Common Cold on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The common cold, or the cold, is a viral
 The typical symptoms of a cold include
The typical symptoms of a cold include
 A cold usually begins with fatigue, a feeling of being chilled, sneezing, and a headache, followed in a couple of days by a runny nose and cough. Symptoms may begin within sixteen hours of exposure and typically peak two to four days after onset. They usually resolve in seven to ten days, but some can last for up to three weeks. The average duration of cough is eighteen days and in some cases people develop a post-viral cough which can linger after the infection is gone. In children, the cough lasts for more than ten days in 35–40% of cases and continues for more than 25 days in 10%.
A cold usually begins with fatigue, a feeling of being chilled, sneezing, and a headache, followed in a couple of days by a runny nose and cough. Symptoms may begin within sixteen hours of exposure and typically peak two to four days after onset. They usually resolve in seven to ten days, but some can last for up to three weeks. The average duration of cough is eighteen days and in some cases people develop a post-viral cough which can linger after the infection is gone. In children, the cough lasts for more than ten days in 35–40% of cases and continues for more than 25 days in 10%.
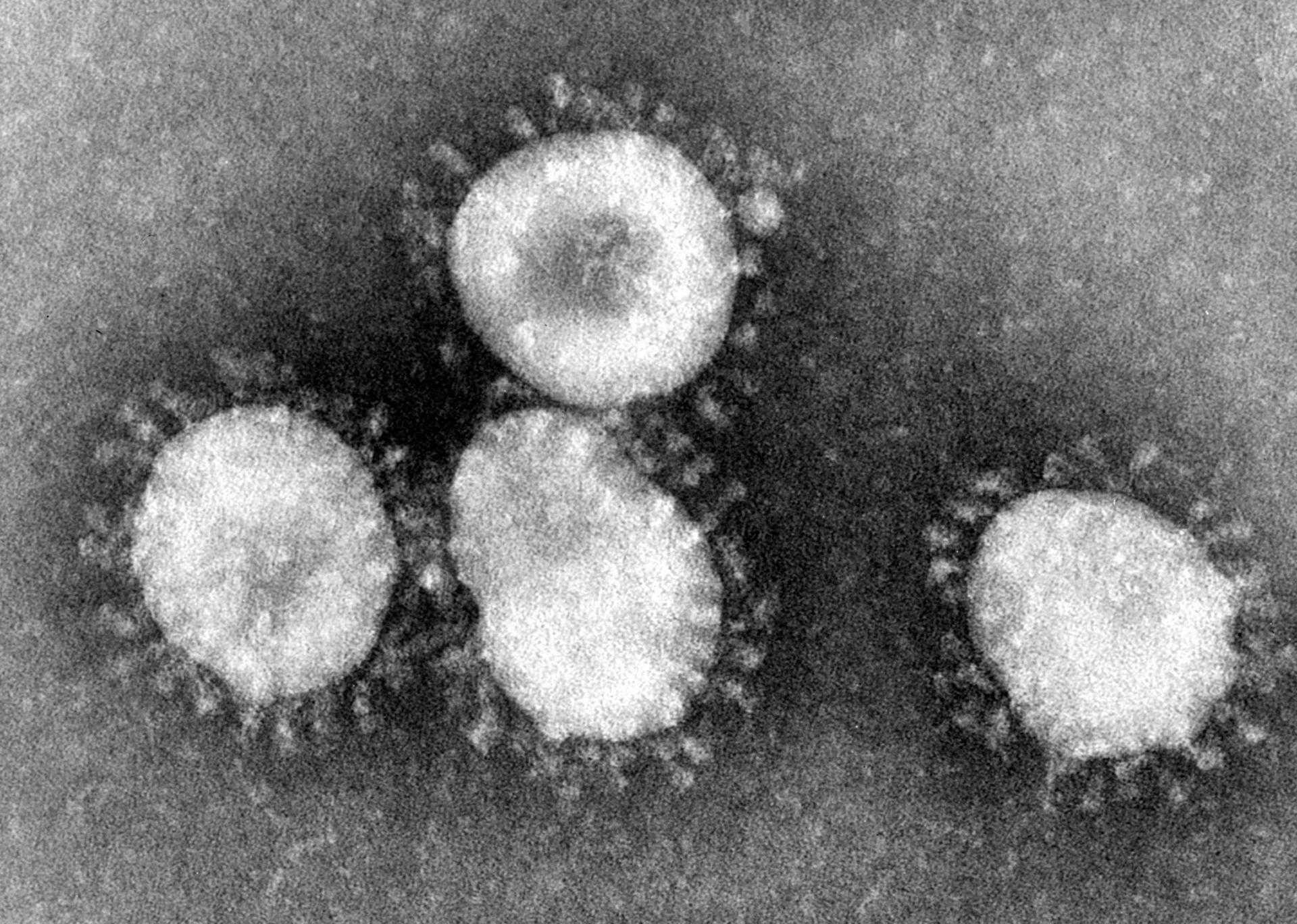 The common cold is an infection of the upper
The common cold is an infection of the upper
 The symptoms of the common cold are believed to be primarily related to the immune response to the virus. The mechanism of this immune response is virus-specific. For example, the rhinovirus is typically acquired by direct contact; it binds to humans via ICAM-1 receptors and the CDHR3 receptor through unknown mechanisms to trigger the release of inflammatory mediators. These inflammatory mediators then produce the symptoms. It does not generally cause damage to the nasal
The symptoms of the common cold are believed to be primarily related to the immune response to the virus. The mechanism of this immune response is virus-specific. For example, the rhinovirus is typically acquired by direct contact; it binds to humans via ICAM-1 receptors and the CDHR3 receptor through unknown mechanisms to trigger the release of inflammatory mediators. These inflammatory mediators then produce the symptoms. It does not generally cause damage to the nasal
 Treatments of the common cold primarily involve medications and other therapies for symptomatic relief. Getting plenty of rest, drinking fluids to maintain hydration, and gargling with warm salt water are reasonable conservative measures. Much of the benefit from symptomatic treatment is, however, attributed to the
Treatments of the common cold primarily involve medications and other therapies for symptomatic relief. Getting plenty of rest, drinking fluids to maintain hydration, and gargling with warm salt water are reasonable conservative measures. Much of the benefit from symptomatic treatment is, however, attributed to the
infectious disease
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
of the upper respiratory tract that primarily affects the respiratory mucosa of the nose
A nose is a sensory organ and respiratory structure in vertebrates. It consists of a nasal cavity inside the head, and an external nose on the face. The external nose houses the nostrils, or nares, a pair of tubes providing airflow through the ...
, throat
In vertebrate anatomy, the throat is the front part of the neck, internally positioned in front of the vertebrae. It contains the Human pharynx, pharynx and larynx. An important section of it is the epiglottis, separating the esophagus from the t ...
, sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoi ...
, and larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ (anatomy), organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal ...
. Signs and symptoms may appear in as little as two days after exposure to the virus. These may include cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and Microorganism, microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex fol ...
ing, sore throat
Sore throat, also known as throat pain, is pain or irritation of the throat. The majority of sore throats are caused by a virus, for which antibiotics are not helpful.
For sore throat caused by bacteria (GAS), treatment with antibiotics may hel ...
, runny nose, sneezing, headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
, fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
, and fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
. People usually recover in seven to ten days, but some symptoms may last up to three weeks. Occasionally, those with other health problems may develop pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
.
Well over 200 virus strains are implicated in causing the common cold, with rhinovirus
The rhinovirus (from the "nose", , romanized: "of the nose", and the ) is a Positive-sense single stranded RNA virus, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus belonging to the genus ''Enterovirus'' in the family ''Picornaviridae''. Rhinoviru ...
es, coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the comm ...
es, adenoviruses
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from the ...
and enterovirus
''Enterovirus'' is a genus of positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses associated with several human and mammalian diseases. Enteroviruses are named by their transmission-route through the intestine ('enteric' meaning intestinal).
Serologic ...
es being the most common. They spread through the air or indirectly through contact with objects in the environment, followed by transfer to the mouth or nose. Risk factors include going to child care
Child care, also known as day care, is the care and supervision of one or more children, typically ranging from three months to 18 years old. Although most parents spend a significant amount of time caring for their child(ren), childcare typica ...
facilities, not sleeping well, and psychological stress
In psychology, stress is a feeling of emotional strain and pressure. Stress is a form of psychological and mental discomfort. Small amounts of stress may be beneficial, as it can improve athletic performance, motivation and reaction to the envi ...
. The symptoms are mostly due to the body's immune response
An immune response is a physiological reaction which occurs within an organism in the context of inflammation for the purpose of defending against exogenous factors. These include a wide variety of different toxins, viruses, intra- and extracellula ...
to the infection rather than to tissue destruction by the viruses themselves.Eccles p. 112 The symptoms of influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
are similar to those of a cold, although usually more severe and less likely to include a runny nose.
There is no vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifi ...
for the common cold. This is due to the rapid mutation and wide variation of viruses that cause the common cold. The primary methods of prevention are hand washing
Hand washing (or handwashing), also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap, soap or handwash and water to remove viruses, bacteria, microorganisms, dirt, grease, and other harmful or unwanted substances stuck to th ...
; not touching the eyes, nose or mouth with unwashed hands; and staying away from sick people. People are considered contagious as long as the symptoms are still present. Some evidence supports the use of face masks.Eccles p. 209 There is also no cure
A cure is a substance or procedure that resolves a medical condition. This may include a medication, a surgery, surgical operation, a lifestyle change, or even a philosophical shift that alleviates a person's suffering or achieves a state of heali ...
, but the symptoms can be treated. Zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
may reduce the duration and severity of symptoms if started shortly after the onset of symptoms. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a Indication (medicine), therapeutic drug class which Analgesic, reduces pain, Anti-inflammatory, decreases inflammation, Antipyretic, decreases fever, and Antithrombotic, prevents bl ...
s (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes dysmenorrhea, painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It can be taken oral administration, ...
may help with pain. Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s, however, should not be used, as all colds are caused by viruses rather than bacteria. There is no good evidence that cough medicines are effective.
The common cold is the most frequent infectious disease in humans.Eccles p. 1 Under normal circumstances, the average adult gets two to three colds a year, while the average child may get six to eight colds a year. Infections occur more commonly during the winter. These infections have existed throughout human history.
Signs and symptoms
 The typical symptoms of a cold include
The typical symptoms of a cold include cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and Microorganism, microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex fol ...
, runny nose, sneezing, nasal congestion
Nasal congestion is the partial or complete blockage of nasal passages, leading to impaired nasal breathing, usually due to membranes lining the nose becoming swollen from inflammation of blood vessels.
Background
In about 85% of cases, nasal ...
, and a sore throat
Sore throat, also known as throat pain, is pain or irritation of the throat. The majority of sore throats are caused by a virus, for which antibiotics are not helpful.
For sore throat caused by bacteria (GAS), treatment with antibiotics may hel ...
, sometimes accompanied by muscle ache, fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
, headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
, and loss of appetite.Eccles p. 24 A sore throat is present in about 40% of cases, a cough in about 50%, and muscle aches in about 50%. In adults, a fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
is generally not present but it is common in infants and young children. The cough is usually mild compared to that accompanying influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
. While a cough and a fever indicate a higher likelihood of influenza in adults, a great deal of similarity exists between these two conditions. A number of the viruses that cause the common cold may also result in asymptomatic infections.
The color of the mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
or nasal secretion may vary from clear to yellow to green and does not indicate the class of agent causing the infection.
Progression
 A cold usually begins with fatigue, a feeling of being chilled, sneezing, and a headache, followed in a couple of days by a runny nose and cough. Symptoms may begin within sixteen hours of exposure and typically peak two to four days after onset. They usually resolve in seven to ten days, but some can last for up to three weeks. The average duration of cough is eighteen days and in some cases people develop a post-viral cough which can linger after the infection is gone. In children, the cough lasts for more than ten days in 35–40% of cases and continues for more than 25 days in 10%.
A cold usually begins with fatigue, a feeling of being chilled, sneezing, and a headache, followed in a couple of days by a runny nose and cough. Symptoms may begin within sixteen hours of exposure and typically peak two to four days after onset. They usually resolve in seven to ten days, but some can last for up to three weeks. The average duration of cough is eighteen days and in some cases people develop a post-viral cough which can linger after the infection is gone. In children, the cough lasts for more than ten days in 35–40% of cases and continues for more than 25 days in 10%.
Causes
Viruses
 The common cold is an infection of the upper
The common cold is an infection of the upper respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respirato ...
which can be caused by many different viruses. The most commonly implicated is a rhinovirus
The rhinovirus (from the "nose", , romanized: "of the nose", and the ) is a Positive-sense single stranded RNA virus, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus belonging to the genus ''Enterovirus'' in the family ''Picornaviridae''. Rhinoviru ...
(30–80%), a type of picornavirus
Picornaviruses are a group of related Viral envelope, nonenveloped RNA viruses which infect vertebrates including fish, mammals, and birds. They are viruses that represent a large family of small, Positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus, positi ...
with 99 known serotype
A serotype or serovar is a distinct variation within a species of bacteria or virus or among immune cells of different individuals. These microorganisms, viruses, or Cell (biology), cells are classified together based on their shared reactivity ...
s. Other commonly implicated viruses include coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the comm ...
es, adenovirus
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from t ...
es, enterovirus
''Enterovirus'' is a genus of positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses associated with several human and mammalian diseases. Enteroviruses are named by their transmission-route through the intestine ('enteric' meaning intestinal).
Serologic ...
es, parainfluenza and RSV. Frequently more than one virus is present. In total, more than 200 viral types are associated with colds. The viral cause of some common colds (20–30%) is unknown.
Transmission
The common cold virus is typically transmitted via airborne droplets, direct contact with infected nasal secretions, orfomites
A fomite () or fomes () is any inanimate object that, when contaminated with or exposed to infectious agents (such as pathogenic bacteria, viruses or fungi), can transfer disease to a new host.
Transfer of pathogens by fomites
A fomite is any ...
(contaminated objects). Which of these routes is of primary importance has not been determined.Eccles pp. 211, 215 As with all respiratory pathogens once presumed to transmit via respiratory droplets, it is highly likely to be carried by the aerosols generated during routine breathing, talking, and singing. The viruses may survive for prolonged periods in the environment (over 18 hours for rhinoviruses) and can be picked up by people's hands and subsequently carried to their eyes or noses where infection occurs. Transmission from animals is considered highly unlikely; an outbreak documented at a British scientific base on Adelaide Island
Adelaide Island is a large, mainly ice-covered island, long and wide, lying at the north side of Marguerite Bay off the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. The Ginger Islands lie off the southern end. Mount Bodys is the easternmost mounta ...
after seventeen weeks of isolation was thought to have been caused by transmission from a contaminated object or an asymptomatic human carrier, rather than from the husky dogs which were also present at the base.
Transmission is common in daycare and schools due to the proximity of many children with little immunity and poor hygiene. These infections are then brought home to other members of the family. There is no evidence that recirculated air during commercial flight is a method of transmission. People sitting close to each other appear to be at greater risk of infection.
Other
Herd immunity, generated from previous exposure to cold viruses, plays an important role in limiting viral spread, as seen with younger populations that have greater rates of respiratory infections. Poor immune function is a risk factor for disease. Insufficient sleep andmalnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
have been associated with a greater risk of developing infection following rhinovirus exposure; this is believed to be due to their effects on immune function. Breast feeding
Breastfeeding, also known as nursing, is the process where breast milk is fed to a child. Infants may suck the milk directly from the breast, or milk may be extracted with a pump and then fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WH ...
decreases the risk of acute otitis media and lower respiratory tract infections among other diseases, and it is recommended that breast feeding be continued when an infant has a cold. In the developed world breast feeding may not be protective against the common cold in and of itself.
Pathophysiology
epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
. The respiratory syncytial virus ( RSV), on the other hand, is contracted by direct contact and airborne droplets. It then replicates in the nose and throat before spreading to the lower respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respirator ...
.Eccles p. 116 RSV does cause epithelium damage. Human parainfluenza virus typically results in inflammation of the nose, throat, and bronchi
A bronchus ( ; : bronchi, ) is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. Thes ...
.Eccles p. 122 In young children, when it affects the trachea
The trachea (: tracheae or tracheas), also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals' lungs. The trachea extends from ...
, it may produce the symptoms of croup
Croup ( ), also known as croupy cough, is a type of respiratory infection that is usually caused by a virus. The infection leads to swelling inside the trachea, which interferes with normal breathing and produces the classic symptoms of "bar ...
, due to the small size of their airways.
Diagnosis
The distinction between viral upper respiratory tract infections is loosely based on the location of symptoms, with the common cold affecting primarily the nose (rhinitis), throat (pharyngitis), and lungs (bronchitis). There can be significant overlap, and more than one area can be affected. Self-diagnosis is frequent. Isolation of the viral agent involved is rarely performed,Eccles pp. 51–52 and it is generally not possible to identify the virus type through symptoms.Prevention
The only useful ways to reduce the spread of cold viruses are physical andengineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
measures such as using correct hand washing technique, respirator
A respirator is a device designed to protect the wearer from inhaling hazardous atmospheres including lead, lead fumes, vapors, gases and particulate matter such as dusts and airborne pathogens such as viruses. There are two main categories o ...
s, and improvement of indoor air. In the healthcare environment, gowns and disposable gloves are also used. Droplet precautions cannot reliably protect against inhalation
Inhalation (or inspiration) happens when air or other gases enter the lungs.
Inhalation of air
Inhalation of air, as part of the cycle of breathing, is a vital process for all human life. The process is autonomic (though there are exceptions ...
of common-cold-laden aerosols. Instead, airborne precautions such as respirator
A respirator is a device designed to protect the wearer from inhaling hazardous atmospheres including lead, lead fumes, vapors, gases and particulate matter such as dusts and airborne pathogens such as viruses. There are two main categories o ...
s, ventilation
Ventilation may refer to:
* Ventilation (physiology), the movement of air between the environment and the lungs via inhalation and exhalation
** Mechanical ventilation, in medicine, using artificial methods to assist breathing
*** Respirator, a ma ...
, and HEPA/ high MERV filters, are the only reliable protection against cold-laden aerosols. Isolation or quarantine
A quarantine is a restriction on the movement of people, animals, and goods which is intended to prevent the spread of disease or pests. It is often used in connection to disease and illness, preventing the movement of those who may have bee ...
is not used as the disease is so widespread and symptoms are non-specific. There is no vaccine to protect against the common cold. Vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating ...
has proven difficult as there are so many viruses involved and because they mutate rapidly. Creation of a broadly effective vaccine is, therefore, highly improbable.
Regular hand washing appears to be effective in reducing the transmission of cold viruses, especially among children. Whether the addition of antivirals
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials ...
or antibacterial
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
s to normal hand washing provides greater benefit is unknown. Wearing face masks when around people who are infected may be beneficial; however, there is insufficient evidence for maintaining a greater social distance
In sociology, social distance describes the distance between individuals or social groups in society, including dimensions such as social class, race/ethnicity, gender or sexuality. Members of different groups mix less than members of the same g ...
.
It is unclear whether zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
supplements affect the likelihood of contracting a cold.
Management
 Treatments of the common cold primarily involve medications and other therapies for symptomatic relief. Getting plenty of rest, drinking fluids to maintain hydration, and gargling with warm salt water are reasonable conservative measures. Much of the benefit from symptomatic treatment is, however, attributed to the
Treatments of the common cold primarily involve medications and other therapies for symptomatic relief. Getting plenty of rest, drinking fluids to maintain hydration, and gargling with warm salt water are reasonable conservative measures. Much of the benefit from symptomatic treatment is, however, attributed to the placebo effect
A placebo ( ) can be roughly defined as a sham medical treatment. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like saline), sham surgery, and other procedures.
Placebos are used in randomized clinical trials ...
. no medications or herbal remedies had been conclusively demonstrated to shorten the duration of infection.
Symptomatic
Treatments that may help with symptoms include pain medication and medications for fevers such asibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes dysmenorrhea, painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It can be taken oral administration, ...
and acetaminophen (paracetamol). However, it is not clear whether acetaminophen helps with symptoms. It is not known if over-the-counter cough medications are effective for treating an acute cough. Cough medicines are not recommended for use in children due to a lack of evidence supporting effectiveness and the potential for harm. In 2009, Canada restricted the use of over-the-counter
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are medicines sold directly to a consumer without a requirement for a prescription from a healthcare professional, as opposed to prescription drugs, which may be supplied only to consumers possessing a valid pres ...
cough and cold medication in children six years and under due to concerns regarding risks and unproven benefits. The misuse of dextromethorphan
Dextromethorphan, sold under the brand name Robitussin among others, is a cough suppressant used in many cough and Common cold, cold medicines. In 2022, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the combination dextromethorphan/bupropi ...
(an over-the-counter cough medicine) has led to its ban in a number of countries. Intranasal corticosteroids have not been found to be useful.
In adults, short term use of nasal decongestants may have a small benefit. Antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides ...
s may improve symptoms in the first day or two; however, there is no longer-term benefit and they have adverse effects such as drowsiness. Other decongestants such as pseudoephedrine appear effective in adults. Combined oral analgesics, antihistaminics, and decongestants are generally effective for older children and adults. Ipratropium nasal spray may reduce the symptoms of a runny nose but has little effect on stuffiness. Ipratropium may also help with coughs in adults. The safety and effectiveness of nasal decongestant use in children is unclear.
Due to lack of studies, it is not known whether increased fluid intake improves symptoms or shortens respiratory illness. As of 2017, heated and humidified air, such as via RhinoTherm, is of unclear benefit. One study has found chest vapor rub to provide some relief of nocturnal cough, congestion, and sleep difficulty.
Some experts advise against physical exercise
Exercise or workout is physical activity that enhances or maintains fitness and overall health. It is performed for various reasons, including weight loss or maintenance, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardio ...
if there are symptoms such as fever, widespread muscle aches or fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
. It is regarded as safe to perform moderate exercise if the symptoms are confined to the head
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple ani ...
, including runny nose, nasal congestion
Nasal congestion is the partial or complete blockage of nasal passages, leading to impaired nasal breathing, usually due to membranes lining the nose becoming swollen from inflammation of blood vessels.
Background
In about 85% of cases, nasal ...
, sneezing, or a minor sore throat
Sore throat, also known as throat pain, is pain or irritation of the throat. The majority of sore throats are caused by a virus, for which antibiotics are not helpful.
For sore throat caused by bacteria (GAS), treatment with antibiotics may hel ...
. There is a popular belief that having a hot drink can help with cold symptoms, but evidence to support this is very limited.
Antibiotics and antivirals
Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
have no effect against viral infections, including the common cold. Due to their side effects, antibiotics cause overall harm but nevertheless are still frequently prescribed. Some of the reasons that antibiotics are so commonly prescribed include people's expectations for them, physicians' desire to help, and the difficulty in excluding complications that may be amenable to antibiotics. There are no effective antiviral drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials ...
s for the common cold even though some preliminary research has shown benefits.Eccles p. 218
Zinc
Zinc supplements may shorten the duration of colds by up to 33% and reduce the severity of symptoms if supplementation begins within 24 hours of the onset of symptoms. Some zinc remedies directly applied to the inside of the nose have led to the loss of the sense of smell. A 2017 review did not recommend the use of zinc for the common cold for various reasons; whereas a 2017 and 2018 review both recommended the use of zinc, but also advocated further research on the topic.Alternative medicine
While there are manyalternative medicine
Alternative medicine refers to practices that aim to achieve the healing effects of conventional medicine, but that typically lack biological plausibility, testability, repeatability, or supporting evidence of effectiveness. Such practices are ...
s and Chinese herbal medicines supposed to treat the common cold, there is insufficient scientific evidence
Scientific evidence is evidence that serves to either support or counter a scientific theory or hypothesis, although scientists also use evidence in other ways, such as when applying theories to practical problems. "Discussions about empirical ev ...
to support their use. As of 2015, there is weak evidence to support nasal irrigation with saline. There is no firm evidence that Echinacea
''Echinacea'' is a genus of herbaceous flowering plants in the daisy family. It has ten species, which are commonly called coneflowers. They are native only in eastern and central North America, where they grow in wet to dry prairies and open ...
products or garlic
Garlic (''Allium sativum'') is a species of bulbous flowering plants in the genus '' Allium''. Its close relatives include the onion, shallot, leek, chives, Welsh onion, and Chinese onion. Garlic is native to central and south Asia, str ...
provide any meaningful benefit in treating or preventing colds.
Vitamins C and D
Vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables. It is also a generic prescription medication and in some countries is sold as a non-prescription di ...
supplementation does not affect the incidence of the common cold, but may reduce its duration if taken on a regular basis. There is no conclusive evidence that vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
supplementation is efficacious in the prevention or treatment of respiratory tract infections.
Prognosis
The common cold is generally mild and self-limiting with most symptoms generally improving in a week. In children, half of cases resolve in 10 days and 90% in 15 days. Severe complications, if they occur, are usually in the very old, the very young, or those who are immunosuppressed. Secondary bacterial infections may occur resulting insinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is an inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include production of thick nasal mucus, nasal congestion, facial congestion, facial pain, facial pressure ...
, pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is inflammation of the back of the throat, known as the pharynx. It typically results in a sore throat and fever. Other symptoms may include a runny nose, cough, headache, difficulty swallowing, swollen lymph nodes, and a hoarse vo ...
, or an ear infection. It is estimated that sinusitis occurs in 8% and ear infection in 30% of cases.Eccles p. 90
Epidemiology
The common cold is the most common human disease and affects people all over the globe. Adults typically have two to three infections annually, and children may have six to ten colds a year (and up to twelve colds a year for school children). Rates of symptomatic infections increase in the elderly due to declining immunity.Eccles p. 78Weather
A common misconception is that one can "catch a cold" merely through prolonged exposure to cold weather. Although it is now known that colds are viral infections, the prevalence of many such viruses are indeed seasonal, occurring more frequently during cold weather. The reason for the seasonality has not been conclusively determined. Possible explanations may include cold temperature-induced changes in the respiratory system, decreased immune response, and low humidity causing an increase in viral transmission rates, perhaps due to dry air allowing small viral droplets to disperse farther and stay in the air longer. The apparent seasonality may also be due to social factors, such as people spending more time indoors near infected people,Eccles p. 80 and especially children at school. Although normal exposure to cold does not increase one's risk of infection, severe exposure leading to significant reduction of body temperature (hypothermia
Hypothermia is defined as a body core temperature below in humans. Symptoms depend on the temperature. In mild hypothermia, there is shivering and mental confusion. In moderate hypothermia, shivering stops and confusion increases. In severe ...
) may put one at a greater risk for the common cold: although controversial, the majority of evidence suggests that it may increase susceptibility to infection.
History
While the cause of the common cold was identified in the 1950s, the disease appears to have been with humanity since its early history. Its symptoms and treatment are described in the EgyptianEbers papyrus
The Ebers Papyrus, also known as Papyrus Ebers, is an Egyptian medical papyrus of herbal knowledge dating to (the late Second Intermediate Period or early New Kingdom). Among the oldest and most important medical papyri of Ancient Egypt, it ...
, the oldest existing medical text, written before the 16th century BCE. The name "cold" came into use in the 16th century, due to the similarity between its symptoms and those of exposure to cold weather.
In the United Kingdom, the Common Cold Unit (CCU) was set up by the Medical Research Council in 1946 and it was where the rhinovirus was discovered in 1956. In the 1970s, the CCU demonstrated that treatment with interferon
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten ...
during the incubation phase of rhinovirus infection protects somewhat against the disease, but no practical treatment could be developed. The unit was closed in 1989, two years after it completed research of zinc gluconate lozenges in the prevention and treatment of rhinovirus colds, the only successful treatment in the history of the unit.
Research directions
Antivirals
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials ...
have been tested for effectiveness in the common cold; as of 2009, none had been both found effective and licensed for use. There are trials of the anti-viral drug pleconaril which shows promise against picornavirus
Picornaviruses are a group of related Viral envelope, nonenveloped RNA viruses which infect vertebrates including fish, mammals, and birds. They are viruses that represent a large family of small, Positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus, positi ...
es as well as trials of BTA-798.Eccles p. 226 The oral form of pleconaril had safety issues and an aerosol form is being studied. The genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
s of all known human rhinovirus strains have been sequenced.
Societal impact
The economic impact of the common cold is not well understood in much of the world. In the United States, the common cold leads to 75–100 million physician visits annually at a conservative cost estimate of $7.7 billion per year. Americans spend $2.9 billion on over-the-counter drugs and another $400 million on prescription medicines for symptom relief. More than one-third of people who saw a doctor received an antibiotic prescription, which has implications forantibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from antimicrobials, which are drugs used to treat infections. This resistance affects all classes of microbes, including bacteria (antibiotic resis ...
. An estimated 22–189 million school days are missed annually due to a cold. As a result, parents missed 126 million workdays to stay home to care for their children. When added to the 150 million workdays missed by employees who have a cold, the total economic impact of cold-related work loss exceeds $20 billion per year. This accounts for 40% of time lost from work in the United States.
References
Notes Bibliography *External links
{{Authority control Acute upper respiratory infections Animal viral diseases Airborne diseases Common cold Coronavirus-associated diseases Enterovirus-associated diseases Inflammations Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate (full) Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate