Diaschisma on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

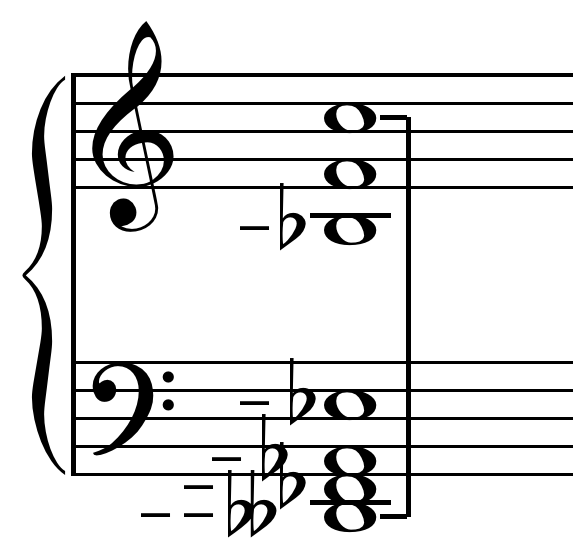 The diaschisma (or diacisma) is a small
The diaschisma (or diacisma) is a small
Columbian cyclopedia, Volume 9
', np. Garretson, Cox & Company. pre-ISBN. Medieval theorists Tempering out the diaschisma, in the modern meaning of the term, leads to a diaschismic temperament. The diaschisma is tempered out in the usual system of
Tempering out the diaschisma, in the modern meaning of the term, leads to a diaschismic temperament. The diaschisma is tempered out in the usual system of

 The diaschisma (or diacisma) is a small
The diaschisma (or diacisma) is a small musical interval
In music theory, an interval is a difference in pitch (music), pitch between two sounds. An interval may be described as horizontal, linear, or melodic if it refers to successively sounding tones, such as two adjacent pitches in a melody, and v ...
defined as the difference between three octave
In music, an octave (: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is an interval between two notes, one having twice the frequency of vibration of the other. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referr ...
s and four perfect fifth
In music theory, a perfect fifth is the Interval (music), musical interval corresponding to a pair of pitch (music), pitches with a frequency ratio of 3:2, or very nearly so.
In classical music from Western culture, a fifth is the interval f ...
s plus two major thirds (in just intonation
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is a musical tuning, tuning system in which the space between notes' frequency, frequencies (called interval (music), intervals) is a natural number, whole number ratio, ratio. Intervals spaced in thi ...
). It can be represented by the ratio 2048:2025 and is about 19.5 cents. The use of the name diaschisma for this interval is due to Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (; ; 31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894; "von" since 1883) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The ...
; earlier Rameau
Jean-Philippe Rameau (; ; – ) was a French composer and music theorist. Regarded as one of the most important French composers and music theorists of the 18th century, he replaced Jean-Baptiste Lully as the dominant composer of French opera a ...
had called that interval a "diminished comma" or comma minor.
A diaschisma is the difference between a schisma
In music, the schisma (also spelled ''skhisma'') is the interval between the syntonic comma (81:80) and the Pythagorean comma which is slightly larger. It equals or ≈ 1.00113, which corresponds to 1.9537 cents (). It may also ...
and a syntonic comma
In music theory
Music theory is the study of theoretical frameworks for understanding the practices and possibilities of music. ''The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory": The first i ...
, as well as the difference between the greater chromatic semitone
A semitone, also called a minor second, half step, or a half tone, is the smallest musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most dissonant when sounded harmonically.
It is defined as the interval between t ...
(135:128 = 92.18 cents) and the just minor second
A semitone, also called a minor second, half step, or a half tone, is the smallest musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most dissonant when sounded harmonically.
It is defined as the interval between ...
(16:15 = 111.73 cents).(1897). Columbian cyclopedia, Volume 9
', np. Garretson, Cox & Company. pre-ISBN. Medieval theorists
Boethius
Anicius Manlius Severinus Boethius, commonly known simply as Boethius (; Latin: ''Boetius''; 480–524 AD), was a Roman Roman Senate, senator, Roman consul, consul, ''magister officiorum'', polymath, historian, and philosopher of the Early Middl ...
and Tinctoris
Jehan le Taintenier or Jean Teinturier (Latinised as Johannes Tinctoris; also Jean de Vaerwere; – 1511) was a Renaissance music theorist and composer from the Low Countries. Up to his time, he is perhaps the most significant European writer ...
described the diaschisma as one-half of the Pythagorean minor second
A semitone, also called a minor second, half step, or a half tone, is the smallest interval (music), musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most Consonance and dissonance#Dissonance, dissonant when sounde ...
, or 256/243, which would make the other half either 25/24 (70.67 cents) or about 45 cents. The diaschisma may be approximated by 89/88, 19.56 cents.
 Tempering out the diaschisma, in the modern meaning of the term, leads to a diaschismic temperament. The diaschisma is tempered out in the usual system of
Tempering out the diaschisma, in the modern meaning of the term, leads to a diaschismic temperament. The diaschisma is tempered out in the usual system of 12 equal temperament
12 equal temperament (12-ET) is the musical system that divides the octave into 12 parts, all of which are Equal temperament, equally tempered (equally spaced) on a logarithmic scale, with a ratio equal to the Twelfth root of two, 12th root of 2 ...
; in fact, 12 equal temperament can be characterized as the 5-limit
Five-limit tuning, 5-limit tuning, or 5-prime-limit tuning (not to be confused with 5-odd-limit tuning), is any system for tuning a musical instrument that obtains the frequency of each note by multiplying the frequency of a given reference not ...
temperament that tempers out both the syntonic comma of 81/80 and the diaschisma. However, it is possible to improve the tuning a good deal over that of 12-et and still temper out the diaschisma; the equal temperaments with 22, 34 and 46 notes all temper it out.
See also
*Comma (music)
In music theory, a comma is a very small interval (music), interval, the difference resulting from Musical tuning, tuning one note (music), note two different ways. Traditionally, there are two most common commata; the syntonic comma (80:81), " ...
References
5-limit tuning and intervals Commas (music) {{music-theory-stub