Deneb Algedi on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Delta Capricorni, or δ Capricorni, is a
 Delta Capricorni A is an
Delta Capricorni A is an
binary star
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in ...
located 38,7 light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 101 ...
s from the Sun in the constellation of Capricornus
Capricornus is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for "horned goat" or "goat horn" or "having horns like a goat's", and it is commonly represented in the form of a sea goat: a mythical creature that is half goat, half fi ...
(the Sea Goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of ...
). The system consists of an eclipsing binary
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in ...
, Delta Capricorni A, and two visual companions that are over 10 magnitudes fainter, labeled B and C. Delta Capricorni A's two components are designated Delta Capricorni Aa (formally named Deneb Algedi , the traditional name of the system) and Ab. The primary star, Aa, is a white giant
A giant star is a star with substantially larger radius and luminosity than a main-sequence (or ''dwarf'') star of the same surface temperature.Giant star, entry in ''Astronomy Encyclopedia'', ed. Patrick Moore, New York: Oxford University Press ...
and the combined light of Aa and Ab makes it the brightest star in the constellation.
Delta Capricorni is 2.6 degrees south of the ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agai ...
and can be occulted
An occultation is an event that occurs when one object is hidden from the observer by another object that passes between them. The term is often used in astronomy, but can also refer to any situation in which an object in the foreground blocks ...
by the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width ...
, and (rarely) by planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a ...
s.
Nomenclature
''δ Capricorni'' ( Latinised to ''Delta Capricorni'') is the system'sBayer designation
A Bayer designation is a stellar designation in which a specific star is identified by a Greek or Latin letter followed by the genitive form of its parent constellation's Latin name. The original list of Bayer designations contained 1,564 stars. T ...
. The designations of the three constituents as ''Delta Capricorni A'', ''B'' and ''C'', and those of ''A's'' components – ''Delta Capricorni Aa'' and ''Ab'' – derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star system
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a ''star cluster'' or ''galaxy'', although, broadly speaking ...
s, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach ...
(IAU).
The system bore the traditional names ''Deneb Algedi'', derived from the Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
ذنب الجدي (''ðanab al-jady''), meaning "the tail of the goat", referring to the fishlike tail of the celestial sea-goat Capricorn, and ''Scheddi''. In 2016, the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach ...
organized a Working Group on Star Names
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) established a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) in May 2016 to catalog and standardize List of proper names of stars, proper names for stars for the international astronomical community. It operates under ...
(WGSN) to catalogue and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN decided to attribute proper names to individual stars rather than entire multiple systems. It approved the name ''Deneb Algedi'' for the component Delta Capricornii Aa on February 1, 2017 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names.
In Chinese astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categorized in the t ...
, Delta Capricorni is known as (), meaning 'The Fourth Star of the Line of Ramparts'. This refers to its presence among an asterism known as ' The Line of Ramparts', which also includes Kappa Capricorni, Epsilon Capricorni, Gamma Capricorni, Iota Aquarii, Lambda Aquarii, Sigma Aquarii, Phi Aquarii, 27 Piscium
27 Piscium is a binary star system in the zodiac constellation of Pisces. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.88. Based upon an annual parallax shift of , it is located about 234 light years away. ...
, 29 Piscium
9 (nine) is the natural number following and preceding .
Evolution of the Arabic digit
In the beginning, various Indians wrote a digit 9 similar in shape to the modern closing question mark without the bottom dot. The Kshatrapa, Andhra a ...
, 33 Piscium
33 Piscium is a binary star system in the zodiac constellation of Pisces. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.61. The distance to this system, as determined from an annual parallax shift of , is about ...
and 30 Piscium
30 Piscium (HIP 154) is a solitary variable star in the zodiac constellation of Pisces. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.37. Its calculated mid-value of antiposed parallax shift as the earth moves aro ...
. ''中國星座神話'', written by 陳久金. Published by 台灣書房出版有限公司, 2005, .
Observational history
In 1906 astronomer Vesto Slipher ofLowell Observatory
Lowell Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Flagstaff, Arizona, United States. Lowell Observatory was established in 1894, placing it among the oldest observatories in the United States, and was designated a National Historic Landmark ...
discovered that Delta Capricorni A was a spectroscopic binary. The orbit was determined in 1921 by Clifford Crump using 69 radial velocity
The radial velocity or line-of-sight velocity, also known as radial speed or range rate, of a target with respect to an observer is the rate of change of the distance or range between the two points. It is equivalent to the vector projection ...
measurements obtained at Yerkes Observatory
Yerkes Observatory ( ) is an astronomical observatory located in Williams Bay, Wisconsin, United States. The observatory was operated by the University of Chicago Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics from its founding in 1897 to 2018. Owner ...
. However the eclipsing binary
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in ...
nature of the system was not discovered until 1956 by Olin J. Eggen
Olin Jeuck Eggen (July 9, 1919 – October 2, 1998) was an American astronomer.
Biography
Olin Jeuck Eggen was born to Olin Eggen and Bertha Clare Jeuck in the village of Orfordville in Rock County, Wisconsin. Both of his parents were of Norw ...
at Lick Observatory.
Lunar occultations have been observed in 1951, 1962, and 1988.
Delta Capricorni was recognised as a metallic-line star in 1957 and included in a 1958 catalog of magnetic stars. It has also been associated with extreme ultraviolet
Extreme ultraviolet radiation (EUV or XUV) or high-energy ultraviolet radiation is electromagnetic radiation in the part of the electromagnetic spectrum spanning wavelengths from 124 nm down to 10 nm, and therefore (by the Planck–E ...
and radio sources, believed to be from coronal activity in the secondary star.
Stellar system
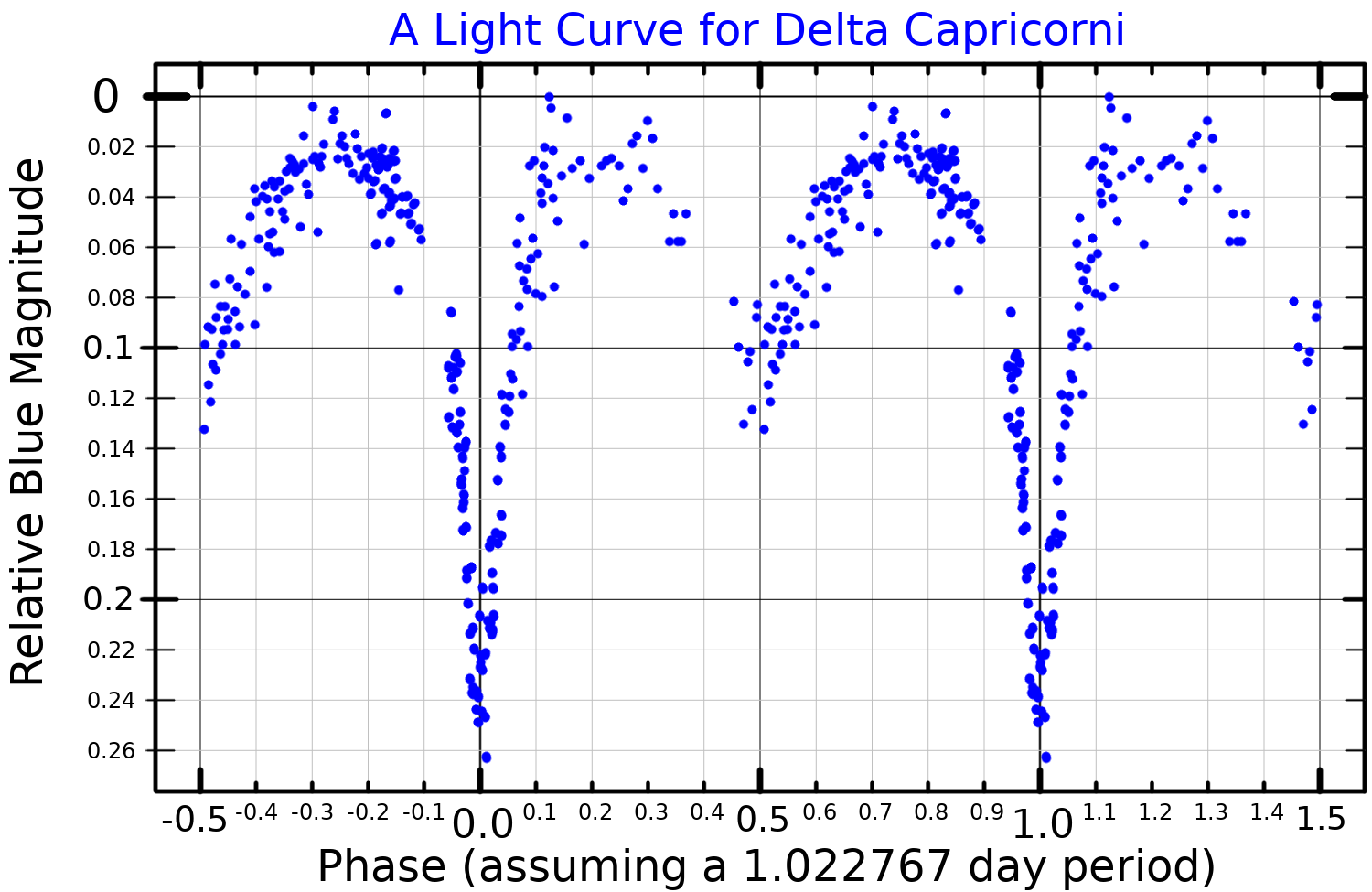
 Delta Capricorni A is an
Delta Capricorni A is an Algol
ALGOL (; short for "Algorithmic Language") is a family of imperative computer programming languages originally developed in 1958. ALGOL heavily influenced many other languages and was the standard method for algorithm description used by th ...
-type eclipsing binary star
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in wh ...
, with an orbital period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets ...
of 1.022768 days and an inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a Plane of reference, reference plane and the orbital plane or Axis of rotation, axis of direction of the orbiting object ...
close to the line of sight from the Earth. The peak apparent visual magnitude of the pair is 2.81. During an eclipse of the primary, this magnitude drops by 0.24. When the primary is eclipsing the secondary, the magnitude decreases by 0.09.
Delta Capricorni A has an overall stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting t ...
of A7m III, indicating that it is a giant star
A giant star is a star with substantially larger radius and luminosity than a main-sequence (or ''dwarf'') star of the same surface temperature.Giant star, entry in ''Astronomy Encyclopedia'', ed. Patrick Moore, New York: Oxford University Press ...
that has exhausted the supply of hydrogen at its core. More specifically, this is a chemically-peculiar Am star An Am star or metallic-line star is a type of chemically peculiar star of spectral type A whose spectrum has strong and often variable absorption lines of metals such as zinc, strontium, zirconium, and barium, and deficiencies of others, such as c ...
with a spectral type of kA5hF0mF2 III under the revised MK system. This notation indicates that the calcium K-line matches the temperature of an A5 star, the hydrogen spectral type matches an F0 star, and the metallic absorption lines match an F2 star.
In the past this star was suspected of being a Delta Scuti variable, which is rare for an Am star. This categorization was brought into question during observations in 1994 and it is most likely not inherently variable. The primary has double the Sun's mass
The solar mass () is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. It is approximately equal to the mass of ...
and nearly twice its radius. It is rotating rapidly with a projected rotational velocity
Stellar rotation is the angular motion of a star about its axis. The rate of rotation can be measured from the spectrum of the star, or by timing the movements of active features on the surface.
The rotation of a star produces an equatorial bulge ...
of 105 km s−1. (This rotation rate is synchronous with the orbital period.) Note that it is unusual for an Am star to have such a high rotational velocity. The outer envelope of the star is radiating energy at an effective temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature ...
of 7,301 K, giving it the white-hued glow of an A-type star. The secondary component is a G-type
Gaea
Gaea is one of the Elder Gods of Earth.
Gaia
Gaia, also known as the Guardian of the Universal Amalgamator, is a fictional superhero, depicted as possibly being a mutant or extraterrestrial. Created by Larry Hama, she first appeared in ...
or K-type star with around 90% of the mass of the Sun.
There are two optical companions. A fifteenth magnitude star is one arcminute
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The na ...
away, and a thirteenth magnitude star is over two arcminutes away from the primary star and that distance is increasing.
In culture
According toastrology
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Di ...
, Delta Capricorni's representation of a flexible tail is reflected in its association with both good and bad fortune alike. It was one of the fifteen Behenian stars of medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
astrology, associated with chalcedony
Chalcedony ( , or ) is a cryptocrystalline form of silica, composed of very fine intergrowths of quartz and moganite. These are both silica minerals, but they differ in that quartz has a trigonal crystal structure, while moganite is monocl ...
, marjoram and the kabbalistic
Kabbalah ( he, קַבָּלָה ''Qabbālā'', literally "reception, tradition") is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal ( ''Məqūbbāl'' "receiver"). The defin ...
symbol .
See also
*Alpha Capricorni
Alpha Capricorni (α Capricorni, abbreviated Alpha Cap, α Cap) is an optical double star in the constellation of Capricornus. The two physically unrelated components are designated:
* α¹ Capricorni
* α² Capricorni (also named Algedi).
They ...
* Deneb
References
Further reading
*links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Delta Capricorni Capricorni, Delta Capricornus (constellation) Algol variables Eclipsing binaries Spectroscopic binaries Deneb Algedi A-type giants Capricorni, 49 107556 8322 F-type giants 207098 Durchmusterung objects Am stars Gliese and GJ objects