Compression-ignition engine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The diesel engine, named after
The diesel engine, named after
"10 Diesel Cars That Time Forgot"
April 13, 2021, ''
2013, ''Environmental Sciences Europe,'' volume 25, Article number: 15, retrieved December 5, 2022 "List of diesel automobiles," ''Wikipedia,'' retrieved December 5, 2022 According to Konrad Reif (2012), the EU average for diesel cars at the time accounted for half of newly registered cars. However,
"Every New 2021 Diesel for Sale in the U.S. Today,"
March 6, 2021, ''
"The Best 15 Best Diesel Vehicles of 2021,"
April 23, 2021, '' U.S. News,'' retrieved December 5, 2022. Though aviation has traditionally avoided diesel engines, aircraft diesel engines have become increasingly available in the 21st century. Since the late 1990s, for various reasons -- including the diesel's normal advantages over gasoline engines, but also for recent issues peculiar to aviation -- development and production of diesel engines for aircraft has surged, with over 5000 such engines delivered worldwide between 2002 and 2018, particularly for light airplanes and
August 1, 2018, ''
"Diamond Rolls Out 500th DA40 NG,"
December 30, 2020 Updated: December 31, 2020, '' Avweb,'' retrieved December 5, 2022

 In 1878,
In 1878,
 * 1901: Imanuel Lauster designs the first
* 1901: Imanuel Lauster designs the first
 * 1923: At the Königsberg DLG exhibition, the first agricultural tractor with a diesel engine, the prototype Benz-Sendling S6, is presented.
* 1923: December 15, the first
* 1923: At the Königsberg DLG exhibition, the first agricultural tractor with a diesel engine, the prototype Benz-Sendling S6, is presented.
* 1923: December 15, the first
 * 1950s:
* 1950s:
 * 1964: Summer, Daimler-Benz switches from precombustion chamber injection to helix-controlled direct injection.
* 1962–65: A diesel compression braking system, eventually to be manufactured by the Jacobs Manufacturing Company and nicknamed the "Jake Brake", is invented and patented by Clessie Cummins.
* 1964: Summer, Daimler-Benz switches from precombustion chamber injection to helix-controlled direct injection.
* 1962–65: A diesel compression braking system, eventually to be manufactured by the Jacobs Manufacturing Company and nicknamed the "Jake Brake", is invented and patented by Clessie Cummins.
 * 1981/82: Uniflow scavenging for two-stroke marine diesel engines becomes standard.
* 1985: December, road testing of a common rail injection system for lorries using a modified 6VD 12,5/12 GRF-E engine in an IFA W50 takes place.
* 1986: The BMW E28 524td is the world's first passenger car equipped with an electronically controlled injection pump (developed by Bosch).
* 1987: Daimler-Benz introduces the electronically controlled injection pump for lorry diesel engines.
* 1988: The Fiat Croma becomes the first mass-produced passenger car in the world to have a direct injected diesel engine.
* 1989: The Audi 100 is the first passenger car in the world with a turbocharged, direct injected, and electronically controlled diesel engine.
* 1981/82: Uniflow scavenging for two-stroke marine diesel engines becomes standard.
* 1985: December, road testing of a common rail injection system for lorries using a modified 6VD 12,5/12 GRF-E engine in an IFA W50 takes place.
* 1986: The BMW E28 524td is the world's first passenger car equipped with an electronically controlled injection pump (developed by Bosch).
* 1987: Daimler-Benz introduces the electronically controlled injection pump for lorry diesel engines.
* 1988: The Fiat Croma becomes the first mass-produced passenger car in the world to have a direct injected diesel engine.
* 1989: The Audi 100 is the first passenger car in the world with a turbocharged, direct injected, and electronically controlled diesel engine.
 * 2000: Peugeot introduces the diesel particulate filter for passenger cars.
* 2002:
* 2000: Peugeot introduces the diesel particulate filter for passenger cars.
* 2002:
 The diesel internal combustion engine differs from the gasoline powered
The diesel internal combustion engine differs from the gasoline powered
 Medium-speed engines are used in large electrical generators, railway diesel locomotives, ship propulsion and mechanical drive applications such as large compressors or pumps. Medium speed diesel engines operate on either diesel fuel or heavy fuel oil by direct injection in the same manner as low-speed engines. Usually, they are four-stroke engines with trunk pistons; a notable exception being the EMD 567, EMD 645, 645, and EMD 710, 710 engines, which are all two-stroke.
The power output of medium-speed diesel engines can be as high as 21,870 kW, with the effective efficiency being around 47...48% (1982). Most larger medium-speed engines are started with compressed air direct on pistons, using an air distributor, as opposed to a pneumatic starting motor acting on the flywheel, which tends to be used for smaller engines.
Medium-speed engines intended for marine applications are usually used to power (Roll-on/roll-off, ro-ro) ferries, passenger ships or small freight ships. Using medium-speed engines reduces the cost of smaller ships and increases their transport capacity. In addition to that, a single ship can use two smaller engines instead of one big engine, which increases the ship's safety.
; Low-speed diesel engines
Medium-speed engines are used in large electrical generators, railway diesel locomotives, ship propulsion and mechanical drive applications such as large compressors or pumps. Medium speed diesel engines operate on either diesel fuel or heavy fuel oil by direct injection in the same manner as low-speed engines. Usually, they are four-stroke engines with trunk pistons; a notable exception being the EMD 567, EMD 645, 645, and EMD 710, 710 engines, which are all two-stroke.
The power output of medium-speed diesel engines can be as high as 21,870 kW, with the effective efficiency being around 47...48% (1982). Most larger medium-speed engines are started with compressed air direct on pistons, using an air distributor, as opposed to a pneumatic starting motor acting on the flywheel, which tends to be used for smaller engines.
Medium-speed engines intended for marine applications are usually used to power (Roll-on/roll-off, ro-ro) ferries, passenger ships or small freight ships. Using medium-speed engines reduces the cost of smaller ships and increases their transport capacity. In addition to that, a single ship can use two smaller engines instead of one big engine, which increases the ship's safety.
; Low-speed diesel engines
 Low-speed diesel engines are usually very large in size and mostly used to power ships. There are two different types of low-speed engines that are commonly used: Two-stroke engines with a crosshead, and four-stroke engines with a regular trunk-piston. Two-stroke engines have a limited rotational frequency and their charge exchange is more difficult, which means that they are usually bigger than four-stroke engines and used to directly power a ship's propeller. Four-stroke engines on ships are usually used to power an electric generator. An electric motor powers the propeller. Both types are usually very undersquare. Low-speed diesel engines (as used in ships and other applications where overall engine weight is relatively unimportant) often have an effective efficiency of up to 55%. Like medium-speed engines, low-speed engines are started with compressed air, and they use heavy oil as their primary fuel.
Low-speed diesel engines are usually very large in size and mostly used to power ships. There are two different types of low-speed engines that are commonly used: Two-stroke engines with a crosshead, and four-stroke engines with a regular trunk-piston. Two-stroke engines have a limited rotational frequency and their charge exchange is more difficult, which means that they are usually bigger than four-stroke engines and used to directly power a ship's propeller. Four-stroke engines on ships are usually used to power an electric generator. An electric motor powers the propeller. Both types are usually very undersquare. Low-speed diesel engines (as used in ships and other applications where overall engine weight is relatively unimportant) often have an effective efficiency of up to 55%. Like medium-speed engines, low-speed engines are started with compressed air, and they use heavy oil as their primary fuel.
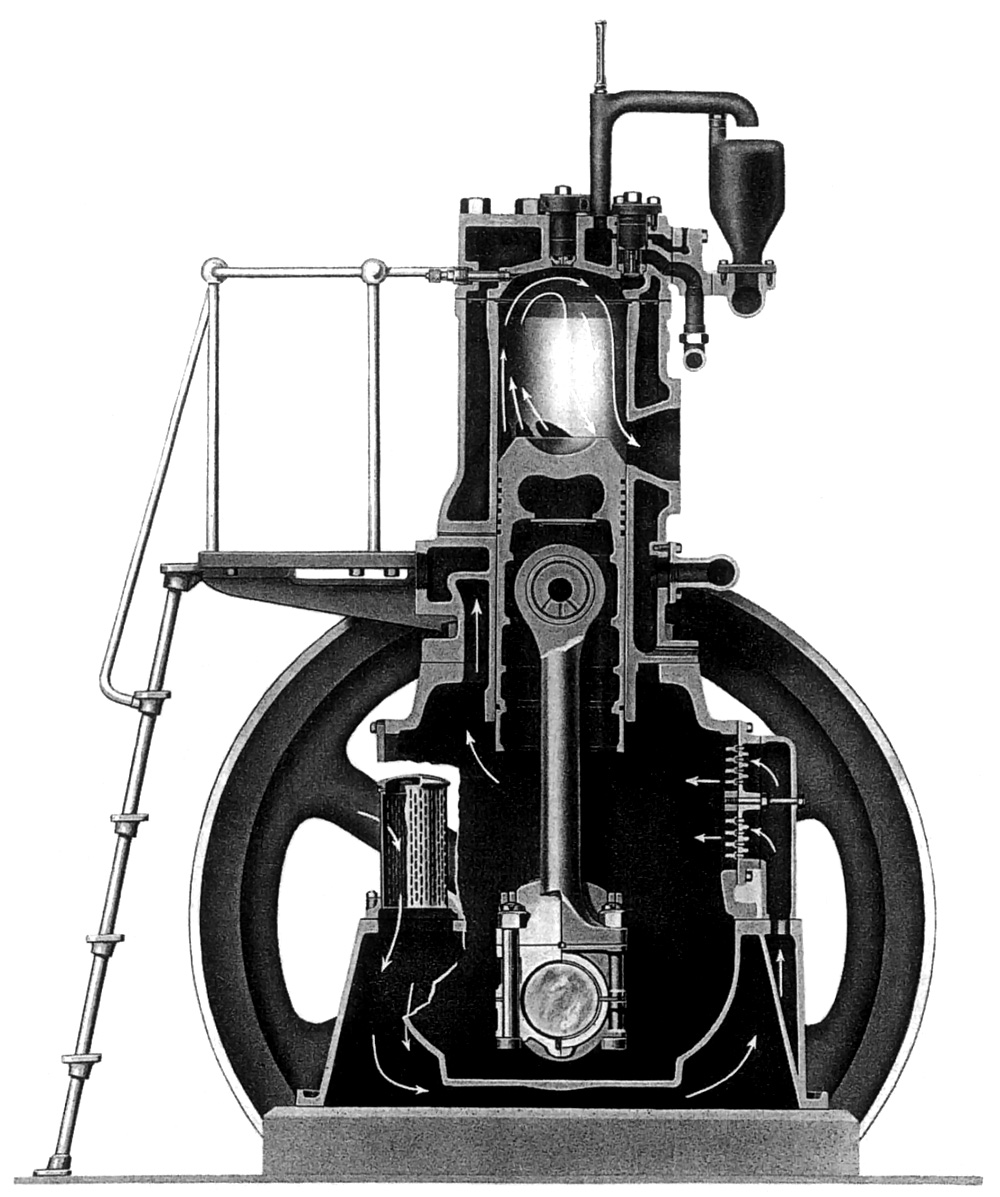
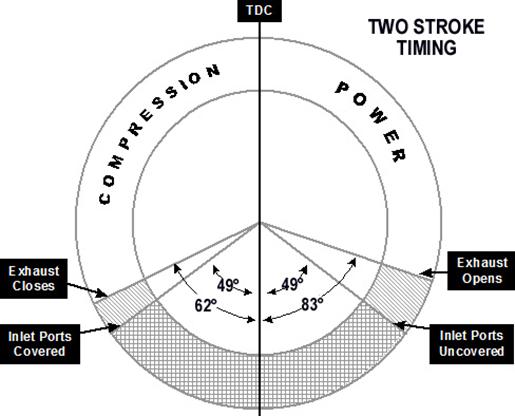 Four-stroke engines use the combustion cycle described earlier.
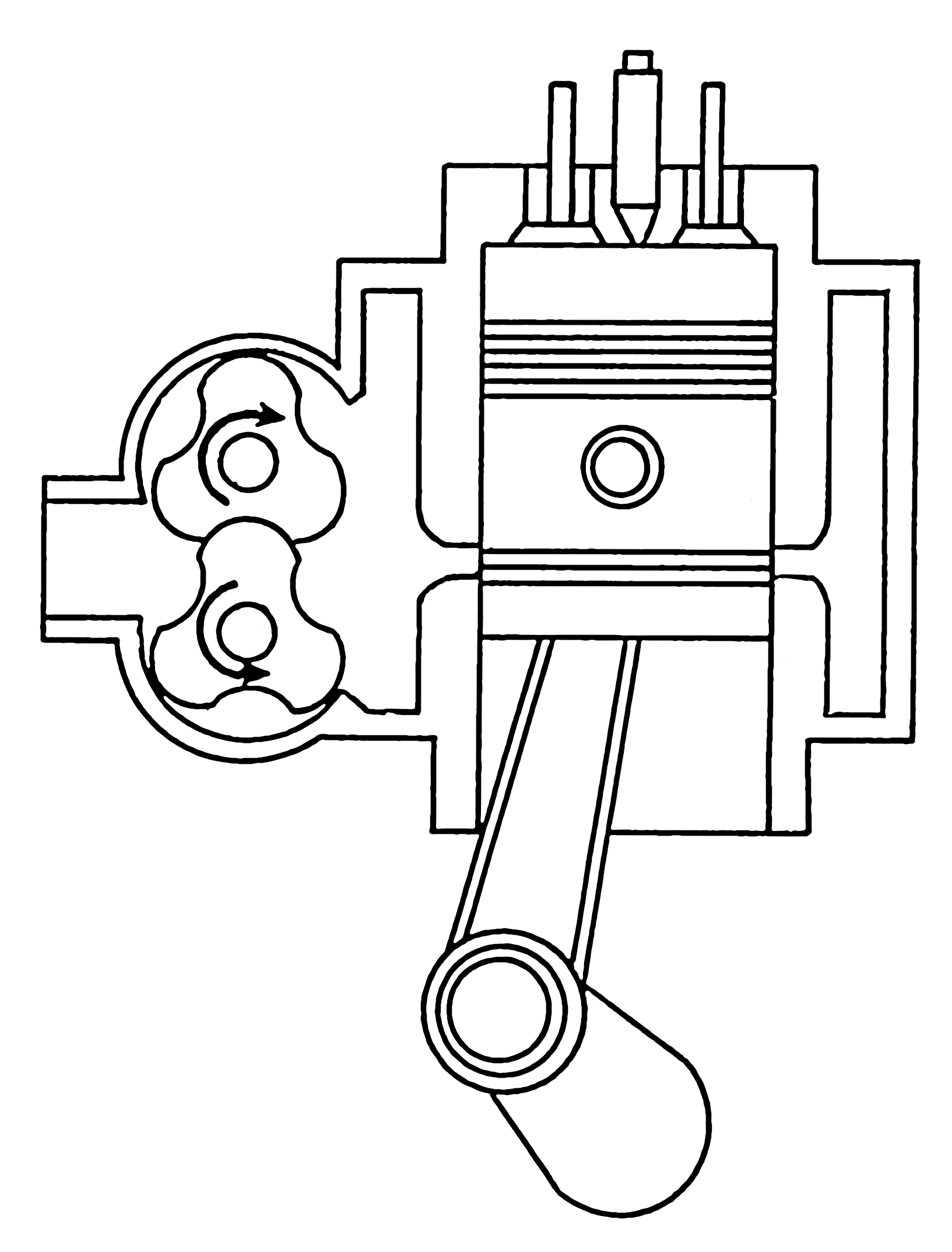
Two-stroke diesel engine, Two-stroke engines use a combustion cycle which is completed in two strokes instead of four strokes. Filling the cylinder with air and compressing it takes place in one stroke, and the power and exhaust strokes are combined. The compression in a two-stroke diesel engine is similar to the compression that takes place in a four-stroke diesel engine: As the piston passes through bottom centre and starts upward, compression commences, culminating in fuel injection and ignition. Instead of a full set of valves, two-stroke diesel engines have simple intake ports, and exhaust ports (or exhaust valves). When the piston approaches bottom dead centre, both the intake and the exhaust ports are "open", which means that there is atmospheric pressure inside the cylinder. Therefore, some sort of pump is required to blow the air into the cylinder and the combustion gasses into the exhaust. This process is called ''scavenging''. The pressure required is approximately 10 - 30 kPa.
Due to the lack of discrete exhaust and intake strokes, all two-stroke diesel engines use a scavenge blower or some form of compressor to charge the cylinders with air and assist in scavenging. Roots-type superchargers were used for ship engines until the mid-1950s, however since 1955 they have been widely replaced by turbochargers. Usually, a two-stroke ship diesel engine has a single-stage turbocharger with a turbine that has an axial inflow and a radial outflow.
Four-stroke engines use the combustion cycle described earlier.
Two-stroke diesel engine, Two-stroke engines use a combustion cycle which is completed in two strokes instead of four strokes. Filling the cylinder with air and compressing it takes place in one stroke, and the power and exhaust strokes are combined. The compression in a two-stroke diesel engine is similar to the compression that takes place in a four-stroke diesel engine: As the piston passes through bottom centre and starts upward, compression commences, culminating in fuel injection and ignition. Instead of a full set of valves, two-stroke diesel engines have simple intake ports, and exhaust ports (or exhaust valves). When the piston approaches bottom dead centre, both the intake and the exhaust ports are "open", which means that there is atmospheric pressure inside the cylinder. Therefore, some sort of pump is required to blow the air into the cylinder and the combustion gasses into the exhaust. This process is called ''scavenging''. The pressure required is approximately 10 - 30 kPa.
Due to the lack of discrete exhaust and intake strokes, all two-stroke diesel engines use a scavenge blower or some form of compressor to charge the cylinders with air and assist in scavenging. Roots-type superchargers were used for ship engines until the mid-1950s, however since 1955 they have been widely replaced by turbochargers. Usually, a two-stroke ship diesel engine has a single-stage turbocharger with a turbine that has an axial inflow and a radial outflow.
 Most direct injection diesel engines have a combustion cup in the top of the piston where the fuel is sprayed. Many different methods of injection can be used. Usually, an engine with helix-controlled mechanic direct injection has either an inline or a distributor injection pump. For each engine cylinder, the corresponding plunger in the fuel pump measures out the correct amount of fuel and determines the timing of each injection. These engines use fuel injection, injectors that are very precise spring-loaded valves that open and close at a specific fuel pressure. Separate high-pressure fuel lines connect the fuel pump with each cylinder. Fuel volume for each single combustion is controlled by a slanted Groove (engineering), groove in the plunger which rotates only a few degrees releasing the pressure and is controlled by a mechanical governor, consisting of weights rotating at engine speed constrained by springs and a lever. The injectors are held open by the fuel pressure. On high-speed engines the plunger pumps are together in one unit. The length of fuel lines from the pump to each injector is normally the same for each cylinder in order to obtain the same pressure delay. Direct injected diesel engines usually use orifice-type fuel injectors.
Electronic control of the fuel injection transformed the direct injection engine by allowing much greater control over the combustion.
; Common rail
Most direct injection diesel engines have a combustion cup in the top of the piston where the fuel is sprayed. Many different methods of injection can be used. Usually, an engine with helix-controlled mechanic direct injection has either an inline or a distributor injection pump. For each engine cylinder, the corresponding plunger in the fuel pump measures out the correct amount of fuel and determines the timing of each injection. These engines use fuel injection, injectors that are very precise spring-loaded valves that open and close at a specific fuel pressure. Separate high-pressure fuel lines connect the fuel pump with each cylinder. Fuel volume for each single combustion is controlled by a slanted Groove (engineering), groove in the plunger which rotates only a few degrees releasing the pressure and is controlled by a mechanical governor, consisting of weights rotating at engine speed constrained by springs and a lever. The injectors are held open by the fuel pressure. On high-speed engines the plunger pumps are together in one unit. The length of fuel lines from the pump to each injector is normally the same for each cylinder in order to obtain the same pressure delay. Direct injected diesel engines usually use orifice-type fuel injectors.
Electronic control of the fuel injection transformed the direct injection engine by allowing much greater control over the combustion.
; Common rail
 An indirect diesel injection system (IDI) engine delivers fuel into a small chamber called a swirl chamber, precombustion chamber, pre chamber or ante-chamber, which is connected to the cylinder by a narrow air passage. Generally the goal of the pre chamber is to create increased turbulence for better air / fuel mixing. This system also allows for a smoother, quieter running engine, and because fuel mixing is assisted by turbulence, injector pressures can be lower. Most IDI systems use a single orifice injector. The pre-chamber has the disadvantage of lowering efficiency due to increased heat loss to the engine's cooling system, restricting the combustion burn, thus reducing the efficiency by 5–10%. IDI engines are also more difficult to start and usually require the use of glow plugs. IDI engines may be cheaper to build but generally require a higher compression ratio than the DI counterpart. IDI also makes it easier to produce smooth, quieter running engines with a simple mechanical injection system since exact injection timing is not as critical. Most modern automotive engines are DI which have the benefits of greater efficiency and easier starting; however, IDI engines can still be found in the many ATV and small diesel applications. Indirect injected diesel engines use pintle-type fuel injectors.
An indirect diesel injection system (IDI) engine delivers fuel into a small chamber called a swirl chamber, precombustion chamber, pre chamber or ante-chamber, which is connected to the cylinder by a narrow air passage. Generally the goal of the pre chamber is to create increased turbulence for better air / fuel mixing. This system also allows for a smoother, quieter running engine, and because fuel mixing is assisted by turbulence, injector pressures can be lower. Most IDI systems use a single orifice injector. The pre-chamber has the disadvantage of lowering efficiency due to increased heat loss to the engine's cooling system, restricting the combustion burn, thus reducing the efficiency by 5–10%. IDI engines are also more difficult to start and usually require the use of glow plugs. IDI engines may be cheaper to build but generally require a higher compression ratio than the DI counterpart. IDI also makes it easier to produce smooth, quieter running engines with a simple mechanical injection system since exact injection timing is not as critical. Most modern automotive engines are DI which have the benefits of greater efficiency and easier starting; however, IDI engines can still be found in the many ATV and small diesel applications. Indirect injected diesel engines use pintle-type fuel injectors.
 Early diesel engines injected fuel with the assistance of compressed air, which atomised the fuel and forced it into the engine through a nozzle (a similar principle to an aerosol spray). The nozzle opening was closed by a Needle valve, pin valve actuated by the camshaft. Although the engine was also required to drive an air compressor used for air-blast injection, the efficiency was nonetheless better than other combustion engines of the time. However the system was heavy and it was slow to react to changing torque demands, making it unsuitable for road vehicles.
Early diesel engines injected fuel with the assistance of compressed air, which atomised the fuel and forced it into the engine through a nozzle (a similar principle to an aerosol spray). The nozzle opening was closed by a Needle valve, pin valve actuated by the camshaft. Although the engine was also required to drive an air compressor used for air-blast injection, the efficiency was nonetheless better than other combustion engines of the time. However the system was heavy and it was slow to react to changing torque demands, making it unsuitable for road vehicles.
 Forced induction, especially turbocharging is commonly used on diesel engines because it greatly increases efficiency, and torque output. Diesel engines are well suited for forced induction setups due to their operating principle which is characterised by wide ignition limits and the absence of fuel during the compression stroke. Therefore, knocking, pre-ignition or detonation cannot occur, and a lean mixture caused by excess supercharging air inside the combustion chamber does not negatively affect combustion.
Forced induction, especially turbocharging is commonly used on diesel engines because it greatly increases efficiency, and torque output. Diesel engines are well suited for forced induction setups due to their operating principle which is characterised by wide ignition limits and the absence of fuel during the compression stroke. Therefore, knocking, pre-ignition or detonation cannot occur, and a lean mixture caused by excess supercharging air inside the combustion chamber does not negatively affect combustion.
 Therefore, diesel engines can operate on a huge variety of different fuels. In general, fuel for diesel engines should have a proper viscosity, so that the injection pump can pump the fuel to the injection nozzles without causing damage to itself or corrosion of the fuel line. At injection, the fuel should form a good fuel spray, and it should not have a coking effect upon the injection nozzles. To ensure proper engine starting and smooth operation, the fuel should be willing to ignite and hence not cause a high ignition delay, (this means that the fuel should have a high cetane number). Diesel fuel should also have a high lower heating value.
Inline mechanical injector pumps generally tolerate poor-quality or bio-fuels better than distributor-type pumps. Also, indirect injection engines generally run more satisfactorily on fuels with a high ignition delay (for instance, petrol) than direct injection engines. This is partly because an indirect injection engine has a much greater 'swirl' effect, improving vaporisation and combustion of fuel, and because (in the case of vegetable oil-type fuels) lipid depositions can condense on the cylinder walls of a direct-injection engine if combustion temperatures are too low (such as starting the engine from cold). Direct-injected engines with an M-System, MAN centre sphere combustion chamber rely on fuel condensing on the combustion chamber walls. The fuel starts vaporising only after ignition sets in, and it burns relatively smoothly. Therefore, such engines also tolerate fuels with poor ignition delay characteristics, and, in general, they can operate on petrol rated 86 Octane rating#Research Octane Number (RON), RON.
Therefore, diesel engines can operate on a huge variety of different fuels. In general, fuel for diesel engines should have a proper viscosity, so that the injection pump can pump the fuel to the injection nozzles without causing damage to itself or corrosion of the fuel line. At injection, the fuel should form a good fuel spray, and it should not have a coking effect upon the injection nozzles. To ensure proper engine starting and smooth operation, the fuel should be willing to ignite and hence not cause a high ignition delay, (this means that the fuel should have a high cetane number). Diesel fuel should also have a high lower heating value.
Inline mechanical injector pumps generally tolerate poor-quality or bio-fuels better than distributor-type pumps. Also, indirect injection engines generally run more satisfactorily on fuels with a high ignition delay (for instance, petrol) than direct injection engines. This is partly because an indirect injection engine has a much greater 'swirl' effect, improving vaporisation and combustion of fuel, and because (in the case of vegetable oil-type fuels) lipid depositions can condense on the cylinder walls of a direct-injection engine if combustion temperatures are too low (such as starting the engine from cold). Direct-injected engines with an M-System, MAN centre sphere combustion chamber rely on fuel condensing on the combustion chamber walls. The fuel starts vaporising only after ignition sets in, and it burns relatively smoothly. Therefore, such engines also tolerate fuels with poor ignition delay characteristics, and, in general, they can operate on petrol rated 86 Octane rating#Research Octane Number (RON), RON.
 The diesel engine, named after
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel
Rudolf Christian Karl Diesel (, ; 18 March 1858 – 29 September 1913) was a German inventor and mechanical engineer who is famous for having invented the diesel engine, which burns diesel fuel; both are named after him.
Early life and educatio ...
, is an internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal co ...
in which ignition of the fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy bu ...
is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to mechanical compression; thus, the diesel engine is a so-called compression-ignition engine (CI engine). This contrasts with engines using spark plug
A spark plug (sometimes, in British English, a sparking plug, and, colloquially, a plug) is a device for delivering electric current from an ignition system to the combustion chamber of a spark-ignition engine to ignite the compressed fuel/air ...
-ignition of the air-fuel mixture, such as a petrol engine
A petrol engine (gasoline engine in American English) is an internal combustion engine designed to run on petrol (gasoline). Petrol engines can often be adapted to also run on fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas and ethanol blends (such as '' ...
(gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic ...
engine) or a gas engine (using a gaseous fuel like natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon ...
or liquefied petroleum gas).
Diesel engines work by compressing only air, or air plus residual combustion gases from the exhaust (known as exhaust gas recirculation (EGR)). Air is inducted into the chamber during the intake stroke, and compressed during the compression stroke. This increases the air temperature inside the cylinder
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infi ...
to such a high degree that atomised diesel fuel injected into the combustion chamber ignites. With the fuel being injected into the air just before combustion, the dispersion of the fuel is uneven; this is called a heterogeneous air-fuel mixture. The torque a diesel engine produces is controlled by manipulating the air-fuel ratio (λ); instead of throttling the intake air, the diesel engine relies on altering the amount of fuel that is injected, and the air-fuel ratio is usually high.
The diesel engine has the highest thermal efficiency
In thermodynamics, the thermal efficiency (\eta_) is a dimensionless performance measure of a device that uses thermal energy, such as an internal combustion engine, steam turbine, steam engine, boiler, furnace, refrigerator, ACs etc.
For a ...
( engine efficiency) of any practical internal
Internal may refer to:
* Internality as a concept in behavioural economics
*Neijia, internal styles of Chinese martial arts
*Neigong
Neigong, also spelled ''nei kung'', ''neigung'', or ''nae gong'', refers to any of a set of Chinese breathing, ...
or external combustion engine due to its very high expansion ratio and inherent lean burn which enables heat dissipation by the excess air. A small efficiency loss is also avoided compared with non-direct-injection gasoline engines since unburned fuel is not present during valve overlap and therefore no fuel goes directly from the intake/injection to the exhaust. Low-speed diesel engines (as used in ships and other applications where overall engine weight is relatively unimportant) can reach effective efficiencies of up to 55%. The combined cycle gas turbine (Brayton and Rankin cycle) is a combustion engine that is more efficient than a diesel engine, but it is, due to its mass and dimensions, unsuited for vehicles, watercraft
Any vehicle used in or on water as well as underwater, including boats, ships, hovercraft and submarines, is a watercraft, also known as a water vessel or waterborne vessel. A watercraft usually has a propulsive capability (whether by sail ...
, or aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. ...
.The world's largest diesel engines put in service are 14-cylinder, two-stroke marine diesel engines; they produce a peak power of almost 100 MW each.
Diesel engines may be designed as either two-stroke
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes (up and down movements) of the piston during one power cycle, this power cycle being completed in one revolution of t ...
or four-stroke
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direct ...
cycles. They were originally used as a more efficient replacement for stationary steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be ...
s. Since the 1910s, they have been used in submarines and ships. Use in locomotives, buses, trucks, heavy equipment
Heavy equipment or heavy machinery refers to heavy-duty vehicles specially designed to execute construction tasks, most frequently involving earthwork operations or other large construction tasks. ''Heavy equipment'' usually comprises five e ...
, agricultural equipment and electricity generation plants followed later. In the 1930s, they slowly began to be used in a few automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods.
The year 1886 is regarded ...
s. Since the 1970s energy crisis
The 1970s energy crisis occurred when the Western world, particularly the United States, Canada, Western Europe, Australia, and New Zealand, faced substantial petroleum shortages as well as elevated prices. The two worst crises of this period we ...
, demand for higher fuel efficiency has resulted in most major automakers, at some point, offering diesel-powered models, even in very small cars.Ramey, Jay"10 Diesel Cars That Time Forgot"
April 13, 2021, ''
Autoweek
''Autoweek'' is a car culture publication based in Detroit, Michigan. It was first published in 1958 and in 1977 the publication was purchased by Crain Communications Inc, its current parent company. The magazine was published weekly and focused ...
,'' retrieved December 5, 2022"Critical evaluation of the European diesel car boom - global comparison, environmental effects and various national strategies,"2013, ''Environmental Sciences Europe,'' volume 25, Article number: 15, retrieved December 5, 2022 "List of diesel automobiles," ''Wikipedia,'' retrieved December 5, 2022 According to Konrad Reif (2012), the EU average for diesel cars at the time accounted for half of newly registered cars. However,
air pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different type ...
emissions are harder to control in diesel engines than in gasoline engines, so the use of diesel auto engines in the U.S. is now largely relegated to larger on-road and off-road vehicle
An off-road vehicle, sometimes referred to as an overland or adventure vehicle, is considered to be any type of vehicle which is capable of driving on and off paved or gravel surface. It is generally characterized by having large tires with d ...
sHuffman, John Pearley"Every New 2021 Diesel for Sale in the U.S. Today,"
March 6, 2021, ''
Car and Driver
''Car and Driver'' (''CD'' or ''C/D'') is an American automotive enthusiast magazine. In 2006 its total circulation was 1.23 million. It is owned by Hearst Magazines, who purchased prior owner Hachette Filipacchi Media U.S. in 2011. It was f ...
,'' retrieved December 5, 2022Gorzelany, Jim"The Best 15 Best Diesel Vehicles of 2021,"
April 23, 2021, '' U.S. News,'' retrieved December 5, 2022. Though aviation has traditionally avoided diesel engines, aircraft diesel engines have become increasingly available in the 21st century. Since the late 1990s, for various reasons -- including the diesel's normal advantages over gasoline engines, but also for recent issues peculiar to aviation -- development and production of diesel engines for aircraft has surged, with over 5000 such engines delivered worldwide between 2002 and 2018, particularly for light airplanes and
unmanned aerial vehicles
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs are a component of an unmanned aircraft system (UAS), which includes adding a ground-based controlle ...
."Inside the Diesel Revolution,"August 1, 2018, ''
Flying
Flying may refer to:
* Flight, the process of flying
* Aviation, the creation and operation of aircraft
Music
Albums
* ''Flying'' (Grammatrain album), 1997
* ''Flying'' (Jonathan Fagerlund album), 2008
* ''Flying'' (UFO album), 1971
* ''Fl ...
,'' retrieved December 5, 2022O'Connor, Kate"Diamond Rolls Out 500th DA40 NG,"
December 30, 2020 Updated: December 31, 2020, '' Avweb,'' retrieved December 5, 2022
History
Diesel's idea

 In 1878,
In 1878, Rudolf Diesel
Rudolf Christian Karl Diesel (, ; 18 March 1858 – 29 September 1913) was a German inventor and mechanical engineer who is famous for having invented the diesel engine, which burns diesel fuel; both are named after him.
Early life and educatio ...
, who was a student at the "Polytechnikum" in Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and Ha ...
, attended the lectures of Carl von Linde
Carl Paul Gottfried von Linde (11 June 1842 – 16 November 1934) was a German scientist, engineer, and businessman. He discovered a refrigeration cycle and invented the first industrial-scale air separation and gas liquefaction processes, whi ...
. Linde explained that steam engines are capable of converting just 6–10% of the heat energy into work, but that the Carnot cycle
A Carnot cycle is an ideal thermodynamic cycle proposed by French physicist Sadi Carnot in 1824 and expanded upon by others in the 1830s and 1840s. By Carnot's theorem, it provides an upper limit on the efficiency of any classical thermodynam ...
allows conversion of much more of the heat energy into work by means of isothermal change in condition. According to Diesel, this ignited the idea of creating a highly efficient engine that could work on the Carnot cycle. Diesel was also exposed to a fire piston, a traditional fire starter using rapid adiabatic compression principles which Linde had acquired from Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
. After several years of working on his ideas, Diesel published them in 1893 in the essay '' Theory and Construction of a Rational Heat Motor''.
Diesel was heavily criticised for his essay, but only few found the mistake that he made; his ''rational heat motor'' was supposed to utilise a constant temperature cycle (with isothermal compression) that would require a much higher level of compression than that needed for compression ignition. Diesel's idea was to compress the air so tightly that the temperature of the air would exceed that of combustion. However, such an engine could never perform any usable work. In his 1892 US patent (granted in 1895) #542846, Diesel describes the compression required for his cycle:
:"pure atmospheric air is compressed, according to curve 1 2, to such a degree that, before ignition or combustion takes place, the highest pressure of the diagram and the highest temperature are obtained-that is to say, the temperature at which the subsequent combustion has to take place, not the burning or igniting point. To make this more clear, let it be assumed that the subsequent combustion shall take place at a temperature of 700°. Then in that case the initial pressure must be sixty-four atmospheres, or for 800° centigrade the pressure must be ninety atmospheres, and so on. Into the air thus compressed is then gradually introduced from the exterior finely divided fuel, which ignites on introduction, since the air is at a temperature far above the igniting-point of the fuel. The characteristic features of the cycle according to my present invention are therefore, increase of pressure and temperature up to the maximum, not by combustion, but prior to combustion by mechanical compression of air, and there upon the subsequent performance of work without increase of pressure and temperature by gradual combustion during a prescribed part of the stroke determined by the cut-oil".
By June 1893, Diesel had realised his original cycle would not work and he adopted the constant pressure cycle. Diesel describes the cycle in his 1895 patent application. Notice that there is no longer a mention of compression temperatures exceeding the temperature of combustion. Now it is simply stated that the compression must be sufficient to trigger ignition.
:"1. In an internal-combustion engine, the combination of a cylinder and piston constructed and arranged to compress air to a degree producing a temperature above the igniting-point of the fuel, a supply for compressed air or gas; a fuel-supply; a distributing-valve for fuel, a passage from the air supply to the cylinder in communication with the fuel-distributing valve, an inlet to the cylinder in communication with the air-supply and with the fuel-valve, and a cut-oil, substantially as described." See US patent # 608845 filed 1895 / granted 1898
In 1892, Diesel received patents in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
, Switzerland, the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
and the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
for "Method of and Apparatus for Converting Heat into Work". In 1894 and 1895, he filed patents and addenda in various countries for his engine; the first patents were issued in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
(No. 16,654), France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
(No. 243,531) and Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
(No. 113,139) in December 1894, and in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
(No. 86,633) in 1895 and the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
(No. 608,845) in 1898.
Diesel was attacked and criticised over a time period of several years. Critics claimed that Diesel never invented a new motor and that the invention of the diesel engine is fraud. Otto Köhler and were two of the most prominent critics of Diesel's time. Köhler had published an essay in 1887, in which he describes an engine similar to the engine Diesel describes in his 1893 essay. Köhler figured that such an engine could not perform any work. Emil Capitaine had built a petroleum engine with glow-tube ignition in the early 1890s; he claimed against his own better judgement that his glow-tube ignition engine worked the same way Diesel's engine did. His claims were unfounded and he lost a patent lawsuit against Diesel. Other engines, such as the Akroyd engine and the Brayton engine, also use an operating cycle that is different from the diesel engine cycle. Friedrich Sass says that the diesel engine is Diesel's "very own work" and that any "Diesel myth" is "falsification of history
Historical negationism, also called denialism, is falsification or distortion of the historical record. It should not be conflated with ''historical revisionism'', a broader term that extends to newly evidenced, fairly reasoned academic reinterp ...
".
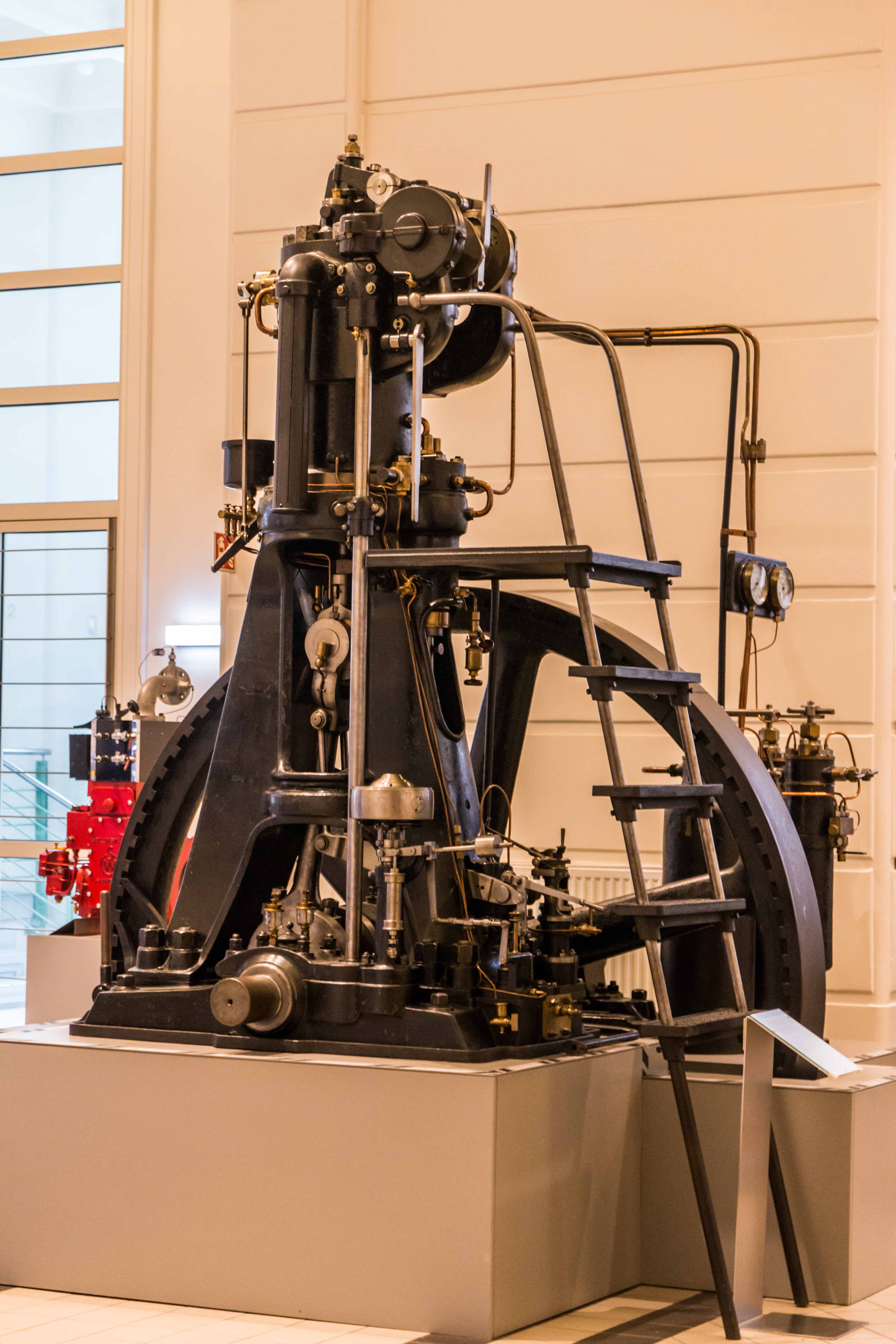
The first diesel engine
Diesel sought out firms and factories that would build his engine. With the help of Moritz Schröter and , he succeeded in convincing bothKrupp
The Krupp family (see pronunciation), a prominent 400-year-old German dynasty from Essen, is notable for its production of steel, artillery, ammunition and other armaments. The family business, known as Friedrich Krupp AG (Friedrich Krupp ...
in Essen and the Maschinenfabrik Augsburg. Contracts were signed in April 1893, and in early summer 1893, Diesel's first prototype engine was built in Augsburg. On 10 August 1893, the first ignition took place, the fuel used was petrol. In winter 1893/1894, Diesel redesigned the existing engine, and by 18 January 1894, his mechanics had converted it into the second prototype. During January that year, an air-blast injection
Air-blast injection is a historical direct injection system for Diesel engines. Unlike modern designs, air-blast injected Diesel engines do not have an injection pump. A simple low-pressure fuel-feed-pump is used instead to supply the injectio ...
system was added to the engine's cylinder head and tested. Friedrich Sass argues that, it can be presumed that Diesel copied the concept of air-blast injection from George B. Brayton, albeit that Diesel substantially improved the system. On 17 February 1894, the redesigned engine ran for 88 revolutions – one minute; with this news, Maschinenfabrik Augsburg's stock rose by 30%, indicative of the tremendous anticipated demands for a more efficient engine. On 26 June 1895, the engine achieved an effective efficiency of 16.6% and had a fuel consumption of 519 g·kW−1·h−1.
However, despite proving the concept, the engine caused problems, and Diesel could not achieve any substantial progress. Therefore, Krupp considered rescinding the contract they had made with Diesel. Diesel was forced to improve the design of his engine and rushed to construct a third prototype engine. Between 8 November and 20 December 1895, the second prototype had successfully covered over 111 hours on the test bench. In the January 1896 report, this was considered a success.
In February 1896, Diesel considered supercharging the third prototype. Imanuel Lauster, who was ordered to draw the third prototype " Motor 250/400", had finished the drawings by 30 April 1896. During summer that year the engine was built, it was completed on 6 October 1896. Tests were conducted until early 1897. First public tests began on 1 February 1897. Moritz Schröter's test on 17 February 1897 was the main test of Diesel's engine. The engine was rated 13.1 kW with a specific fuel consumption of 324 g·kW−1·h−1, resulting in an effective efficiency of 26.2%. By 1898, Diesel had become a millionaire.
Timeline
1890s
* 1893:Rudolf Diesel
Rudolf Christian Karl Diesel (, ; 18 March 1858 – 29 September 1913) was a German inventor and mechanical engineer who is famous for having invented the diesel engine, which burns diesel fuel; both are named after him.
Early life and educatio ...
's essay titled '' Theory and Construction of a Rational Heat Motor'' appears.
* 1893: February 21, Diesel and the Maschinenfabrik Augsburg sign a contract that allows Diesel to build a prototype engine.
* 1893: February 23, Diesel obtains a patent (RP 67207) titled "''Arbeitsverfahren und Ausführungsart für Verbrennungsmaschinen''" (Working Methods and Techniques for Internal Combustion Engines).
* 1893: April 10, Diesel and Krupp sign a contract that allows Diesel to build a prototype engine.
* 1893: April 24, both Krupp and the Maschinenfabrik Augsburg decide to collaborate and build just a single prototype in Augsburg.
* 1893: July, the first prototype is completed.
* 1893: August 10, Diesel injects fuel (petrol) for the first time, resulting in combustion, destroying the indicator.
* 1893: November 30, Diesel applies for a patent (RP 82168) for a modified combustion process. He obtains it on 12 July 1895.
* 1894: January 18, after the first prototype had been modified to become the second prototype, testing with the second prototype begins.
* 1894: February 17, The second prototype runs for the first time.
* 1895: March 30, Diesel applies for a patent (RP 86633) for a starting process with compressed air.
* 1895: June 26, the second prototype passes brake testing for the first time.
* 1895: Diesel applies for a second patent US Patent # 608845
* 1895: November 8 – December 20, a series of tests with the second prototype is conducted. In total, 111 operating hours are recorded.
* 1896: April 30, Imanuel Lauster completes the third and final prototype's drawings.
* 1896: October 6, the third and final prototype engine is completed.
* 1897: February 1, Diesel's prototype engine is running and finally ready for efficiency testing and production.
* 1897: October 9, Adolphus Busch licenses rights to the diesel engine for the US and Canada.
* 1897: 29 October, Rudolf Diesel obtains a patent (DRP 95680) on supercharging the diesel engine.
* 1898: February 1, the Diesel Motoren-Fabrik Actien-Gesellschaft is registered.
* 1898: March, the first commercial diesel engine, rated 2×30 PS (2×22 kW), is installed in the Kempten plant of the Vereinigte Zündholzfabriken A.G.
* 1898: September 17, the Allgemeine Gesellschaft für Dieselmotoren A.-G. is founded.
* 1899: The first two-stroke diesel engine, invented by Hugo Güldner, is built.
1900s
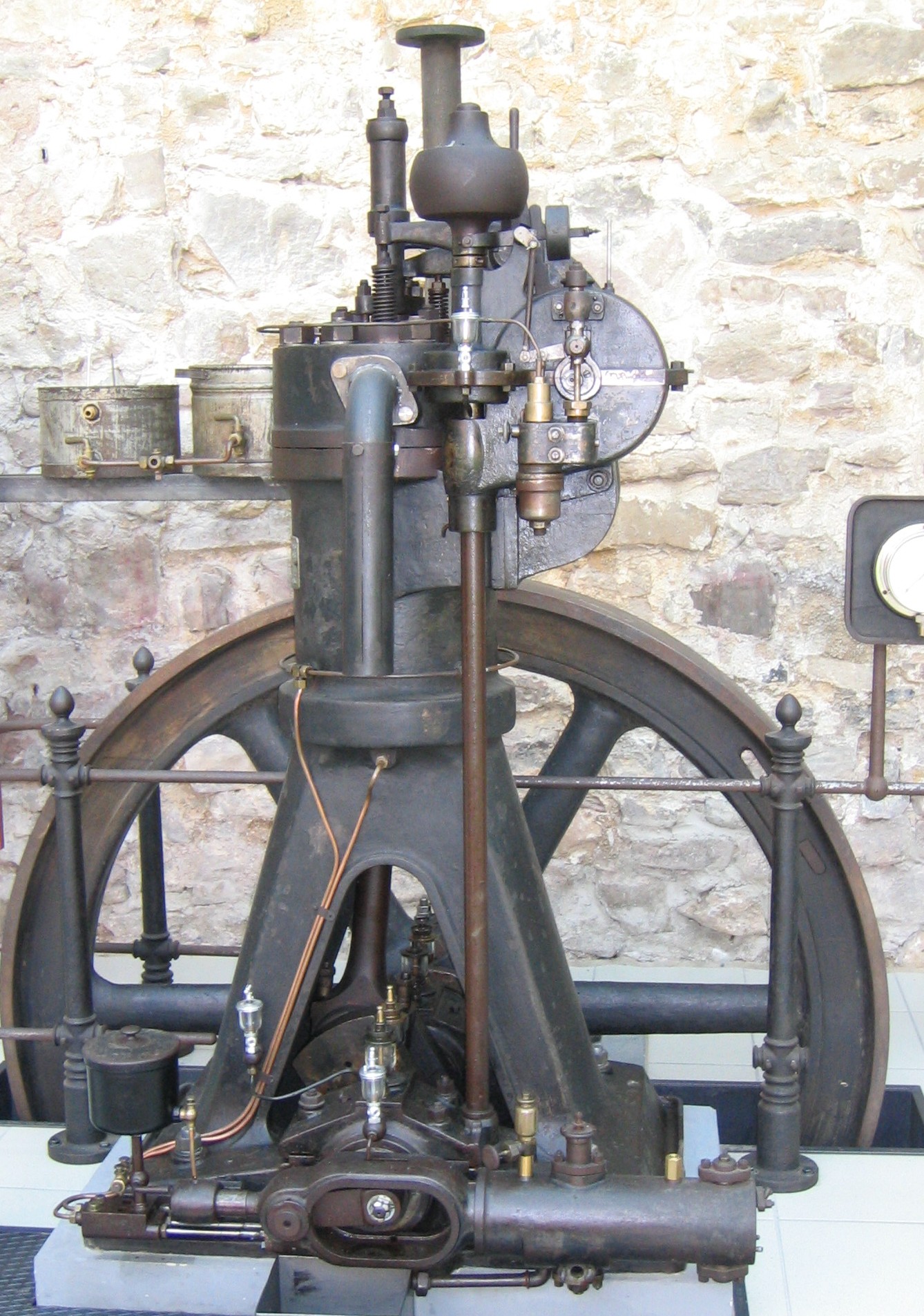
 * 1901: Imanuel Lauster designs the first
* 1901: Imanuel Lauster designs the first trunk piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tig ...
diesel engine (DM 70).
* 1901: By 1901, MAN
A man is an adult male human. Prior to adulthood, a male human is referred to as a boy (a male child or adolescent). Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chrom ...
had produced 77 diesel engine cylinders for commercial use.
* 1903: Two first diesel-powered ships are launched, both for river and canal operations: The ''Vandal
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area bet ...
'' naphtha
Naphtha ( or ) is a flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixture.
Mixtures labelled ''naphtha'' have been produced from natural gas condensates, petroleum distillates, and the distillation of coal tar and peat. In different industries and regions ...
tanker and the '' Sarmat''.
* 1904: The French launch the first diesel submarine, the Aigrette
The term aigrette (; from the French for egret, or ''lesser white heron'') refers to the tufted crest or head-plumes of the egret, used for adorning a headdress. The word may also identify any similar ornament, in gems.
History and description
...
.
* 1905: January 14: Diesel applies for a patent on unit injection (L20510I/46a).
* 1905: The first diesel engine turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pr ...
s and intercooler
An intercooler is a heat exchanger used to cool a gas after compression. Often found in turbocharged engines, intercoolers are also used in air compressors, air conditioners, refrigeration and gas turbines.
Internal combustion engines
...
s are manufactured by Büchi.
* 1906: The Diesel Motoren-Fabrik Actien-Gesellschaft is dissolved.
* 1908: Diesel's patents expire.
* 1908: The first lorry
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame constructi ...
(truck) with a diesel engine appears.
* 1909: March 14, Prosper L'Orange applies for a patent on precombustion chamber injection. He later builds the first diesel engine with this system.
1910s
* 1910: MAN starts making two-stroke diesel engines. * 1910: November 26, James McKechnie applies for a patent on unit injection. Unlike Diesel, he managed to successfully build working unit injectors. * 1911: November 27, the Allgemeine Gesellschaft für Dieselmotoren A.-G. is dissolved. * 1911: The Germania shipyard in Kiel builds 850 PS (625 kW) diesel engines for German submarines. These engines are installed in 1914. * 1912: MAN builds the first double-acting piston two-stroke diesel engine. * 1912: The first locomotive with a diesel engine is used on the Swiss Winterthur-Romanshorn railroad. * 1912: The '' Selandia'' is the first ocean-going ship with diesel engines. * 1913: NELSECO diesels are installed on commercial ships andUS Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
submarines.
* 1913: September 29, Rudolf Diesel
Rudolf Christian Karl Diesel (, ; 18 March 1858 – 29 September 1913) was a German inventor and mechanical engineer who is famous for having invented the diesel engine, which burns diesel fuel; both are named after him.
Early life and educatio ...
dies mysteriously when crossing the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" ( Cotentinais) or (Jèrriais), ( Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kan ...
on the .
* 1914: MAN builds 900 PS (662 kW) two-stroke engines for Dutch submarines.
* 1919: Prosper L'Orange obtains a patent on a Precombustion chamber insert incorporating a needle injection nozzle. First diesel engine from Cummins
Cummins Inc. is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and distributes engines, filtration, and power generation products. Cummins also services engines and related equipment, including fuel systems, controls, air ...
.
1920s
 * 1923: At the Königsberg DLG exhibition, the first agricultural tractor with a diesel engine, the prototype Benz-Sendling S6, is presented.
* 1923: December 15, the first
* 1923: At the Königsberg DLG exhibition, the first agricultural tractor with a diesel engine, the prototype Benz-Sendling S6, is presented.
* 1923: December 15, the first lorry
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame constructi ...
with a direct-injected diesel engine is tested by MAN. The same year, Benz builds a lorry with a pre-combustion chamber injected diesel engine.
* 1923: The first two-stroke diesel engine with counterflow scavenging appears.
* 1924: Fairbanks-Morse
Fairbanks, Morse and Company was an American manufacturing company in the late 19th and early 20th century. Originally a weighing scale manufacturer, it later diversified into pumps, engines, windmills, coffee grinders, radios, farm tractors, ...
introduces the two-stroke Y-VA (later renamed to Model 32).
* 1925: Sendling starts mass-producing a diesel-powered agricultural tractor.
* 1927: Bosch introduces the first inline injection pump for motor vehicle diesel engines.
* 1929: The first passenger car with a diesel engine appears. Its engine is an Otto engine modified to use the diesel principle and Bosch's injection pump. Several other diesel car prototypes follow.
1930s
* 1933: Junkers Motorenwerke in Germany start production of the most successful mass-produced aviation diesel engine of all time, theJumo 205
The Jumo 205 aircraft engine was the most famous of a series of aircraft diesel engines produced by Junkers. The Jumo 204 first entered service in 1932. Later engines of this type comprised the experimental Jumo 206 and Jumo 208, with the Jumo 2 ...
. By the outbreak of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, over 900 examples are produced. Its rated take-off power is 645 kW.
* 1933: General Motors uses its new roots-blown, unit-injected two-stroke Winton 201A diesel engine to power its automotive assembly exhibit at the Chicago World's Fair ('' A Century of Progress''). The engine is offered in several versions ranging from 600 to 900 hp (447–671 kW).
* 1934: The Budd Company builds the first diesel–electric passenger train in the US, the '' Pioneer Zephyr 9900'', using a Winton engine.
* 1935: The Citroën Rosalie
The original Citroën Rosalie was a light-weight racing car that established a succession of records at the Montlhéry racing circuit. More generally the Rosalie was a range of three models/sizes of automobile that comprised the core of Citro� ...
is fitted with an early swirl chamber injected diesel engine for testing purposes. Daimler-Benz
The Mercedes-Benz Group AG (previously named Daimler-Benz, DaimlerChrysler and Daimler) is a German multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Stuttgart, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is one of the world's leading car manufactu ...
starts manufacturing the Mercedes-Benz OM 138
The Mercedes-Benz OM 138 is a diesel engine manufactured by Daimler-Benz. In total, 5,719 units were produced between 1935 and 1940.According to Oswald, 1,082 engines were made for the L 1100 and 2,670 were made for the L 1500. Daimler says ...
, the first mass-produced diesel engine for passenger cars, and one of the few marketable passenger car diesel engines of its time. It is rated 45 PS (33 kW).
* 1936: March 4, the airship LZ 129 Hindenburg
LZ 129 ''Hindenburg'' (; Registration: D-LZ 129) was a German commercial passenger-carrying rigid airship, the lead ship of the ''Hindenburg'' class, the longest class of flying machine and the largest airship by envelope volume. It was de ...
, the biggest aircraft ever made, takes off for the first time. She is powered by four V16 Daimler-Benz LOF 6 diesel engines, rated 1200 PS (883 kW) each.
* 1936: Manufacture of the first mass-produced passenger car with a diesel engine ( Mercedes-Benz 260 D) begins.
* 1937: Konstantin Fyodorovich Chelpan develops the V-2 diesel engine, later used in the Soviet T-34
The T-34 is a Soviet medium tank introduced in 1940. When introduced its 76.2 mm (3 in) tank gun was less powerful than its contemporaries while its 60-degree sloped armour provided good protection against anti-tank weapons. The Chri ...
tanks, widely regarded as the best tank chassis of World War II.
* 1938: General Motors forms the GM Diesel Division, later to become Detroit Diesel, and introduces the Series 71 inline high-speed medium-horsepower two-stroke
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes (up and down movements) of the piston during one power cycle, this power cycle being completed in one revolution of t ...
engine, suitable for road vehicles and marine use.
1940s
* 1946: Clessie Cummins obtains a patent on a ''fuel feeding and injection apparatus for oil-burning engines'' that incorporates separate components for generating injection pressure and injection timing. * 1946: Klöckner-Humboldt-Deutz (KHD) introduces an air-cooled mass-production diesel engine to the market.1950s
 * 1950s:
* 1950s: KHD
KHD Humboldt Wedag is an engineering company that supplies machinery, parts, and services, including process engineering and project management to the global cement industry. The holding company KHD Humboldt Wedag International AG, based in ...
becomes the air-cooled diesel engine global market leader.
* 1951: J. Siegfried Meurer obtains a patent on the '' M-System'', a design that incorporates a central sphere combustion chamber in the piston (DBP 865683).
* 1953: First mass-produced swirl chamber injected passenger car diesel engine (Borgward/Fiat).
* 1954: Daimler-Benz introduces the Mercedes-Benz OM 312 A, a 4.6 litre straight-6 series-production industrial diesel engine with a turbocharger, rated 115 PS (85 kW). It proves to be unreliable.
* 1954: Volvo
The Volvo Group ( sv, Volvokoncernen; legally Aktiebolaget Volvo, shortened to AB Volvo, stylized as VOLVO) is a Swedish multinational manufacturing corporation headquartered in Gothenburg. While its core activity is the production, distributio ...
produces a small batch series of 200 units of a turbocharged version of the TD 96 engine. This 9.6 litre engine is rated 136 kW.
* 1955: Turbocharging for MAN two-stroke marine diesel engines becomes standard.
* 1959: The Peugeot 403 becomes the first mass-produced passenger sedan/saloon manufactured outside West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
to be offered with a diesel engine option.
1960s
 * 1964: Summer, Daimler-Benz switches from precombustion chamber injection to helix-controlled direct injection.
* 1962–65: A diesel compression braking system, eventually to be manufactured by the Jacobs Manufacturing Company and nicknamed the "Jake Brake", is invented and patented by Clessie Cummins.
* 1964: Summer, Daimler-Benz switches from precombustion chamber injection to helix-controlled direct injection.
* 1962–65: A diesel compression braking system, eventually to be manufactured by the Jacobs Manufacturing Company and nicknamed the "Jake Brake", is invented and patented by Clessie Cummins.
1970s
* 1972: KHD introduces the AD-System, ''Allstoff-Direkteinspritzung'', (anyfuel direct-injection), for its diesel engines. AD-diesels can operate on virtually any kind of liquid fuel, but they are fitted with an auxiliary spark plug that fires if the ignition quality of the fuel is too low. * 1976: Development of thecommon rail
Common rail direct fuel injection is a direct fuel injection system built around a high-pressure (over ) fuel rail feeding solenoid valves, as opposed to a low-pressure fuel pump feeding unit injectors (or pump nozzles). High-pressure injectio ...
injection begins at the ETH Zürich.
* 1976: The Volkswagen Golf
The Volkswagen Golf () is a compact car/ small family car ( C-segment) produced by the German automotive manufacturer Volkswagen since 1974, marketed worldwide across eight generations, in various body configurations and under various namepla ...
becomes the first compact passenger sedan/saloon to be offered with a diesel engine option.
* 1978: Daimler-Benz produces the first passenger car diesel engine with a turbocharger ( Mercedes-Benz OM 617).
* 1979: First prototype of a low-speed two-stroke crosshead engine with common rail injection.
1980s
 * 1981/82: Uniflow scavenging for two-stroke marine diesel engines becomes standard.
* 1985: December, road testing of a common rail injection system for lorries using a modified 6VD 12,5/12 GRF-E engine in an IFA W50 takes place.
* 1986: The BMW E28 524td is the world's first passenger car equipped with an electronically controlled injection pump (developed by Bosch).
* 1987: Daimler-Benz introduces the electronically controlled injection pump for lorry diesel engines.
* 1988: The Fiat Croma becomes the first mass-produced passenger car in the world to have a direct injected diesel engine.
* 1989: The Audi 100 is the first passenger car in the world with a turbocharged, direct injected, and electronically controlled diesel engine.
* 1981/82: Uniflow scavenging for two-stroke marine diesel engines becomes standard.
* 1985: December, road testing of a common rail injection system for lorries using a modified 6VD 12,5/12 GRF-E engine in an IFA W50 takes place.
* 1986: The BMW E28 524td is the world's first passenger car equipped with an electronically controlled injection pump (developed by Bosch).
* 1987: Daimler-Benz introduces the electronically controlled injection pump for lorry diesel engines.
* 1988: The Fiat Croma becomes the first mass-produced passenger car in the world to have a direct injected diesel engine.
* 1989: The Audi 100 is the first passenger car in the world with a turbocharged, direct injected, and electronically controlled diesel engine.
1990s
* 1992: 1 July, the Euro 1 emission standard comes into effect. * 1993: First passenger car diesel engine with four valves per cylinder, the Mercedes-Benz OM 604. * 1994: Unit injector system by Bosch for lorry diesel engines. * 1996: First diesel engine with direct injection and four valves per cylinder, used in theOpel Vectra
The Opel Vectra is a mid-size car ( large family car) that was engineered and produced by the German automaker Opel from 1988 until 2010. Available in saloon, hatchback and estate body styles, the Vectra was also sold by the Vauxhall marq ...
.
* 1996: First radial piston distributor injection pump by Bosch.
* 1997: First mass-produced common rail
Common rail direct fuel injection is a direct fuel injection system built around a high-pressure (over ) fuel rail feeding solenoid valves, as opposed to a low-pressure fuel pump feeding unit injectors (or pump nozzles). High-pressure injectio ...
diesel engine for a passenger car, the Fiat 1.9 JTD.
* 1998: BMW wins the 24 Hours Nürburgring race with a modified BMW E36. The car, called 320d, is powered by a 2-litre, straight-four diesel engine with direct injection and a helix-controlled distributor injection pump (Bosch VP 44), producing 180 kW. The fuel consumption is 23 L/100 km, only half the fuel consumption of a similar Otto-powered car.
* 1998: Volkswagen
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post ...
introduces the VW EA188 Pumpe-Düse engine (1.9 TDI), with Bosch-developed electronically controlled unit injectors.
* 1999: Daimler-Chrysler presents the first common rail
Common rail direct fuel injection is a direct fuel injection system built around a high-pressure (over ) fuel rail feeding solenoid valves, as opposed to a low-pressure fuel pump feeding unit injectors (or pump nozzles). High-pressure injectio ...
three-cylinder diesel engine used in a passenger car (the Smart City Coupé).
2000s
 * 2000: Peugeot introduces the diesel particulate filter for passenger cars.
* 2002:
* 2000: Peugeot introduces the diesel particulate filter for passenger cars.
* 2002: Piezoelectric
Piezoelectricity (, ) is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied mechanical stress. The word ' ...
injector technology by Siemens.
* 2003: Piezoelectric injector technology by Bosch, and Delphi.
* 2004: BMW introduces dual-stage turbocharging with the BMW M57 engine.
* 2006: The world's most powerful diesel engine, the Wärtsilä RT-flex96C
Wärtsilä Oyj Abp (), trading internationally as Wärtsilä Corporation, is a Finnish company which manufactures and services power sources and other equipment in the marine and energy markets. The core products of Wärtsilä include technolo ...
, is produced. It is rated 80,080 kW.
* 2006: Audi R10 TDI, equipped with a 5.5-litre V12-TDI engine, rated 476 kW, wins the 2006 24 Hours of Le Mans.
* 2006: Daimler-Chrysler launches the first series-production passenger car engine with selective catalytic reduction
Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) is a means of converting nitrogen oxides, also referred to as with the aid of a catalyst into diatomic nitrogen (), and water (). A reductant, typically anhydrous ammonia (), aqueous ammonia (), or a urea ...
exhaust gas treatment, the Mercedes-Benz OM 642. It is fully complying with the Tier2Bin8 emission standard.
* 2008: Volkswagen introduces the LNT catalyst for passenger car diesel engines with the VW 2.0 TDI engine.
* 2008: Volkswagen starts series production of the biggest passenger car diesel engine, the Audi 6-litre V12 TDI.
* 2008: Subaru introduces the first horizontally opposed
A flat engine is a piston engine where the cylinders are located on either side of a central crankshaft. Flat engines are also known as horizontally opposed engines, however this is distinct from the less common opposed-piston engine design, w ...
diesel engine to be fitted to a passenger car. It is a 2-litre common rail engine, rated 110 kW.
2010s
* 2010:Mitsubishi
The is a group of autonomous Japanese multinational companies in a variety of industries.
Founded by Yatarō Iwasaki in 1870, the Mitsubishi Group historically descended from the Mitsubishi zaibatsu, a unified company which existed from 187 ...
developed and started mass production of its 4N13 1.8 L DOHC I4, the world's first passenger car diesel engine that features a variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with varia ...
system.
* 2012: BMW introduces dual-stage turbocharging with three turbochargers for the BMW N57 engine.
* 2015: Common rail
Common rail direct fuel injection is a direct fuel injection system built around a high-pressure (over ) fuel rail feeding solenoid valves, as opposed to a low-pressure fuel pump feeding unit injectors (or pump nozzles). High-pressure injectio ...
systems working with pressures of 2,500 bar launched.
* 2015: In the Volkswagen emissions scandal
The Volkswagen emissions scandal, sometimes known as Dieselgate or Emissionsgate, began in September 2015, when the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) issued a notice of violation of the Clean Air Act to German automaker V ...
, the US EPA
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an Independent agencies of the United States government, independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon pro ...
issued a notice of violation of the Clean Air Act to Volkswagen Group
Volkswagen AG (), known internationally as the Volkswagen Group, is a German multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. The company designs, manufactures and distributes passenger and commercial ...
after it was found that Volkswagen had intentionally programmed turbocharged direct injection
TDI (Turbocharged Direct Injection) is Volkswagen Group's term for its current common rail direct injection turbodiesel engine range that have an intercooler in addition to the turbo compressor.
TDI engines are used in motor vehicles sold by th ...
(TDI) diesel engines to activate certain emissions controls only during laboratory emissions testing
Vehicle emissions control is the study of reducing the emissions produced by motor vehicles, especially internal combustion engines.
Types of emissions
Emissions of many air pollutants have been shown to have variety of negative effects on public ...
.
Operating principle
Overview
The characteristics of a diesel engine are * Use of compression ignition, instead of an ignition apparatus such as aspark plug
A spark plug (sometimes, in British English, a sparking plug, and, colloquially, a plug) is a device for delivering electric current from an ignition system to the combustion chamber of a spark-ignition engine to ignite the compressed fuel/air ...
.
* Internal mixture formation. In diesel engines, the mixture of air and fuel is only formed inside the combustion chamber.
* Quality torque control. The amount of torque a diesel engine produces is not controlled by throttling the intake air (unlike a traditional spark-ignition petrol engine, where the airflow is reduced in order to regulate the torque output), instead, the volume of air entering the engine is maximised at all times, and the torque output is regulated solely by controlling the amount of injected fuel.
* High air-fuel ratio. Diesel engines run at global air-fuel ratios significantly leaner than the stoichiometric ratio.
* Diffusion flame: At combustion, oxygen first has to diffuse into the flame, rather than having oxygen and fuel already mixed before combustion, which would result in a premixed flame.
* Heterogeneous
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts often used in the sciences and statistics relating to the uniformity of a substance or organism. A material or image that is homogeneous is uniform in composition or character (i.e. color, shape, siz ...
air-fuel mixture: In diesel engines, there is no even dispersion of fuel and air inside the cylinder. That is because the combustion process begins at the end of the injection phase, before a homogeneous mixture of air and fuel can be formed.
* Preference for the fuel to have a high ignition performance (Cetane number
Cetane number (cetane rating) is an indicator of the combustion speed of diesel fuel and compression needed for ignition. It plays a similar role for diesel as octane rating does for gasoline. The CN is an important factor in determining the qu ...
), rather than a high knocking resistance ( octane rating) that is preferred for petrol engines.
Thermodynamic cycle
Otto cycle
An Otto cycle is an idealized thermodynamic cycle that describes the functioning of a typical spark ignition piston engine. It is the thermodynamic cycle most commonly found in automobile engines.
The Otto cycle is a description of what ha ...
by using highly compressed hot air to ignite the fuel rather than using a spark plug (''compression ignition'' rather than ''spark ignition'').
In the diesel engine, only air is initially introduced into the combustion chamber. The air is then compressed with a compression ratio typically between 15:1 and 23:1. This high compression causes the temperature of the air to rise. At about the top of the compression stroke, fuel is injected directly into the compressed air in the combustion chamber. This may be into a (typically toroidal) void in the top of the piston or a ''pre-chamber'' depending upon the design of the engine. The fuel injector ensures that the fuel is broken down into small droplets, and that the fuel is distributed evenly. The heat of the compressed air vaporises fuel from the surface of the droplets. The vapour is then ignited by the heat from the compressed air in the combustion chamber, the droplets continue to vaporise from their surfaces and burn, getting smaller, until all the fuel in the droplets has been burnt. Combustion occurs at a substantially constant pressure during the initial part of the power stroke. The start of vaporisation causes a delay before ignition and the characteristic diesel knocking sound as the vapour reaches ignition temperature and causes an abrupt increase in pressure above the piston (not shown on the P-V indicator diagram). When combustion is complete the combustion gases expand as the piston descends further; the high pressure in the cylinder drives the piston downward, supplying power to the crankshaft.
As well as the high level of compression allowing combustion to take place without a separate ignition system, a high compression ratio
The compression ratio is the ratio between the volume of the cylinder and combustion chamber in an internal combustion engine at their maximum and minimum values.
A fundamental specification for such engines, it is measured two ways: the stat ...
greatly increases the engine's efficiency. Increasing the compression ratio in a spark-ignition engine where fuel and air are mixed before entry to the cylinder is limited by the need to prevent pre-ignition, which would cause engine damage. Since only air is compressed in a diesel engine, and fuel is not introduced into the cylinder until shortly before top dead centre (TDC TDC may refer to:
Organisations
* Hong Kong Trade Development Council
* Taiwan Design Center, an art organization based in Taipei, Taiwan
* TDC A/S, a Danish telecommunications company
* Teradata Corporation (U.S. ticker symbol)
* Texas Departm ...
), premature detonation is not a problem and compression ratios are much higher.
The p–V diagram is a simplified and idealised representation of the events involved in a diesel engine cycle, arranged to illustrate the similarity with a Carnot cycle
A Carnot cycle is an ideal thermodynamic cycle proposed by French physicist Sadi Carnot in 1824 and expanded upon by others in the 1830s and 1840s. By Carnot's theorem, it provides an upper limit on the efficiency of any classical thermodynam ...
. Starting at 1, the piston is at bottom dead centre and both valves are closed at the start of the compression stroke; the cylinder contains air at atmospheric pressure. Between 1 and 2 the air is compressed adiabatically – that is without heat transfer to or from the environment – by the rising piston. (This is only approximately true since there will be some heat exchange with the cylinder walls
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infini ...
.) During this compression, the volume is reduced, the pressure and temperature both rise. At or slightly before 2 (TDC) fuel is injected and burns in the compressed hot air. Chemical energy is released and this constitutes an injection of thermal energy (heat) into the compressed gas. Combustion and heating occur between 2 and 3. In this interval the pressure remains constant since the piston descends, and the volume increases; the temperature rises as a consequence of the energy of combustion. At 3 fuel injection and combustion are complete, and the cylinder contains gas at a higher temperature than at 2. Between 3 and 4 this hot gas expands, again approximately adiabatically. Work is done on the system to which the engine is connected. During this expansion phase the volume of the gas rises, and its temperature and pressure both fall. At 4 the exhaust valve opens, and the pressure falls abruptly to atmospheric (approximately). This is unresisted expansion and no useful work is done by it. Ideally the adiabatic expansion should continue, extending the line 3–4 to the right until the pressure falls to that of the surrounding air, but the loss of efficiency caused by this unresisted expansion is justified by the practical difficulties involved in recovering it (the engine would have to be much larger). After the opening of the exhaust valve, the exhaust stroke follows, but this (and the following induction stroke) are not shown on the diagram. If shown, they would be represented by a low-pressure loop at the bottom of the diagram. At 1 it is assumed that the exhaust and induction strokes have been completed, and the cylinder is again filled with air. The piston-cylinder system absorbs energy between 1 and 2 – this is the work needed to compress the air in the cylinder, and is provided by mechanical kinetic energy stored in the flywheel of the engine. Work output is done by the piston-cylinder combination between 2 and 4. The difference between these two increments of work is the indicated work output per cycle, and is represented by the area enclosed by the p–V loop. The adiabatic expansion is in a higher pressure range than that of the compression because the gas in the cylinder is hotter during expansion than during compression. It is for this reason that the loop has a finite area, and the net output of work during a cycle is positive.
Efficiency
The fuel efficiency of diesel engines is better than most other types of combustion engines, due to their high compression ratio, high air-fuel ratio#Air–fuel equivalence ratio (λ), air–fuel equivalence ratio (λ), and the lack of intake air restrictions (i.e. throttle valves). Theoretically, the highest possible efficiency for a diesel engine is 75%. However, in practice the efficiency is much lower, with efficiencies of up to 43% for passenger car engines, up to 45% for large truck and bus engines, and up to 55% for large two-stroke marine engines. The average efficiency over a motor vehicle driving cycle is lower than the diesel engine's peak efficiency (for example, a 37% average efficiency for an engine with a peak efficiency of 44%). That is because the fuel efficiency of a diesel engine drops at lower loads, however, it does not drop quite as fast as the Otto (spark ignition) engine's.Emissions
Diesel engines are combustion engines and, therefore, emit combustion products in their exhaust gas. Due to incomplete combustion, diesel engine exhaust gases include carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, Particulates, particulate matter, and nitrogen oxides pollutants. About 90 per cent of the pollutants can be removed from the exhaust gas using exhaust gas treatment technology. Road vehicle diesel engines have no sulphur dioxide emissions, because motor vehicle diesel fuel has been sulphur free since 2003. Helmut Tschöke argues that particulate matter emitted from motor vehicles has negative impacts on human health. The particulate matter in diesel exhaust emissions is sometimes classified as a carcinogen or "probable carcinogen" and is known to increase the risk of heart and respiratory diseases.Electrical system
In principle, a diesel engine does not require any sort of electrical system. However, most modern diesel engines are equipped with an electrical fuel pump, and an electronic engine control unit. However, there is no high-voltage electrical ignition system present in a diesel engine. This eliminates a source of Electromagnetic interference, radio frequency emissions (which can interfere with navigation and communication equipment), which is why only diesel-powered vehicles are allowed in some parts of the American National Radio Quiet Zone.Torque control
To control the torque output at any given time (i.e. when the driver of a car adjusts the accelerator pedal, a governor (device), governor adjusts the amount of fuel injected into the engine. Mechanical governors have been used in the past, however electronic governors are more common on modern engines. Mechanical governors are usually driven by the engine's Serpentine belt, accessory belt or a gear-drive system and use a combination of springs and weights to control fuel delivery relative to both load and speed. Electronically-governed engines use an electronic control unit (ECU) or electronic control module (ECM) to control the fuel delivery. The ECM/ECU uses various sensors (such as engine speed signal, intake manifold pressure and fuel temperature) to determine the amount of fuel injected into the engine. Due to the amount of air being constant (for a given RPM) while the amount of fuel varies, very high ("lean") air-fuel ratios are used in situations where minimal torque output is required. This differs from a petrol engine, where a throttle is used to also reduce the amount of intake air as part of regulating the engine's torque output. Controlling the timing of the start of injection of fuel into the cylinder is similar to controlling the ignition timing in a petrol engine. It is therefore a key factor in controlling the power output, fuel consumption and exhaust emissions.Classification
There are several different ways of categorising diesel engines, as outlined in the following sections.RPM operating range
Günter Mau categorises diesel engines by their rotational speeds into three groups: * High-speed engines (> 1,000 rpm), * Medium-speed engines (300–1,000 rpm), and * Slow-speed engines (< 300 rpm). ; High-speed diesel engines High-speed engines are used to power trucks (lorries), buses, tractors, automobile, cars, yachts, Gas compressor, compressors, pumps and small electrical generators. As of 2018, most high-speed engines have Direct fuel injection, direct injection. Many modern engines, particularly in on-highway applications, havecommon rail
Common rail direct fuel injection is a direct fuel injection system built around a high-pressure (over ) fuel rail feeding solenoid valves, as opposed to a low-pressure fuel pump feeding unit injectors (or pump nozzles). High-pressure injectio ...
Direct fuel injection, direct injection. On bigger ships, high-speed diesel engines are often used for powering electric generators. The highest power output of high-speed diesel engines is approximately 5 MW.
; Medium-speed diesel engines
 Medium-speed engines are used in large electrical generators, railway diesel locomotives, ship propulsion and mechanical drive applications such as large compressors or pumps. Medium speed diesel engines operate on either diesel fuel or heavy fuel oil by direct injection in the same manner as low-speed engines. Usually, they are four-stroke engines with trunk pistons; a notable exception being the EMD 567, EMD 645, 645, and EMD 710, 710 engines, which are all two-stroke.
The power output of medium-speed diesel engines can be as high as 21,870 kW, with the effective efficiency being around 47...48% (1982). Most larger medium-speed engines are started with compressed air direct on pistons, using an air distributor, as opposed to a pneumatic starting motor acting on the flywheel, which tends to be used for smaller engines.
Medium-speed engines intended for marine applications are usually used to power (Roll-on/roll-off, ro-ro) ferries, passenger ships or small freight ships. Using medium-speed engines reduces the cost of smaller ships and increases their transport capacity. In addition to that, a single ship can use two smaller engines instead of one big engine, which increases the ship's safety.
; Low-speed diesel engines
Medium-speed engines are used in large electrical generators, railway diesel locomotives, ship propulsion and mechanical drive applications such as large compressors or pumps. Medium speed diesel engines operate on either diesel fuel or heavy fuel oil by direct injection in the same manner as low-speed engines. Usually, they are four-stroke engines with trunk pistons; a notable exception being the EMD 567, EMD 645, 645, and EMD 710, 710 engines, which are all two-stroke.
The power output of medium-speed diesel engines can be as high as 21,870 kW, with the effective efficiency being around 47...48% (1982). Most larger medium-speed engines are started with compressed air direct on pistons, using an air distributor, as opposed to a pneumatic starting motor acting on the flywheel, which tends to be used for smaller engines.
Medium-speed engines intended for marine applications are usually used to power (Roll-on/roll-off, ro-ro) ferries, passenger ships or small freight ships. Using medium-speed engines reduces the cost of smaller ships and increases their transport capacity. In addition to that, a single ship can use two smaller engines instead of one big engine, which increases the ship's safety.
; Low-speed diesel engines
 Low-speed diesel engines are usually very large in size and mostly used to power ships. There are two different types of low-speed engines that are commonly used: Two-stroke engines with a crosshead, and four-stroke engines with a regular trunk-piston. Two-stroke engines have a limited rotational frequency and their charge exchange is more difficult, which means that they are usually bigger than four-stroke engines and used to directly power a ship's propeller. Four-stroke engines on ships are usually used to power an electric generator. An electric motor powers the propeller. Both types are usually very undersquare. Low-speed diesel engines (as used in ships and other applications where overall engine weight is relatively unimportant) often have an effective efficiency of up to 55%. Like medium-speed engines, low-speed engines are started with compressed air, and they use heavy oil as their primary fuel.
Low-speed diesel engines are usually very large in size and mostly used to power ships. There are two different types of low-speed engines that are commonly used: Two-stroke engines with a crosshead, and four-stroke engines with a regular trunk-piston. Two-stroke engines have a limited rotational frequency and their charge exchange is more difficult, which means that they are usually bigger than four-stroke engines and used to directly power a ship's propeller. Four-stroke engines on ships are usually used to power an electric generator. An electric motor powers the propeller. Both types are usually very undersquare. Low-speed diesel engines (as used in ships and other applications where overall engine weight is relatively unimportant) often have an effective efficiency of up to 55%. Like medium-speed engines, low-speed engines are started with compressed air, and they use heavy oil as their primary fuel.
Combustion cycle

 Four-stroke engines use the combustion cycle described earlier.
Two-stroke diesel engine, Two-stroke engines use a combustion cycle which is completed in two strokes instead of four strokes. Filling the cylinder with air and compressing it takes place in one stroke, and the power and exhaust strokes are combined. The compression in a two-stroke diesel engine is similar to the compression that takes place in a four-stroke diesel engine: As the piston passes through bottom centre and starts upward, compression commences, culminating in fuel injection and ignition. Instead of a full set of valves, two-stroke diesel engines have simple intake ports, and exhaust ports (or exhaust valves). When the piston approaches bottom dead centre, both the intake and the exhaust ports are "open", which means that there is atmospheric pressure inside the cylinder. Therefore, some sort of pump is required to blow the air into the cylinder and the combustion gasses into the exhaust. This process is called ''scavenging''. The pressure required is approximately 10 - 30 kPa.
Due to the lack of discrete exhaust and intake strokes, all two-stroke diesel engines use a scavenge blower or some form of compressor to charge the cylinders with air and assist in scavenging. Roots-type superchargers were used for ship engines until the mid-1950s, however since 1955 they have been widely replaced by turbochargers. Usually, a two-stroke ship diesel engine has a single-stage turbocharger with a turbine that has an axial inflow and a radial outflow.
Four-stroke engines use the combustion cycle described earlier.
Two-stroke diesel engine, Two-stroke engines use a combustion cycle which is completed in two strokes instead of four strokes. Filling the cylinder with air and compressing it takes place in one stroke, and the power and exhaust strokes are combined. The compression in a two-stroke diesel engine is similar to the compression that takes place in a four-stroke diesel engine: As the piston passes through bottom centre and starts upward, compression commences, culminating in fuel injection and ignition. Instead of a full set of valves, two-stroke diesel engines have simple intake ports, and exhaust ports (or exhaust valves). When the piston approaches bottom dead centre, both the intake and the exhaust ports are "open", which means that there is atmospheric pressure inside the cylinder. Therefore, some sort of pump is required to blow the air into the cylinder and the combustion gasses into the exhaust. This process is called ''scavenging''. The pressure required is approximately 10 - 30 kPa.
Due to the lack of discrete exhaust and intake strokes, all two-stroke diesel engines use a scavenge blower or some form of compressor to charge the cylinders with air and assist in scavenging. Roots-type superchargers were used for ship engines until the mid-1950s, however since 1955 they have been widely replaced by turbochargers. Usually, a two-stroke ship diesel engine has a single-stage turbocharger with a turbine that has an axial inflow and a radial outflow.
Scavenging in two-stroke engines
In general, there are three types of scavenging possible: * Uniflow scavenging * Crossflow scavenging * Schnuerle porting, Reverse flow scavenging Crossflow scavenging is incomplete and limits the stroke, yet some manufacturers used it. Reverse flow scavenging is a very simple way of scavenging, and it was popular amongst manufacturers until the early 1980s. Uniflow scavenging is more complicated to make but allows the highest fuel efficiency; since the early 1980s, manufacturers such as MAN and Sulzer have switched to this system. It is standard for modern marine two-stroke diesel engines.Fuel used
So-called dual-fuel diesel engines or gas diesel engines burn two different types of fuel ''simultaneously'', for instance, a gaseous fuel and diesel engine fuel. The diesel engine fuel auto-ignites due to compression ignition, and then ignites the gaseous fuel. Such engines do not require any type of spark ignition and operate similar to regular diesel engines.Fuel injection
The fuel is injected at high pressure into either the combustion chamber, the "swirl chamber" or the "pre-chamber" (unlike older petrol engines where the fuel is added in the inlet manifold or carburettor). Engines where the fuel is injected into the main combustion chamber are called "direct injection" (DI) engines, while those which use a swirl chamber or pre-chamber are called "indirect injection" (IDI) engines.Direct injection
Common rail
Common rail direct fuel injection is a direct fuel injection system built around a high-pressure (over ) fuel rail feeding solenoid valves, as opposed to a low-pressure fuel pump feeding unit injectors (or pump nozzles). High-pressure injectio ...
(CR) direct injection systems do not have the fuel metering, pressure-raising and delivery functions in a single unit, as in the case of a Bosch distributor-type pump, for example. A high-pressure pump supplies the CR. The requirements of each cylinder injector are supplied from this common high pressure reservoir of fuel. An Electronic Diesel Control (EDC) controls both rail pressure and injections depending on engine operating conditions. The injectors of older CR systems have solenoid-driven plungers for lifting the injection needle, whilst newer CR injectors use plungers driven by piezoelectricity, piezoelectric actuators that have fewer moving mass and therefore allow even more injections in a very short period of time. Early common rail system were controlled by mechanical means.
The injection pressure of modern CR systems ranges from 140 MPa to 270 MPa.
Indirect injection
 An indirect diesel injection system (IDI) engine delivers fuel into a small chamber called a swirl chamber, precombustion chamber, pre chamber or ante-chamber, which is connected to the cylinder by a narrow air passage. Generally the goal of the pre chamber is to create increased turbulence for better air / fuel mixing. This system also allows for a smoother, quieter running engine, and because fuel mixing is assisted by turbulence, injector pressures can be lower. Most IDI systems use a single orifice injector. The pre-chamber has the disadvantage of lowering efficiency due to increased heat loss to the engine's cooling system, restricting the combustion burn, thus reducing the efficiency by 5–10%. IDI engines are also more difficult to start and usually require the use of glow plugs. IDI engines may be cheaper to build but generally require a higher compression ratio than the DI counterpart. IDI also makes it easier to produce smooth, quieter running engines with a simple mechanical injection system since exact injection timing is not as critical. Most modern automotive engines are DI which have the benefits of greater efficiency and easier starting; however, IDI engines can still be found in the many ATV and small diesel applications. Indirect injected diesel engines use pintle-type fuel injectors.
An indirect diesel injection system (IDI) engine delivers fuel into a small chamber called a swirl chamber, precombustion chamber, pre chamber or ante-chamber, which is connected to the cylinder by a narrow air passage. Generally the goal of the pre chamber is to create increased turbulence for better air / fuel mixing. This system also allows for a smoother, quieter running engine, and because fuel mixing is assisted by turbulence, injector pressures can be lower. Most IDI systems use a single orifice injector. The pre-chamber has the disadvantage of lowering efficiency due to increased heat loss to the engine's cooling system, restricting the combustion burn, thus reducing the efficiency by 5–10%. IDI engines are also more difficult to start and usually require the use of glow plugs. IDI engines may be cheaper to build but generally require a higher compression ratio than the DI counterpart. IDI also makes it easier to produce smooth, quieter running engines with a simple mechanical injection system since exact injection timing is not as critical. Most modern automotive engines are DI which have the benefits of greater efficiency and easier starting; however, IDI engines can still be found in the many ATV and small diesel applications. Indirect injected diesel engines use pintle-type fuel injectors.
Air-blast injection
 Early diesel engines injected fuel with the assistance of compressed air, which atomised the fuel and forced it into the engine through a nozzle (a similar principle to an aerosol spray). The nozzle opening was closed by a Needle valve, pin valve actuated by the camshaft. Although the engine was also required to drive an air compressor used for air-blast injection, the efficiency was nonetheless better than other combustion engines of the time. However the system was heavy and it was slow to react to changing torque demands, making it unsuitable for road vehicles.
Early diesel engines injected fuel with the assistance of compressed air, which atomised the fuel and forced it into the engine through a nozzle (a similar principle to an aerosol spray). The nozzle opening was closed by a Needle valve, pin valve actuated by the camshaft. Although the engine was also required to drive an air compressor used for air-blast injection, the efficiency was nonetheless better than other combustion engines of the time. However the system was heavy and it was slow to react to changing torque demands, making it unsuitable for road vehicles.
Unit injectors
A ''unit injector'' system, also known as "Pumpe-Düse" (''pump-nozzle'' in German) combines the injector and fuel pump into a single component, which is positioned above each cylinder. This eliminates the high-pressure fuel lines and achieves a more consistent injection. Under full load, the injection pressure can reach up to 220 MPa. Unit injectors are operated by a cam and the quantity of fuel injected is controlled either mechanically (by a rack or lever) or electronically. Due to increased performance requirementss, unit injectors have been largely replaced by common-rail injection systems.Diesel engine particularities
Mass
The average diesel engine has a poorer power-to-mass ratio than an equivalent petrol engine. The lower engine speeds (RPM) of typical diesel engines results in a lower Power (physics), power output. Also, the mass of a diesel engine is typically higher, since the higher operating pressure inside the combustion chamber increases the internal forces, which requires stronger (and therefore heavier) parts to withstand these forces.Noise ('diesel clatter')
The distinctive noise of a diesel engine, particularly at idling speeds, is sometimes called "diesel clatter". This noise is largely caused by the sudden ignition of the diesel fuel when injected into the combustion chamber, which causes a pressure wave that sounds like knocking. Engine designers can reduce diesel clatter through: indirect injection; pilot or pre-injection; injection timing; injection rate; compression ratio; turbo boost; and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR). Common rail diesel injection systems permit multiple injection events as an aid to noise reduction. Through measures such as these, diesel clatter noise is greatly reduced in modern engines. Diesel fuels with a higher cetane rating are more likely to ignite and hence reduce diesel clatter.Cold weather starting
In warmer climates, diesel engines do not require any starting aid (aside from the Starter (engine), starter motor). However, many diesel engines include some form of preheating for the combustion chamber, to assist starting in cold conditions. Engines with a displacement of less than 1 litre per cylinder usually have glowplugs, whilst larger heavy-duty engines have flame-start systems. The minimum starting temperature that allows starting without pre-heating is 40 °C for precombustion chamber engines, 20 °C for swirl chamber engines, and 0 °C for direct injected engines. In the past, a wider variety of cold-start methods were used. Some engines, such as Detroit Diesel engines used a system to introduce small amounts of Diethyl ether, ether into the inlet manifold to start combustion. Instead of glowplugs, some diesel engines are equipped with starting aid systems that change valve timing. The simplest way this can be done is with a decompression lever. Activating the decompression lever locks the outlet valves in a slight down position, resulting in the engine not having any compression and thus allowing for turning the crankshaft over with significantly less resistance. When the crankshaft reaches a higher speed, flipping the decompression lever back into its normal position will abruptly re-activate the outlet valves, resulting in compression − the flywheel's mass moment of inertia then starts the engine. Other diesel engines, such as the precombustion chamber engine XII Jv 170/240 made by Ganz & Co., have a valve timing changing system that is operated by adjusting the inlet valve camshaft, moving it into a slight "late" position. This will make the inlet valves open with a delay, forcing the inlet air to heat up when entering the combustion chamber.Supercharging & turbocharging
 Forced induction, especially turbocharging is commonly used on diesel engines because it greatly increases efficiency, and torque output. Diesel engines are well suited for forced induction setups due to their operating principle which is characterised by wide ignition limits and the absence of fuel during the compression stroke. Therefore, knocking, pre-ignition or detonation cannot occur, and a lean mixture caused by excess supercharging air inside the combustion chamber does not negatively affect combustion.
Forced induction, especially turbocharging is commonly used on diesel engines because it greatly increases efficiency, and torque output. Diesel engines are well suited for forced induction setups due to their operating principle which is characterised by wide ignition limits and the absence of fuel during the compression stroke. Therefore, knocking, pre-ignition or detonation cannot occur, and a lean mixture caused by excess supercharging air inside the combustion chamber does not negatively affect combustion.
Fuel and fluid characteristics
Diesel engines can combust a huge variety of fuels, including several fuel oils that have advantages over fuels such as petrol. These advantages include: ** Low fuel costs, as fuel oils are relatively cheap ** Good lubrication properties ** High energy density ** Low risk of catching fire, as they do not form a flammable vapour ** Biodiesel is an easily synthesised, non-petroleum-based fuel (through transesterification) which can run directly in many diesel engines, while gasoline engines either need adaptation to run synthetic fuels or else use them as an additive to gasoline (e.g., ethanol added to gasohol). In diesel engines, a mechanical injector system atomizes the fuel directly into the combustion chamber (as opposed to a Aspirator (pump), Venturi jet in a carburetor, or a Fuel injection, fuel injector in a manifold injection system atomizing fuel into the intake manifold or intake runners as in a petrol engine). Because only air is inducted into the cylinder in a diesel engine, the compression ratio can be much higher as there is no risk of pre-ignition provided the injection process is accurately timed. This means that cylinder temperatures are much higher in a diesel engine than a petrol engine, allowing less volatile fuels to be used. Therefore, diesel engines can operate on a huge variety of different fuels. In general, fuel for diesel engines should have a proper viscosity, so that the injection pump can pump the fuel to the injection nozzles without causing damage to itself or corrosion of the fuel line. At injection, the fuel should form a good fuel spray, and it should not have a coking effect upon the injection nozzles. To ensure proper engine starting and smooth operation, the fuel should be willing to ignite and hence not cause a high ignition delay, (this means that the fuel should have a high cetane number). Diesel fuel should also have a high lower heating value.
Inline mechanical injector pumps generally tolerate poor-quality or bio-fuels better than distributor-type pumps. Also, indirect injection engines generally run more satisfactorily on fuels with a high ignition delay (for instance, petrol) than direct injection engines. This is partly because an indirect injection engine has a much greater 'swirl' effect, improving vaporisation and combustion of fuel, and because (in the case of vegetable oil-type fuels) lipid depositions can condense on the cylinder walls of a direct-injection engine if combustion temperatures are too low (such as starting the engine from cold). Direct-injected engines with an M-System, MAN centre sphere combustion chamber rely on fuel condensing on the combustion chamber walls. The fuel starts vaporising only after ignition sets in, and it burns relatively smoothly. Therefore, such engines also tolerate fuels with poor ignition delay characteristics, and, in general, they can operate on petrol rated 86 Octane rating#Research Octane Number (RON), RON.
Therefore, diesel engines can operate on a huge variety of different fuels. In general, fuel for diesel engines should have a proper viscosity, so that the injection pump can pump the fuel to the injection nozzles without causing damage to itself or corrosion of the fuel line. At injection, the fuel should form a good fuel spray, and it should not have a coking effect upon the injection nozzles. To ensure proper engine starting and smooth operation, the fuel should be willing to ignite and hence not cause a high ignition delay, (this means that the fuel should have a high cetane number). Diesel fuel should also have a high lower heating value.
Inline mechanical injector pumps generally tolerate poor-quality or bio-fuels better than distributor-type pumps. Also, indirect injection engines generally run more satisfactorily on fuels with a high ignition delay (for instance, petrol) than direct injection engines. This is partly because an indirect injection engine has a much greater 'swirl' effect, improving vaporisation and combustion of fuel, and because (in the case of vegetable oil-type fuels) lipid depositions can condense on the cylinder walls of a direct-injection engine if combustion temperatures are too low (such as starting the engine from cold). Direct-injected engines with an M-System, MAN centre sphere combustion chamber rely on fuel condensing on the combustion chamber walls. The fuel starts vaporising only after ignition sets in, and it burns relatively smoothly. Therefore, such engines also tolerate fuels with poor ignition delay characteristics, and, in general, they can operate on petrol rated 86 Octane rating#Research Octane Number (RON), RON.
Fuel types
In his 1893 work '' Theory and Construction of a Rational Heat Motor'', Rudolf Diesel considers using coal dust as fuel for the diesel engine. However, Diesel just ''considered'' using coal dust (as well as liquid fuels and gas); his actual engine was designed to operate on petroleum, which was soon replaced with regular petrol and kerosene for further testing purposes, as petroleum proved to be too viscous. In addition to kerosene and petrol, Diesel's engine could also operate on ligroin. Before diesel engine fuel was standardised, fuels such as petrol, kerosene, gas oil, vegetable oil and Lubricant#Mineral oil, mineral oil, as well as mixtures of these fuels, were used. Typical fuels specifically intended to be used for diesel engines were petroleum distillates and creosote, coal-tar distillates such as the following; these fuels have specific lower heating values of: * Diesel oil: 10,200 kcal·kg−1 (42.7 MJ·kg−1) up to 10,250 kcal·kg−1 (42.9 MJ·kg−1) * Heating oil: 10,000 kcal·kg−1 (41.8 MJ·kg−1) up to 10,200 kcal·kg−1 (42.7 MJ·kg−1) * Coal-tar creosote: 9,150 kcal·kg−1 (38.3 MJ·kg−1) up to 9,250 kcal·kg−1 (38.7 MJ·kg−1) * Kerosene: up to 10,400 kcal·kg−1 (43.5 MJ·kg−1) ''Source:'' The first diesel fuel standards were the DIN 51601, VTL 9140-001, and NATO F 54, which appeared after World War II. The modern European EN 590 diesel fuel standard was established in May 1993; the modern version of the NATO F 54 standard is mostly identical wit