Counterforce Strike on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 A counterforce exchange was one scenario mooted for a possible limited nuclear war. The concept was that one side might launch a counterforce strike against the other; the victim would recognize the limited nature of the attack and respond in kind. That would leave the military capability of both sides largely destroyed. The war might then come to an end because both sides would recognize that any further action would lead to attacks on the civilian population from the remaining nuclear forces, a countervalue strike.
Critics of that idea claimed that since even a counterforce strike would kill millions of civilians since some strategic military facilities like bomber airbases were often located near large cities. That would make it unlikely that escalation to a full-scale countervalue war could be prevented.
A counterforce exchange was one scenario mooted for a possible limited nuclear war. The concept was that one side might launch a counterforce strike against the other; the victim would recognize the limited nature of the attack and respond in kind. That would leave the military capability of both sides largely destroyed. The war might then come to an end because both sides would recognize that any further action would lead to attacks on the civilian population from the remaining nuclear forces, a countervalue strike.
Critics of that idea claimed that since even a counterforce strike would kill millions of civilians since some strategic military facilities like bomber airbases were often located near large cities. That would make it unlikely that escalation to a full-scale countervalue war could be prevented.
nuclear strategy
Nuclear strategy involves the development of military doctrine, doctrines and strategy, strategies for the production and use of nuclear weapons.
As a sub-branch of military strategy, nuclear strategy attempts to match nuclear weapons as means ...
, a counterforce target is one that has a military value, such as a launch silo for intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range (aeronautics), range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more Thermonuclear weapon, thermonuclear warheads). Conven ...
s, an airbase at which nuclear-armed bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft that utilizes
air-to-ground weaponry to drop bombs, launch aerial torpedo, torpedoes, or deploy air-launched cruise missiles.
There are two major classifications of bomber: strategic and tactical. Strateg ...
s are stationed, a homeport for ballistic missile submarine
A ballistic missile submarine is a submarine capable of deploying submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) with nuclear warheads. These submarines became a major weapon system in the Cold War because of their nuclear deterrence capabi ...
s, or a command and control installation.
The intent of a counterforce strategy (attacking counterforce targets with nuclear weapons) is to conduct a preemptive nuclear strike which has as its aim to disarm an adversary by destroying its nuclear weapons before they can be launched. That would minimize the impact of a retaliatory second strike
In nuclear strategy, a retaliatory strike or second-strike capability is a country's assured ability to respond to a nuclear attack with powerful nuclear retaliation against the attacker. To have such an ability (and to convince an opponent of its ...
. However, counterforce attacks are possible in a second strike as well, especially with weapons like UGM-133 Trident II
The UGM-133A Trident II, or Trident D5 is a submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM), built by Lockheed Martin Space in Sunnyvale, California, and deployed with the United States Navy and Royal Navy. It was first deployed in March 1990, an ...
. A counterforce target is distinguished from a countervalue
In nuclear strategy, countervalue is the targeting of an opponent's assets that are of value but not actually a military threat, such as cities and civilian populations. Counterforce is the targeting of an opponent's military forces and faciliti ...
target, which includes an adversary's population, knowledge, economic, or political resources. In short, a counterforce strike is directed against an adversary's military capabilities, while a countervalue strike is directed against an adversary's civilian-centered institutions.
A closely related tactic is the decapitation strike
Decapitation is a military strategy aimed at removing the leadership or command and control of a hostile government or group.
In nuclear warfare
In nuclear warfare theory, a decapitation strike is a pre-emptive first strike attack that aims ...
, which destroys an enemy's nuclear command and control facilities and similarly has a goal to eliminate or reduce the enemy's ability to launch a second strike. Counterforce targets are almost always near to civilian population centers, which would not be spared in the event of a counterforce strike.
Theory
Innuclear warfare
Nuclear warfare, also known as atomic warfare, is a War, military conflict or prepared Policy, political strategy that deploys nuclear weaponry. Nuclear weapons are Weapon of mass destruction, weapons of mass destruction; in contrast to conven ...
, enemy targets are divided into two types: counterforce and countervalue. A counterforce target is an element of the military infrastructure, usually either specific weapons or the bases that support them. A counterforce strike is an attack that targets those elements but leaving the civilian
A civilian is a person who is not a member of an armed force. It is war crime, illegal under the law of armed conflict to target civilians with military attacks, along with numerous other considerations for civilians during times of war. If a civi ...
infrastructure, the countervalue targets, as undamaged as possible. Countervalue refers to the targeting of an opponent's cities and civilian populations.
Counterforce weapons may be seen to provide more credible deterrence in future conflict by providing options for leaders. One option considered by the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
in the 1970s was basing missiles in orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
.
Cold War
Counterforce is a type of attack which was originally proposed during theCold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
.
Because of the low accuracy (circular error probable
Circular error probable (CEP),Circular Error Probable (CEP), Air Force Operational Test and Evaluation Center Technical Paper 6, Ver 2, July 1987, p. 1 also circular error probability or circle of equal probability, is a measure of a weapon s ...
) of early generation intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range (aeronautics), range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more Thermonuclear weapon, thermonuclear warheads). Conven ...
s (and especially submarine-launched ballistic missile
A submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) is a ballistic missile capable of being launched from Ballistic missile submarine, submarines. Modern variants usually deliver multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), each of which ...
s), counterforce strikes were initially possible only against very large, undefended targets like bomber airfields and naval bases. Later-generation missiles, with much-improved accuracy, made possible counterforce attacks against the opponent's hardened military facilities, like missile silos and command and control centers.
Both sides in the Cold War took steps to protect at least some of their nuclear forces from counterforce attacks. At one point, the US kept B-52 Stratofortress
The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress is an American long-range, subsonic aircraft, subsonic, jet-powered strategic bomber. The B-52 was designed and built by Boeing, which has continued to provide support and upgrades. It has been operated by the ...
bombers permanently in flight so that they would remain operational after any counterforce strike. Other bombers were kept ready for launch on short notice, allowing them to escape their bases before intercontinental ballistic missiles, launched from land, could destroy them. The deployment of nuclear weapons on ballistic missile submarine
A ballistic missile submarine is a submarine capable of deploying submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) with nuclear warheads. These submarines became a major weapon system in the Cold War because of their nuclear deterrence capabi ...
s changed the equation considerably, as submarines launching from positions off the coast would likely destroy airfields before bombers could launch, which would reduce their ability to survive an attack. Submarines themselves, however, are largely immune from counterforce strikes unless they are moored at their naval bases, and both sides fielded many such weapons during the Cold War.
 A counterforce exchange was one scenario mooted for a possible limited nuclear war. The concept was that one side might launch a counterforce strike against the other; the victim would recognize the limited nature of the attack and respond in kind. That would leave the military capability of both sides largely destroyed. The war might then come to an end because both sides would recognize that any further action would lead to attacks on the civilian population from the remaining nuclear forces, a countervalue strike.
Critics of that idea claimed that since even a counterforce strike would kill millions of civilians since some strategic military facilities like bomber airbases were often located near large cities. That would make it unlikely that escalation to a full-scale countervalue war could be prevented.
A counterforce exchange was one scenario mooted for a possible limited nuclear war. The concept was that one side might launch a counterforce strike against the other; the victim would recognize the limited nature of the attack and respond in kind. That would leave the military capability of both sides largely destroyed. The war might then come to an end because both sides would recognize that any further action would lead to attacks on the civilian population from the remaining nuclear forces, a countervalue strike.
Critics of that idea claimed that since even a counterforce strike would kill millions of civilians since some strategic military facilities like bomber airbases were often located near large cities. That would make it unlikely that escalation to a full-scale countervalue war could be prevented.
MIRV
A multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRV) is an exoatmospheric ballistic missile payload containing several warheads, each capable of being aimed to hit a different target. The concept is almost invariably associated with i ...
ed land-based ICBM
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range (aeronautics), range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more Thermonuclear weapon, thermonuclear warheads). Conven ...
s are considered destabilizing because they tend to put a premium on striking first. For example, suppose that each side has 100 missiles, with five warheads each, and each side has a 95 percent chance of neutralizing the opponent's missiles in their silos by firing two warheads at each silo. In that case, the side that strikes first can reduce the enemy ICBM force from 100 missiles to about five by firing 40 missiles with 200 warheads and keeping the remaining 60 missiles in reserve. For such an attack to be successful, the warheads would have to strike their targets before the enemy launched a counterattack (see second strike
In nuclear strategy, a retaliatory strike or second-strike capability is a country's assured ability to respond to a nuclear attack with powerful nuclear retaliation against the attacker. To have such an ability (and to convince an opponent of its ...
and launch on warning
Launch on warning (LOW), or fire on warning, is a strategy of nuclear weapon retaliation where a retaliatory strike is launched upon warning of enemy nuclear attack and while its missiles are still in the air, before detonation occurs. It gaine ...
). This type of weapon was therefore banned under the START II
START II (Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty) was a bilateral treaty between the United States and Russia on the Reduction and Limitation of Strategic Offensive Arms. It was signed by US President George H. W. Bush and Russian President Boris Yel ...
agreement, which was not ratified and therefore ineffectual.
Counterforce disarming first-strike weapons
* Ababeel.MIRV
A multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRV) is an exoatmospheric ballistic missile payload containing several warheads, each capable of being aimed to hit a different target. The concept is almost invariably associated with i ...
nuclear capable ballistic missile developed by Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
in response to India's development of a Ballistic Missile Defence system.
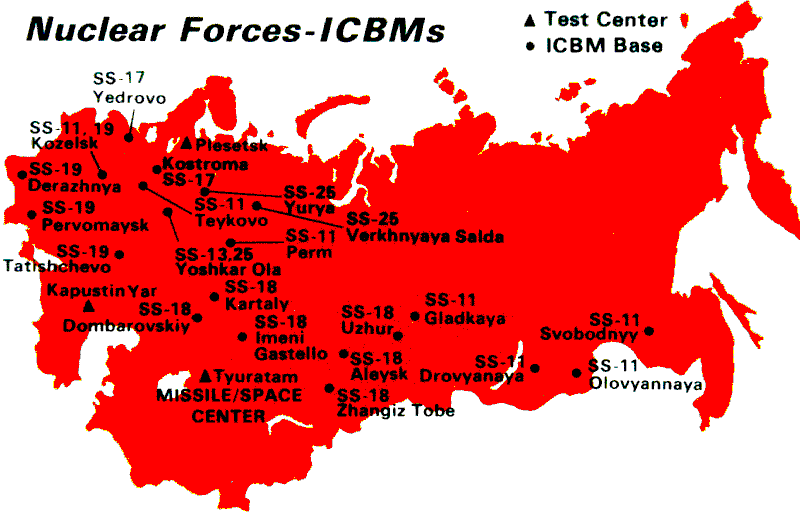
* R-36M (SS-18 Satan). Deployed in 1976, this counterforce MIRV ICBM had single (20 Mt) or ten MIRV (550-750 kt each) warheads, with a circular error probable
Circular error probable (CEP),Circular Error Probable (CEP), Air Force Operational Test and Evaluation Center Technical Paper 6, Ver 2, July 1987, p. 1 also circular error probability or circle of equal probability, is a measure of a weapon s ...
(CEP) of . Targeted against Minuteman III silos as well as CONUS
''Conus'' is a genus of venomous and predatory cone snails.Bouchet, P.; Gofas, S. (2015). Conus Linnaeus, 1758. In: MolluscaBase (2015). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&i ...
command, control, and communications facilities. Has sufficient throw-weight
A ballistic missile is a type of missile that uses projectile motion to deliver warheads on a target. These weapons are powered only during relatively brief periods—most of the flight is unpowered. Short-range ballistic missiles (SRBM) typica ...
to carry up to 10 RVs and 40 penaids. Still in service.
* RSD-10 (SS-20 Saber). Deployed in 1978, this counterforce MIRV IRBM could hide behind the Urals in Asian Russia, and launch its highly accurate three warhead payload (150 kt each, with a CEP) against NATO command, control, and communications installations, bunkers, air fields, air defense sites, and nuclear facilities in Europe. Extremely short flight time ensured NATO would be unable to respond prior to weapon impact. Triggered development and deployment of the Pershing II by NATO in 1983.
* Peacekeeper (MX Missile). Deployed in 1986, this missile boasted ten MIRV warheads each with a 300 kt yield, CEP . Decommissioned.
* Pershing II. Deployed in 1983, this single warhead MRBM boasted 50 m CEP with terminal active radar homing
Active radar homing (ARH) is a missile guidance method in which a missile contains a radar transceiver (in contrast to semi-active radar homing, which uses only a passive radar, receiver) and the electronics necessary for it to find and track it ...
/ DSMAC guidance. Short, seven-minute flight-time (which makes launch on warning
Launch on warning (LOW), or fire on warning, is a strategy of nuclear weapon retaliation where a retaliatory strike is launched upon warning of enemy nuclear attack and while its missiles are still in the air, before detonation occurs. It gaine ...
much harder), variable yield warhead of 5-50 kt, and range of , allowed this weapon to strike command, control, and communications installations, bunkers, air fields, air defense sites, and ICBM silos in the European part of the Soviet Union with scarcely any warning. Decommissioned.
* RT-23 Molodets (SS-24 Scalpel). Deployed in 1987, this MIRV ICBM carried ten warheads, each with 300-550 kt yield and a CEP of .
* UGM-133 Trident II
The UGM-133A Trident II, or Trident D5 is a submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM), built by Lockheed Martin Space in Sunnyvale, California, and deployed with the United States Navy and Royal Navy. It was first deployed in March 1990, an ...
. Deployed in 1990, this intercontinental-range SLBM carries up to eight RVs with CEP of and yield of 100/475 kt. Main purpose is second strike countervalue retaliation, but the excellent CEP and much shorter flight-time due to submarine launch (reducing the possibility of launch on warning
Launch on warning (LOW), or fire on warning, is a strategy of nuclear weapon retaliation where a retaliatory strike is launched upon warning of enemy nuclear attack and while its missiles are still in the air, before detonation occurs. It gaine ...
) makes it an excellent first-strike weapon. However, that any nuclear power would be willing to place its nuclear submarines close to enemy shores during times of strategic tension is highly questionable. Has sufficient throw-weight to deploy up to twelve warheads, but the post-boost vehicle is only capable of deploying eight, and on average about four are deployed in current practice.
See also
*Balance of power (international relations)
The balance of power theory in international relations suggests that states may secure their survival by preventing any one state from gaining enough military power to dominate all others. If one state becomes much stronger, the theory predicts ...
* Balance of terror
"Balance of Terror" is the fourteenth episode of the first season of the American science fiction television series ''Star Trek''. Written by Paul Schneider and directed by Vincent McEveety, it first aired on December 15, 1966.
The series, ...
* Deterrence theory
Deterrence theory refers to the scholarship and practice of how threats of using force by one party can convince another party to refrain from initiating some other course of action. The topic gained increased prominence as a military strategy d ...
* Limited first strike
* Peace through strength
"Peace through strength" is a phrase that suggests that military power can help preserve peace. It has been used by many leaders from Roman Emperor Hadrian in the second century AD to former US President Ronald Reagan in the 1980s. The concept h ...
References
{{reflist Military strategy Nuclear warfare Nuclear strategy Cold War terminology