conching on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
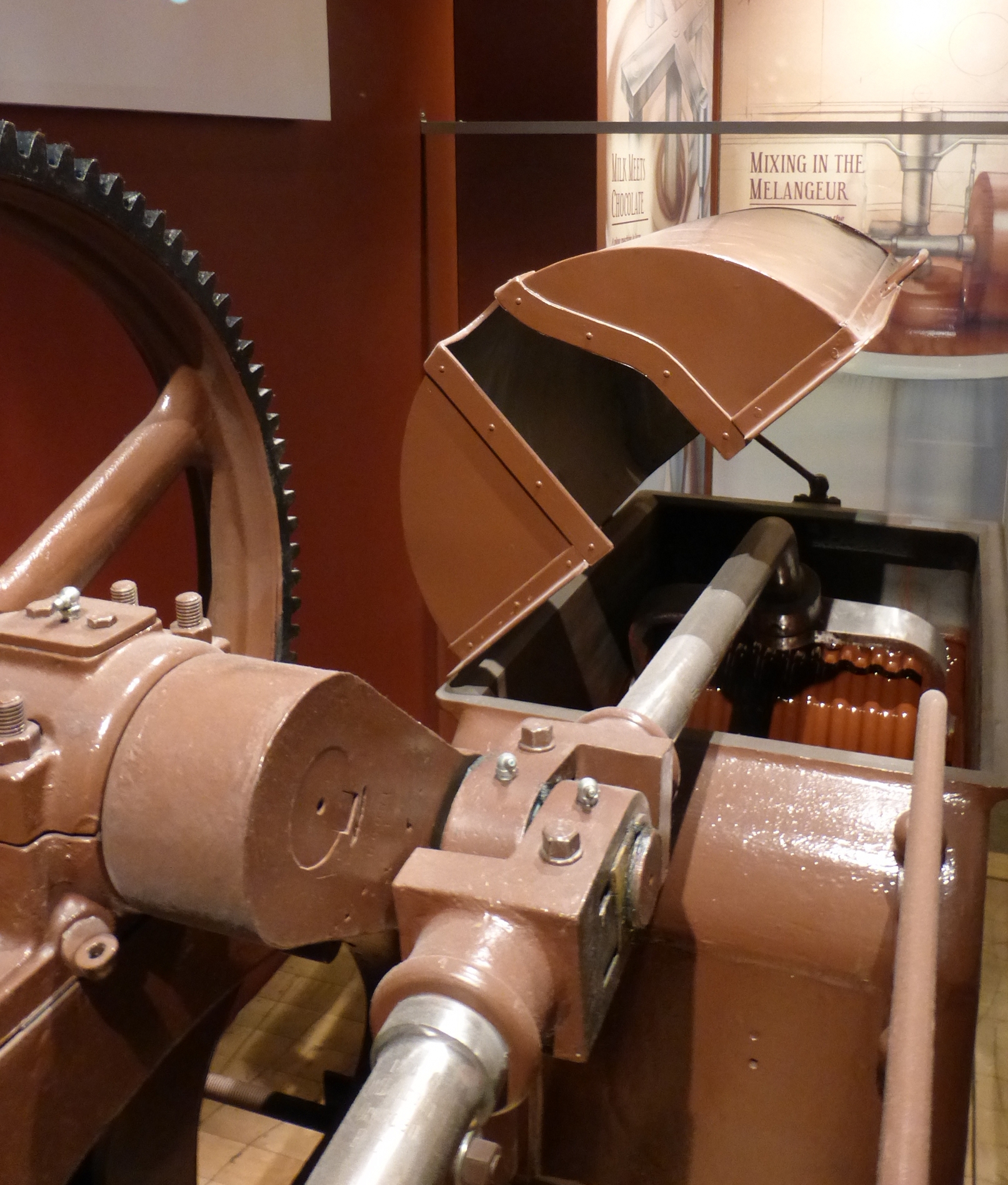
upright=1.35, Conche (in the Imhoff-Schokoladenmuseum)
 Conching is a process used in the manufacture of
Conching is a process used in the manufacture of
 Conching redistributes the substances from the dry cocoa that create flavor into the
Conching redistributes the substances from the dry cocoa that create flavor into the
Refining and Conching - Grenada Chocolate
Manufacturer's illustration of production-size conche and mixing shaft
{{Chocolate Chocolate Cooking techniques Articles containing video clips Swiss inventions
 Conching is a process used in the manufacture of
Conching is a process used in the manufacture of chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cocoa beans that can be a liquid, solid, or paste, either by itself or to flavoring, flavor other foods.
Cocoa beans are the processed seeds of the cacao tree (''Theobroma cacao''); unprocesse ...
whereby a surface scraping mixer and agitator, known as a conche, evenly distributes cocoa butter
Cocoa butter, also called theobroma oil, is a pale-yellow, edible Vegetable oil, fat extracted from the cocoa bean (''Theobroma cacao''). It is used to make chocolate, as well as some ointments, toiletries, and pharmaceuticals. Cocoa butter h ...
within chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cocoa beans that can be a liquid, solid, or paste, either by itself or to flavoring, flavor other foods.
Cocoa beans are the processed seeds of the cacao tree (''Theobroma cacao''); unprocesse ...
and may act as a "polisher" of the particle
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscle in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass.
They vary greatly in size or quantity, from s ...
s. It also promotes flavor development through friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. Types of friction include dry, fluid, lubricated, skin, and internal -- an incomplete list. The study of t ...
al heat, release of volatiles and acids, and oxidation. The name arises from the shape of the vessels initially used which resembled conch
Conch ( , , ) is a common name of a number of different medium-to-large-sized sea snails. Conch shells typically have a high Spire (mollusc), spire and a noticeable siphonal canal (in other words, the shell comes to a noticeable point on both ...
shells.
When ingredient
In a general sense, an ingredient is a substance which forms part of a mixture. In cooking, recipes specify which ingredients are used to prepare a dish, and the term may also refer to a specific food item in relation to its use in different re ...
s are mixed in this way, sometimes for up to 78 hours, chocolate can be produced with a mild, rich taste. Since the process is so important to the final texture and flavor of chocolate, manufacturers keep the details of their conching process proprietary.McClements, D. Julian ''Understanding and Controlling the Microstructure of Complex Foods'', Woodhead Publishing, 2007, , page 654.
The conching technique was introduced in Switzerland in the late 19th century. Conched chocolates were distinguished from ordinary chocolates with the French adjective ''fondant'' or ''crémant''.
History
Rodolphe Lindt invented the conche inBern
Bern (), or Berne (), ; ; ; . is the ''de facto'' Capital city, capital of Switzerland, referred to as the "federal city".; ; ; . According to the Swiss constitution, the Swiss Confederation intentionally has no "capital", but Bern has gov ...
in 1879. It produced chocolate with superior aroma
An odor (American English) or odour (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is a smell or a scent caused by one or more volatilized chemical compounds generally found in low concentrations that humans and many animals can perceive v ...
and melting characteristics compared to other processes used at that time. The Lindt chocolate company states that Lindt (perhaps mistakenly) allowed a mixer containing chocolate to run over a weekend (or possibly overnight, according to other variants of the possibly apocryphal
Apocrypha () are biblical or related writings not forming part of the accepted canon of scripture, some of which might be of doubtful authorship or authenticity. In Christianity, the word ''apocryphal'' (ἀπόκρυφος) was first applied to ...
story). Upon returning to the device, Lindt recognised the final product to have a smoother texture and greater shine than conventionally processed chocolate of the time. Lindt's invention made the mass-production of chocolate bar
A chocolate bar is a confection containing chocolate, which may also contain layerings or mixtures that include nut (fruit), nuts, fruit, caramel, nougat, and wafers. A flat, easily breakable, chocolate bar is also called a tablet. In some variet ...
s more practical, eventually replacing chocolate beverages as the primary means of mass chocolate consumption.Talbot, Geoff (ed), ''Science and Technology of Enrobed and Filled Chocolate, Confectionery and Bakery Products'', Woodhead Publishing, 2009, , chapter 2.5 ''Conching''. The adoption of conching also generalized the use of additional cocoa butter
Cocoa butter, also called theobroma oil, is a pale-yellow, edible Vegetable oil, fat extracted from the cocoa bean (''Theobroma cacao''). It is used to make chocolate, as well as some ointments, toiletries, and pharmaceuticals. Cocoa butter h ...
in the chocolate production; until then, molded chocolate often simply consisted of cocoa mass and sugar.
The original machine used by Lindt was developed in the early 1800s by an Italian chocolatier named Bozelli. The Bozelli grinding process was based on ancient Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El S ...
n practices of grinding cocoa beans on curved stones, which were called ''metate
A metate (or mealing stone) is a type or variety of quern, a ground stone tool used for processing grain and seeds. In traditional Mesoamerican cultures, metates are typically used by women who would grind nixtamalized maize and other organi ...
s''.
Lindt's original conche consisted of a granite roller and granite trough; such a configuration is now called a "long conche" and can take more than a day to process a tonne of chocolate. The ends of the trough were shaped to allow the chocolate to be thrown back over the roller at the end of each stroke, increasing the surface area exposed to air. A modern rotary conche can process 3 to 10 tonnes of chocolate in less than 12 hours. Modern conches have cooled jacketed vessels containing long mixer shafts with radial arms that press the chocolate against vessel sides. A single machine can carry out all the steps of grinding, mixing, and conching required for small batches of chocolate.
The conching process remained mostly a trade secret until the end of the century. In the 1890s, Cailler launched a similar chocolate. A long conche was manufactured by J. M. Lehmann from 1899.
Process
 Conching redistributes the substances from the dry cocoa that create flavor into the
Conching redistributes the substances from the dry cocoa that create flavor into the fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specif ...
phase. Air flowing through the conche removes some unwanted acetic, propionic, and butyric acids from the chocolate and reduces moisture. Even a small amount of moisture greatly increases the viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent drag (physics), resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for e ...
of the finished chocolate, so machinery is cleaned with cocoa butter instead of water.Ranken, M. D.; Kill, R. C.; Baker, C. G. J. (ed.), ''Food Industries Manual (24th Edition)'', Springer-Verlag, 1997, , pages 438–439. Some of the substances produced in the roasting of cocoa beans are oxidized
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
in the conche, mellowing the flavor of the product.
The temperature of the conche is controlled and varies for different types of chocolate. Generally, higher temperature leads to a shorter required processing time. Temperature varies from around for milk chocolate to up to for dark chocolate. The elevated temperature leads to a partially caramelized flavor and in milk chocolate promotes the Maillard reaction.Emmanuel Ohene Afoakwa, ''Chocolate Science and Technology'', John Wiley and Sons, 2010, , pages 43, 65–66.
The chocolate passes through three phases during conching. In the dry phase the material is in powdery form, and the mixing coats the particles with fat. Air movement through the conche removes some moisture and volatile substances, which may give an acidic note to the flavor. Moisture balance affects the flavor and texture of the finished product because, after the particles are coated with fat, moisture and volatile chemicals are less likely to escape.
In the pasty phase more of the particles are coated with the fats from the cocoa. The power required to turn the conche shafts increases at this step.
The final liquid phase allows minor adjustment to the viscosity of the finished product by addition of fats and emulsifier
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Althou ...
s, depending on the intended use of the chocolate.
While most conches are batch-process machines, continuous-flow conches separate the stages with weirs, over which the product travels through separate parts of the machine. A continuous conche can reduce the conching time for milk chocolate to as little as four hours.
After conching is completed, the flavor continues to change as it tastes increasingly acidic.
See also
* Melanger * History of chocolateReferences
Sources
*Further reading
*External links
Refining and Conching - Grenada Chocolate
Manufacturer's illustration of production-size conche and mixing shaft
{{Chocolate Chocolate Cooking techniques Articles containing video clips Swiss inventions