color bars on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 SMPTE color bars are a television test pattern used where the NTSC video standard is utilized, including countries in
SMPTE color bars are a television test pattern used where the NTSC video standard is utilized, including countries in 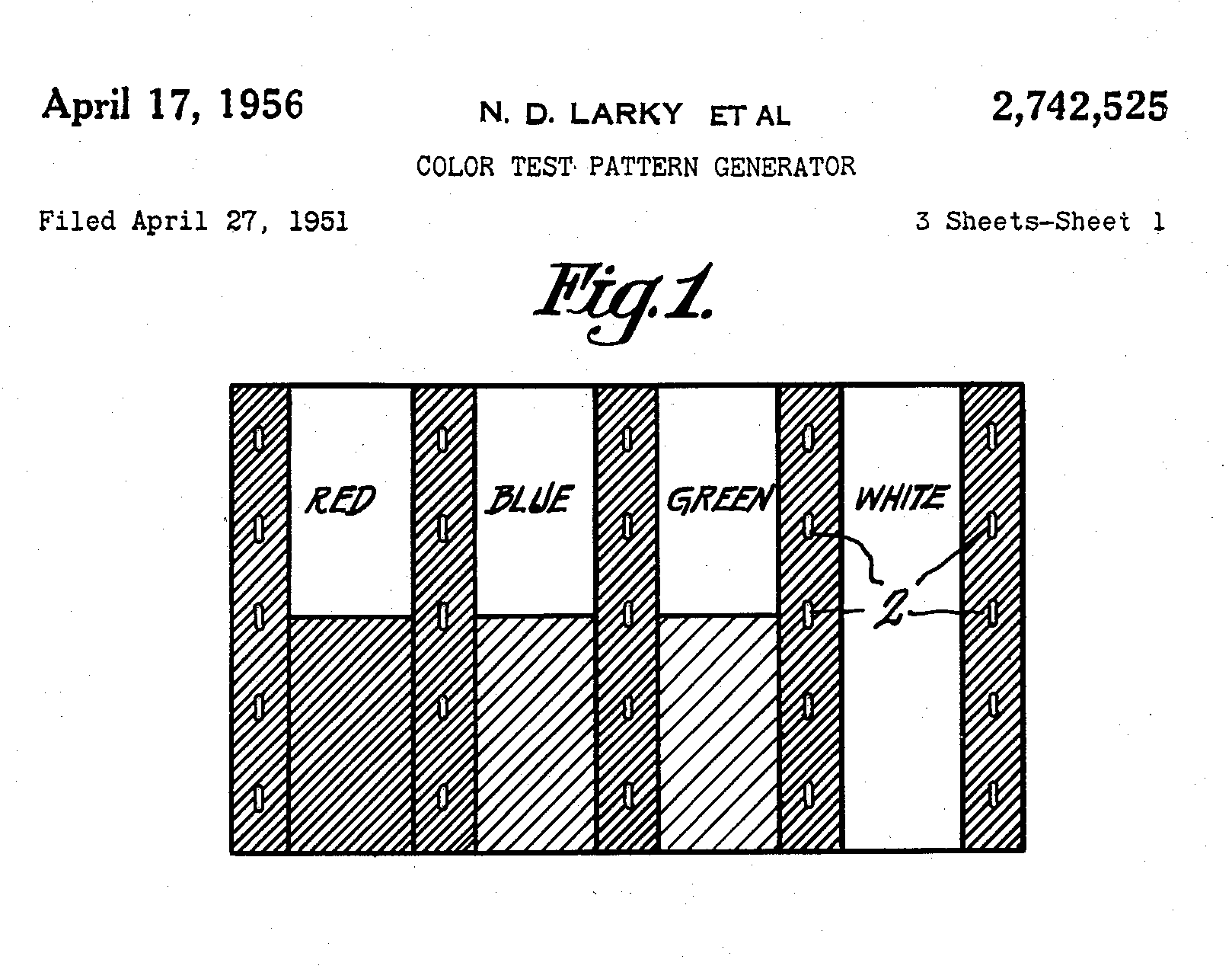
 An extended version of the SMPTE color bars, SMPTE RP 219:2002 was introduced to test HDTV signals (see subsection).
Although color bars were originally designed to calibrate analog NTSC equipment, they remain widely used in transmission and within modern digital television facilities. In the current context color bars are used to maintain accurate chroma and luminance levels in CRT, LCD, LED, plasma, and other video displays, as well as duplication, satellite, fiber-optic and microwave transmission, and television and webcast equipment.
In a survey of the top standards of the organizations' first 100 years, SMPTE EG-1 was voted as the 5th-most important SMPTE standard.
An extended version of the SMPTE color bars, SMPTE RP 219:2002 was introduced to test HDTV signals (see subsection).
Although color bars were originally designed to calibrate analog NTSC equipment, they remain widely used in transmission and within modern digital television facilities. In the current context color bars are used to maintain accurate chroma and luminance levels in CRT, LCD, LED, plasma, and other video displays, as well as duplication, satellite, fiber-optic and microwave transmission, and television and webcast equipment.
In a survey of the top standards of the organizations' first 100 years, SMPTE EG-1 was voted as the 5th-most important SMPTE standard.
Values sourced from the Tektronix TSG95 test pattern generator manual''
 An extended version of SMPTE Color Bars signal, developed by the Japanese Association of Radio Industry and Businesses as ARIB STD-B28 and standardized as SMPTE RP 219:2002 (High-Definition, Standard-Definition Compatible Color Bar Signal) was introduced to test HDTV signal with an aspect ratio of 16:9 that can be down converted to a
An extended version of SMPTE Color Bars signal, developed by the Japanese Association of Radio Industry and Businesses as ARIB STD-B28 and standardized as SMPTE RP 219:2002 (High-Definition, Standard-Definition Compatible Color Bar Signal) was introduced to test HDTV signal with an aspect ratio of 16:9 that can be down converted to a
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
. The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) refers to the pattern as Engineering Guideline (EG) 1-1990. Its components are a known standard, and created by test pattern generators. Comparing it as received to the known standard gives video engineers an indication of how an NTSC video signal has been altered by recording or transmission and what adjustments must be made to bring it back to specification. It is also used for setting a television monitor or receiver to reproduce NTSC chrominance and luminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through, is emitted from, or is reflected from a particular area, and falls withi ...
information correctly.
A precursor to the SMPTE test pattern was conceived by Norbert D. Larky (1927–2018) and David D. Holmes (1926–2006) of RCA Laboratories and first published in RCA Licensee Bulletin LB-819 on February 7, 1951. U.S. patent 2,742,525 Color Test Pattern Generator (now expired) was awarded on April 17, 1956, to Larky and Holmes. Later, the EIA published a standard, RS-189A, which in 1976 became EIA-189A, which described a Standard Color Bar Signal, intended for use as a test signal for adjustment of color monitors, adjustment of encoders, and rapid checks of color television transmission systems. In 1977, A. A. Goldberg, of the CBS Technology Center, described an improved color bar test signal developed at the center by Hank Mahler (1936–2021) that was then submitted to the SMPTE TV Video Technology Committee for consideration as a SMPTE recommended practice. This improved test signal was published as the standard SMPTE ECR 1-1978. Its development by CBS was awarded a Technology & Engineering Emmy Award in 2002. CBS did not file a patent application on the test signal, thereby putting it into the public domain for general use by the industry.

SMPTE ECR 1-1978 (SDTV)
In a SMPTE color barimage
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensiona ...
, the top two-thirds of the television picture contain seven vertical bars of 75% intensity. In order from left to right, the colors are white or gray, yellow, cyan
Cyan () is the color between green and blue on the visible spectrum of light. It is evoked by light with a predominant wavelength between 490 and 520 nm, between the wavelengths of green and blue.
In the subtractive color system, or CMYK color ...
, green, magenta, red, and blue. The choice of white or gray depends on whether that bar's luminance is 100% or not. This sequence runs through all seven possible combinations that use at least one of the three basic color components of green, red, and blue, with blue cycling on and off between every bar, red cycling on and off every two bars, and green on for the leftmost four bars and off for the rightmost three. Because green contributes the largest share of luminance, followed by red, then blue, this sequence of bars thus appears on a waveform monitor in luminance mode as a downward staircase from left to right. The graticule of a vectorscope is etched with boxes showing the permissible regions where the traces from these seven bars are supposed to fall if the signal is properly adjusted.
Below the main set of seven bars is a strip of blue, magenta, cyan
Cyan () is the color between green and blue on the visible spectrum of light. It is evoked by light with a predominant wavelength between 490 and 520 nm, between the wavelengths of green and blue.
In the subtractive color system, or CMYK color ...
, and white or gray castellations. When a television receiver is set to filter out all colors except for blue, these castellations, combined with the main set of color bars, are used to adjust the color controls; they appear as four solid blue bars, with no visible distinction between the bars and the castellations if the color controls are properly adjusted.
The bottom section contains a square of 100% intensity white and a rectangle of 7.5% intensity black, for use in setting the luminance range. More modern versions of the pattern feature a ''PLUGE
For television, televisions the picture line-up generation equipment (PLUGE or pluge) is the greyscale test patterns used in order to adjust the black level and contrast (vision), contrast of the picture monitor. Various PLUGE patterns can be gen ...
pulse''. The white square lines up so that it is below the yellow and cyan bars, on a waveform monitor this will show up with the white bar overlapping the peak of the yellow and cyan chroma at 100 IRE units. The ''pluge'' (short for picture line-up generation equipment) pulse is positioned within the black rectangle, below the red bar (it is present in the illustration but may be hard to see). It comprises three small vertical bars, a rightmost one with intensity 4% above black level (11.5 IRE), a middle one with intensity exactly equal to black (7.5 IRE), and a leftmost one with intensity 4% below black (super-black or ''blacker than black'', 3.5 IRE). The pluge pulse aids in adjusting the bottom of the luminance range to avoid either washing out the black tones into grays or collapsing picture information into the signal clipping that occurs a small distance below the black level (known as ''crushing the blacks''). When a monitor is properly adjusted, the rightmost pluge bar should be just barely visible, while the left two should appear indistinguishable from each other and completely black. Also in the bottom section are two sections that contain -In-phase and +Quadrature signals (see YIQ), centered on black level and having the same gain as the color burst signal; these show up on the pattern as a square of very dark blue, and a square of very dark purple. On a vectorscope, they appear as two short lines ninety degrees apart. These are used to ensure that the television receiver is properly demodulating the 3.58 MHz color subcarrier portion of the signal. The vectors for the -I and +Q blocks should fall exactly on the I and Q axes on the vectorscope if the chrominance signal is demodulated properly.
These bars give rise to the former portion of the casual term ''bars and tone''. Typically, a television network, TV station, or other originator of video programming transmits SMPTE color bars together with a continuous 1,000 Hz sine wave
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the '' sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic function. It occurs often in ...
before sending program material, in order to assert ownership of the transmission line or medium, and so that receiving stations and intermediary telecommunications providers may adjust their equipment. Likewise, producers of television programs typically record ''bars and tone'' at the beginning of a videotape or other recording medium so that the playback equipment can be calibrated
In measurement technology and metrology, calibration is the comparison of measurement values delivered by a device under test with those of a Standard (metrology), calibration standard of known accuracy. Such a standard could be another measurem ...
. Often, the name or callsign
In broadcasting and radio communications, a call sign (also known as a call name or call letters—and historically as a call signal—or abbreviated as a call) is a Identifier, unique identifier for a transmitter station. A call sign can be form ...
of the TV station, other information such as a real-time clock, or another signal source is graphically superimposed over the bars.
Analog NTSC
Values of 75% (75/7.5/75/7.5) SMPTE ECR 1-1978 color bars as analog NTSC signals: ''Note: IRE units apply to both NTSCcomposite video
Composite video is an analog video signal format that carries standard-definition video (typically at 525 lines or 625 lines) as a single channel. Video information is encoded on one channel, unlike the higher-quality S-Video (two channe ...
and broadcast signals while mV values only apply to NTSC composite video.Values sourced from the Tektronix TSG95 test pattern generator manual''
Digital video
For digital video sources, the 10-bitYCbCr
YCbCr, Y′CbCr, or Y Pb/Cb Pr/Cr, also written as YCBCR or Y′CBCR, is a family of color spaces used as a part of the color image pipeline in video and digital photography systems. Y′ is the Luma (video), luma component and CB and CR are t ...
values for SD color bars are based on the SMPTE formula for Y from the NTSC system ( Y = 0.299R + 0.587G + 0.114B). The following table show the expected digital values, for example when measured using a signal analyzer A signal analyzer is an instrument that measures the magnitude and phase of the input signal at a single frequency within the IF bandwidth of the instrument. It employs digital techniques to extract useful information that is carried by an electric ...
.
Note: Values sourced from "''Leader Teleproduction Test Volume 3 Number 4 - Digital Video Levels''"
The colors below are presented using sRGB
sRGB is a standard RGB (red, green, blue) color space that HP and Microsoft created cooperatively in 1996 to use on monitors, printers, and the World Wide Web. It was subsequently standardized by the International Electrotechnical Commission ...
transfer of CSS
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a style sheet language used for describing the presentation of a document written in a markup language such as HTML or XML (including XML dialects such as SVG, MathML or XHTML). CSS is a cornerstone t ...
. Since sRGB is the standard colorspace for webpages and computer screens, this gives only an idea of the intended colors. They are not completely representative of how they look on TV displays, since these follow the ITU-R BT.1886
ITU-R BT.1886 is the reference EOTF of SDR-TV. It is a gamma 2.4 transfer function (a power law with a 2.4 exponent) considered as a satisfactory approximation of the response characteristic of CRT to electrical signal. It has been standardized ...
standard, specifying a different gamma correction
Gamma correction or gamma is a nonlinear operation used to encode and decode luminance or tristimulus values in video or still image systems. Gamma correction is, in the simplest cases, defined by the following power-law expression:
: V_\text ...
value, and thus colors below will look darker on such a display, and those darker colors will be the reference ones. The off-by-one errors (for example 254 instead of 255 and 1 instead of 0) happen because the 8 bit Y'PbPr values were used when decoding to R'G'B', if you use 10-bit Y'PbPr that does not happen.
Y'PbPr
YPbPr or Y'PbPr, also written as , is a color space used in video electronics, in particular in reference to component video cables. YPBPR is gamma corrected YCBCR color space (it is not analog YUV that was used for analog TV, though compo ...
(and Y'CbCr
YCbCr, Y′CbCr, or Y Pb/Cb Pr/Cr, also written as YCBCR or Y′CBCR, is a family of color spaces used as a part of the color image pipeline in video and digital photography systems. Y′ is the luma component and CB and CR are the blue-dif ...
) values of 75% (100/0/75/0) SMPTE ECR 1-1978 color bars (0.75 * 219 + 16 = 180) using BT.709-2 matrix coefficients as written in RP 219:2002:
The source data for 10-bit and 12-bit Y'PbPr is 8-bit Studio R'G'B', so 10-bit data is not just a bitshift operation (that means multiply by 4) from 8-bit Y'PbPr, as usually the case. For example, for 75% Blue 28-212-120 would be just 112-848-480, but it is actually 111-848-481.
SMPTE RP 219:2002 (HDTV version)
SDTV
Standard-definition television (SDTV, SD, often shortened to standard definition) is a television system which uses a resolution that is not considered to be either high or enhanced definition. "Standard" refers to it being the prevailing spe ...
color bar signal with an aspect ratio of either 4:3 or 16:9. The Color Bar signal is generated with unconventionally slow rise and fall time value to facilitate video level control and monitor color adjustments of HDTV and SDTV equipment. Digital test images generated following the SMPTE RP 219:2002 specifications and adapted to perfectly fit 114 standard and non-standard resolutions for both 16bpp and 8bpp, are freely available in the COLOR dataset of the TESTIMAGES archive. Later RP 219:2002 became RP 219-1:2014 and then RP 219-2:2016 was added for UHD (and ARIB STD-B66). Then ITU-R Rec. BT.2111 was done with PQ and HLG HDR transfer functions (like ARIB STD-B72).
Values
The values of 100% (100/0/100/0) SMPTE RP 219:2002 color bars (1.00 * 219 + 16 = 235) using BT.709 matrix coefficients (only white and black are the same using BT.601 matrix), taken from the standard:ITU-R
The ITU Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) is one of the three sectors (divisions or units) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and is responsible for radio communications.
Its role is to manage the international radio-frequency sp ...
Rec. BT.1729 specified the last two 100% colors, green and magenta. It also specified all 100% colors for BT.601 matrix, not only BT.709.
See also
*EBU color bars
The EBU colour bars is a television test card used to check if a video signal has been altered by recording or transmission, and what adjustments must be made to bring it back to specification. It is also used for setting a television monitor ...
* China Girl (filmmaking)
In the motion picture industry, a China girl is a type of test film, an image of a woman accompanied by color bars that appears for a few frames (typically one to four) in the reel leader. A "China Girl" was used by the lab technician for calibr ...
* Indian-head test pattern
The Indian-head test pattern is a test card created by RCA of Harrison, New Jersey, which became the standard image of the RCA TK-1 monoscope. It features a drawing of a Native American wearing a headdress and numerous graphic elements designed ...
* Test Card F
Test Card F is a test card that was created by the BBC and used on television in the United Kingdom and in countries elsewhere in the world for more than four decades. Like other test cards, it was usually shown while no programmes were being ...
* 2-pop
Used in television production and filmmaking post-production, a 2-pop is a 1 kHz tone that is one frame long and placed 2 seconds before the start of a program. It is a simple and effective method of ensuring synchronization between sound ...
* Philips PM5544
The Philips PM5544 is a television pattern generator, most commonly used to provide a television station with a complex test card commonly referred to as a Philips Pattern or PTV Circle pattern. The content and layout of the pattern was designed ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Smpte Color Bars SMPTE standards Test cards Television terminology Articles containing video clips de:Testbild#SMPTE-Testbild