dense irregular connective tissue on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
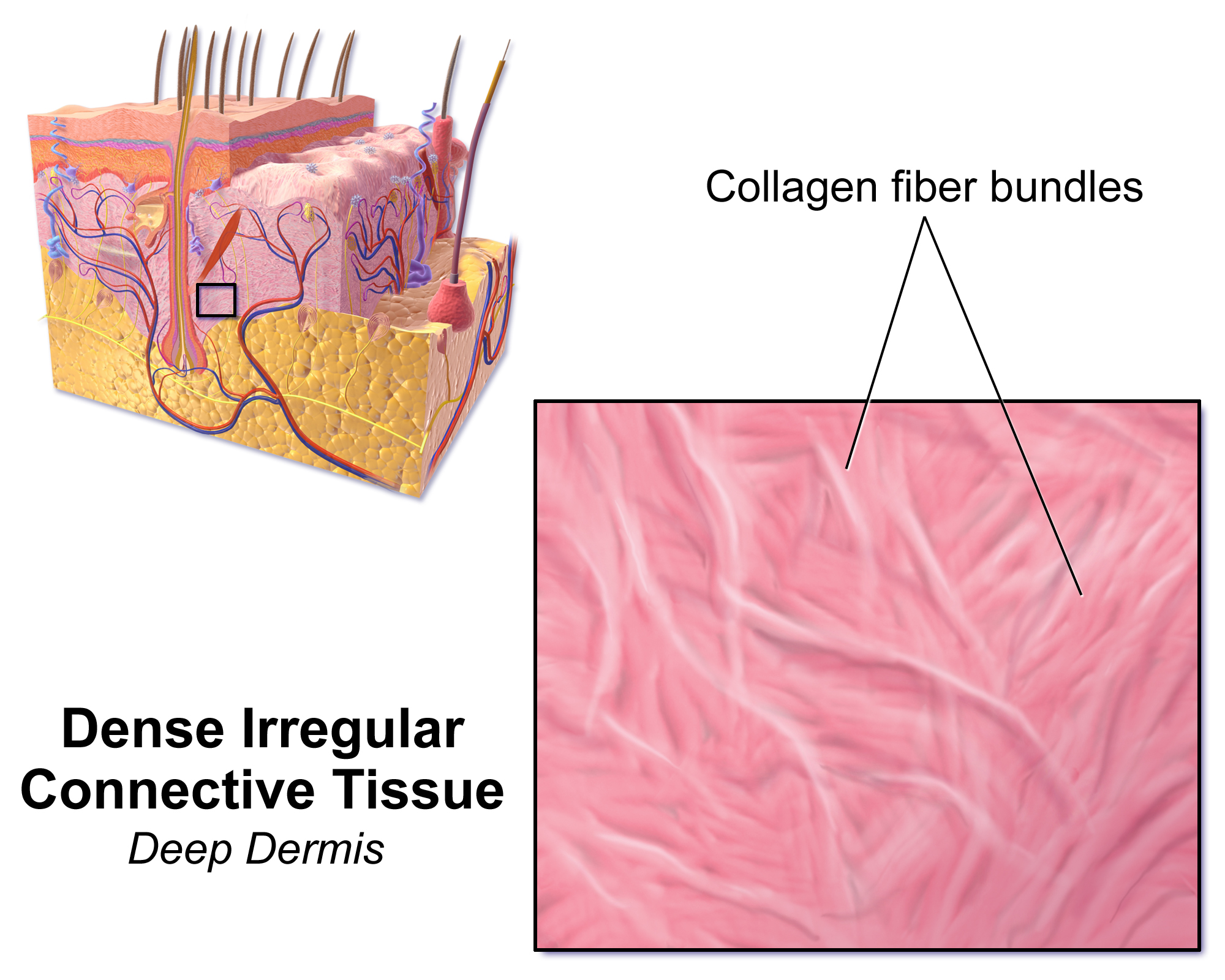 Dense irregular connective tissue has fibers that are not arranged in parallel bundles as in
Dense irregular connective tissue has fibers that are not arranged in parallel bundles as in
 Dense irregular connective tissue has fibers that are not arranged in parallel bundles as in
Dense irregular connective tissue has fibers that are not arranged in parallel bundles as in dense regular connective tissue
Dense regular connective tissue (DRCT) provides connection between different tissues in the human body. The collagen fibers in dense regular connective tissue are bundled in a parallel fashion. DRCT is divided into white fibrous connective tissue ...
.
Dense irregular connective tissue has less ground substance than loose connective tissue
Loose connective tissue, also known as areolar tissue, is a cellular connective tissue with thin and relatively sparse collagen fibers. They have a semi-fluid matrix with lesser proportions of fibers. Its ground substance occupies more vol ...
. Fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of cell (biology), biological cell typically with a spindle shape that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (Stroma (tissue), stroma) for animal Tissue (biology), tissues, and ...
s are the predominant cell type, scattered sparsely across the tissue.
Function
This type of connective tissue is found mostly in the reticular layer (or deep layer) of thedermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (skin), epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis (anatomy), cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from s ...
. It is also in the sclera
The sclera, also known as the white of the eye or, in older literature, as the tunica albuginea oculi, is the opaque, fibrous, protective outer layer of the eye containing mainly collagen and some crucial elastic fiber.
In the development of t ...
and in the deeper skin layers. Due to high portions of collagenous fibers, dense irregular connective tissue provides strength, making the skin resistant to tearing by stretching forces from different directions.
Dense irregular connective tissue also makes up submucosa
The submucosa (or tela submucosa) is a thin layer of tissue in various organs of the gastrointestinal, respiratory, and genitourinary tracts. It is the layer of dense irregular connective tissue that supports the mucosa (mucous membrane) an ...
of the digestive tract, lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
s, and some types of fascia
A fascia (; : fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; ) is a generic term for macroscopic membranous bodily structures. Fasciae are classified as superficial, visceral or deep, and further designated according to their anatomical location.
...
. Other examples include periosteum
The periosteum is a membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones, except at the articular surfaces (i.e. the parts within a joint space) of long bones. (At the joints of long bones the bone's outer surface is lined with "articular cartila ...
and perichondrium of bones, and the tunica albuginea of testis. In the submucosa layer, the fiber bundles course in varying planes allowing the organ to resist excessive stretching and distension.
References
Tissues (biology) {{musculoskeletal-stub