Commodore 65 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
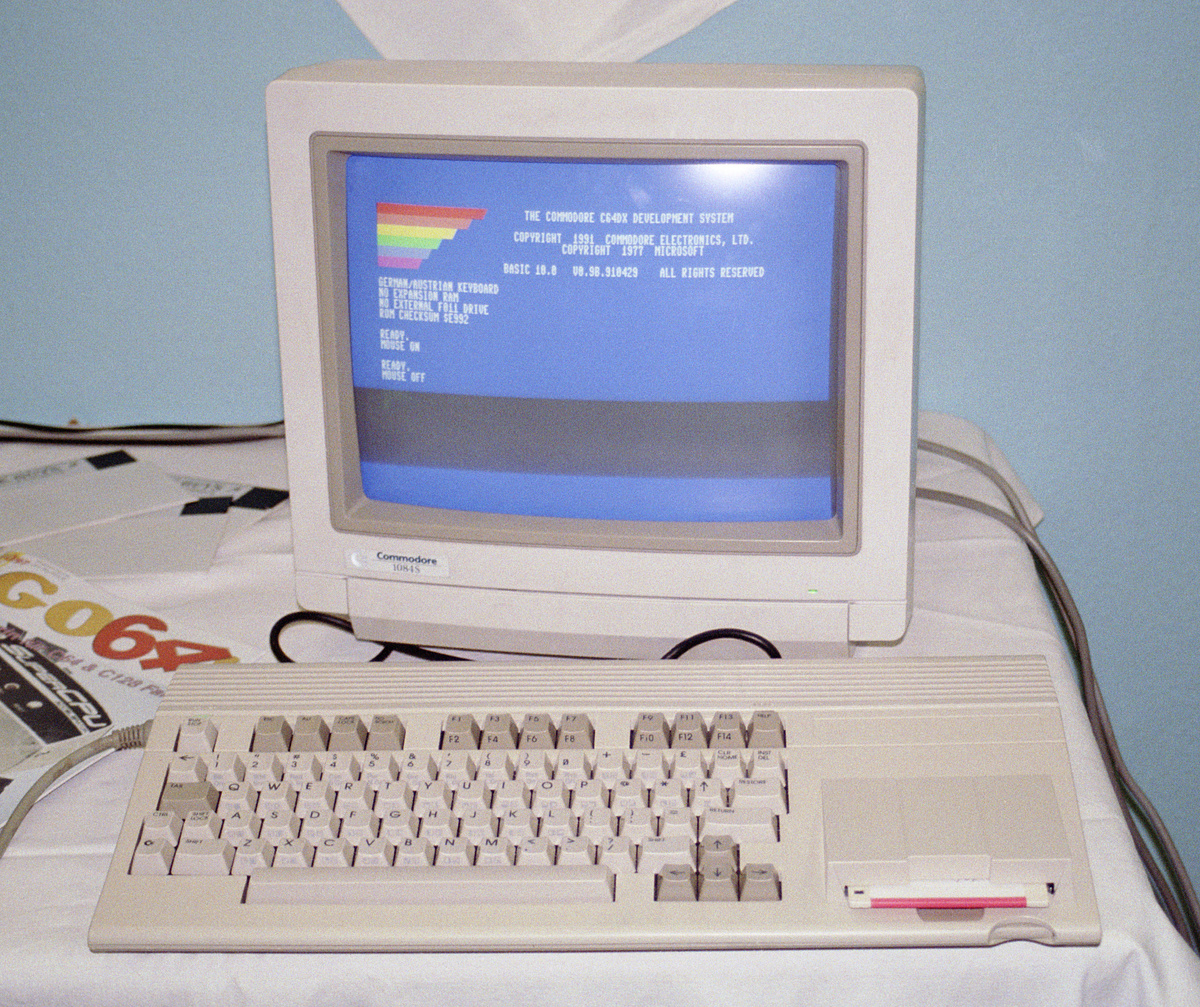







 The Commodore 65 (also known as the C64DX) is a
The Commodore 65 (also known as the C64DX) is a
On the Edge: The Spectacular Rise and Fall of Commodore
(2005), Variant Press. .
By Cameron Kaiser and The Commodore Knowledge Base * tp://ftp.zimmers.net/pub/cbm/c65 FTP directory for the C65 at ftp.zimmers.net
Andre Kaesmacher's C64DX Development Site
C65 System ROMs and Utility Software
old-computers.com: LD-COMPUTERS.COM museum ~ Commodore C65
article on C65
8-Bit-Nirvana: Commodore 65
German C65-site with many photos and info
toxic-waste.de: Commodore C65 Information Page by TXW
{{Commodore International Commodore 64 Commodore computers Home computers Prototypes








 The Commodore 65 (also known as the C64DX) is a
The Commodore 65 (also known as the C64DX) is a prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototyp ...
computer created at Commodore Business Machines in 1990–1991. It is an improved version of the Commodore 64
The Commodore 64, also known as the C64, is an 8-bit home computer introduced in January 1982 by Commodore International (first shown at the Consumer Electronics Show, January 7–10, 1982, in Las Vegas). It has been listed in the Guinness ...
, and it was meant to be backwards-compatible with the older computer, while still providing a number of advanced features close to those of the Amiga
Amiga is a family of personal computers introduced by Commodore in 1985. The original model is one of a number of mid-1980s computers with 16- or 32-bit processors, 256 KB or more of RAM, mouse-based GUIs, and significantly improved graphi ...
.
History
In September 1989 '' Compute!'s Gazette'' noted that "Sales of the 64 have diminished rapidly,Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto, Japan. It develops video games and video game consoles.
Nintendo was founded in 1889 as by craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi and originally produce ...
has eaten big holes in the market, and the life of the old warhorse computer should somehow be extended." Noting that Apple had developed the IIGS to extend the life of its Apple II series
The Apple II series (trademarked with square brackets as "Apple ] ''" and rendered on later models as "Apple //") is a family of home computers, one of the first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products, designed primaril ...
, the magazine asked "Will Commodore Business Machines, Commodore take the same tack?", then continued:
The ''Gazette'' added, "Our sources also report that there is a great deal of infighting at Commodore as to whether the machine should be released. The sales staff wants to get the machine out the door, while the naysaying engineers have dubbed it 'son of Plus/4
The Commodore Plus/4 is a home computer released by Commodore International in 1984. The "Plus/4" name refers to the four-application ROM resident office suite (word processor, spreadsheet, database, and graphing); it was billed as "the produc ...
.'" While the next issue reported that "the latest rumor is that such a machine will never see the light of day", Fred Bowen and others at Commodore in 1990–1991 developed the Commodore 65 (C65) as a successor to the C64. In the end of 1990 the decision to create the C65 was taken. The project was cancelled by Commodore's chairman Irving Gould in 1991.
When Commodore International was liquidated in 1994, a number of prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototyp ...
s were sold on the open market, and thus a few people actually own a Commodore 65. Estimates as to the actual number of machines found on the open market range from 50 to 2000 units. As the C65 project was cancelled, the final 8-bit
In computer architecture, 8-bit Integer (computer science), integers or other Data (computing), data units are those that are 8 bits wide (1 octet (computing), octet). Also, 8-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) arc ...
offering from CBM remained the triple-mode, 1–2 MHz, 128 KB (expandable), C64-compatible Commodore 128
The Commodore 128, also known as the C128, C-128, C= 128,The "C=" represents the graphical part of the logo. is the last 8-bit home computer that was commercially released by Commodore Business Machines (CBM). Introduced in January 1985 at the ...
of 1985.
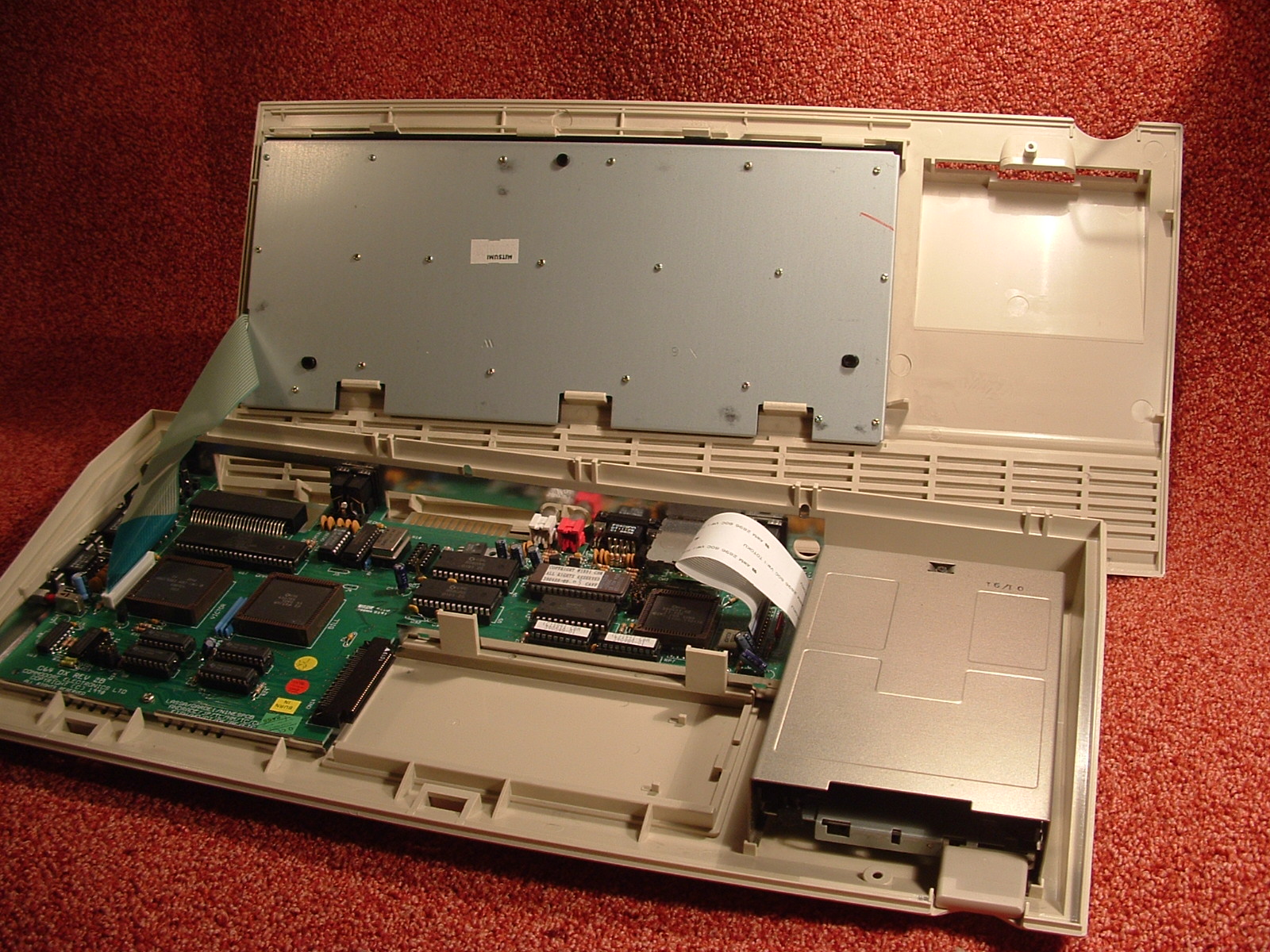
Technical specifications
* TheCPU
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and ...
named CSG 4510 R3 is a custom CSG 65CE02 (a MOS 6502 derivative), combined with two MOS 6526 complex interface adapters (CIAs), a UART serial interface, and a memory mapper to allow for an addressable space of 1MB
* 3.54 MHz clock frequency (the C64 runs at 1 MHz)
* A new VIC-III graphics chip
A video display controller or VDC (also called a display engine or display interface) is an integrated circuit which is the main component in a video-signal generator, a device responsible for the production of a TV video signal in a computin ...
named CSG 4567 R5, capable of producing 256 colors from a palette of 4096 colors; available modes include 320×200×256 (8), 640×200×16 (4), 640×400×16 (4), 1280×200×4 (2), and 1280×400×4(2) ( X×Y×color depth, i.e. number of colors ( bit planes) )
** Supports all video modes of VIC-II
** Textmode with 40/80 × 25 characters
** Synchronizable with external video source ( genlock)
** Integrated DMA
DMA may refer to:
Arts
* ''DMA'' (magazine), a defunct dance music magazine
* Dallas Museum of Art, an art museum in Texas, US
* Danish Music Awards, an award show held in Denmark
* BT Digital Music Awards, an annual event in the UK
* Doctor of M ...
controller ( bit blit)
* Two CSG 8580R5 SID sound chips producing stereo
Stereophonic sound, or more commonly stereo, is a method of sound reproduction that recreates a multi-directional, 3-dimensional audible perspective. This is usually achieved by using two independent audio channels through a configuration ...
sound (the C64 has one SID)
** Separate control (left / right) for volume, filter and modulation
* 128 KB RAM, expandable with up to 1 MB using a RAM expansion port similar to that of the Commodore Amiga 500
* 128 KB ROM
* Heavily improved BASIC: Commodore BASIC 10.0 (the C64 has the relatively feature-weak BASIC 2.0, which was almost 10 years old by this time.)
* One internal 3½" DS DD floppy disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, or a diskette) is an obsolescent type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined w ...
drive
* Keyboard with 77 keys and an inverted T directional cursor block
Different views
Ports
Left side: * Power +5V DC at 2.2A and +12V DC at 0.85A * 2× Control ports DE9M Back: * Expansion port 50-pin * CBM-488 bus using a 6-pin DIN for1541
__NOTOC__
Year 1541 ( MDXLI) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
January–June
* February 12 – Pedro de Valdivia founds Santiago del Nuevo Extremo, whi ...
/1571
Year 1571 ( MDLXXI) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
January–June
* January 11 – The Austrian nobility are granted freedom of religion.
* January 23 &nd ...
/1581
1581 ( MDLXXXI) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) in the Julian calendar, and a common year starting on Thursday (link will display full calendar) of the Proleptic Gregorian calendar.
Events
Ja ...
* User port: parallel 24-pin (without 9V AC)
* Stereo 2× RCA connector for left and right channel
* RGBA video DE9F
* RF video
* Composite video 8-pin DIN
* External fast floppy drive port - mini-DIN-8
Bottom flap:
* RAM expansion
Dimensions: ≈46 cm wide, 20 cm deep, 5.1 cm high
Chipset names
The custom chips of the C65 were not meant to have names like the custom chips in theAmiga
Amiga is a family of personal computers introduced by Commodore in 1985. The original model is one of a number of mid-1980s computers with 16- or 32-bit processors, 256 KB or more of RAM, mouse-based GUIs, and significantly improved graphi ...
. Although there are names printed near the chip sockets on various revisions of the circuit board, they were not intended as names for the chips. According to former Commodore engineer Bill Gardei, "The Legend on the PCB was to let others in the organization know homto go to for advice on the chips. We did have an issue with that. But that wasn't the name of the chip at the time. The 4567 was always called the VIC-3. I can see why others outside of Commodore made the connection. But again—no—we never called these chips 'Victor' or 'Bill'."
The custom chips for the C65 are:
* CSG 4510: processor (commonly called "Victor" after Victor Andrade)
* CSG 4567: VIC-III graphics processor (commonly called "Bill" after Bill Gardei)
* CSG 4151: DMAgic DMA controller (designed by Paul Lassa)
* F011C: FDC (floppy disk controller, also designed by Bill Gardei)
The C65 also contains one or two programmable logic arrays depending on the version:
* ELMER: PAL16L8 (C65 versions 1.1, 2A, 2B), PAL20L8 (C65 versions 3-5)
* IGOR: PAL16L8 (C65 version 2B only)
Graphics subsystem
The main memory of the C65 is shared between the graphics subsystem and the CPU. The memory clock runs at almost twice the speed of the C64. To further increase the bandwidth of the graphics subsystem, the memory is divided into 2× 8-bit wide banks of 64 Kbyte which can be accessed by the CSG-4567 simultaneously. This provides an effective video-DMA bandwidth of 7.2 Mbytes/second which is the same specification as the original 16-bit Commodore Amiga chipset (OCS/ECS). The CPU can use up to half the available bandwidth, since it can only access a single 8-bit bank at a time. In higher demanding video modes, the CPU is slowed down due to increased cycle stealing from the video controller.Enhanced VIC-II modes
In addition to having all of the C64 video modes, the CSG-4567 also supports several new character attributes such as "blink" or "bold" and can display any of the new or old video modes in 80 column or 640 horizontal pixel format, as well as the older 40 column 320 pixel format These enhanced "VIC-II" modes take up to 16 KB of system RAM. The sprite capabilities in all VIC modes are equivalent to the C64.= Bitplane modes
= A new "bitplane" video mode was added to allow the displaying of true bitplane type video, with-up to eight bitplanes in 320 pixel mode and up to four in 640 pixel mode. The CSG-4567 can also time-multiplex the bitplanes to give a true four-color 1280 pixel picture. Vertical resolution is maintained at 200 lines as standard, but can be doubled to 400 with interlace The VIC-III bitplane modes take up to 64 KB of system RAM in non-interlaced or 128 KB RAM in interlaced (400 line) modes. Since the C65 is equipped with only 128 KB in its basic configuration, these modes would consume the entire RAM, and are therefore only useful in a RAM expanded system. On a basic system, it would probably have made more sense to write software which uses less demanding resolutions with fewer bitplanes - partly because this would consume less of the confined RAM space, but also because more bitplanes would demand a higher video DMA bandwidth and consequently slow down the CPU as a result.DAT and Blitter
The bitplanes on the C65 are organized in a less straightforward manner than e.g. on the Commodore Amiga, which organizes the bitplanes as straight rows of pixels: On the C65, the bytes within the bitplanes are organized as 25 rows of 40 or 80 stacks of 8 sequential bytes, similar to the original 320×200 VIC modes. Because this makes it harder to derive individual byte and pixel addresses from their position in the XY coordinate frame, the C65 provides a conversion mechanism in hardware called Display Address Translator (DAT). Further aid to the programmer comes in the form of a bit-blitter, which supports * Copy (up,down,invert), Fill, Swap, Mix (boolean Minterms) Hold, Modulus (window), Interrupt, and Resume modes * Block operations from 1 byte to 64 KBDOS
In contrast to previous 8-bit computers from Commodore, the C65 has a complete DOS through which the built-in 3.5-inch floppy disk drive can be controlled. Disks used by the C65 have a storage capacity of 880 KB and the drive is compatible with C1581. Since this format was uncommon for the former C64 owners, the C65 retains the serial IEC port for external Commodore disk drives. It's possible to use a1541
__NOTOC__
Year 1541 ( MDXLI) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
January–June
* February 12 – Pedro de Valdivia founds Santiago del Nuevo Extremo, whi ...
, 1571
Year 1571 ( MDLXXI) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
January–June
* January 11 – The Austrian nobility are granted freedom of religion.
* January 23 &nd ...
, 1581
1581 ( MDLXXXI) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) in the Julian calendar, and a common year starting on Thursday (link will display full calendar) of the Proleptic Gregorian calendar.
Events
Ja ...
, or other similar model.
The DOS itself is based on the Commodore PET IEEE 8250 drive DOS. Since it can only deal with two floppy disk drives, including the internal, only one external drive may be connected to the internal floppy disk controller. Like earlier systems, up to 4 drives can be daisy-chained on the IEC port.
Interfaces
The C65 includes the same ports of the C64. In addition, there is a DMA port for memory expansion. The latter is attached just like on the Amiga 500 via a flap in the bottom of the board. The built-in floppy disk drive is connected in parallel, serial Commodore drives can be connected via the usual IEC port. A plug for a genlock was also provided. Only the port for the C64datasette
The third, most common version of the 1530 C2N Datassette
The Commodore 1530 (C2N) Datasette, later also Datassette (a portmanteau of ''data'' and ''cassette''), is Commodore's dedicated magnetic tape data storage device. Using compact cassettes ...
is no longer available, and the user port missing—like the Aldi C64—the 9 volt AC line. The expansion port differs significantly from all prior C64 variants and rather resembles that of C16.
Sales
In December 2009, a working C65 on the online auction site eBay achieved a sales price of €6060. A computer with missing parts was in October 2011 sold for about US$20,100. In April 2013 an eBay auction reached a price of 17,827 EUR. In February 2015 an eBay auction closed at 20,050 EUR. An eBay auction in November 2016 reached 15,605 EUR. On September 7, 2017 a non-functional C65 missing a VIC-III chip, sold via eBay auction for US$18,350. On October 8, 2017 a user at lemon64.com notified members their intent to sell a fully functioning C65 with the asking price of US$27,000. In November 2017, a C65 prototype with RAM expansion board were sold for 81,450 €. On December 30, 2017, a non-functioning C65 motherboard without most of the chips was sold on EBay for US$790. On May 18, 2019, a functional C65 was sold on eBay at 20,550 EUR. On April 24, 2022, a working C65 was sold on eBay for 47,105 EUR.Legacy
Because this computer was only a prototype, not many units were made. If one appears on eBay, it may sell for around $20,000.MEGA65
On April 22, 2015 the Museum of Electronic Games & Art (MEGA) announced a recreation of this computer featuring similar specifications and technologies. Also backwards compatible with the Commodore 64, the MEGA65 features Commodore 65 compatible hardware recreated inFPGA
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturinghence the term '' field-programmable''. The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a hardware de ...
and is compatible with newer technologies such as HDMI. MEGA initially aimed to release their recreation of the Commodore 65 computer for the third quarter of 2016, as of September 2020, the pre-release dev-kit (r3) has been sold out and the in total 100 Dev-kits were delivered in Q4 2020. As per 30 September 2021, the final version of the MEGA65 with recreated C65 case, was available for pre-order. The first batch of 400 computers has been released to the customers as of May 2022.https://shop.trenz-electronic.de/en/TE0765-03-S001-MEGA65-highly-advanced-C64-and-C65-compatible-8-bit-computer?
(davidjseibuhr journalist, reports: New Mega65 Corporation began thereafter, they periodically remanufactured pcb revised computers, prebuilt or kits)
Cc=564
References
Further reading
On the Edge: The Spectacular Rise and Fall of Commodore
(2005), Variant Press. .
External links
By Cameron Kaiser and The Commodore Knowledge Base * tp://ftp.zimmers.net/pub/cbm/c65 FTP directory for the C65 at ftp.zimmers.net
Andre Kaesmacher's C64DX Development Site
C65 System ROMs and Utility Software
old-computers.com: LD-COMPUTERS.COM museum ~ Commodore C65
article on C65
8-Bit-Nirvana: Commodore 65
German C65-site with many photos and info
toxic-waste.de: Commodore C65 Information Page by TXW
{{Commodore International Commodore 64 Commodore computers Home computers Prototypes