DAPI on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
DAPI (pronounced 'DAPPY', /ˈdæpiː/), or 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, is a fluorescent stain that binds strongly to adenine– thymine-rich regions in
DAPI Nucleic Acid Stain
. accessed 2009-12-08. DAPI will also bind to DAPI's blue emission is convenient for microscopists who wish to use multiple fluorescent stains in a single sample. There is some fluorescence overlap between DAPI and green-fluorescent molecules like fluorescein and green fluorescent protein (GFP) but the effect of this is small.
Outside of analytical fluorescence light microscopy DAPI is also popular for labeling of cell cultures to detect the DNA of contaminating '' Mycoplasma'' or
DAPI's blue emission is convenient for microscopists who wish to use multiple fluorescent stains in a single sample. There is some fluorescence overlap between DAPI and green-fluorescent molecules like fluorescein and green fluorescent protein (GFP) but the effect of this is small.
Outside of analytical fluorescence light microscopy DAPI is also popular for labeling of cell cultures to detect the DNA of contaminating '' Mycoplasma'' or
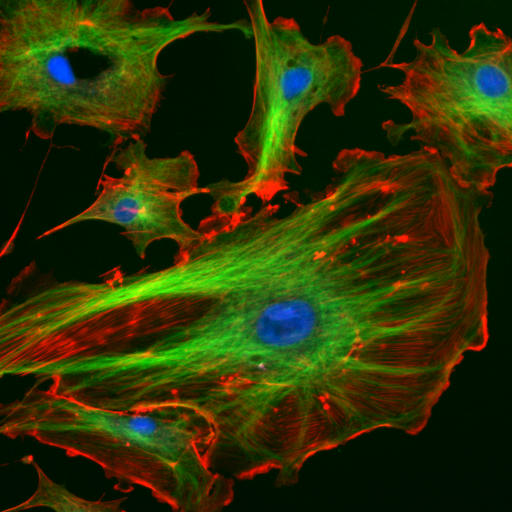 The Hoechst stains are similar to DAPI in that they are also blue-fluorescent DNA stains which are compatible with both live- and fixed-cell applications, as well as visible using the same equipment filter settings as for DAPI.
The Hoechst stains are similar to DAPI in that they are also blue-fluorescent DNA stains which are compatible with both live- and fixed-cell applications, as well as visible using the same equipment filter settings as for DAPI.
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
. It is used extensively in fluorescence microscopy. As DAPI can pass through an intact cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
, it can be used to stain both live and fixed cells, though it passes through the membrane less efficiently in live cells and therefore provides a marker for membrane viability.
History
DAPI was first synthesised in 1971 in the laboratory of Otto Dann as part of a search for drugs to treat trypanosomiasis. Although it was unsuccessful as a drug, further investigation indicated it bound strongly to DNA and became more fluorescent when bound. This led to its use in identifyingmitochondria
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is us ...
l DNA in ultracentrifugation in 1975, the first recorded use of DAPI as a fluorescent DNA stain.
Strong fluorescence when bound to DNA led to the rapid adoption of DAPI for fluorescent staining of DNA for fluorescence microscopy. Its use for detecting DNA in plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
, metazoa and bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
cells and virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are ...
particles was demonstrated in the late 1970s, and quantitative staining of DNA inside cells was demonstrated in 1977. Use of DAPI as a DNA stain for flow cytometry was also demonstrated around this time.
When bound to double-stranded DNA, DAPI has an absorption maximum at a wavelength of 358 nm (ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
) and its emission maximum is at 461 nm (blue). Therefore, for fluorescence microscopy, DAPI is excited with ultraviolet light and is detected through a blue/cyan filter. The emission peak is fairly broad.InvitrogenDAPI Nucleic Acid Stain
. accessed 2009-12-08. DAPI will also bind to
RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
, though it is not as strongly fluorescent. Its emission shifts to around 500 nm when bound to RNA.
 DAPI's blue emission is convenient for microscopists who wish to use multiple fluorescent stains in a single sample. There is some fluorescence overlap between DAPI and green-fluorescent molecules like fluorescein and green fluorescent protein (GFP) but the effect of this is small.
Outside of analytical fluorescence light microscopy DAPI is also popular for labeling of cell cultures to detect the DNA of contaminating '' Mycoplasma'' or
DAPI's blue emission is convenient for microscopists who wish to use multiple fluorescent stains in a single sample. There is some fluorescence overlap between DAPI and green-fluorescent molecules like fluorescein and green fluorescent protein (GFP) but the effect of this is small.
Outside of analytical fluorescence light microscopy DAPI is also popular for labeling of cell cultures to detect the DNA of contaminating '' Mycoplasma'' or virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are ...
. The labelled ''Mycoplasma'' or virus particles in the growth medium fluoresce once stained by DAPI making them easy to detect.
Modelling of absorption and fluorescence properties
This DNA fluorescent probe has been effectively modeled using the time-dependent density functional theory, coupled with the IEF version of the polarizable continuum model. This quantum-mechanical modeling has rationalized the absorption and fluorescence behavior given by minor groove binding and intercalation in the DNA pocket, in term of a reduced structural flexibility and polarization.Live cells and toxicity
DAPI can be used for fixed cell staining. The concentration of DAPI needed for live cell staining is generally very high; it is rarely used for live cells. It is labeled non-toxic in its MSDS and though it was not shown to have mutagenicity to ''E. coli'', it is labelled as a known mutagen in manufacturer information. As it is a small DNA binding compound, it is likely to have somecarcinogenic
A carcinogen () is any agent that promotes the development of cancer. Carcinogens can include synthetic chemicals, naturally occurring substances, physical agents such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, and Biological agent, biologic agent ...
effects and care should be taken in its handling and disposal.
Alternatives
 The Hoechst stains are similar to DAPI in that they are also blue-fluorescent DNA stains which are compatible with both live- and fixed-cell applications, as well as visible using the same equipment filter settings as for DAPI.
The Hoechst stains are similar to DAPI in that they are also blue-fluorescent DNA stains which are compatible with both live- and fixed-cell applications, as well as visible using the same equipment filter settings as for DAPI.
References
See also
* DNA binding ligand * Hoechst stain * Lexitropsin * Netropsin * Pentamidine {{DEFAULTSORT:Dapi Staining dyes Fluorescent dyes DNA-binding substances Indoles Amidines