Daugavgrīva Castle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Daugavgrīva Castle (; ; or ''Ust`-Dvinsk'') is a former
Daugavgrīva Castle (; ; or ''Ust`-Dvinsk'') is a former
here
the monastery and its tombs were destroyed, although the monks rebuilt the abbey after fighting died down. They also had to endure abuse by the undisciplined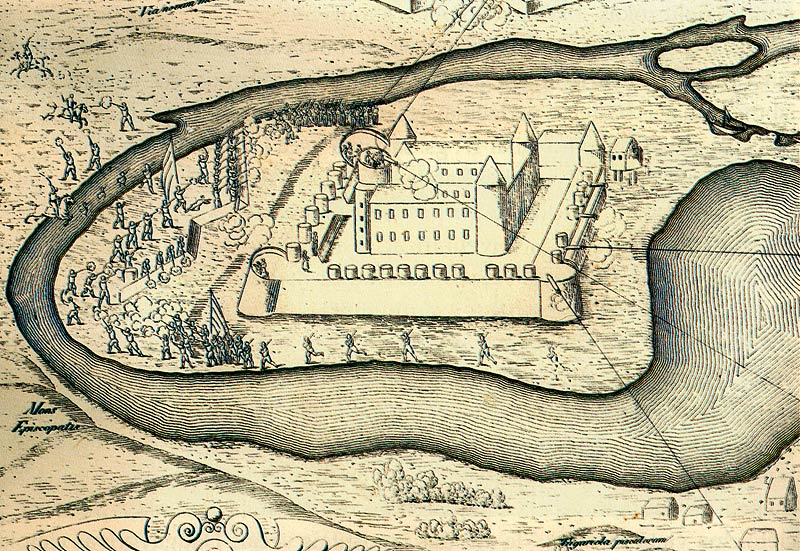
The fortress of Daugavgriva
with contemporary illustrations
on Ambermarks website *
The fortress of Daugavgriva
on 1201 website *
Discussion and pictures
on Fortification website {{DEFAULTSORT:Daugavgriva castle Buildings and structures completed in 1205 Castles of the Livonian Order Castles in Vidzeme Buildings and structures in Riga
 Daugavgrīva Castle (; ; or ''Ust`-Dvinsk'') is a former
Daugavgrīva Castle (; ; or ''Ust`-Dvinsk'') is a former monastery
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of Monasticism, monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in Cenobitic monasticism, communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a ...
converted into a castle, located at Vecdaugava
Vecdaugava is a neighbourhood of Riga, the capital of Latvia.
Neighbourhoods in Riga
{{Riga-stub ...
oxbow on the right bank of Daugava
The Daugava ( ), also known as the Western Dvina or the Väina River, is a large river rising in the Valdai Hills of Russia that flows through Belarus and Latvia into the Gulf of Riga of the Baltic Sea. The Daugava rises close to the source of ...
, in the northern part of Riga
Riga ( ) is the capital, Primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Latvia, largest city of Latvia. Home to 591,882 inhabitants (as of 2025), the city accounts for a third of Latvia's total population. The population of Riga Planni ...
city, in the Vidzeme
Vidzeme (; Old Latvian orthography: ''Widda-semme'', ) is one of the Historical Latvian Lands. The capital of Latvia, Riga, is situated in the southwestern part of the region. Literally meaning "the Middle Land", it is situated in north-centra ...
region of Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
. Nowadays here are seen only earthen ramparts.
History
The first settlement,Daugavgrīva Abbey
Daugavgrīva Abbey or Dünamünde Abbey (; ; ) was a Cistercian monastery in Daugavgrīva () in Latvia, about 12 kilometres from Riga, of which Daugavgrīva has formed a district since 1959. The site was re-developed from 1305 as Daugavgrīva Castl ...
, was established on the right bank of the Daugava river, 13 miles from Bishop Albert of Riga
Albert of Riga or Albert of Livonia ( – 17 January 1229) was the third Catholic Bishop of Riga in Livonia. As the Bishop of Livonia, in 1201, he founded Riga, the modern capital city of Latvia, and the city was later made a bishopric. The bu ...
's residence in Riga, by Cistercian
The Cistercians (), officially the Order of Cistercians (, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint Benedict, as well as the contri ...
monks from Pforta
Schulpforta, otherwise known as Pforta, is a school located in Pforta monastery, a former Cistercian monastery (1137–1540). The school is located near Naumburg on the Saale River in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt.
The site has been a sch ...
in 1205. Theoderich von Treyden
Theoderich (or Theoderich von Treyden) (died 15 June 1219) was the second known missionary in Livonia after Saint Meinhard, the first Bishop of Livonia. He was previously a Cistercian monk working as a priest in Turaida (1191–1202), the first a ...
was an early abbot
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the head of an independent monastery for men in various Western Christian traditions. The name is derived from ''abba'', the Aramaic form of the Hebrew ''ab'', and means "father". The female equivale ...
, while during the 1210s Count Bernhard II of Lippe
Lippe () is a ''Kreis'' (district) in the east of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Neighboring districts are Herford, Minden-Lübbecke, Höxter, Paderborn, Gütersloh, and district-free Bielefeld, which forms the region Ostwestfalen-Lippe. ...
was its abbot. During a raid of tribal Curonians
:''The Kursenieki are also sometimes known as Curonians.''
The Curonians or Kurs (; ) were a medieval Balts, Baltic tribe living on the shores of the Baltic Sea in the 5th–16th centuries, in what are now western parts of Latvia and Lithuania. ...
in 1228,See the ''Livonian Chronicle'' by Hermann de Wartberge
Hermann von Wartberge (died ca. 1380) was a chronicler of the Livonian Order. Born in Westphalia, Wartberge was a Catholic priest and author of the valuable Latin chronicle ''Chronicon Livoniale'' covering the history of the Livonian Crusade from ...
, as citehere
the monastery and its tombs were destroyed, although the monks rebuilt the abbey after fighting died down. They also had to endure abuse by the undisciplined
crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding ...
of the Livonian Order
The Livonian Order was an autonomous branch of the Teutonic Order,
formed in 1237. From 1435 to 1561 it was a member of the Livonian Confederation.
History
The order was formed from the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword after thei ...
. Those knights were defeated at the Battle of Saule
The Battle of Saule (; ; ) was fought on 22 September 1236, between the Livonian Brothers of the Sword and pagan troops of Samogitians and Semigallians. Between 48 and 60 knights were killed, including the Livonian Master, Volkwin. It was the ea ...
, however, and their remnants were incorporated into the Teutonic Knights
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to t ...
in 1237. Until 1452 the territory of Siggelkow
Siggelkow is a municipality in the Ludwigslust-Parchim district, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to ...
in Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schwerin, Neubrandenburg, Wismar and Güstrow. ...
was owned by the monastery. In 1305, the local abbot sold the monastery to the Livonian Branch of the Teutonic Knights, who began construction of the fortress of Dünamünde.
In 1329, the knights' castle
A castle is a type of fortification, fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by Military order (monastic society), military orders. Scholars usually consider a ''castle'' to be the private ...
was taken by the burghers of Riga, who were forced to return it to the knights in 1435. In 1481, the knights closed the Daugava
The Daugava ( ), also known as the Western Dvina or the Väina River, is a large river rising in the Valdai Hills of Russia that flows through Belarus and Latvia into the Gulf of Riga of the Baltic Sea. The Daugava rises close to the source of ...
to navigation by stretching an iron chain from Dünamünde to the opposite riverbank, thus hoping to ruin Riga's trade. In retaliation the citizens of Riga captured Dünamünde and destroyed it. The knights returned to rebuild the stronghold eight years later. Because Riga itself was controlled by the Archbishops
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdioc ...
, the local administrative seat (''Komtur
Commander (; ; ; ; ), or Knight Commander, is a title of honor prevalent in chivalric orders and fraternal orders.
The title of Commander occurred in the medieval military orders, such as the Knights Hospitaller, for a member senior to a Knight. ...
ei'') of the monastic state of the Teutonic Knights
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to t ...
was located in Dünamünde.
In 1561 during the Livonian War
The Livonian War (1558–1583) concerned control of Terra Mariana, Old Livonia (in the territory of present-day Estonia and Latvia). The Tsardom of Russia faced a varying coalition of the Denmark–Norway, Dano-Norwegian Realm, the Kingdom ...
, Dünamünde became part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, ...
and afterwards of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
.
The Skanstnieki homestead was built inside the ramparts in the 19th century.

See also
*List of castles in Latvia
This is the List of castles in Latvia, which includes fortified residences of Western European conquerors built in the area of present-day Latvia before the 17th century. There are about 140 medieval castles in the area, therefore this list is not ...
* Daugavgrīva
Daugavgrīva (; ; or ''Ust`-Dvinsk'') is a neighbourhood in North West Riga, Latvia on the left bank of the Daugava river. In this neighbourhood there is a Swedish-built fortress on the Daugava River's left bank, commanding its mouth.
Fortre ...
* Capture of Daugavgrīva (1608)
* Battle of Daugavgriva (1609)
References
Sources
*External links
* *The fortress of Daugavgriva
with contemporary illustrations
on Ambermarks website *
The fortress of Daugavgriva
on 1201 website *
Discussion and pictures
on Fortification website {{DEFAULTSORT:Daugavgriva castle Buildings and structures completed in 1205 Castles of the Livonian Order Castles in Vidzeme Buildings and structures in Riga