 1002 to 1014. He ended the domination of the High King of Ireland, High Kingship of Ireland by the Uí Néill, and is likely responsible for ending Vikings, Viking invasio ...
, medieval high king of Ireland
High King of Ireland ( ) was a royal title in Gaelic Ireland held by those who had, or who are claimed to have had, lordship over all of Ireland. The title was held by historical kings and was later sometimes assigned anachronously or to leg ...
.
His parents had married about 1590. He was one of seven siblings (two brothers and five sisters). See the list in his father's article.
Religion
Although most Irish remained Catholics under the Protestant monarchs Henry VIII and Queen Elizabeth, both of MacCarty's grandfathers were Protestants. His paternal grandfather, Cormac MacDermot MacCarthy, had conformed to the established religion. MacCarty's maternal grandfather, Donogh O'Brien, 4th Earl of Thomond, had been brought up as Protestant at the English court. MacCarty's father seems to have been a protestant in his youth but later became Catholic.Early life, marriage, and children
When MacCarty's mother died, his father remarried to Ellen Roche. She was the eldest daughter ofDavid Roche, 7th Viscount Fermoy
David Roche, 7th Viscount Fermoy (1573–1635) was an Irish magnate, soldier, and politician.
Birth and origins
David was born about 1573, probably in Castletownroche, County Cork, Ireland. He was the only surviving son of Maurice Roche and ...
and widow of Donal MacCarthy Reagh of Kilbrittain, who had died in 1636. None of the cited works mentions children from his father's second marriage. MacCarty's stepmother's father was a zealous Catholic but a loyal supporter of the government.
In 1616 MacCarty's father succeeded as the 17th Lord of Muskerry. In 1628 King Charles I created MacCarty's father Baron Blarney and Viscount Muskerry. The titles were probably purchased. They had a special remainder
In mathematics, the remainder is the amount "left over" after performing some computation. In arithmetic, the remainder is the integer "left over" after dividing one integer by another to produce an integer quotient ( integer division). In a ...
that designated Donough as successor, excluding his elder brother, who was alive at the time but probably had an intellectual disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability (in the United Kingdom), and formerly mental retardation (in the United States), Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010).Archive is a generalized neurodevelopmental ...
.
MacCarty married Eleanor Butler some time before 1633 as their eldest son was born in 1633 or 1634. She was a Catholic, the eldest daughter of Thomas Butler, Viscount Thurles. The Butlers were an Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
family descending from Theobald Walter, who came to Ireland during the reign of King Henry II. MacCarty was already in his late thirties while she was about twenty. He had been married before and had a son Donall from this wife, but this earlier marriage seems to have been ignored by his family. His marriage to Eleanor made him a brother-in-law of James Butler, who succeeded as 12th Earl of Ormond in 1633, just before or just after MacCarty's marriage. Ormond was a Protestant, as he had been brought up in England.
Donough and Eleanor had three sons:
# Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English language, English and French language, French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic, Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''* ...
(1633 or 1634 – 1665), also called Cormac, predeceased his father, being slain at sea in the Battle of Lowestoft
# Callaghan (), succeeded his elder brother's infant son, Charles James, as the 3rd Earl of Clancarty
# Justin
Justin may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Justin (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Justin (historian), Latin historian who lived under the Roman Empire
* Justin I (c. 450–527) ...
( – 1694), fought for the Jacobites and became Viscount Mountcashel
—and two daughters:
# Helen (), became countess of Clanricarde
Clanricarde ( ), also known as Mac William Uachtar (Upper Mac William) or the Galway Burkes, were a fully Gaelicised branch of the Hiberno-Norman House of Burgh who were important landowners in Ireland from the 13th to the 20th centuries.
Terr ...
. She married 1st Sir John FitzGerald of Dromana and 2ndly William Burke, 7th Earl of Clanricarde.
# Margaret (), became countess of Fingall by marrying Luke Plunket, 3rd Earl of Fingall
House of Commons
When Charles I summoned the Irish Parliament of 1634–1635, MacCarty, already in his forties, stood forCounty Cork
County Cork () is the largest and the southernmost Counties of Ireland, county of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, named after the city of Cork (city), Cork, the state's second-largest city. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster ...
and was elected as one of its two " knights of the shire" as county MPs were then called. He had been knighted in 1634. The Lord Deputy of Ireland, Thomas Wentworth (the future Lord Strafford) asked to vote taxes: six subsidies of £50,000 (equivalent to about £ in ) were passed unanimously. The parliament also belatedly and incompletely ratified the Graces of 1628, in which the King conceded rights for money.
MacCarty was re-elected for County Cork to the Irish Parliament of 1640–1649. The parliamentary records list him as a knight, but about 1638 his father had bought him a baronetcy of Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
. The King sold these for 3,000 merk Scots each or £166 13s. 4d. sterling (equivalent to about £ in ). Under Strafford's guidance, the parliament unanimously voted four subsidies of £45,000 (equivalent to about £ in ) to raise an Irish army of 9,000 for use against the Scots in the Second Bishops' War.
In April Strafford left Ireland to advise the King during the Short Parliament
The Short Parliament was a Parliament of England that was summoned by King Charles I of England on 20 February 1640 and sat from 13 April to 5 May 1640. It was so called because of its short session of only three weeks.
After 11 years of per ...
at Westminster. The Irish Commons saw their chance to complain about Strafford's authoritarian regime. They formed a committee for grievances of which MacCarty was a member. The committee prepared a remonstrance, called the November Petition, which was signed by all its members. The petition was then voted and approved by the Commons. MacCarty also was part of the delegation of 13 MPs that went to London in November to submit the petition to the King. The Lords sent a separate delegation for their grievances. MacCarty's father was part of it.
Viscount Muskerry
In February 1641, MacCarty's father, aged about 70, died in London during his parliamentary mission. He was buried inWestminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an Anglican church in the City of Westminster, London, England. Since 1066, it has been the location of the coronations of 40 English and British m ...
. MacCarty succeeded as 2nd Viscount Muskerry. He lost his seat in the Commons where he was replaced by Redmond Roche
Redmond Roche ( – after 1654) was an Irish politician who sat for County Cork (Parliament of Ireland constituency), County Cork in the 2nd Irish Parliament of King Charles I, Parliament of 1640–1649. He was a Protestant during his earlier ...
, an uncle by his stepmother. As his ailing elder brother had died some time before, the title's special remainder did not need to be invoked. In March when Strafford was tried by the English House of Lords
The House of Lords is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the lower house, the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. One of the oldest ext ...
, Muskerry gave evidence that Strafford had prevented Irish people from seeing the King. When he came back to Dublin, Muskerry took his seat in the Irish House of Lords
The Irish House of Lords was the upper house of the Parliament of Ireland that existed from medieval times until the end of 1800. It was also the final court of appeal of the Kingdom of Ireland.
It was modelled on the House of Lords of Englan ...
.

Irish wars
Ireland suffered 11 years of war from 1641 to 1652, which can be divided into the Rebellion of 1641, the Confederate Wars, and the Cromwellian Conquest. This Eleven Year War or Eleven Years War was a theatre of theWars of the Three Kingdoms
The Wars of the Three Kingdoms were a series of conflicts fought between 1639 and 1653 in the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, then separate entities in a personal union un ...
, also known as the British Civil Wars.
Rebellion
Seeing the King weak and trying to oppose plantations, Sir Phelim O'Neill launched the Rebellion from the northern province ofUlster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); t ...
in October 1641. He pretended, in his Proclamation of Dungannon, to have a royal commission sanctioning his actions. In Munster
Munster ( or ) is the largest of the four provinces of Ireland, located in the south west of the island. In early Ireland, the Kingdom of Munster was one of the kingdoms of Gaelic Ireland ruled by a "king of over-kings" (). Following the Nor ...
Muskerry socialised with Richard Boyle, 1st Earl of Cork
Richard Boyle, 1st Earl of Cork (13 October 1566 – 15 September 1643), also known as 'the Great Earl of Cork', was an English politician who served as Lord Treasurer of the Kingdom of Ireland.
Lord Cork was an important figure in the continu ...
, an English Protestant established in Ireland, with whom he had opposed Strafford. News of the rebellion reached Lord Cork at a dinner at Castlelyons where David Barry, 1st Earl of Barrymore entertained Muskerry and Cork's son Roger, Lord Broghill. Barrymore was an Irish Protestant and Cork's son-in-law. Muskerry would later oppose Barrymore and Broghill in battle, but in February 1642 Muskerry still sided with Sir William St Leger, Lord President of Munster, against the insurgents. Muskerry offered to raise an armed force of his tenants and dependants to maintain law and order. He and his wife tried to save Protestants fleeing from the insurgents. In January 1642 the Munster insurgents under Maurice Roche, 8th Viscount Fermoy besieged Lord Cork in Youghal
Youghal ( ; ) is a seaside resort town in County Cork, Ireland. Located on the estuary of the Munster Blackwater, River Blackwater, the town is a former military and economic centre. Located on the edge of a steep riverbank, the town has a long ...
.
However, the rebellion was gaining ground, and on 2 March, Muskerry changed sides, to defend the Catholic faith and the King as he explained on 17 March in a letter to Barrymore. Muskerry believed Phelim O'Neill acted under a royal warrant, but the King had already denounced the Irish insurgents as traitors in January. Hearing of his defection, the Irish Parliament declared Muskerry's estates forfeit. He lost the Dublin townhouse that his father had built about 1640, but the government could not seize his Munster estates.
Like many Catholic royalists, Muskerry imagined Charles could be convinced to accept Catholicism in Ireland as he accepted Presbyterianism in Scotland. He was also prompted to take up arms by the atrocities committed by William St Leger against the Catholic population and by the approach of Richard Butler, 3rd Viscount Mountgarret with his rebel army. Muskerry refused to serve under Mountgarret and competed for the leadership in Munster with Fermoy, an uncle by his stepmother. Fermoy had led the rebellion in Munster before Muskerry joined and outclassed him in terms of precedence, but Muskerry was richer. At a meeting of the leaders at Blarney, Garret Barry, a veteran of the Spanish Army of Flanders, was made general of the Munster insurgents' army as a compromise. Muskerry was his second-in-command.
In March and April, Muskerry and Fermoy with 4,000 men unsuccessfully besieged St Leger in Cork City. On 13 April Murrough O'Brien, 6th Baron Inchiquin, an Irish Protestant, lifted the siege by driving the insurgents from their base at Rochfordstown. Muskerry lost his armour, tent, and trunks in this action. He and his lady stayed nearby at Blarney Castle at the time. On 16 May, Muskerry and Fermoy captured Barrymore Castle
Barrymore is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*Barrymore family of American actors
*Earl of Barrymore, a title in the Kingdom of Ireland dating to 1622
People with the surname Barrymore
*Deborah Barrymore aka Deborah Moore (bor ...
at Castlelyons, Barrymore's seat. St Leger died on 2 July, and Inchiquin, the vice-president, took over the command of the government forces in Munster.
Siege of Limerick
In May and June 1642, Muskerry, Garret Barry, Patrick Purcell of Croagh, and Fermoy attacked Limerick. The town opened its gates willingly, but the Protestants defended King John's Castle in the Siege of Limerick. They were led by George Courtenay, 1st Baronet, of Newcastle, who was the constable of Limerick Castle. Muskerry had a cannon placed on the tower of St Mary's Cathedral, which overlooked the castle. The besiegers attacked the castle's eastern wall and thebastion
A bastion is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fire from the ...
on its south-east corner by digging mines. The castle surrendered on 21 June and Muskerry took possession. The insurgents had already attacked castles in the Connello area west of Limerick, which had been settled with English during the Plantation of Munster. On 26 March Patrick Purcell had laid siege to Castletown, defended by Hardress Waller, the future Cromwellian general. The castle fell in May. In July, Muskerry and Patrick Purcell used artillery, captured at King John's Castle, to take Kilfinny, defended by Elizabeth Dowdall, Waller's mother-in-law.
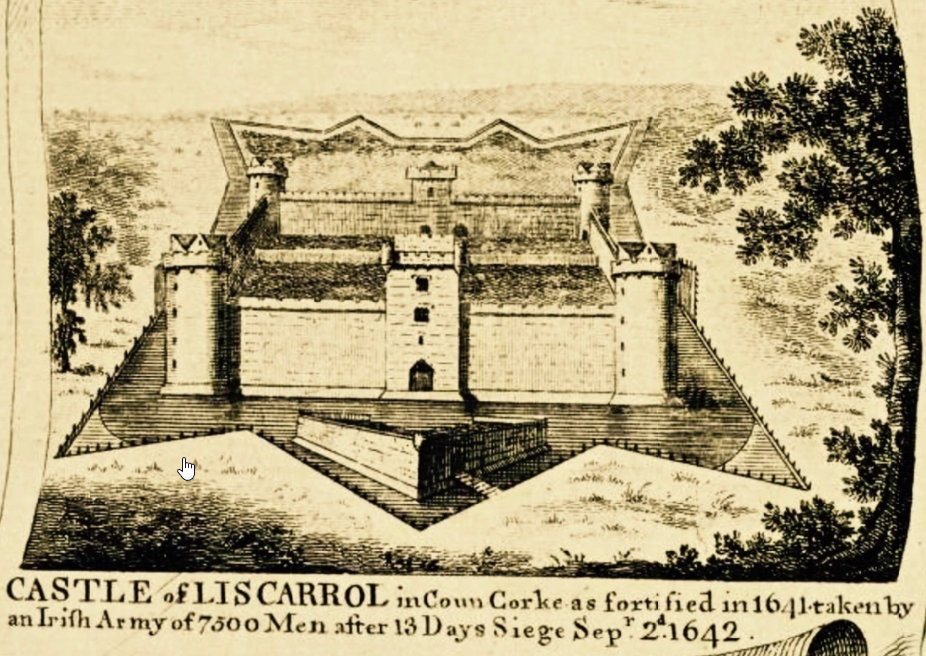
Siege and Battle of Liscarroll
 The Munster insurgents then attacked the castles of Sir Philip Perceval. In the summer of 1642 Muskerry took Annagh Castle,
The Munster insurgents then attacked the castles of Sir Philip Perceval. In the summer of 1642 Muskerry took Annagh Castle, County Tipperary
County Tipperary () is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster and the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern Region. The county is named after the town of Tipperary (tow ...
, and in August besieged Liscarroll Castle, County Cork. The castle surrendered on 2 September. The next day Inchiquin with his army appeared before the castle. Despite inferior numbers Inchiquin defeated the insurgents under General Garret Barry in the ensuing Battle of Liscarroll. Muskerry allegedly panicked, fled, and caused others to flee. His Protestant acquaintance Barrymore died in September, supposedly of wounds received in the battle.
Confederation
In 1642 the insurgents organised themselves in the Irish Catholic Confederation. In May the Catholic Church declared the war lawful. An oath of association was dawn up. In October Muskerry attended the first Confederate General Assembly at Kilkenny where Mountgarret was elected president of the Confederation. Muskerry was not elected to the Supreme Council, but his rival Fermoy was. Garret Barry was made general of the Munster Army, despite his recent defeat and advanced age. Barry seems to have held the position until his death in March 1646 in Limerick, but others commanded in his stead. In 1643 Muskerry and Fermoy were both elected to the Supreme Council. Muskerry commanded the infantry at the Battle of Cloughleagh on 4 June 1643 where the Irish cavalry underJames Tuchet, 3rd Earl of Castlehaven
James Tuchet, 3rd Earl of Castlehaven ( - 11 October 1684) was the son of Mervyn Tuchet, 2nd Earl of Castlehaven and his first wife, Elizabeth Barnham (1592 - ). Castlehaven played a prominent role in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms that took pla ...
, routed a detachment of Inchiquin's troops under Sir Charles Vavasour, 1st Baronet, of Killingthorpe, who had taken the Cloughleagh Tower House near Fermoy
Fermoy () is a town on the Munster Blackwater, River Blackwater in east County Cork, Ireland. As of the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census, the town and environs had a population of approximately 6,700 people. It is located in the barony (Ir ...
the day before. Muskerry with the infantry arrived only after the decisive cavalry charge. Castlehaven considered him slow and called him "the old general".
Later that year, Muskerry led the Munster Army in an offensive against Inchiquin in County Waterford
County Waterford () is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster and is part of the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern Region. It is named after the city of Waterford. ...
. Lieutenant-Colonel, Patrick Purcell, unsuccessfully besieged Lismore Castle, the seat of the Earls of Cork. Muskerry was about to take Cappoquin
Cappoquin (), also sometimes spelt Cappaquin, is a town in western County Waterford, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is on the Munster Blackwater, Blackwater river at the junction of the N72 road (Ireland), N72 national secondary road and the R ...
but engaged in parleys and was outwitted by Inchiquin, who delayed the town's surrender until September when the cease-fire ended the war.
Cessation and Oxford conference
Muskerry, like most of themagnates
The term magnate, from the late Latin ''magnas'', a great man, itself from Latin ''magnus'', "great", means a man from the higher nobility, a man who belongs to the high office-holders or a man in a high social position, by birth, wealth or ot ...
among the Confederates, was afraid to lose title and land when the King regained control. He therefore adhered to a faction within the Confederates, called the peace party or the Ormondists, that sought an agreement that would protect against such a loss. The King, on the other hand, sought peace with the Confederates to be able to withdraw troops from Ireland for use in the English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of th ...
. In 1643, the King asked Ormond to open talks with the Confederates. On 15 September 1643 at Sigginstown, Strafford's unfinished house, the Confederates signed a cease-fire with Ormond, called the "Cessation". Muskerry was one of the signatories. The Confederates agreed to pay the King £30,000 (equivalent to about £ in ) in several instalments. In return, the Confederates gained some degree of diplomatic recognition. The articles of the Cessation gave Lismore Castle and Cappoquin to Inchiquin.
In November 1643 the Supreme Council appointed seven delegates, with Muskerry as leader, to submit grievances to the King and negotiate a peace treaty. In January 1644 they obtained safe-conducts from the Lords Justices. It must have been their last days in office as Ormond was sworn-in as lord lieutenant of Ireland
Lord Lieutenant of Ireland (), or more formally Lieutenant General and General Governor of Ireland, was the title of the chief governor of Ireland from the Williamite Wars of 1690 until the Partition of Ireland in 1922. This spanned the K ...
on 21 January. The delegates arrived on 24 March at Oxford
Oxford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and non-metropolitan district in Oxfordshire, England, of which it is the county town.
The city is home to the University of Oxford, the List of oldest universities in continuou ...
where the King held his court. Muskerry demanded public exercise of the Catholic religion, independence from the English parliament, and full amnesty for their rebellion. The King offered Muskerry an earldom, which he refused. A competing Irish Protestant delegation arrived on 17 April. End of June the Confederate delegates returned to Ireland empty-handed.
The Cessation allowed the Confederates to focus on their war with the Covenanters
Covenanters were members of a 17th-century Scottish religious and political movement, who supported a Presbyterian Church of Scotland and the primacy of its leaders in religious affairs. It originated in disputes with James VI and his son ...
in Ulster, who were aligned with the English Parliament. Owen Roe O'Neill led the Confederate Ulster army, deployed on that front, but the Supreme Council imposed Castlehaven as general-in-chief for the campaign of 1644. Castlehaven marched north to Charlemont but did not bring the Covenanters to battle. In July Inchiquin declared for Parliament, reactivating the southern front around the city of Cork, where the Munster Army was deployed. The fourth general assembly, in July 1644, elected the fourth Supreme Council. Muskerry regained his seat, but Fermoy did not. The cessation had a duration of one year, expiring on 15 September 1644. It was extended twice:
by Muskerry and Ormond in August 1644 until 1 December; and by Muskerry and Lord Chancellor Bolton
Bolton ( , locally ) is a town in Greater Manchester in England. In the foothills of the West Pennine Moors, Bolton is between Manchester, Blackburn, Wigan, Bury, Greater Manchester, Bury and Salford. It is surrounded by several towns and vill ...
in September until 31 January 1645.
In the campaign of 1645, Castlehaven commanded the Munster Army in its fight against Inchiquin. Under Castlehaven's command Patrick Purcell took Lismore Castle, but Inchiquin doggedly defended the rest. In the fifth general assembly in summer 1645, Muskerry was re-elected to the Supreme Council.

Glamorgan Treaty
In 1645 the King sent Edward Somerset, Earl of Glamorgan, to Ireland to speed up the peace negotiations with the Confederates. Glamorgan was an English Catholic and son of Henry Somerset, 1st Marquess of Worcester, an important royalist. Ormond sent Glamorgan to Kilkenny with a letter of introduction to Muskerry dated 11 August. He was received by Mountgarret and Muskerry. On 25 August Glamorgan signed the first Glamorgan Treaty with the Confederates. Muskerry was one of the signatories. The treaty was kept secret. It ceded to the Catholics the churches that the Confederates had seized since the beginning of the rebellion. Sir Charles Coote divulged it in October after he found a copy in the luggage of Malachy Queally, bishop of Tuam, killed in action near Sligo. The King disavowed the treaty in January 1646.Nuncio
In 1645 the pope sent Giovanni Battista Rinuccini asnuncio
An apostolic nuncio (; also known as a papal nuncio or simply as a nuncio) is an ecclesiastical diplomat, serving as an envoy or a permanent diplomatic representative of the Holy See to a state or to an international organization. A nuncio is ...
to the Irish Catholic Confederation. Rinuccini landed in October on Ireland's south-west coast with money and weapons. On his way to Kilkenny
Kilkenny ( , meaning 'church of Cainnech of Aghaboe, Cainnech'). is a city in County Kilkenny, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is located in the South-East Region, Ireland, South-East Region and in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinst ...
, the Confederate capital, Rinuccini visited Macroom Castle where Lady Muskerry and her 11-year-old eldest son, Charles, received him while her husband was negotiating with Ormond in Dublin. The nuncio stayed for four days and then continued to Kilkenny arriving on 12 November.
In town, the nuncio was attended to by Muskerry, who had just returned from Dublin, and by General Preston. They accompanied him to Kilkenny Castle for his official reception by Mountgarret and escorted him back to his residence.
First Ormond Peace
The Confederate assembly on 6 March 1646 authorised its delegates to conclude a peace with Ormond. Muskerry signed the "First Ormond Peace" on 28 March 1646 for the Confederates. The treaty's 30 articles covered civil rights, but left the religious ones to be decided by a future Irish parliament. The parties agreed to defer the treaty's publication for now. According to the treaty, the Confederates were expected to send an Irish army of 10,000 men, about half the Confederate army, to England before 1 May, but by then it was already too late.Bristol
Bristol () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, the most populous city in the region. Built around the River Avon, Bristol, River Avon, it is bordered by t ...
had fallen in September 1645 and Chester
Chester is a cathedral city in Cheshire, England, on the River Dee, Wales, River Dee, close to the England–Wales border. With a built-up area population of 92,760 in 2021, it is the most populous settlement in the borough of Cheshire West an ...
in February 1646, depriving the King of his main harbours on the Irish sea. Admiral Richard Swanley and Captain William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer, religious thinker, and influential Quakers, Quaker who founded the Province of Pennsylvania during the British colonization of the Americas, British colonial era. An advocate of democracy and religi ...
patrolled the sea with the Irish Squadron of the Parliamentarian Navy. Muskerry wrote to Ormond on 3 April that the Irish army's expedition to England had to be abandoned. The First English Civil War ended shortly after the First Ormond Peace was signed. The Scots took the King into custody on 5 May.
Siege of Bunratty
As the Confederates sent no troops to the King, their armies kept their full strength. The Munster Army, under Glamorgan, favoured by Rinuccini, was sent to besiege Bunratty Castle near Limerick, into which the 6th Earl of Thomond, a Protestant, had admitted a Parliamentarian garrison in March 1646. The Confederates lacked money to pay their army. After a setback on 1 April, in which the garrison drove the besiegers from their camp at Sixmilebridge, the Supreme Council replaced Glamorgan with Muskerry at the end of May. Muskerry had Lieutenant-General Purcell, Major-General Stephenson, and Colonel Purcell under him with three Leinster regiments and all the Munster forces. The castle's defences had been modernised by surrounding the castle proper, essentially a big tower house, with modern earthworks and forts defended by cannons. These fortifications abutted on the sea and Bunratty was supported by a small squadron of the Parliamentarian Navy under now-Vice-Admiral Penn. On 9 May, Lord Thomond left Bunratty for England by sea. On 13 June arrived the news of Owen Roe O'Neill's victory over the Covenanters at Benburb, won with the financial support from the nuncio. At the end of June Rinuccini came and paid the soldiers £600 (equivalent of about £ in ), exhausting the last of his funds. Muskerry brought two heavy cannons from Limerick for the siege. His rivals accused him of having spared the castle because Thomond was his uncle. When on 1 July a chance shot through a window killed McAdam, the Parliamentarian commander, Muskerry pressed on and the castle capitulated on 14 July. The garrison was evacuated to Cork by the Parliamentarian Navy, but had to leave arms, ammunition, and provisions behind. Early in 1646, while Muskerry was at the siege of Bunratty, Broghill with a Parliamentarian force from Cork captured Blarney Castle. It must have been a bold coup as Muskerry was accused of having betrayed the castle. In May, Lady Muskerry, with her children was brought to Dublin for their security. Similar rescues were organised for her mother, Lady Thurles, and her sisters, Lady Hamilton and Lady Loughmoe.Rejection of the First Ormond Peace
Muskerry and Ormond confirmed and signed the First Ormond Peace again in July 1646. The peace was thus concluded twice: on 28 March and in July 1646. Muskerry got the treatyratified
Ratification is a principal's legal confirmation of an act of its agent. In international law, ratification is the process by which a state declares its consent to be bound to a treaty. In the case of bilateral treaties, ratification is usuall ...
by a vote in the Supreme Council despite the nuncio's opposition. Ormond had it proclaimed in Dublin on 30 July and the Supreme Council did so in Kilkenny on 3 August.
Rinuccini held a meeting of the clergy at Waterford
Waterford ( ) is a City status in Ireland, city in County Waterford in the South-East Region, Ireland, south-east of Ireland. It is located within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster. The city is situated at the head of Waterford H ...
, which on 12 August 1646 condemned the treaty. Rinuccini then excommunicated
Excommunication is an institutional act of religious censure used to deprive, suspend, or limit membership in a religious community or to restrict certain rights within it, in particular those of being in communion with other members of the con ...
Muskerry and others who supported it. On 18 September, Rinuccini overturned the Confederate government in a coup d'état with help of the Ulster Army, which Owen Roe O'Neill had marched to Leinster. On 26 September Rinuccini made himself president and appointed a new, the seventh, Supreme Council in which sat Glamorgan, Fermoy, and Owen Roe O'Neill. Rinuccini arrested Muskerry, Richard Bellings, and other Ormondist members of the previous Supreme Council. Most were detained in Kilkenny Castle, but Muskerry was put under house arrest. Muskerry had to cede the command of the Munster Army to Glamorgan. Being under arrest in Kilkenny Muskerry missed out on the attempted siege of Dublin by Owen Roe O'Neill and Preston in November 1646.
Having failed to take Dublin, Rinuccini released Muskerry and other political prisoners as demanded by Nicholas Plunkett, and called a general assembly, which met on 10 January 1647 in Kilkenny. It lasted until the beginning of April. The assembly elected a new Supreme Council, the eighth, with the Marquess of Antrim as president. It was dominated by the clerical faction but also included Muskerry and three other Ormondists.
Mutiny of the Munster Army
The Supreme Council had in 1647 confirmed Glamorgan, who had become the 2nd Marquess of Worcester in December 1646, as general of the Munster Army, but the Confederation lacked the funds to pay the army. Worcester was unpopular with the troops and the Munster gentry because he was English. Several regiments mutinied demanding that Muskerry should be appointed general. Three Dominican chaplains of the army insinuated that killing Muskerry would not be a sin. One of them was Patrick Hackett, a Gaelic poet. Gaelic was still the predominant language among the rank and file. Early in June 1647 the Supreme Council met atClonmel
Clonmel () is the county town and largest settlement of County Tipperary, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The town is noted in Irish history for its resistance to the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland, Cromwellian army which sacked the towns of Dro ...
near the Munster Army's camp. On 12 June Muskerry, together with Patrick Purcell, rode over from the council meeting to the army's camp where the troops acclaimed him as their leader and turned Worcester out of his command. The Supreme Council ignored Muskerry's de facto take-over, upheld Worcester as the de jure commander who then passed the command officially to Muskerry. Early in August Muskerry handed the command over to Theobald Viscount Taaffe of Corren. Neither Worcester, nor Muskerry, nor Taaffe stopped Inchiquin, who took Cappoquin and Dungarvan in May and sacked Cashel in September.
Decline of the Confederation
Meanwhile, on 6 June 1647, Ormond had accepted Colonel Michael Jones with 2,000 Parliamentarian troops into Dublin. On 28 July, Ormond handed Dublin over to the Parliamentarians and left for England. In August Preston tried to march on Dublin with the Leinster army, but Jones defeated him at Dungan's Hill. Muskerry called in Owen Roe O'Neill to defend Leinster. In November, Taaffe lost the Battle of Knocknanuss against Inchiquin. Towards the end of 1647, the Supreme Council sent Muskerry, Geoffrey Browne, and the Marquess of Antrim to negotiate with the exiled QueenHenrietta Maria
Henrietta Maria of France (French language, French: ''Henriette Marie''; 25 November 1609 – 10 September 1669) was List of English royal consorts, Queen of England, List of Scottish royal consorts, Scotland and Ireland from her marriage to K ...
, at the Château-Neuf de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France. They wanted to invite the Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales (, ; ) is a title traditionally given to the male heir apparent to the History of the English monarchy, English, and later, the British throne. The title originated with the Welsh rulers of Kingdom of Gwynedd, Gwynedd who, from ...
, the future Charles II, then aged 17, to Ireland, and negotiate another peace to replace the one concluded with Ormond. In February 1648 Ormond left England and joined the Queen. Antrim departed before Muskerry and Browne and arrived early in March. Muskerry and Browne departed in February and had reached Saint-Germain by 23 March. On 24 March 1648, the Queen received the three envoys in an audience. However, 1648 was the year of the Second English Civil War
The Second English Civil War took place between February and August 1648 in Kingdom of England, England and Wales. It forms part of the series of conflicts known collectively as the 1639–1653 Wars of the Three Kingdoms, which include the 164 ...
and plans were made for the Prince of Wales to go to Scotland to support the Engagers
The Engagers were a faction of the Scottish Covenanters, who made "The Engagement" with King Charles I in December 1647 while he was imprisoned in Carisbrooke Castle by the English Parliamentarians after his defeat in the First Civil War.
...
rather than to go to Ireland, but eventually, he stayed in France. With regard to a new peace, Antrim, representing the clerical faction, insisted that no peace should be accepted in Ireland without the pope's approval and that a Catholic lord lieutenant should be appointed, an office he hoped to obtain for himself.
On 3 April 1648, Inchiquin changed sides, leaving the Parliamentarians and declaring for the king. Muskerry convinced the Queen to appoint Ormond as lord lieutenant and accept Inchiquin as an ally. Muskerry returned to Ireland in June to prepare for Ormond's arrival. Ormond landed at Cork in September. Muskerry was made Irish lord high admiral and president of the high Court of Admiralty. In November he signed letters of marque for the privateers '' Mary of Antrim'' and the '' St John of Waterford''.
In January 1649, the Second Ormond Peace was signed. The Irish Catholic Confederation was dissolved, and replaced with a provisional royalist government. Power was handed to 12 Commissioners of Trust. Muskerry was one of them.
Cromwellian conquest
On 15 August 1649,Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English statesman, politician and soldier, widely regarded as one of the most important figures in British history. He came to prominence during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, initially ...
landed in Dublin. He wanted to avenge the uprising of 1641, confiscate enough Irish Catholic-owned land to pay off the English Parliament's debts, and eliminate a dangerous outpost of royalism.
Henry Ireton
Henry Ireton (baptised 3 November 1611; died 26 November 1651) was an English general in the Parliamentarian army during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, and a son-in-law of Oliver Cromwell. He died of disease outside Limerick in November 165 ...
on 19 May.
In April 1651 Ulick Burke, 1st Marquess of Clanricarde, appointed Muskerry supreme commander in Munster. Muskerry tried to relieve the Siege of Limerick, but Broghill intercepted and defeated him on 26 July 1651 at the Battle of Knocknaclashy (also called Knockbrack), near Dromagh Castle, west of Kanturk, the war's last pitched battle. Limerick surrendered in October.
Muskerry fell back into the mountains of Kerry and based himself at Ross Castle near Killarney, owned by Sir Valentine Browne, his nephew by his sister Mary. Browne, born in 1638, was a minor and had become Muskerry's ward after his father's untimely death. In 1652 the government put a bounty of £500
(about £ in ) on Muskerry's head. Muskerry hoped that the Duke of Lorraine would intervene to save the Irish royalists.
 Edmund Ludlow besieged Muskerry in Ross Castle, on the shore of Lough Leane. The defenders were supplied by boat over the lake. Ludlow brought boats of his own whereupon Muskerry surrendered on 27 June 1652 after a siege of three weeks. The terms took a possible prosecution into account. Muskerry gave two hostages to guarantee his compliance with the terms: one of his sons and "Daniel O'Brien". Daniel O'Brien. This son probably was Callaghan, whereas the Daniel O'Brien probably was the future 3rd Viscount Clare, about 30 at the time, rather than the future 1st Viscount, who was about 70. Muskerry disbanded his 5,000-strong army. He was excluded from pardon of life and estate in the Commonwealth's Act of Settlement on 12 August and therefore lost his estates. His surrender was one of the last, but Clanricarde, 28 June, and Philip O'Reilly, 27 April 1653, surrendered later.
Edmund Ludlow besieged Muskerry in Ross Castle, on the shore of Lough Leane. The defenders were supplied by boat over the lake. Ludlow brought boats of his own whereupon Muskerry surrendered on 27 June 1652 after a siege of three weeks. The terms took a possible prosecution into account. Muskerry gave two hostages to guarantee his compliance with the terms: one of his sons and "Daniel O'Brien". Daniel O'Brien. This son probably was Callaghan, whereas the Daniel O'Brien probably was the future 3rd Viscount Clare, about 30 at the time, rather than the future 1st Viscount, who was about 70. Muskerry disbanded his 5,000-strong army. He was excluded from pardon of life and estate in the Commonwealth's Act of Settlement on 12 August and therefore lost his estates. His surrender was one of the last, but Clanricarde, 28 June, and Philip O'Reilly, 27 April 1653, surrendered later.
Exile and prosecution
Muskerry was allowed to embark for Spain where he was rejected as Ormondist. He then sought employment with the Venetian Republic for himself and the Irish soldiers that he brought with him, but the project fell through. He returned to Ireland late in 1653 landing at Cork to recruit soldiers for service on the continent but was arrested forwar crimes
A war crime is a violation of the laws of war that gives rise to individual criminal responsibility for actions by combatants in action, such as intentionally killing civilians or intentionally killing prisoners of war, torture, taking hos ...
and detained until the opening of his trial on 1 December in Dublin. He was accused of having been an accessory to murders of English settlers on three occasions.
The first case was the murder of William Deane and others at Kilfinny, County Limerick, by soldiers of the Munster army on 29 July 1642. The victims died when Lady Dowdall surrendered Kilfinny Castle to Patrick Purcell, who commanded the besiegers. It had been agreed that the English would be allowed to leave escorted by a detachment sent by Inchiquin. The second case was the murder of Mrs Hussey and others near Blarney Castle, County Cork, by Irish soldiers on 1 August 1642. The victims were refugees that Muskerry had sheltered at Macroom and was sending to Cork in a guarded convoy so that they could leave the country. The third case was the murder of Roger Skinner and others at Inniskerry, County Cork, in August 1642. Muskerry was acquitted of these three charges.
In February 1654 he was tried for having participated in royalist conspiracies. Lady Ormond, who had been allowed to return to Ireland from her French exile, secretly visited Gerard Lowther, president of the High Court of Justice at the time, who gave her legal advice for Muskerry. This helped him convince the court of his innocence and he was acquitted.
In May 1654 he had to defend himself against another murder charge concerning the killing of an unnamed man and woman. He was acquitted.
Muskerry was again allowed to embark for Spain but went to France. Henrietta Maria, now the Queen Mother, still lived there, but in July 1654 Charles II and his exile court were about to leave France and start their wanderings in the Netherlands and Germany. Lady Muskerry lived in Paris. Muskerry's daughter Helen found shelter at the abbey of Port-Royal-des-Champs near Versailles. The abbess, La Mère Angélique, tried to help Muskerry and his Irish soldiers in their need. In November 1654 she wrote to Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga of Poland proposing to employ Muskerry and his followers – 5,000 men – in Polish service. In 1655 Muskerry and Bellings led them to the Polish King, who fought the Swedes in the Second Northern War
The second (symbol: s) is a unit of time derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes, and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of ...
. Muskerry and Bellings returned with £20,000 for Charles II. In 1657 the King sent Muskerry to Madrid to ask the Spanish to let the Irish exiles now in Spain invade Ireland. They stayed seven months but achieved nothing. Muskerry's eldest son fought the French and Cromwell's English at the Battle of the Dunes in June 1658 The King, in exile at Brussels, rewarded Muskerry in November 1658 with the title of Earl of Clancarty. His title of Viscount Muskerry, now subsidiary
A subsidiary, subsidiary company, or daughter company is a company (law), company completely or partially owned or controlled by another company, called the parent company or holding company, which has legal and financial control over the subsidia ...
, passed to his eldest son Charles, his heir apparent
An heir apparent is a person who is first in the order of succession and cannot be displaced from inheriting by the birth of another person. A person who is first in the current order of succession but could be displaced by the birth of a more e ...
, as courtesy title
A courtesy title is a title that does not have legal significance but is rather used by custom or courtesy, particularly, in the context of nobility, the titles used by children of members of the nobility (cf. substantive title).
In some context ...
.
Restoration and death
At the Restoration of the Stuarts, Clancarty, as he now was, returned to Ireland. He used Ormond's influence to recover his estates, which Charles II confirmed to him in his "Gracious Declaration" of 30 November 1660. The Cromwellian occupiers had to leave at once. Now-Admiral William Penn, to whom Macroom had been granted in 1654, was compensated with land at Shanagarry (east of Cork). Broghill had to return Blarney and Kilcrea. The Clancartys repaired and enlarged Macroom Castle. Clancarty also recovered his townhouse, which now became Clancarty House. Clancarty found wealthy Irish spouses for his eldest son and his two daughters. This son married Margaret Bourke in 1660 or 1661. She was a rich heiress, the only child of Ulick Burke, 1st Marquess of Clanricarde. Clancarty's elder daughter Helen married twice. First, after 1660 Sir John FitzGerald of Dromana, a Protestant, as his second wife. The marriage was childless. After his death in 1664, Helen married secondly William Burke, 7th Earl of Clanricarde. Clancarty's younger daughter Margaret married Luke Plunket, 3rd Earl of Fingall, before 1666. In the winter of 1661–1662, Clancarty signed the Catholic Remonstrance drawn up by Bellings and promoted by Peter Walsh. in an attempt to improve the Catholics' condition in Ireland by demonstrating their loyalty to the King. However, the remonstrance proved inefficient, mainly because too few of the clergy signed. In August 1660, Charles II made George Monck, 1st Duke of Albemarle, lord lieutenant of Ireland. As Albemarle never went to Ireland, the King appointed three lords justices to govern in his stead. When the King summoned the Parliament of 1661–1666, it was opened by the lords justices on 8 May 1661. Clancarty joined the House of Lords on 20 May. On 11 June Clancarty became the proxy of Lord Inchiquin, therefore voting in his stead. The passing of the Act of Settlement was one of the main purposes of the parliament. Clancarty was absent on 30 May 1662 when the Lords finally passed it. Clancarty sat on the committee that organised the gift of £30,000 (about £ in ) made to the Duke of Ormond. However, Clancarty's eldest son, Charles MacCarty, replaced him in that function on 19 August. On 11 December, the Lords passed the Irish version of theTenures Abolition Act 1660
The Tenures Abolition Act 1660 ( 12 Cha. 2. c. 24), sometimes known as the Statute of Tenures, was an act of the Parliament of England which changed the nature of several types of feudal land tenure in England. The long title of the act was ' ...
. Clancarty attended parliament regularly until April 1663 when he moved to London. He visited his Irish estates in 1664 for a last time and returned to England.
On 3 June 1665, Charles, Viscount Muskerry, Clancarty's eldest son and heir apparent, was killed during the Second Anglo-Dutch War
The Second Anglo-Dutch War, began on 4 March 1665, and concluded with the signing of the Treaty of Breda (1667), Treaty of Breda on 31 July 1667. It was one in a series of Anglo-Dutch Wars, naval wars between Kingdom of England, England and the D ...
in the Battle of Lowestoft, a naval engagement with the Dutch and buried in Westminster Abbey as his grandfather, the 1st Viscount, had been.77/> Charles left an infant son, called Charles James, who became the new heir apparent. Only one and a half months later, on 4 or 5 August 1665, Clancarty died at Ormond's house at Moor Park, Hertfordshire. Ormond, despite being a Protestant, called in a Catholic priest for the last rites of his friend. The Catholic political pamphlet ''The Unkinde Deserter of Loyall Men and True Frinds'' claims that in his last hour Clancarty expressed regret at having trusted Ormond. Charles's infant son Charles James succeeded his grandfather as the 2nd Earl of Clancarty but died a year later. The succession then reverted to the 1st Earl's second son, Callaghan, who succeeded as the 3rd Earl of Clancarty.
Arms
Notes and references
Notes
Citations
Sources
Subject matter monographs: * Click here. McGrath 1997a in ''A Biographical Dictionary of the Membership of the Irish House of Commons 1640 to 1641'' * Click here. Ohlmeyer 2004 inOxford Dictionary of National Biography
The ''Dictionary of National Biography'' (''DNB'') is a standard work of reference on notable figures from History of the British Isles, British history, published since 1885. The updated ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' (''ODNB'') ...
* Click here. Ó Siochrú in Dictionary of Irish Biography
The ''Dictionary of Irish Biography'' (DIB) is a biographical dictionary of notable Irish people and people not born in the country who had notable careers in Ireland, including both Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland.
History
The ...
* Click here. Seccombe 1893 in Dictionary of National Biography
The ''Dictionary of National Biography'' (''DNB'') is a standard work of reference on notable figures from British history, published since 1885. The updated ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' (''ODNB'') was published on 23 September ...
—This is about the 4th earl but the 1st earl is treated as a co-subject
* Click here. Webb 1878 in ''Compendium of Irish Biography''
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* – 1603 to 1642
* – 1642 to 1660
* – 1221 to 1690
*
* – Known as Baron Broghill 1628 to 1660
*
*
*
*
* – Volume title: Irish Women's Writing and Traditions (for Lady Dowdall's narration)
*
*
* – Leinster (continued (Carlow, Kildare, Queen’s County, King’s County, Meath, Westmeath, Longford, Louth), & Munster
*
*
*
* (for MacCarty and Thomond)
* – (for Ormond)
*
* – West Carbery
*
* – 1613 to 1641
* – 1641 to 1643
* – 1643 to 1660
*
*
* – Marriages, baptisms and burials from about 1660 to 1875
*
*
*
*
* – D to F (for Fermoy)
* – L to M (for Mountcashel & Muskerry)
* – S to T (for Strafford and Thomond)
* – 1611 to 1625 (for Browne)
* – 1625 to 1649 (for the subject)
* – Canonteign to Cutts (for Clancarty and Fermoy)
* – Eardley of Spalding to Goojerat (for Fermoy and Fingall)
* – ODBC on line
* – Moels to Nuneham
* – 1641 to 1645 (Preview)
* – 1645 to 1649 (Preview)
* – 1650 to 1653 (Preview)
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* – 1611 to 1659
*
* – 1625 to 1655
*
*
*
*
* – Contains "The Unkinde Desertor of Loyall Men and True Frinds"
* – (for timeline)
* – 1642 to 1644
*
* – 1645 to 1647
* – 1647 to 1649 & Index
*
* – to 1603
* – 1603 to 1860
*
* – Aphorismical Discovery, 1641 to 1648
* – History based on Richard Bellings’s memoirs
* – Letters, acts, and Lady Dowdall's narration
*
*
* – 1649 to 1653
*
* – (for Donough)
*
* – (Preview)
*
*
*
* – Preface, Introduction, Depositions
* – Depositions (continued), Records of the High Court of Justice, and Appendix
*
*
* – 1634 to 1699
*
* – 1661 to 1665
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* – (Preview)
*
*
*
* – Earls
* – Viscounts
* – Viscounts, barons
* – Barons (for his sister Mary)
*
* – 1655 to 1657
*
*
*
*
*
*
* – Parliaments & Biographies (PDF downloadable from given URL)
* – Parliaments & Biographies (PDF downloadable from given URL)
* – Parliaments & Biographies (PDF downloadable from given URL)
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* – House of Lords
*
*
* – (Snippet view)
*
*
*
*
*
* – Irish stem
* – (Snippet view)
*
* – (Preview)
* – (PDF downloadable from given URL)
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* – (Preview)
*
*
*
*
*
* – 1534–1691
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* – History
*
*
* – Online edition
*
*
* – 1643 to 1660 and index
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* – (Preview)
*
*
External links
Portrait
at the Hunt Museum, Limerick
Biography of Donough MacCarthy, Viscount Muskerry
online at the British Civil War Project {{DEFAULTSORT:MacCarty, Donough, 1st Earl of Clancarty 1594 births 1665 deaths Earls of Clancarty Irish generals MacCarty, Donough Irish Roman Catholic Confederates MacCarthy dynasty Members of the Parliament of Ireland (pre-1801) for County Cork constituencies MacCarthy Military personnel from County Cork