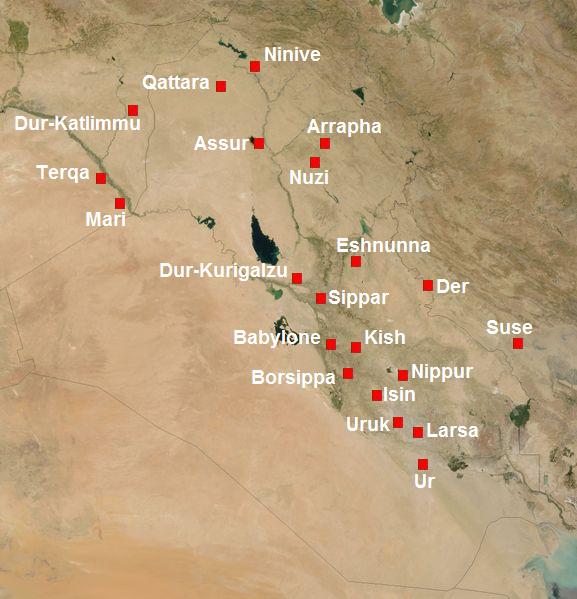
Der (Sumer) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Der ( Sumerian: 𒌷𒂦𒀭𒆠 ''uruBAD3.ANki''; Akkadian: 𒌷𒂦𒀭𒆠 ''uruBAD3.ANki'' or ''urude-e-ru(ki)'') was a
 In the second millennium, Der was mentioned in a tablet discovered at Mari sent by Yarim-Lim I of
In the second millennium, Der was mentioned in a tablet discovered at Mari sent by Yarim-Lim I of
Stela at British Museum mentioning Der
Sumerian cities Archaeological sites in Iraq Former populated places in Iraq History of Wasit Governorate City-states Former kingdoms
Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
ian city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world throughout history, including cities such as Rome, ...
at the site of modern Tell Aqar near al-Badra in Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
's Wasit Governorate. It was east of the Tigris River on the border between Sumer and Elam
Elam () was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of modern-day southern Iraq. The modern name ''Elam'' stems fr ...
. At one time it was thought that it might have been ancient Durum ( Sumerian: ''uruBAD3ki'') but more recent scholarship has rebutted that.
The principal god of Der was Ištaran. In the 1st millennium BC, he was also referred to as ''Anu rabû'' ("''Great Anu''") in Akkadian. The name of his temple at Der was Edimgalkalama.
History
Early Bronze
Der was occupied from the Early Dynastic period through Neo-Assyrian times. The local deity of the city was named Ishtaran, represented on Earth by his minister, the snake god Nirah.Ur III period
In the late 3rd millennium, during the reign of Sulgi of theThird Dynasty of Ur
The Third Dynasty of Ur or Ur III was a Sumerian dynasty based in the city of Ur in the 22nd and 21st centuries BC ( middle chronology). For a short period they were the preeminent power in Mesopotamia and their realm is sometimes referred to by ...
, Der was mentioned twice. The Sulgi year name 11 was named "Year Ishtaran of Der was brought into his temple", and year 21 was named "Year Der was destroyed". During the time of Amar-Sin, when the king launched a long military campaign against Huhnuri, prince Shu-Sin
Shu-Sin, also Šu-Suen (: '' DŠu D Sîn'', after the Moon God Sîn", the "𒀭" being a silent honorific for "Divine", formerly read Gimil-Sin) (died c. 2028 BC) was king of Sumer and Akkad, and was the fourth king of the Ur III dynasty. He su ...
, crown prince, left his post in Der to return and hold Ur.
Middle Bronze
Yamhad
Yamhad (Yamḫad) was an ancient Semitic languages, Semitic-speaking kingdom centered on Ḥalab (Aleppo) in Syria (region), Syria. The kingdom emerged at the end of the 19th century BC and was ruled by the Yamhad dynasty, who counted on both mi ...
; the tablet includes a reminder to Yasub-Yahad king of Der about the military help given to him for fifteen years by Yarim-Lim, followed by a declaration of war against the city in retaliation for what Yarim-Lim described as evil deeds committed by Yasub-Yahad. Rim-Sin I of Larsa
Larsa (, read ''Larsamki''), also referred to as Larancha/Laranchon (Gk. Λαραγχων) by Berossus, Berossos and connected with the biblical Arioch, Ellasar, was an important city-state of ancient Sumer, the center of the Cult (religious pra ...
reported destroying Der in his 20th year. Ammi-Ditana
Ammi-Ditana was a king of Babylon who reigned from 1683–1640s BC. He was preceded by Abi-Eshuh. Year-names survive for the first 37 years of his reign, plus fragments for a few possible additional years. His reign was a largely peaceful one; ...
of Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
also recorded destroying the city wall of Der in his 37th year, that he said had been built earlier by Damqi-ilishu of the Sealand Dynasty.
In an inscription little known early Old Babylonian period ruler of Der, Ilum-muttabbil, claimed defeating the armies of Anshan
Anshan ( zh, s=鞍山, p=Ānshān, l=saddle mountain) is an inland prefecture-level city in central-southeast Liaoning province, People's Republic of China, about south of the provincial capital Shenyang. As of the 2020 census, it was Liaoning' ...
, Elam, and Simaski, in
alliance with Marhaši.
Iron Age
In 720 BC theAssyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
n king Sargon II
Sargon II (, meaning "the faithful king" or "the legitimate king") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 722 BC to his death in battle in 705. Probably the son of Tiglath-Pileser III (745–727), Sargon is generally believed to have be ...
moved against Elam, but the Assyrian host was defeated near Der by the combined army of king Humban-Nikash I of Elam and king Marduk-apla-iddina II of Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
. Following the Persian conquest of Babylon in 539 BC, the Cyrus Cylinder mentions repatriating the people and restoring the sanctuary of the god of Der, among other cities.
Archaeology
While it appears that no excavation has occurred at Der, several notable objects have been discovered nearby, including akudurru
A kudurru was a type of stone document used as a boundary stone and as a record of land grants to vassals by the Kassites and later dynasties in ancient Babylonia between the 16th and 7th centuries BC. The original kudurru would typically be stor ...
(discovered in Sippar) which confirmed the name of the site. The site itself has been heavily damaged by water over the centuries and was considered not worth excavating.Sidney Smith, An Egyptian in Babylonia, The Journal of Egyptian Archaeology
The ''Journal of Egyptian Archaeology (JEA)'' is a bi-annual Peer review, peer-reviewed international academic journal published by the Egypt Exploration Society. Covering Egyptology, Egyptological research, the JEA publishes scholarly articles, f ...
, vol. 18, no. 1/2, pp. 28-32, 1932
List of rulers
The following list should not be considered complete:See also
*List of cities of the ancient Near East
The earliest cities in history were in the ancient Near East, an area covering roughly that of the modern Middle East: its history began in the 4th millennium BC and ended, depending on the interpretation of the term, either with the conquest by ...
* Tell
Notes
{{reflistFurther reading
*P. Michalowski, Durum and Uruk during the Ur III Period, Mesopotamia, vol. 12, pp. 83 –96, 1977External links
Stela at British Museum mentioning Der
Sumerian cities Archaeological sites in Iraq Former populated places in Iraq History of Wasit Governorate City-states Former kingdoms