Comparison of computer form factors on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
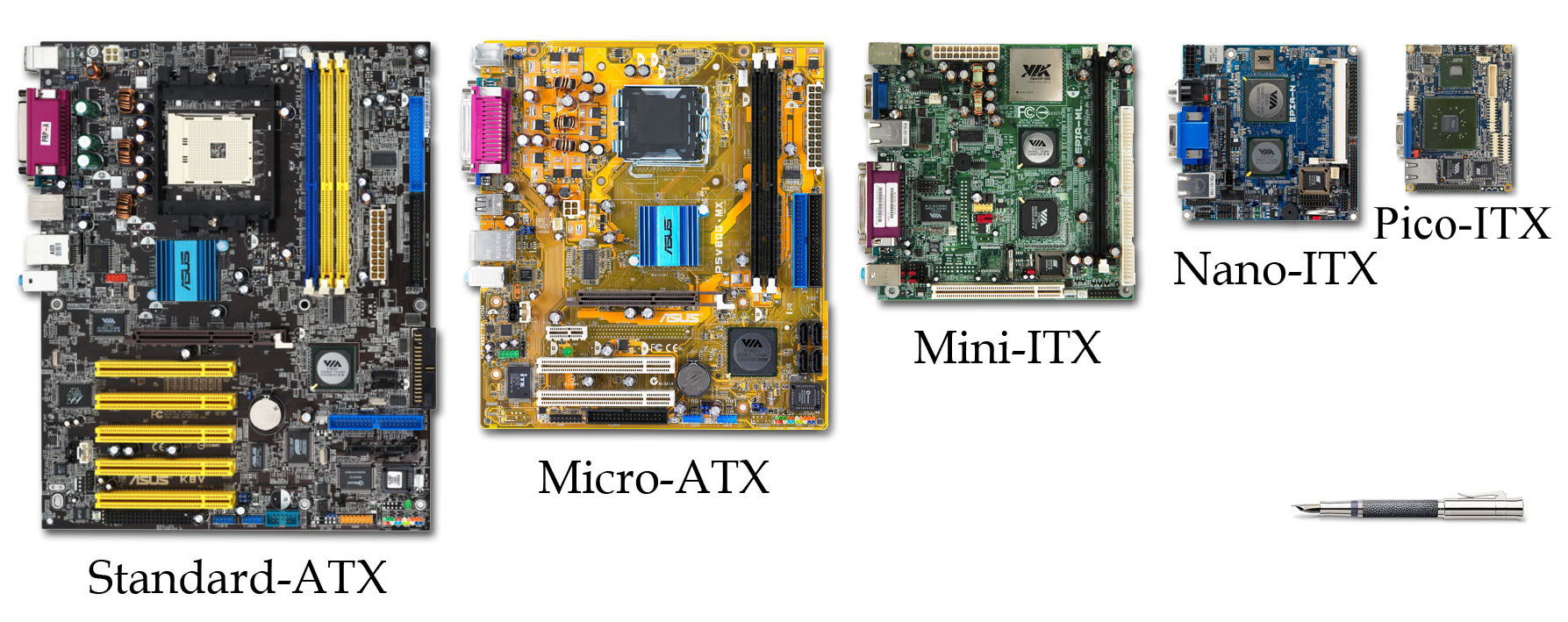
File:Abit-kt7-large.jpg, ATX
( Abit KT7) File:Mini-itx-motherboard.jpg, mini-ITX
(VIA EPIA 5000AG) File:Top_EPIA_PX10000G_Motherboard_new.jpg, Pico-ITX
(VIA EPIA PX10000G)
File:Intel NUC as Asterisk-based PBX.jpg, Intel NUC
File:Gigabyte-BRIX GB-BXBT-2807.jpg, Gigabyte BRIX
Form Factors: Micro ATX vs. Mini ITX vs. ATX
The official Intel Form factors website containing form factor descriptions
Micro ATX vs Mini ITX vs ATX
{{DEFAULTSORT:Computer Form Factor Computing comparisons
 In
In computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, hardware and softw ...
, the motherboard form factor is the specification of a motherboard
A motherboard, also called a mainboard, a system board, a logic board, and informally a mobo (see #Nomenclature, "Nomenclature" section), is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It ho ...
– the dimensions, power supply type, location of mounting holes, number of ports on the back panel, etc. Specifically, in the IBM PC compatible
An IBM PC compatible is any personal computer that is hardware- and software-compatible with the IBM Personal Computer (IBM PC) and its subsequent models. Like the original IBM PC, an IBM PC–compatible computer uses an x86-based central p ...
industry, standard form factors ensure that parts are interchangeable across competing vendors and generations of technology, while in enterprise computing, form factors ensure that server modules fit into existing rackmount
A 19-inch rack is a standardized frame or enclosure for mounting multiple electronic equipment modules. Each module has a front panel that is wide. The 19 inch dimension includes the edges or ''ears'' that protrude from each side of the ...
systems. Traditionally, the most significant specification is for that of the motherboard, which generally dictates the overall size of the case
Case or CASE may refer to:
Instances
* Instantiation (disambiguation), a realization of a concept, theme, or design
* Special case, an instance that differs in a certain way from others of the type
Containers
* Case (goods), a package of relate ...
. Small form factor
Small form factor (SFF) is a classification of desktop computers and for some of their components, chassis and motherboard, to indicate that they are designed in accordance with one of several standardized form factors intended to minimize the vo ...
s have been developed and implemented.
Overview of form factors
A PC motherboard is the maincircuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a laminated sandwich structure of conductive and insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes and other features (similar to wires on a flat surface) ...
within a typical desktop computer
A desktop computer, often abbreviated as desktop, is a personal computer designed for regular use at a stationary location on or near a desk (as opposed to a portable computer) due to its size and power requirements. The most common configuratio ...
, laptop
A laptop computer or notebook computer, also known as a laptop or notebook, is a small, portable personal computer (PC). Laptops typically have a Clamshell design, clamshell form factor (design), form factor with a flat-panel computer scree ...
or server
Server may refer to:
Computing
*Server (computing), a computer program or a device that provides requested information for other programs or devices, called clients.
Role
* Waiting staff, those who work at a restaurant or a bar attending custome ...
. Its main functions are as follows:
* To serve as a central backbone to which all other modular parts such as CPU
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes instructions of a computer program, such as arithmetic, log ...
, RAM
Ram, ram, or RAM most commonly refers to:
* A male sheep
* Random-access memory, computer memory
* Ram Trucks, US, since 2009
** List of vehicles named Dodge Ram, trucks and vans
** Ram Pickup, produced by Ram Trucks
Ram, ram, or RAM may also ref ...
, and hard drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, pla ...
s can be attached as required to create a computer
* To be interchangeable (in most cases) with different components (in particular CPU and expansion card
In computing, an expansion card (also called an expansion board, adapter card, peripheral card or accessory card) is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot (also referred to as a bus sl ...
s) for the purposes of customization and upgrading
* To distribute power
Power may refer to:
Common meanings
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power, a type of energy
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
Math ...
to other circuit boards
* To electronically co-ordinate and interface the operation of the components
As new generations of components have been developed, the standards of motherboards have changed too. For example, the introduction of AGP and, more recently, PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a high-speed standard used to connect hardware components inside computers. It is designed to replace older expansion bus standards such as Peripher ...
have influenced motherboard design. However, the standardized size and layout of motherboards have changed much more slowly and are controlled by their own standards. The list of components required on a motherboard changes far more slowly than the components themselves. For example, north bridge microchips
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
have changed many times since their introduction with many manufacturers bringing out their own versions, but in terms of form factor standards, provisions for north bridges have remained fairly static for many years.
Although it is a slower process, form factors do evolve regularly in response to changing demands. IBM's long-standing standard, AT (Advanced Technology), was superseded in 1995 by the current industry standard ATX
ATX (Advanced Technology Extended) is a motherboard and power supply configuration specification, patented by David Dent in 1995 at Intel, to improve on previous de facto standard, ''de facto'' standards like the AT (form factor), AT design. ...
(Advanced Technology Extended), which still governs the size and design of the motherboard in most modern PCs. The latest update to the ATX standard was released in 2007. A divergent standard by chipset
In a computer system, a chipset is a set of electronic components on one or more integrated circuits that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals. The chipset is usually found on the motherboard of computers. Chips ...
manufacturer VIA
Via or VIA may refer to the following:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Via'' (Volumes album), 2011
* Via (Thalia Zedek album), 2013
* VIA (music), Soviet and Russian term for a music collective
Businesses and organisations
* Via Foundation, a Cz ...
called EPIA
VIA EPIA (''VIA Technologies, VIA Embedded Platform Innovative Architecture'') is a series of mini-ITX, em-ITX, nano-ITX, pico-ITX and pico-ITXe motherboards with integrated VIA Microprocessor, processors. They are small and consume less power t ...
(also known as ITX, and not to be confused with EPIC) is based upon smaller form factors and its own standards.
Differences between form factors are most apparent in terms of their intended market sector, and involve variations in size, design compromises and typical features. Most modern computers have very similar requirements, so form factor differences tend to be based upon subsets and supersets of these. For example, a desktop computer may require more sockets for maximum flexibility and many optional connectors and other features on board, whereas a computer to be used in a multimedia
Multimedia is a form of communication that uses a combination of different content forms, such as Text (literary theory), writing, Sound, audio, images, animations, or video, into a single presentation. T ...
system may need to be optimized for heat and size, with additional plug-in cards being less common. The smallest motherboards may sacrifice CPU flexibility in favor of a fixed manufacturer's choice. The E-ATX form factor is not standardized and may vary according to the motherboard manufacturer.
Comparisons
Tabular information
Size variants
List is incompleteMaximum number of expansion card slots
ATX case compatible:Visual examples of different form factors
( Abit KT7) File:Mini-itx-motherboard.jpg, mini-ITX
(VIA EPIA 5000AG) File:Top_EPIA_PX10000G_Motherboard_new.jpg, Pico-ITX
(VIA EPIA PX10000G)
PC/104 and EBX
PC/104 is an embedded computer standard which defines both a form factor and computer bus. PC/104 is intended for embedded computing environments. Single-board computers built to this form factor are often sold byCOTS
COTS may refer to:
* Commercial off-the-shelf, products that are commercially available and can be bought "as is"
* Commercial Orbital Transportation Services, a NASA program for delivery to the International Space Station by private companies
* ...
vendors, which benefits users who want a customized rugged system, without months of design and paper work.
The PC/104 form factor was standardized by the PC/104 Consortium in 1992. An IEEE standard corresponding to PC/104 was drafted as IEEE P996.1, but never ratified.
The 5.75 × 8.0 in Embedded Board eXpandable (EBX) specification, which was derived from Ampro's proprietary Little Board form-factor, resulted from a collaboration between Ampro and Motorola Computer Group
Motorola, Inc. () was an American multinational telecommunications company based in Schaumburg, Illinois. It was founded by brothers Paul and Joseph Galvin in 1928 and had been named Motorola since 1947. Many of Motorola's products had been r ...
.
As compared with PC/104 modules, these larger (but still reasonably embeddable) SBCs tend to have everything of a full PC on them, including application oriented interfaces like audio, analog, or digital I/O in many cases. Also it's much easier to fit Pentium CPUs, whereas it's a tight squeeze (or expensive) to do so on a PC/104 SBC. Typically, EBX SBCs contain: the CPU; upgradeable RAM subassemblies (e.g., DIMM); Flash memory for solid state drive; multiple USB, serial, and parallel ports; onboard expansion via a PC/104 module stack; off-board expansion via ISA and/or PCI buses (from the PC/104 connectors); networking interface (typically Ethernet); and video (typically CRT, LCD, and TV).
Mini PC
Mini PC is a PC small form factor very close in size to an external CD orDVD
The DVD (common abbreviation for digital video disc or digital versatile disc) is a digital optical disc data storage format. It was invented and developed in 1995 and first released on November 1, 1996, in Japan. The medium can store any ki ...
drive
Drive or The Drive may refer to:
Motoring
* Driving, the act of controlling a vehicle
* Road trip, a journey on roads
Roadways
Roadways called "drives" may include:
* Driveway, a private road for local access to structures, abbreviated "drive"
* ...
. Mini PCs have proven popular for use as HTPCs.
Examples
*AOpen
AOPEN (, stylized AOPEN) is a major Taiwanese electronics manufacturer that makes computers and its parts. AOPEN used to be the Open System Business Unit of Acer Computer Inc. which designed, manufactured and sold computer components.
It was ...
'' XC mini''
* Apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
Mac mini
Mac Mini (stylized as Mac mini) is a small form factor (desktop and motherboard), small form factor desktop computer developed and marketed by Apple Inc. It is one of the company's four current Mac (computer), Mac desktop computers, positioned ...
* Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer compo ...
NUC
* Gigabyte
The gigabyte () is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. The SI prefix, prefix ''giga-, giga'' means 109 in the International System of Units (SI). Therefore, one gigabyte is one billion bytes. The unit symbol for the gigabyte i ...
Brix
* Zotac ZBOX
* Asus
ASUSTeK Computer Inc. (, , , ; stylized as ASUSTeK or ASUS) is a Taiwanese Multinational corporation, multinational computer, phone hardware and electronics manufacturer headquartered in Beitou District, Taipei, Taiwan. Its products include deskto ...
Vivopc
* Lenovo
Lenovo Group Limited, trading as Lenovo ( , zh, c=联想, p=Liánxiǎng), is a Chinese multinational technology company specializing in designing, manufacturing, and marketing consumer electronics, personal computers, software, servers, conv ...
ThinkCentre Tiny
* Dell
Dell Inc. is an American technology company that develops, sells, repairs, and supports personal computers (PCs), Server (computing), servers, data storage devices, network switches, software, computer peripherals including printers and webcam ...
Optiplex Mini/Micro
* Acer Veriton
See also
* Hard-disk-drive form factors *Small form factor
Small form factor (SFF) is a classification of desktop computers and for some of their components, chassis and motherboard, to indicate that they are designed in accordance with one of several standardized form factors intended to minimize the vo ...
* PICOe
Notes
References
External links
Form Factors: Micro ATX vs. Mini ITX vs. ATX
The official Intel Form factors website containing form factor descriptions
Micro ATX vs Mini ITX vs ATX
{{DEFAULTSORT:Computer Form Factor Computing comparisons