Convergence Zone on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A convergence zone in
A convergence zone in
 An example of a convergence zone is the
An example of a convergence zone is the  The
The
Elsinore Convergence Zone
in the U.S. state of
 A convergence zone in
A convergence zone in meteorology
Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere and short-term atmospheric phenomena (i.e. weather), with a focus on weather forecasting. It has applications in the military, aviation, energy production, transport, agricultur ...
is a region in the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
where two prevailing flows meet and interact, usually resulting in distinctive weather conditions.
This causes a mass accumulation that eventually leads to a vertical movement and to the formation of clouds and precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
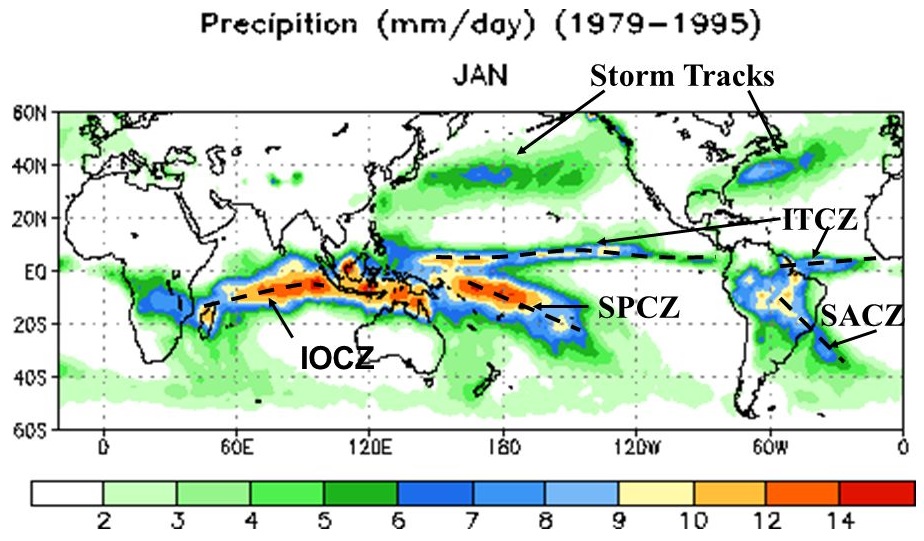
. Large-scale convergence, called synoptic-scale convergence, is associated with weather systems such as baroclinic troughs, low-pressure areas, and cyclones. The large-scale convergence zone formed over the equator, the Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ , or ICZ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the t ...
, has condensed and intensified as a result of the global increase in temperature. Small-scale convergence will give phenomena from isolated cumulus cloud
Cumulus clouds are clouds that have flat cloud base, bases and are often described as puffy, cotton-like, or fluffy in appearance. Their name derives from the Latin , meaning "heap" or "pile". Cumulus clouds are low-level clouds, generally less ...
s to large areas of thunderstorms.
The inverse of convergence is divergence, such as the horse latitudes.
Large scale
 An example of a convergence zone is the
An example of a convergence zone is the Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ , or ICZ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the t ...
(ITCZ), a low pressure area which girdles the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
at the Equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
.Waliser, D.E.; Jiang, X. (2015). "Tropical Meteorology and Climate: Intertropical Convergence Zone". ''Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences'' 6(2): 121-131. Another example is the South Pacific convergence zone that extends from the western Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
toward French Polynesia
French Polynesia ( ; ; ) is an overseas collectivity of France and its sole #Governance, overseas country. It comprises 121 geographically dispersed islands and atolls stretching over more than in the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean. The t ...
. The
The Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ , or ICZ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the t ...
is the result of the northeasterly trade winds and southeasterly trade winds converging in an area of high latent heat and low pressure. As the two trade winds converge, the cool, dry air collects moisture from the warm ocean and rises, contributing to cloud formation and precipitation. The low pressure area that is created by the movement of the trade winds acts as a vacuum, drawing in the cooler, dry air from high pressure areas (divergence zones), creating a convection cell commonly known as the Hadley Cell.
Sea surface temperature is directly related to the position of the Sun or the location of the " energy flux equator," thus the ITCZ shifts corresponding to the seasons. Due to the position of the Sun, the sea surface temperature near the equator (30°S to 30°N), during an equinox
A solar equinox is a moment in time when the Sun appears directly above the equator, rather than to its north or south. On the day of the equinox, the Sun appears to rise directly east and set directly west. This occurs twice each year, arou ...
, is higher than any other latitudes. During the summer solstice
The summer solstice or estival solstice occurs when one of Earth's poles has its maximum tilt toward the Sun. It happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere ( Northern and Southern). The summer solstice is the day with the longest peri ...
in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
(June 21), the ITCZ is shifted north, following the position of the Sun.Schneider, Tapio; Bischoff, Tobias; Haug, Gerald H. (2014). "Migrations and dynamics of the Intertropical Convergence Zone." ''Nature'' 513: 45–53. The ITCZ is shifted farther south during the winter solstice
The winter solstice, or hibernal solstice, occurs when either of Earth's geographical pole, poles reaches its maximum axial tilt, tilt away from the Sun. This happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere (Northern Hemisphere, Northern and So ...
(in the Northern Hemisphere), when the solar radiation is focused at 23.5°S.
Mesoscale
Convergence zones also occur at a smaller scale. Convergence lines form rows of showers or thunderstorms over a more local area. Sea breezes colliding can trigger development of a convergence line. The heavy rain caused in a short period of time can cause severe flooding. Some examples are the Puget Sound Convergence Zone which occurs in thePuget Sound
Puget Sound ( ; ) is a complex estuary, estuarine system of interconnected Marine habitat, marine waterways and basins located on the northwest coast of the U.S. state of Washington (state), Washington. As a part of the Salish Sea, the sound ...
region in the U.S. state of Washington; Mohawk–Hudson convergence in the U.S. state of New York; thElsinore Convergence Zone
in the U.S. state of
California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
; the Brown Willy effect which can be generated when south-westerly winds blow over Bodmin Moor
Bodmin Moor () is a granite moorland in north-eastern Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is in size, and dates from the Carboniferous period of geology, geological history. It includes Brown Willy, the highest point in Cornwall, and Rough To ...
in Cornwall
Cornwall (; or ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is also one of the Celtic nations and the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, ...
; and the Pembrokeshire Dangler which can form when northerly winds blow down the Irish Sea
The Irish Sea is a body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Celtic Sea in the south by St George's Channel and to the Inner Seas off the West Coast of Scotland in the north by the North Ch ...
. Flooding in Boscastle, Cornwall, England in August 2004 was the result of thunderstorms developing on a convergence line.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Convergence Zone Atmosphere Gliding technology