covalent on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A covalent bond is a
A covalent bond is a
 Bonds with one or three electrons can be found in radical species, which have an odd number of electrons. The simplest example of a 1-electron bond is found in the dihydrogen cation, . One-electron bonds often have about half the bond energy of a 2-electron bond, and are therefore called "half bonds". However, there are exceptions: in the case of dilithium, the bond is actually stronger for the 1-electron than for the 2-electron Li2. This exception can be explained in terms of hybridization and inner-shell effects.
The simplest example of three-electron bonding can be found in the helium dimer cation, . It is considered a "half bond" because it consists of only one shared electron (rather than two); in molecular orbital terms, the third electron is in an anti-bonding orbital which cancels out half of the bond formed by the other two electrons. Another example of a molecule containing a 3-electron bond, in addition to two 2-electron bonds, is nitric oxide, NO. The oxygen molecule, O2 can also be regarded as having two 3-electron bonds and one 2-electron bond, which accounts for its
Bonds with one or three electrons can be found in radical species, which have an odd number of electrons. The simplest example of a 1-electron bond is found in the dihydrogen cation, . One-electron bonds often have about half the bond energy of a 2-electron bond, and are therefore called "half bonds". However, there are exceptions: in the case of dilithium, the bond is actually stronger for the 1-electron than for the 2-electron Li2. This exception can be explained in terms of hybridization and inner-shell effects.
The simplest example of three-electron bonding can be found in the helium dimer cation, . It is considered a "half bond" because it consists of only one shared electron (rather than two); in molecular orbital terms, the third electron is in an anti-bonding orbital which cancels out half of the bond formed by the other two electrons. Another example of a molecule containing a 3-electron bond, in addition to two 2-electron bonds, is nitric oxide, NO. The oxygen molecule, O2 can also be regarded as having two 3-electron bonds and one 2-electron bond, which accounts for its
Covalent Bonds and Molecular Structure
{{Authority control Chemical bonding
chemical bond
A chemical bond is the association of atoms or ions to form molecules, crystals, and other structures. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons a ...
that involves the sharing of electrons
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
to form electron pairs between atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
s, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full valence shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration. In organic chemistry, covalent bonding is much more common than ionic bonding
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that involves the Coulomb's law, electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, or between two atoms with sharply different electronegativities, and is the primary interaction occurring in io ...
.
Covalent bonding also includes many kinds of interactions, including σ-bonding, π-bonding, metal-to-metal bonding, agostic interactions, bent bonds, three-center two-electron bonds and three-center four-electron bonds. The term "covalence" was introduced by Irving Langmuir in 1919, with Nevil Sidgwick using "co-valent link" in the 1920s. Merriam-Webster dates the specific phrase ''covalent bond'' to 1939, recognizing its first known use. The prefix ''co-'' (jointly, partnered) indicates that "co-valent" bonds involve shared " valence", as detailed in valence bond theory.
In the molecule , the hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
atoms share the two electrons via covalent bonding. Covalency is greatest between atoms of similar electronegativities. Thus, covalent bonding does not necessarily require that the two atoms be of the same elements, only that they be of comparable electronegativity. Covalent bonding that entails the sharing of electrons over more than two atoms is said to be delocalized.
History
The term ''covalence'' in regard to bonding was first used in 1919 by Irving Langmuir in a '' Journal of the American Chemical Society'' article entitled "The Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms and Molecules". Langmuir wrote that "we shall denote by the term ''covalence'' the number of pairs of electrons that a given atom shares with its neighbors." The idea of covalent bonding can be traced several years before 1919 to Gilbert N. Lewis, who in 1916 described the sharing of electron pairs between atoms (and in 1926 he also coined the term "photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
" for the smallest unit of radiant energy). He introduced the '' Lewis notation'' or ''electron dot notation'' or ''Lewis dot structure'', in which valence electrons (those in the outer shell) are represented as dots around the atomic symbols. Pairs of electrons located between atoms represent covalent bonds. Multiple pairs represent multiple bonds, such as double bonds and triple bonds. An alternative form of representation, not shown here, has bond-forming electron pairs represented as solid lines.
Lewis proposed that an atom forms enough covalent bonds to form a full (or closed) outer electron shell. In the diagram of methane shown here, the carbon atom has a valence of four and is, therefore, surrounded by eight electrons (the octet rule
The octet rule is a chemical rule of thumb that reflects the theory that main-group elements tend to bond in such a way that each atom has eight electrons in its valence shell, giving it the same electronic configuration as a noble gas. The ru ...
), four from the carbon itself and four from the hydrogens bonded to it. Each hydrogen has a valence of one and is surrounded by two electrons (a duet rule) – its own one electron plus one from the carbon. The numbers of electrons correspond to full shells in the quantum theory of the atom; the outer shell of a carbon atom is the ''n'' = 2 shell, which can hold eight electrons, whereas the outer (and only) shell of a hydrogen atom is the ''n'' = 1 shell, which can hold only two.
While the idea of shared electron pairs provides an effective qualitative picture of covalent bonding, quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is ...
is needed to understand the nature of these bonds and predict the structures and properties of simple molecules. Walter Heitler and Fritz London are credited with the first successful quantum mechanical explanation of a chemical bond (molecular hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
) in 1927. English translation in Their work was based on the valence bond model, which assumes that a chemical bond is formed when there is good overlap between the atomic orbitals of participating atoms.
Types of covalent bonds
Atomic orbitals (except for s orbitals) have specific directional properties leading to different types of covalent bonds. Sigma (σ) bonds are the strongest covalent bonds and are due to head-on overlapping of orbitals on two different atoms. A single bond is usually a σ bond. Pi (π) bonds are weaker and are due to lateral overlap between p (or d) orbitals. A double bond between two given atoms consists of one σ and one π bond, and a triple bond is one σ and two π bonds. Covalent bonds are also affected by theelectronegativity
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the ...
of the connected atoms which determines the chemical polarity of the bond. Two atoms with equal electronegativity will make nonpolar covalent bonds such as H–H. An unequal relationship creates a polar covalent bond such as with H−Cl. However polarity also requires geometric asymmetry
Asymmetry is the absence of, or a violation of, symmetry (the property of an object being invariant to a transformation, such as reflection). Symmetry is an important property of both physical and abstract systems and it may be displayed in pre ...
, or else dipoles may cancel out, resulting in a non-polar molecule.
Covalent structures
There are several types of structures for covalent substances, including individual molecules, molecular structures, macromolecular structures and giant covalent structures. Individual molecules have strong bonds that hold the atoms together, but generally, there are negligible forces of attraction between molecules. Such covalent substances are usually gases, for example, HCl, SO2, CO2, and CH4. In molecular structures, there are weak forces of attraction. Such covalent substances are low-boiling-temperature liquids (such asethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
), and low-melting-temperature solids (such as iodine and solid CO2). Macromolecular structures have large numbers of atoms linked by covalent bonds in chains, including synthetic polymers such as polyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging (plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including bott ...
and nylon
Nylon is a family of synthetic polymers characterised by amide linkages, typically connecting aliphatic or Polyamide#Classification, semi-aromatic groups.
Nylons are generally brownish in color and can possess a soft texture, with some varieti ...
, and biopolymers such as protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s and starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
. Network covalent structures (or giant covalent structures) contain large numbers of atoms linked in sheets (such as graphite
Graphite () is a Crystallinity, crystalline allotrope (form) of the element carbon. It consists of many stacked Layered materials, layers of graphene, typically in excess of hundreds of layers. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable ...
), or 3-dimensional structures (such as diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of e ...
and quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The Atom, atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tet ...
). These substances have high melting and boiling points, are frequently brittle, and tend to have high electrical resistivity. Elements that have high electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the ...
, and the ability to form three or four electron pair bonds, often form such large macromolecular structures.
One- and three-electron bonds
paramagnetism
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior, ...
and its formal bond order of 2. Chlorine dioxide
Chlorine dioxide is a chemical compound with the formula ClO2 that exists as yellowish-green gas above 11 °C, a reddish-brown liquid between 11 °C and −59 °C, and as bright orange crystals below −59 °C. It is usually ...
and its heavier analogues bromine dioxide and iodine dioxide also contain three-electron bonds.
Molecules with odd-electron bonds are usually highly reactive. These types of bond are only stable between atoms with similar electronegativities.
Dioxygen
There are several known allotropes of oxygen. The most familiar is molecular oxygen (), present at significant levels in Earth's atmosphere and also known as dioxygen or triplet oxygen. Another is the highly reactive ozone (). Others are:
* Ato ...
is sometimes represented as obeying the octet rule with a double bond (O=O) containing two pairs of shared electrons. However the ground state of this molecule is paramagnetic, indicating the presence of unpaired electrons. Pauling proposed that this molecule actually contains two three-electron bonds and one normal covalent (two-electron) bond. The octet on each atom then consists of two electrons from each three-electron bond, plus the two electrons of the covalent bond, plus one lone pair of non-bonding electrons. The bond order is 1+0.5+0.5=2.
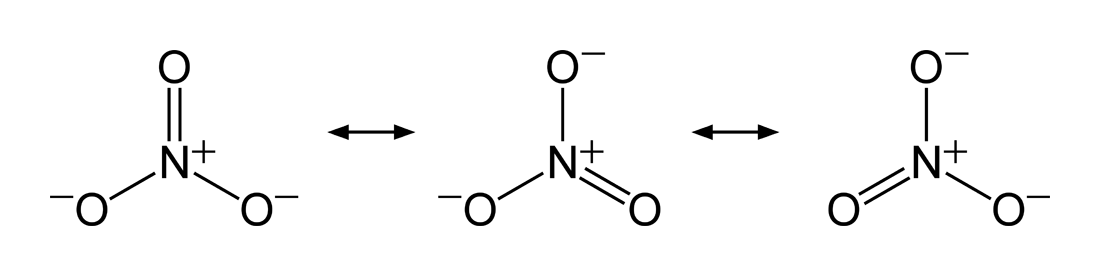
Resonance
There are situations whereby a single Lewis structure is insufficient to explain the electron configuration in a molecule and its resulting experimentally-determined properties, hence a superposition of structures is needed. The same two atoms in such molecules can be bonded differently in different Lewis structures (a single bond in one, a double bond in another, or even none at all), resulting in a non-integer bond order. Thenitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in wa ...
ion is one such example with three equivalent structures. The bond between the nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
and each oxygen is a double bond in one structure and a single bond in the other two, so that the average bond order for each N–O interaction is = .

Aromaticity
Inorganic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain ...
, when a molecule with a planar ring obeys Hückel's rule, where the number of π electrons fit the formula 4''n'' + 2 (where ''n'' is an integer), it attains extra stability and symmetry. In benzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hyd ...
, the prototypical aromatic compound, there are 6 π bonding electrons (''n'' = 1, 4''n'' + 2 = 6). These occupy three delocalized π molecular orbitals ( molecular orbital theory) or form conjugate π bonds in two resonance structures that linearly combine ( valence bond theory), creating a regular hexagon exhibiting a greater stabilization than the hypothetical 1,3,5-cyclohexatriene.
In the case of heterocyclic aromatics and substituted benzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hyd ...
s, the electronegativity differences between different parts of the ring may dominate the chemical behavior of aromatic ring bonds, which otherwise are equivalent.
Hypervalence
Certain molecules such as xenon difluoride and sulfur hexafluoride have higher coordination numbers than would be possible due to strictly covalent bonding according to theoctet rule
The octet rule is a chemical rule of thumb that reflects the theory that main-group elements tend to bond in such a way that each atom has eight electrons in its valence shell, giving it the same electronic configuration as a noble gas. The ru ...
. This is explained by the three-center four-electron bond ("3c–4e") model which interprets the molecular wavefunction in terms of non-bonding highest occupied molecular orbitals in molecular orbital theory and resonance
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration whose frequency matches a resonant frequency (or resonance frequency) of the system, defined as a frequency that generates a maximu ...
of sigma bonds in valence bond theory.
Electron deficiency
In three-center two-electron bonds ("3c–2e") three atoms share two electrons in bonding. This type of bonding occurs in boron hydrides such as diborane (B2H6), which are often described as electron deficient because there are not enough valence electrons to form localized (2-centre 2-electron) bonds joining all the atoms. However, the more modern description using 3c–2e bonds does provide enough bonding orbitals to connect all the atoms so that the molecules can instead be classified as electron-precise. Each such bond (2 per molecule in diborane) contains a pair of electrons which connect the boron atoms to each other in a banana shape, with a proton (the nucleus of a hydrogen atom) in the middle of the bond, sharing electrons with both boron atoms. In certain cluster compounds, so-called four-center two-electron bonds also have been postulated.Quantum mechanical description
After the development of quantum mechanics, two basic theories were proposed to provide a quantum description of chemical bonding: valence bond (VB) theory and molecular orbital (MO) theory. A more recent quantum description is given in terms of atomic contributions to the electronic density of states.Comparison of VB and MO theories
The two theories represent two ways to build up the electron configuration of the molecule. For valence bond theory, the atomic hybrid orbitals are filled with electrons first to produce a fully bonded valence configuration, followed by performing a linear combination of contributing structures (resonance
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration whose frequency matches a resonant frequency (or resonance frequency) of the system, defined as a frequency that generates a maximu ...
) if there are several of them. In contrast, for molecular orbital theory, a linear combination of atomic orbitals is performed first, followed by filling of the resulting molecular orbitals with electrons.
The two approaches are regarded as complementary, and each provides its own insights into the problem of chemical bonding. As valence bond theory builds the molecular wavefunction out of localized bonds, it is more suited for the calculation of bond energies and the understanding of reaction mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical reaction occurs.
A chemical mechanism is a theoretical conjecture that tries to describe in detail what takes place at each stage ...
s. As molecular orbital theory builds the molecular wavefunction out of delocalized orbitals, it is more suited for the calculation of ionization energies and the understanding of spectral absorption bands.
At the qualitative level, both theories contain incorrect predictions. Simple (Heitler–London) valence bond theory correctly predicts the dissociation of homonuclear diatomic molecules into separate atoms, while simple (Hartree–Fock) molecular orbital theory incorrectly predicts dissociation into a mixture of atoms and ions. On the other hand, simple molecular orbital theory correctly predicts Hückel's rule of aromaticity, while simple valence bond theory incorrectly predicts that cyclobutadiene has larger resonance energy than benzene.
Although the wavefunctions generated by both theories at the qualitative level do not agree and do not match the stabilization energy by experiment, they can be corrected by configuration interaction. This is done by combining the valence bond covalent function with the functions describing all possible ionic structures or by combining the molecular orbital ground state function with the functions describing all possible excited states using unoccupied orbitals. It can then be seen that the simple molecular orbital approach overestimates the weight of the ionic structures while the simple valence bond approach neglects them. This can also be described as saying that the simple molecular orbital approach neglects electron correlation
Electronic correlation is the interaction between electrons in the electronic structure of a quantum system. The correlation energy is a measure of how much the movement of one electron is influenced by the presence of all other electrons.
At ...
while the simple valence bond approach overestimates it.
Modern calculations in quantum chemistry
Quantum chemistry, also called molecular quantum mechanics, is a branch of physical chemistry focused on the application of quantum mechanics to chemical systems, particularly towards the quantum-mechanical calculation of electronic contributions ...
usually start from (but ultimately go far beyond) a molecular orbital rather than a valence bond approach, not because of any intrinsic superiority in the former but rather because the MO approach is more readily adapted to numerical computations. Molecular orbitals are orthogonal, which significantly increases the feasibility and speed of computer calculations compared to nonorthogonal valence bond orbitals.
Covalency from atomic contribution to the electronic density of states
Evaluation of bond covalency is dependent on the basis set for approximate quantum-chemical methods such as COOP (crystal orbital overlap population), COHP (Crystal orbital Hamilton population), and BCOOP (Balanced crystal orbital overlap population). To overcome this issue, an alternative formulation of the bond covalency can be provided in this way. The mass center of an atomic orbital withquantum number
In quantum physics and chemistry, quantum numbers are quantities that characterize the possible states of the system.
To fully specify the state of the electron in a hydrogen atom, four quantum numbers are needed. The traditional set of quantu ...
s for atom A is defined as
:
where is the contribution of the atomic orbital of the atom A to the total electronic density of states of the solid
:
where the outer sum runs over all atoms A of the unit cell. The energy window is chosen in such a way that it encompasses all of the relevant bands participating in the bond. If the range to select is unclear, it can be identified in practice by examining the molecular orbitals that describe the electron density along with the considered bond.
The relative position of the mass center of levels of atom A with respect to the mass center of levels of atom B is given as
:
where the contributions of the magnetic and spin quantum numbers are summed. According to this definition, the relative position of the A levels with respect to the B levels is
:
where, for simplicity, we may omit the dependence from the principal quantum number in the notation referring to
In this formalism, the greater the value of the higher the overlap of the selected atomic bands, and thus the electron density described by those orbitals gives a more covalent bond. The quantity is denoted as the ''covalency'' of the bond, which is specified in the same units of the energy .
Analogous effect in nuclear systems
An analogous effect to covalent binding is believed to occur in some nuclear systems, with the difference that the shared fermions are quarks rather than electrons. High energyproton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an e ...
-proton scattering
In physics, scattering is a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including particles and radiat ...
cross-section indicates that quark interchange of either u or d quarks is the dominant process of the nuclear force at short distance. In particular, it dominates over the Yukawa interaction where a meson
In particle physics, a meson () is a type of hadronic subatomic particle composed of an equal number of quarks and antiquarks, usually one of each, bound together by the strong interaction. Because mesons are composed of quark subparticles, the ...
is exchanged. Therefore, covalent binding by quark interchange is expected to be the dominating mechanism of nuclear binding at small distance when the bound hadrons have covalence quarks in common.
See also
* Bonding in solids * Bond order *Coordinate covalent bond
In coordination chemistry, a coordinate covalent bond, also known as a dative bond, dipolar bond, or coordinate bond is a kind of two-center, two-electron covalent bond in which the two electrons derive from the same atom. The bonding of metal i ...
, also known as a dipolar bond or a dative covalent bond
* Covalent bond classification (or LXZ notation)
* Covalent radius
* Disulfide bond
* Hybridization
* Hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a specific type of molecular interaction that exhibits partial covalent character and cannot be described as a purely electrostatic force. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom, Covalent bond, covalently b ...
* Ionic bond
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond
A chemical bond is the association of atoms or ions to form molecules, crystals, and other structures. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic ...
* Linear combination of atomic orbitals
* Metallic bonding
* Noncovalent bonding
* Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance, also called mesomerism, is a way of describing Chemical bond, bonding in certain molecules or polyatomic ions by the combination of several contributing structures (or ''forms'', also variously known as ''resonance struc ...
References
Sources
* * *External links
Covalent Bonds and Molecular Structure
{{Authority control Chemical bonding