Davis–Beirut Reaction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Davis–Beirut reaction is ''N,N''-bond forming heterocyclization that creates numerous types of 2''H''-
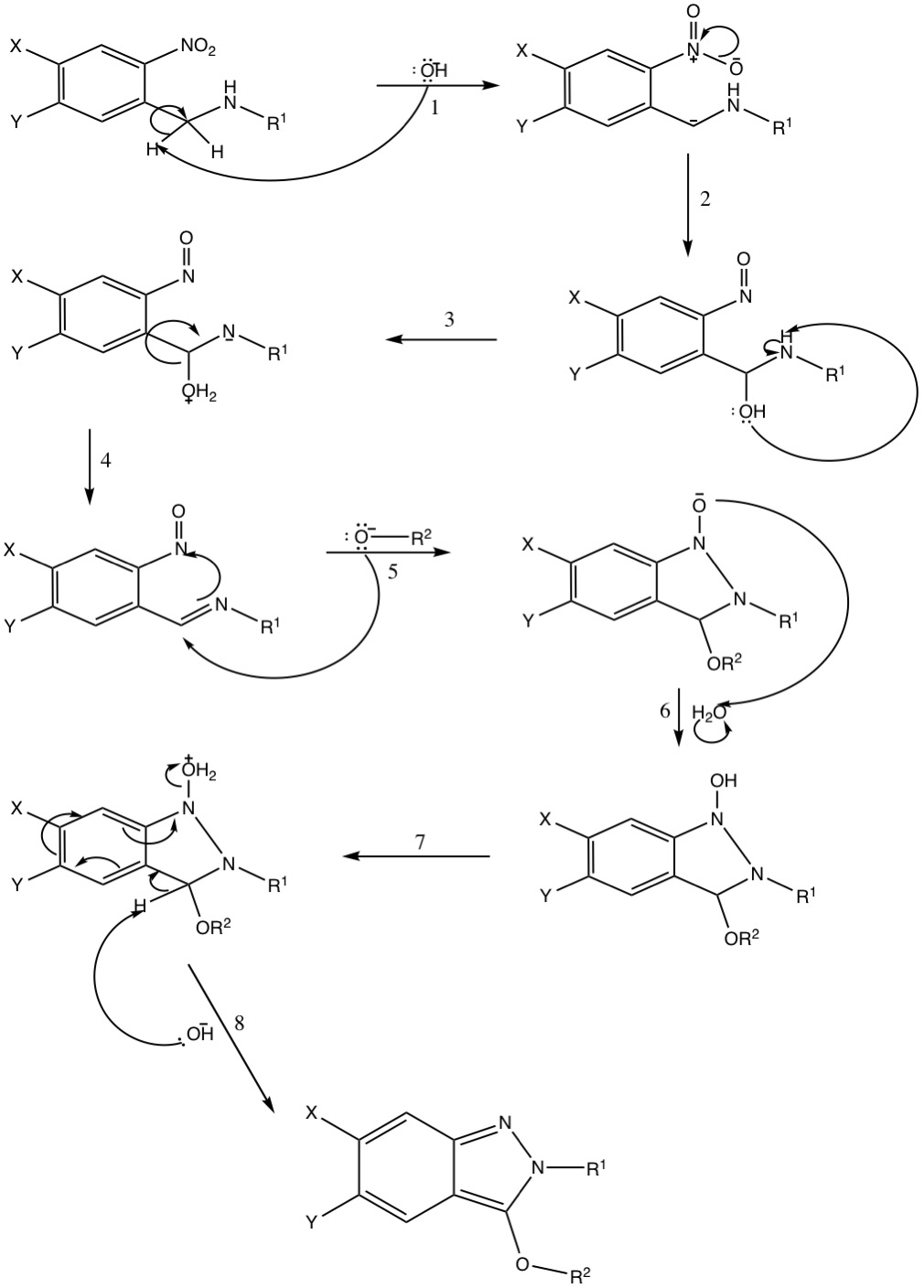 The current proposed mechanism for the Davis–Beirut reaction in base was first published in 2005 by Kurth, Olmstead, and Haddadin. The reaction occurs when a ''N''-substituted 2-nitrobenzylamine is heated in the presence of base, such as NaOH and KOH, and an alcohol and includes the formation of a
The current proposed mechanism for the Davis–Beirut reaction in base was first published in 2005 by Kurth, Olmstead, and Haddadin. The reaction occurs when a ''N''-substituted 2-nitrobenzylamine is heated in the presence of base, such as NaOH and KOH, and an alcohol and includes the formation of a  Furthermore, Davis–Beirut reactions in acids form a carbocation as one of its transition states instead of the proposed carbanion one when the reaction occurs in base.
Furthermore, Davis–Beirut reactions in acids form a carbocation as one of its transition states instead of the proposed carbanion one when the reaction occurs in base.
 Creating 2''H''-indazoles via the Davis–Beirut reaction can also help in producing 1''H''-indazoles, naturally occurring and synthetically made molecules with known pharmaceutical uses such as anti-inflammatories and anti-cancer drugs. By creating 2''H''-indazoles via the Davis–Beirut reaction, the product can subsequently be reacted with electrophiles, such as anhydrides, to create disubstituted 1''H''-indazoles that can be utilized for pharmaceutical and other industrial purposes.
Creating 2''H''-indazoles via the Davis–Beirut reaction can also help in producing 1''H''-indazoles, naturally occurring and synthetically made molecules with known pharmaceutical uses such as anti-inflammatories and anti-cancer drugs. By creating 2''H''-indazoles via the Davis–Beirut reaction, the product can subsequently be reacted with electrophiles, such as anhydrides, to create disubstituted 1''H''-indazoles that can be utilized for pharmaceutical and other industrial purposes.
indazoles
Indazole, also called isoindazole, is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. This bicyclic compound consists of the fusion of benzene and pyrazole.
Indazole is an amphoteric molecule which can be protonated to an indazolium cation or deproto ...
and indazolones in both acidic and basic conditions
The Davis–Beirut reaction is named after Mark Kurth and Makhluf Haddadin
Makhluf J. Haddadin (1935 – September 21, 2022) was a Jordanian chemistry professor at the American University of Beirut.
Biography
Haddadin was born in Ma'in, Jordan in 1935. He won a full scholarship from the Jordanian Ministry of Education, ...
's respective universities; University of California, Davis
The University of California, Davis (UC Davis, UCD, or Davis) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Davis, California, United States. It is the northernmost of the ten campuses of the University ...
and American University of Beirut
The American University of Beirut (AUB; ) is a private, non-sectarian, and independent university chartered in New York with its main campus in Beirut, Lebanon. AUB is governed by a private, autonomous board of trustees and offers programs le ...
, and is appealing because it uses inexpensive starting materials and does not require toxic metals.
:Mechanism in base
 The current proposed mechanism for the Davis–Beirut reaction in base was first published in 2005 by Kurth, Olmstead, and Haddadin. The reaction occurs when a ''N''-substituted 2-nitrobenzylamine is heated in the presence of base, such as NaOH and KOH, and an alcohol and includes the formation of a
The current proposed mechanism for the Davis–Beirut reaction in base was first published in 2005 by Kurth, Olmstead, and Haddadin. The reaction occurs when a ''N''-substituted 2-nitrobenzylamine is heated in the presence of base, such as NaOH and KOH, and an alcohol and includes the formation of a carbanion
In organic chemistry, a carbanion is an anion with a lone pair attached to a tervalent carbon atom. This gives the carbon atom a negative charge.
Formally, a carbanion is the conjugate base of a carbon acid:
:
where B stands for the base (chemist ...
The reaction begins with the base removing a hydrogen (1) adjacent to the secondary amine-group, creating a carbanion. The carbanion then extracts an oxygen from the nitro group
In organic chemistry, nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups (). The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores (functional group that makes a compound explosive) used globally. The nit ...
(2), which is then subsequently protonated, most likely by water. The newly formed hydroxyl group (3), then extracts the secondary amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
s hydrogen, leaving a negative charge on nitrogen and creating a protonated hydroxyl group. The oxygen and its hydrogens then leave as a molecule of water (4), creating a double bond with the previously negatively charged nitrogen atom. The new pi bond makes the carbon adjacent to the nitrogen more susceptible for attack by a present alcohol (5), which in turn creates an oxygen-carbon bond, a bond between the two nitrogen atoms, and pushes electrons onto the oxygen molecule originally from the amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a chemical compound, compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl functional group, groups or hydrogen at ...
. This molecule is then protonated (6) to create an overall net neutral charge. The hydroxyl group is protonated similarly to step three (7), creating a good leaving group. Therefore, when the alpha hydrogen of the nitrogen atom and ether group (8) is extracted by the base, the flow of electrons creates two new carbon-nitrogen bonds and causes the loss of the protonated hydroxyl group as a molecule of water. The final product produced by this mechanism is therefore a 3-oxy-substituted 2''H''-indazole.
Slight variations of this mechanism exists depending on the starting materials and the conditions (acid or base) of the reaction. In instances of intramolecular oxygen attack (i.e. step 5 of the proposed mechanism is intramolecular) an ''o''-nitrobenzylidene imine
In organic chemistry, an imine ( or ) is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond (). The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bon ...
intermediate is formed compared to the secondary imine of the displayed mechanism. Other variants of the Davis–Beirut reaction
By manipulating the starting materials of the Davis–Beirut reaction, researchers can create a large number of 2''H-''indazoles derivatives, many of which can be utilized for further synthesis. In 2014, Thiazolo-, Thiazino-, and Thiazipino-2''H''-indazoles were synthesized utilizing ''o''-nitrobenzaldehydes or ''o''-nitrobenzyl bromides and ''S''-trityl-protected primary aminothiol alkanes with a base, such as KOH, in alcohol. Creating Thiazolo-, Thiazino-, and Thiazipino-2''H''-indazoles is beneficial since they are generally more stable than the oxo-2''H''-indazoles formed without the ''S''-trityl-protected group, and they can easily be oxidized to sulfones.Applications
Heterocycles, especially those containing nitrogen atoms, are highly prevalent in many pharmaceutical drugs currently on the market. Some, like those coming from 1''H''-indazoles, contain naturally occurring molecules, while others are purly synthetic. 2''H''-indazoles, though, are very rare in nature compared to 1''H''-indazole compounds, most likely due to the complex nature of a heterocycle including a nitrogen-nitrogen bond and an ether side chain. The discovery of the Davis–Beirut reaction therefore provides any easy and cost effective way to synthetically create 2''H''-indazoles. Breakthroughs, including the success of introducing thioether moiety at ''C3'' of the 2''H''-indazole structure, has aided in creating drug treatments for a variety of ailments, includingcystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive manner that impairs the normal clearance of Sputum, mucus from the lungs, which facilitates the colonization and infection of the lungs by bacteria, notably ''Staphy ...
, with the use of myeloperoxidase inhibitors. Due to the recentness of the discovery of this reaction, though, most research is primarily headed by Haddadin, Kurth, or both, therefore causing a currently limited scope.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Davis-Beirut reaction Indazoles Nitrogen heterocycle forming reactions Name reactions