Coverage Data on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A coverage is the digital representation of some spatio-temporal phenomenon. ISO 19123 provides the definition:
* '' feature that acts as a function to return values from its range for any direct position within its spatial, temporal or spatiotemporal domain''
Coverages play an important role in
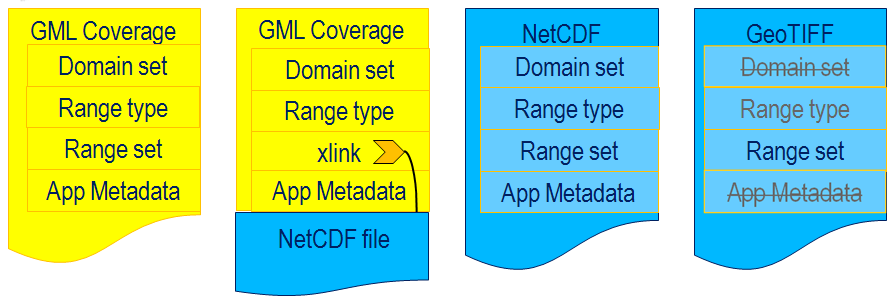 The format-independent logical structure of coverages can be mapped to GML (such as for sensor time series) or to any of a series of data formats, such as
The format-independent logical structure of coverages can be mapped to GML (such as for sensor time series) or to any of a series of data formats, such as
Speeding up Array Query Processing by Just-In-Time Compilation
IEEE Intl Workshop on Spatial and Spatiotemporal Data Mining (SSTDM-08), Pisa, Italy, 15 December 2008, pp. 408 - 413
geographic information system
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with software tools for managing, analyzing, and visualizing those data. In a ...
s (GIS), geospatial
Geographic data and information is defined in the ISO/TC 211 series of standards as data and information having an implicit or explicit association with a location relative to Earth (a geographic location or geographic position).
It is also ca ...
content and services, GIS
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with software tools for managing, analyzing, and visualizing those data. In a ...
data processing
Data processing is the collection and manipulation of digital data to produce meaningful information.
Data processing is a form of '' information processing'', which is the modification (processing) of information in any manner detectable by ...
, and data sharing
Data sharing is the practice of making data used for scholarly research available to other investigators. Many funding agencies, institutions, and publication venues have policies regarding data sharing because transparency and openness are consid ...
.
A coverage is represented by its "domain" (the universe of extent) and a collection representing the coverage's values at each defined location within its range. For example, a satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioiso ...
image derived from remote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Ear ...
might record varying degrees of light pollution
Light pollution is the presence of unwanted, inappropriate, or excessive use of artificial lighting. In a descriptive sense, the term ''light pollution'' refers to the effects of any poorly implemented lighting, during the day or night. Light po ...
. Aerial photography
Aerial photography (or airborne imagery) is the taking of photographs from an aircraft or other airborne platforms. When taking motion pictures, it is also known as aerial videography.
Platforms for aerial photography include fixed-wing aircr ...
, land cover data, and digital elevation model
A digital elevation model (DEM) or digital surface model (DSM) is a 3D computer graphics representation of elevation data to represent terrain or overlaying objects, commonly of a planet, moon, or asteroid. A "global DEM" refers to a discre ...
s all provide coverage data. Generally, a coverage can be multi-dimensional, such as 1-D sensor timeseries, 2-D satellite images, 3-D x/y/t image time series
In mathematics, a time series is a series of data points indexed (or listed or graphed) in time order. Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data. E ...
or x/y/z geo tomograms
Tomography is imaging by sections or sectioning that uses any kind of penetrating wave. The method is used in radiology, archaeology, biology, atmospheric science, geophysics, oceanography, plasma physics, materials science, cosmochemistry, ...
, or 4-D x/y/z/t climate and ocean data.
However, coverages are more general than just regularly gridded imagery. The corresponding standards (see below) address regular and irregular grids, point clouds, and general meshes.
An interoperable service definition for navigating, accessing, processing, and aggregation of coverages is provided by the Open Geospatial Consortium
The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC), an international voluntary consensus standards organization for geospatial content and location-based services, sensor web and Internet of Things, GIS data processing and data sharing. It originated in 199 ...
(OGC) Web Coverage Service (WCS) suite and Web Coverage Processing Service (WCPS), a spatio-temporal coverage query language.
Standards
Coverages represent digital geospatial information representing space/time-varying phenomena. OGC Abstract Topic 6 - which is identical toISO
ISO is the most common abbreviation for the International Organization for Standardization.
ISO or Iso may also refer to: Business and finance
* Iso (supermarket), a chain of Danish supermarkets incorporated into the SuperBest chain in 2007
* Is ...
19123 - defines an abstract model of coverages.
Many implementations are conceivable which all conform to this abstract model while not being interoperable.
This abstract coverage model is concretized to the level of interoperability by the OGC standard GML 3.2.1 Application Schema - Coverages (often referred to as GMLCOV) which in turn is based on the Geography Markup Language (GML) 3.2, an XML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing arbitrary data. It defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. ...
grammar written in XML Schema for the description of application schemas as well as the transport and storage of geographic information.
The European legal framework for a unified Spatial Data Infrastructure, INSPIRE, in its Annex II and III relies on the OGC definitions of coverages as well, but modifies them in places in a way making them less compatible and interoperable with the OGC standard. For example, components of the coverage concept are selectively recombined into new, different definitions of a coverage.
Coverage model
Formally, in GMLCOV AbstractCoverage is a subtype of AbstractFeature (indicating its close relation). An abstract coverage consists of the following components: * coverage domain: the extent where valid values are available; * range set: the set of values ("pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the s ...
s", "voxel
In 3D computer graphics, a voxel represents a value on a regular grid in three-dimensional space. As with pixels in a 2D bitmap, voxels themselves do not typically have their position (i.e. coordinates) explicitly encoded with their values. ...
s") the coverage consists of, together with their locations
* range type: a type definition of the range set values
* metadata: a slot where any kind of metadata can be added
This abstract coverage is refined into several concrete coverage types, which can be instantiated, for example:
* gridded coverages:
** GridCoverage: a regular, equispaced grid which is not spatially referenced (like a raster image which has no geo coordinates associated)
** RectifiedGridCoverage: a regular, equispaced grid which is spatially referenced (like a satellite image which does have geo coordinates associated)
** ReferenceableGridCoverage: a grid which is not necessarily equispaced (like satellite image time series where images do not arrive at regular time intervals, or curvilinear grids following river estuaries)
* multi-feature coverages:
** MultiPointCoverage: sets of values associated with points located in space/time ("point clouds")
** MultiCurveCoverage: sets of values associated with curves located in space/time (such as trajectories)
** MultiSurfaceCoverage: sets of values associated with surfaces located in space/time (such as iso-surfaces)
** MultiSolidCoverage: sets of values associated with solids located in space/time (such as CAD objects)
Among the special cases which can be modeled by coverages are
* set of Thiessen polygons, used to analyse spatially distributed data such as rainfall measurements
* triangulated irregular network (TIN), often used for terrain models
Relationship to Features
A coverage is a special kind ofgeographic feature
A feature (also called an object or entity), in the context of geography and geographic information science, is a discrete phenomenon that exists at a location in the space and scale of relevance to geography; that is, at or near the surface of E ...
, with the distinguishing characteristics that other features have one particular value associated (such as a road number, which remains constant over all the road's extent) whereas a coverage typically conveys different values at different locations within its domain. ISO 19109 (2nd Ed.) explains the relationship between features and coverages as follows (clause 7.2.2):
* ''Many aspects of the real-world may be represented as features whose properties are single-valued and static. These conventional features provide a model of the world in terms of discrete objects located in it. However, in some applications it is more useful to use a model focussing on the variation of property values in space and time, formalized as coverages. ''
Both viewpoints are required since they each express a fundamental meta-model of the world: as a space populated by things, or as a space within which properties vary. Furthermore, requirements relating to both viewpoints may occur in a single application, typically matching a data-flow: from observation through interpretation, and then elaboration and simulation.
Coverage encoding
 The format-independent logical structure of coverages can be mapped to GML (such as for sensor time series) or to any of a series of data formats, such as
The format-independent logical structure of coverages can be mapped to GML (such as for sensor time series) or to any of a series of data formats, such as GeoTIFF GeoTIFF is a public domain metadata standard which allows georeferencing information to be embedded within a TIFF file. The potential additional information includes map projection, coordinate systems, ellipsoids, datums, and everything else nece ...
, NetCDF
NetCDF (Network Common Data Form) is a set of software libraries and self-describing, machine-independent data formats that support the creation, access, and sharing of array-oriented scientific data. The project homepage is hosted by the Unidata ...
, HDF-EOS, or NITF.
As some of these encoding formats are not capable of incorporating all metadata making up a coverage, the coverage model foresees a multipart MIME
Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) is an Internet standard that extends the format of email messages to support text in character sets other than ASCII, as well as attachments of audio, video, images, and application programs. Messa ...
encoding (see Figure) where the first component encodes the coverage description (domain extent, range type, metadata, etc.) and the second part consists of the range set "payload" using some encoding format.
Services
In Web services following the open OGC standards, coverages can be used by various service types: * Web Coverage Service which offers a simple access protocol for coverage subsetting, as well as optional advanced functionality * Web Coverage Processing Service which offers a multi-dimensional coverage query language for ad hoc processing, fusion, aggregation, and filtering *Web Feature Service In computing, the Open Geospatial Consortium Web Feature Service (WFS) Interface Standard provides an interface allowing requests for geographical features across the web using platform-independent calls. One can think of geographical features as ...
(although coverages can only be served as a whole, making it unwieldy in face of the often high-volume coverages, like satellite maps)
* Web Processing Service which allows publishing any kind of algorithm through an advanced remote procedure call style protocol
Industry Terminology: GIS format
Early GIS systems were often characterised as either 'raster' or 'vector' systems, depending on the underlying approach to handling geometry. Raster GIS could be interpreted as using a regular discrete coverage model, while Vector GIS are more feature-oriented. The term "coverage" was most notably applied to the legacy ARC/INFO (ArcInfo) format developed byESRI
Esri (; Environmental Systems Research Institute) is an American multinational geographic information system (GIS) software company. It is best known for its ArcGIS products. With a 43% market share, Esri is the world's leading supplier of GIS ...
. At that time this was a novel concept, extending CAD formats into more spatially aware data that featured linked attributes. This usage was consistent with the coverage concept discussed here, in the sense that an ArcInfo coverage provided a one-to-one mapping from space to the thematic value or classification for each layer or coverage. However, ArcInfo coverages had a particular topological approach to ensure completeness and uniqueness, processed using the BUILD and CLEAN commands are 2D planar datasets that maintain topological
In mathematics, topology (from the Greek words , and ) is concerned with the properties of a geometric object that are preserved under continuous deformations, such as stretching, twisting, crumpling, and bending; that is, without closing ...
information, thus a polygon "knows" which segments of its perimeter it shares with adjacent polygons. Due to the lack of processing power in computing at the time of its development, the Coverage model employs indexed binary file
A binary file is a computer file that is not a text file. The term "binary file" is often used as a term meaning "non-text file". Many binary file formats contain parts that can be interpreted as text; for example, some computer document fi ...
s to store spatial and attribute data separately as opposed to utilizing a RDBMS
A relational database is a (most commonly digital) database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970. A system used to maintain relational databases is a relational database management system (RDBMS). Many relatio ...
.
This has changed with the advent of raster database technology like rasdaman which makes efficient ad hoc filtering and processing feasible.Jucovschi, C., Baumann, P., Stancu-Mara, S.Speeding up Array Query Processing by Just-In-Time Compilation
IEEE Intl Workshop on Spatial and Spatiotemporal Data Mining (SSTDM-08), Pisa, Italy, 15 December 2008, pp. 408 - 413
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Coverage Data Geographic data and information