Constant Speed Unit on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 Three methods are used to vary the pitch: oil pressure, centrifugal weights, or electro-mechanical control.
Engine oil pressure is the usual mechanism used in commercial propeller aircraft and the Continental and Lycoming engines fitted to light aircraft. In aircraft without a constant speed unit (CSU), the pilot controls the propeller blade pitch manually, using oil pressure.
Alternatively, or additionally,
Three methods are used to vary the pitch: oil pressure, centrifugal weights, or electro-mechanical control.
Engine oil pressure is the usual mechanism used in commercial propeller aircraft and the Continental and Lycoming engines fitted to light aircraft. In aircraft without a constant speed unit (CSU), the pilot controls the propeller blade pitch manually, using oil pressure.
Alternatively, or additionally,


 A constant-speed propeller is a variable-pitch propeller that automatically changes its blade pitch in order to maintain a chosen rotational speed, regardless of the operational conditions of the aircraft. This is achieved by use of a constant-speed unit (CSU) or propeller governor, which automatically changes the propeller's blade pitch.
Most engines produce their maximum power in a narrow speed band. The CSU allows the engine to operate in its most economical range of rotational speeds, regardless of whether the aircraft is taking off or cruising. The CSU can be said to be to an aircraft what the
A constant-speed propeller is a variable-pitch propeller that automatically changes its blade pitch in order to maintain a chosen rotational speed, regardless of the operational conditions of the aircraft. This is achieved by use of a constant-speed unit (CSU) or propeller governor, which automatically changes the propeller's blade pitch.
Most engines produce their maximum power in a narrow speed band. The CSU allows the engine to operate in its most economical range of rotational speeds, regardless of whether the aircraft is taking off or cruising. The CSU can be said to be to an aircraft what the
patent
for a variable pitch propeller was filed in the U.S. Patent Office in 1934. Several designs were tried, including a small bladder of pressurized air in the propeller hub providing the necessary force to resist a spring that would drive the blades from fine pitch (take-off) to coarse pitch (level cruising). At a suitable airspeed a disk on the front of the spinner would press sufficiently on the bladder's air-release valve to relieve the pressure and allow the spring to drive the propeller to coarse pitch. These "pneumatic" propellers were fitted on the de Havilland DH.88 Comet aircraft, winner of the famed long-distance 1934 MacRobertson Air Race and in the
aircraft engine development
Kimble D. McCutcheon * Gunston, Bill. ''Development of Piston Aero Engines''. Cambridge, England. Patrick Stephens Limited, 2006. * For more technical information on the first constant speed propeller governor mechanism invented by Elmer E. Woodward, see
External propeller governor description
1941 Cutaway Drawing of Hydromatic Variable Pitch Propeller Operation
on B-24 bomber
* ttp://www.flightglobal.com/pdfarchive/view/1935/1935%20-%200989.html CONTROLLABLE-PITCH AIRSCREWSexplained in Flight 2 May 1935 an
9 May 1935
{{Aircraft gas turbine engine components Propellers Aircraft performance
aeronautics
Aeronautics is the science or art involved with the study, design, and manufacturing of air flight–capable machines, and the techniques of operating aircraft and rockets within the atmosphere. The British Royal Aeronautical Society identifies ...
, a variable-pitch propeller is a type of propeller
A propeller (colloquially often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon ...
(airscrew) with blades that can be rotated around their long axis to change the blade pitch. A controllable-pitch propeller is one where the pitch is controlled manually by the pilot. Alternatively, a constant-speed propeller is one where the pilot sets the desired engine speed ( RPM), and the blade pitch is controlled automatically without the pilot's intervention so that the rotational speed remains constant. The device which controls the propeller pitch and thus speed is called a propeller governor or constant speed unit.
Reversible propellers are those where the pitch can be set to negative values. This creates reverse thrust for braking or going backwards without the need to change the direction of shaft revolution.
Some aircraft have ground-adjustable propellers, however these are not considered variable-pitch. These are typically found only on light aircraft and microlights.
Purpose
When an aircraft is stationary with the propeller spinning (in calm air), the relative wind vector for each propeller blade is from the side. However, as the aircraft starts to move forward, the relative wind vector comes increasingly from the front. The propeller blade pitch must be increased to maintain optimum angle of attack to the relative wind. The first propellers were fixed-pitch, but these propellers are not efficient over a range of conditions. If the propeller blade angle is set to give good takeoff and climb performance, the propeller will be inefficient in cruising flight because the blade will be at too low an angle of attack. In contrast, a propeller set for good cruise performance may stall at low speeds, because the angle of attack is too high. A propeller with adjustable blade angle is more efficient over a range of conditions. A propeller with variable pitch can have a nearly constant efficiency over a range of airspeeds. A shallowerangle of attack
In fluid dynamics, angle of attack (AOA, α, or \alpha) is the angle between a reference line on a body (often the chord line of an airfoil) and the vector representing the relative motion between the body and the fluid through which it is m ...
requires the least torque, but the highest RPM, because the propeller is not moving very much air with each revolution. This is similar to a car operating in low gear. When the motorist reaches cruising speed, they will slow down the engine by shifting into a higher gear, while still producing enough power to keep the vehicle moving. This is accomplished in an airplane by increasing the angle of attack of the propeller. This means that the propeller moves more air per revolution and allows the engine to spin slower while moving an equivalent volume of air, thus maintaining velocity.
Another use of variable-pitch propellers is to feather
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premier ...
the blades of the propeller, in order to reduce drag. This means to rotate the blades so that their leading edges face directly forwards. In a multi-engine aircraft, if one engine fails, it can be feathered to reduce drag so that the aircraft can continue flying using the other engine(s). In a single-engine aircraft, if the engine fails, feathering the propeller will reduce drag and increase glide distance, providing the pilot with more options for the location of a forced landing.
Mechanisms
 Three methods are used to vary the pitch: oil pressure, centrifugal weights, or electro-mechanical control.
Engine oil pressure is the usual mechanism used in commercial propeller aircraft and the Continental and Lycoming engines fitted to light aircraft. In aircraft without a constant speed unit (CSU), the pilot controls the propeller blade pitch manually, using oil pressure.
Alternatively, or additionally,
Three methods are used to vary the pitch: oil pressure, centrifugal weights, or electro-mechanical control.
Engine oil pressure is the usual mechanism used in commercial propeller aircraft and the Continental and Lycoming engines fitted to light aircraft. In aircraft without a constant speed unit (CSU), the pilot controls the propeller blade pitch manually, using oil pressure.
Alternatively, or additionally, centrifugal
Centrifugal (a key concept in rotating systems) may refer to:
*Centrifugal casting (industrial), Centrifugal casting (silversmithing), and Spin casting (centrifugal rubber mold casting), forms of centrifigual casting
*Centrifugal clutch
*Centrifug ...
weights may be attached directly to the propeller as in the Yakovlev Yak-52
The Yakovlev Yak-52 (russian: Яковлев Як-52) is a Soviet primary trainer aircraft which first flew in 1976. It was produced in Romania from 1977 to 1998 by Aerostar, as ''Iak-52'', which gained manufacturing rights under agreement wi ...
. The first attempts at constant-speed propellers were called counterweight propellers, which were driven by mechanisms that operated on centrifugal force. Their operation is identical to the centrifugal governor used by James Watt to limit the speed of steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be trans ...
s. Eccentric weights were set up near or in the spinner, held in by a spring. When the propeller reached a certain RPM, centrifugal force would cause the weights to swing outwards, which would drive a mechanism that twisted the propeller into a steeper pitch. When the propeller slowed, the RPM would decrease enough for the spring to push the weights back in, realigning the propeller to the shallower pitch.
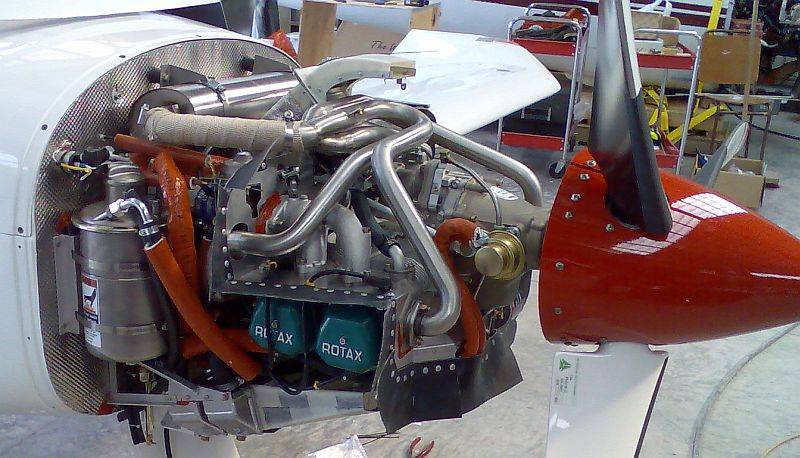
Small, modern engines with a constant speed unit (CSU), such as the Rotax 912
The Rotax 912 is a horizontally-opposed four-cylinder, naturally aspirated, four-stroke aircraft engine with a reduction gearbox. It features liquid-cooled cylinder heads and air-cooled cylinders. Originally equipped with carburetors, late ...
, may use either the conventional hydraulic method or an electrical pitch control mechanism.
Hydraulic operation can be too expensive and bulky for microlights. Instead, these may use propellers that are activated mechanically or electrically.
Constant-speed propellers

continuously variable transmission
A continuously variable transmission (CVT) is an automatic transmission that can change seamlessly through a continuous range of gear ratios. This contrasts with other transmissions that provide a limited number of gear ratios in fixed steps. T ...
is to the motorcar: the engine can be kept running at its optimum speed, regardless of the speed at which the aircraft is flying through the air. The CSU also allows aircraft engine designers to keep the ignition system simple: the automatic spark advance seen in motor vehicle engines is simplified, because aircraft engines run at a roughly constant RPM.
Virtually all high-performance propeller-driven aircraft have constant-speed propellers, as they greatly improve fuel efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or work. Overall fuel efficiency may vary per device, wh ...
and performance, especially at high altitude.
The first attempts at constant-speed propellers were called counterweight propellers, which were driven by mechanisms that operated on centrifugal force. Their operation is identical to the centrifugal governor used by James Watt to control the speed of steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be trans ...
s. Eccentric weights were set up near or in the spinner, held in by a spring. When the propeller reached a certain RPM, centrifugal force would cause the weights to swing outwards, which would drive a mechanism that twisted the propeller into a steeper pitch. When the propeller slowed, the RPM would decrease enough for the spring to push the weights back in, realigning the propeller to the shallower pitch.
Most CSUs use oil pressure to control propeller pitch. Typically, constant-speed units on a single-engine aircraft use oil pressure to increase the pitch. If the CSU fails, the propeller will automatically return to fine pitch, allowing the aircraft to be operated at lower speeds. By contrast, on a multi-engine aircraft, the CSU will typically use oil pressure to decrease the pitch. That way, if the CSU fails, that propeller will automatically feather, reducing drag, while the aircraft continues to be flown on the good engine. An "unfeathering accumulator" will enable such a propeller to return to fine pitch for an in-flight engine restart.
Operation in a single-engine aircraft is as follows: Oil is pumped through the propeller shaft to push on a piston that drives the mechanism to change pitch. The flow of oil and the pitch are controlled by a governor, consisting of a speeder spring, flyweights, and a pilot valve
A pilot valve is a small valve that controls a limited-flow control feed to a separate piloted valve. Typically, this separate valve controls a high pressure or high flow feed. Pilot valves are useful because they allow a small and easily operated ...
. The tension of the spring is set by the propeller control lever, which sets the RPM. The governor will maintain that RPM setting until an engine overspeed or underspeed condition exists. When an overspeed condition occurs, the propeller begins to rotate faster than the desired RPM setting. This would occur as the plane descends and airspeed increases. The flyweights begin to pull outward due to centrifugal force which further compresses the speeder spring. As that happens, the piston moves forward, allowing the pilot valve to open and oil to flow from the oil sump into the hub. This increase in oil pressure will increase the pitch of the propeller angle causing it to slow back down to the desired RPM setting. When an underspeed condition occurs, such as a climb with a loss of airspeed, the opposite takes place. The airspeed decreases, causing the propeller to slow down. This will cause the flyweights to move inward due to a lack in centrifugal force, and tension will be released from the speeder spring. As this happens, the piston will move in the opposite direction causing the pilot valve to allow oil to flow from the hub back to the oil sump. The propeller blade angle will now decrease to a lower pitch allowing the propeller to speed back up to the desired RPM setting. This process usually takes place frequently throughout flight.
A pilot requires some additional training and, in most jurisdictions, a formal sign-off before being allowed to fly aircraft fitted with a CSU. CSUs are not allowed to be fitted to aircraft certified under light-sport aircraft
A light-sport aircraft (LSA), or light sport aircraft, is a fairly new category of small, lightweight aircraft that are simple to fly. LSAs tend to be heavier and more sophisticated than ultralight (aka "microlight") aircraft, but LSA restrictio ...
regulations in the United States.
History
A number of early aviation pioneers, including A. V. Roe andLouis Breguet
Louis Charles Breguet (2 January 1880 in Paris – 4 May 1955 in Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Île-de-France) was a French aircraft designer and builder, one of the early aviation pioneers.
Biography
Louis Charles Breguet was the grandson of L ...
, used propellers that could only be adjusted while the aircraft was on the ground. This was also the case in late World War I with one testbed example, "R.30/16", of the low-production (56 examples in 1917 and 1918) Zeppelin-Staaken R.VI
The Zeppelin-Staaken R.VI was a four-engined Imperial Germany, German biplane strategic bomber of World War I, and the only ''Riesenflugzeug'' ("giant aircraft") design built in any quantity.Gray, P and Thetford, O ''German Aircraft of the First ...
German "giant" four-engined heavy bomber.
In 1919 L. E. Baynes
Leslie Everett Baynes, AFRAeS (23 March 1902 – 13 March 1989) was an English aeronautical engineer.
Early life
Born at Barnes, Surrey, on 23 March 1902 the son of James and Florence Baynes. Baynes was educated at Gresham's School, Norfolk, le ...
patented the first automatic variable-pitch airscrew. Wallace Rupert Turnbull of Saint John, New Brunswick, Canada is credited in Canada for creating the first variable pitch propeller in 1918.
The French aircraft firm Levasseur displayed a variable-pitch propeller at the 1921 Paris Air Show. The firm claimed that the French government had tested the device in a ten-hour run and that it could change pitch at any engine RPM.
Dr Henry Selby Hele-Shaw
Henry Selby Hele-Shaw FRS (1854–1941) was an English mechanical and automobile engineer. He was the inventor of the variable-pitch propeller, which contributed to British success in the Battle of Britain in 1940, and he experimented with flow ...
and T.E. Beacham patented a hydraulically-operated variable-pitch propeller (based on a variable-stroke pump) in 1924 and presented a paper on the subject before the Royal Aeronautical Society in 1928; it met with scepticism as to its utility. The propeller had been developed with Gloster Aircraft Company as the Gloster Hele-Shaw Beacham Variable Pitch propeller and was demonstrated on a Gloster Grebe, where it was used to maintain a near-constant RPM.
The first practical controllable-pitch propeller for aircraft was introduced in 1932. French firm Ratier pioneered variable-pitch propellers of various designs from 1928 onwards, relying on a special ball-bearing helicoidal ramp at the root of the blades for easy operation. Walter S Hoover'patent
for a variable pitch propeller was filed in the U.S. Patent Office in 1934. Several designs were tried, including a small bladder of pressurized air in the propeller hub providing the necessary force to resist a spring that would drive the blades from fine pitch (take-off) to coarse pitch (level cruising). At a suitable airspeed a disk on the front of the spinner would press sufficiently on the bladder's air-release valve to relieve the pressure and allow the spring to drive the propeller to coarse pitch. These "pneumatic" propellers were fitted on the de Havilland DH.88 Comet aircraft, winner of the famed long-distance 1934 MacRobertson Air Race and in the
Caudron C.460 __NOTOC__
The Caudron C.450 and C.460 were French racing aircraft built to participate in the ''Coupe Deutsch de la Meurthe'' race of 1934.
Design
Developed from the Caudron C.362 flown in the previous year's race, a single C.450 and three C.46 ...
winner of the 1936 National Air Races
The National Air Races (also known as Pulitzer Trophy Races) are a series of pylon and cross-country races that have taken place in the United States since 1920. The science of aviation, and the speed and reliability of aircraft and engines grew ...
, flown by . Use of these pneumatic propellers required presetting the propeller to fine pitch prior to take-off. This was done by pressurizing the bladder with a bicycle pump, hence the whimsical nickname ''Gonfleurs d'hélices'' (prop-inflater boys) given to the aircraft ground-mechanics in France up to this day.
A Gloster Hele-Shaw hydraulic propeller was shown at the 1929 International Aero Exhibition at Olympia. American Tom Hamilton of the Hamilton Aero Manufacturing Company saw it and, on returning home, patented it there. As the Hamilton Standard Division of the United Aircraft Company, engineer Frank W. Caldwell developed a hydraulic design, which led to the award of the Collier Trophy
The Robert J. Collier Trophy is an annual aviation award administered by the U.S. National Aeronautic Association (NAA), presented to those who have made "the greatest achievement in aeronautics or astronautics in America, with respect to im ...
of 1933. de Havilland
The de Havilland Aircraft Company Limited () was a British aviation manufacturer established in late 1920 by Geoffrey de Havilland at Stag Lane Aerodrome Edgware on the outskirts of north London. Operations were later moved to Hatfield in H ...
subsequently bought up the rights to produce Hamilton propellers in the UK, while Rolls-Royce and Bristol Engines formed the British company Rotol in 1937 to produce their own designs. The French company of Pierre Levasseur and Smith Engineering Co. in the United States also developed controllable-pitch propellers. Wiley Post (1898-1935) used Smith propellers on some of his flights.
Another electrically-operated mechanism was originally developed by Wallace Turnbull and refined by the Curtiss-Wright Corporation. This was first tested in on June 6, 1927 at Camp Borden, Ontario, Canada, and received a patent in 1929 (). Some pilots in World War II (1939-1945) favoured it, because even when the engine was no longer running the propeller could be feathered. On hydraulically-operated propellers the feathering had to happen before the loss of hydraulic pressure in the engine.
See also
* Variable-pitch propeller (marine) * Propeller (aeronautics) * Gear pump * Governor (device) *V-Prop
The V-Prop is an automatic self-powering electronic variable-pitch propeller developed by Silence Aircraft, the manufacturers of the Silence Twister single-seat elliptical-winged kitplane.
Design and development
The V-Prop was fitted to the pr ...
References
aircraft engine development
Kimble D. McCutcheon * Gunston, Bill. ''Development of Piston Aero Engines''. Cambridge, England. Patrick Stephens Limited, 2006. * For more technical information on the first constant speed propeller governor mechanism invented by Elmer E. Woodward, see
External links
External propeller governor description
1941 Cutaway Drawing of Hydromatic Variable Pitch Propeller Operation
on B-24 bomber
* ttp://www.flightglobal.com/pdfarchive/view/1935/1935%20-%200989.html CONTROLLABLE-PITCH AIRSCREWSexplained in Flight 2 May 1935 an
9 May 1935
{{Aircraft gas turbine engine components Propellers Aircraft performance