Coffin–Siris Syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
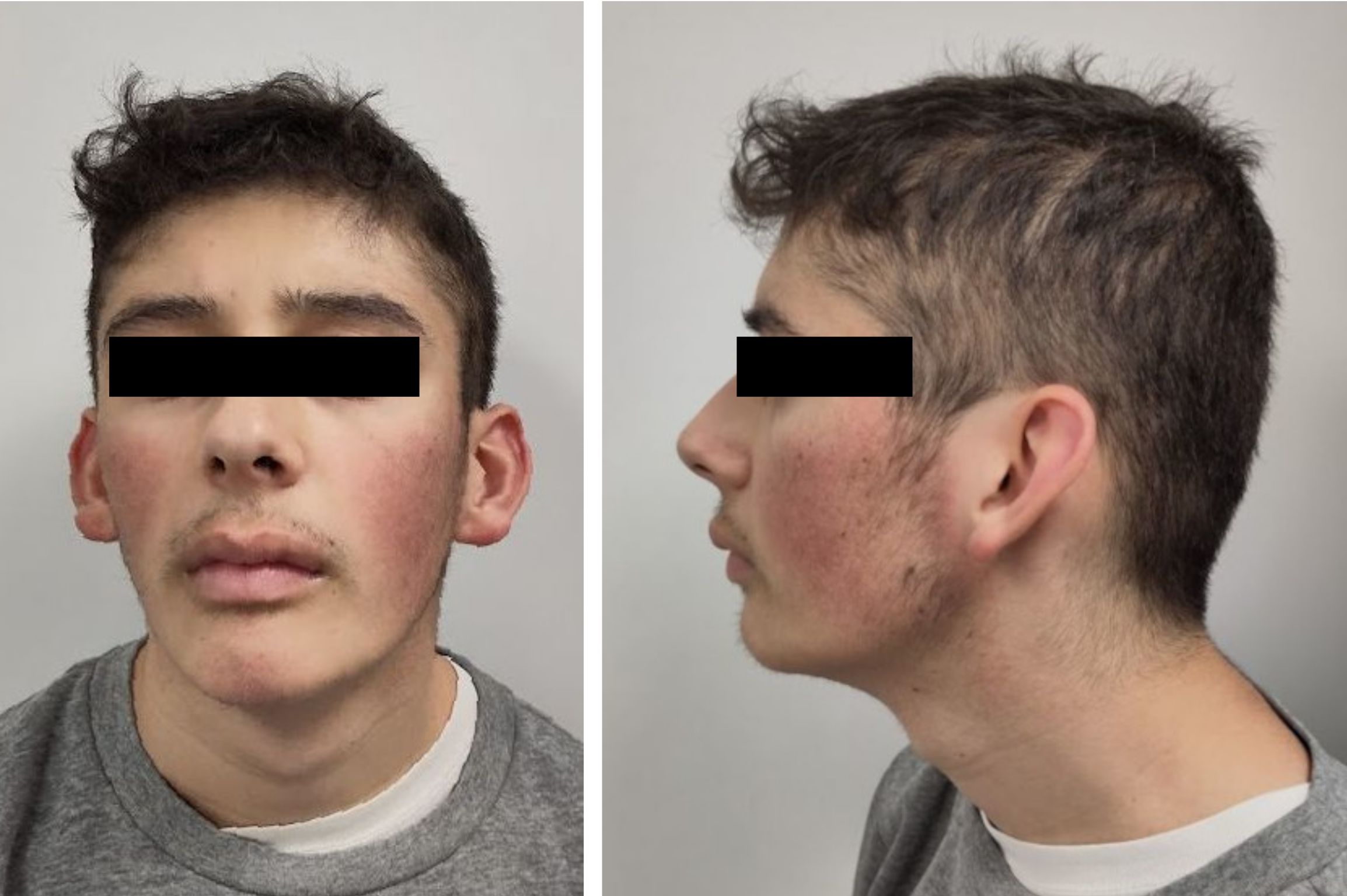 Coffin–Siris Syndrome (CSS), first described in 1970 by Dr Coffin and Dr Siris, is a rare genetic disorder that causes
Coffin–Siris Syndrome (CSS), first described in 1970 by Dr Coffin and Dr Siris, is a rare genetic disorder that causes
 This syndrome has been associated with mutations in the ARID1B gene, which is the most prevalent in CSS.
There are also multiple genes mutations associated to this syndrome, including SOX11, ARID2, DPF2, PHF6,
This syndrome has been associated with mutations in the ARID1B gene, which is the most prevalent in CSS.
There are also multiple genes mutations associated to this syndrome, including SOX11, ARID2, DPF2, PHF6,
Coffin–Siris syndrome
on
 Coffin–Siris Syndrome (CSS), first described in 1970 by Dr Coffin and Dr Siris, is a rare genetic disorder that causes
Coffin–Siris Syndrome (CSS), first described in 1970 by Dr Coffin and Dr Siris, is a rare genetic disorder that causes developmental delays
Specific developmental disorders (SDD) was a classification of disorders characterized by delayed development in one specific area or areas.Ahuja Vyas: ''Textbook of Postgraduate Psychiatry'' (2 Vols.), 2nd ed. 1999 Specific developmental disorders ...
and absent fifth finger
The little finger, or pinkie, also known as the baby finger, fifth digit, or pinky finger, is the most ulnar and smallest digit of the human hand, and next to the ring finger.
Etymology
The word "pinkie" is derived from the Dutch word ''pi ...
and toe nails.
There had been 31 reported cases by 1991. The number of occurrences since then has grown and is now reported to be around 200.
The differential includes Nicolaides–Baraitser syndrome.
Presentation
* mild to moderate to severeintellectual disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability in the United Kingdom and formerly mental retardation, Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010). is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by signif ...
, also called "developmental disability
Developmental disability is a diverse group of chronic conditions, comprising mental or physical impairments that arise before adulthood. Developmental disabilities cause individuals living with them many difficulties in certain areas of life, espe ...
"
* short fifth digits with hypoplastic or absent nails
* low birth weight
* feeding difficulties upon birth
* frequent respiratory infections during infancy
* hypotonia
Hypotonia is a state of low muscle tone (the amount of tension or resistance to stretch in a muscle), often involving reduced muscle strength. Hypotonia is not a specific medical disorder, but a potential manifestation of many different diseases ...
* joint laxity
* delayed bone age Bone age is the degree of a person's skeletal development. In children, bone age serves as a measure of physiological maturity and aids in the diagnosis of growth abnormalities, endocrine disorders, and other medical conditions. As a person grows fr ...
* microcephaly
Microcephaly (from New Latin ''microcephalia'', from Ancient Greek μικρός ''mikrós'' "small" and κεφαλή ''kephalé'' "head") is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it ...
* coarse facial features, including wide nose, wide mouth, and thick eyebrows and lashes
Causes
Disease can be inherited as anautosomal dominant
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and ...
trait, however most cases of CSS appear to be the result of a de novo mutation A de novo mutation is any mutation/alteration in the genome of any organism (humans, animals, plant, microbes, etc.) that wasn't present or transmitted by their parents. This type of mutation (like any other) occurs spontaneously during the process ...
.
 This syndrome has been associated with mutations in the ARID1B gene, which is the most prevalent in CSS.
There are also multiple genes mutations associated to this syndrome, including SOX11, ARID2, DPF2, PHF6,
This syndrome has been associated with mutations in the ARID1B gene, which is the most prevalent in CSS.
There are also multiple genes mutations associated to this syndrome, including SOX11, ARID2, DPF2, PHF6, SMARCA2
Probable global transcription activator SNF2L2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SMARCA2'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the SWI/SNF family of proteins and is highly similar to the brahma protein o ...
, SMARCA4
Transcription activator BRG1 also known as ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler SMARCA4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SMARCA4'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the SWI/SNF family of proteins and i ...
, SMARCB1
SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily B member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SMARCB1'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is part of a complex that relieves repressi ...
, SMARCC2, SMARCE1, SOX4.
The diagnosis is generally based on the presence of major and at least one minor clinical sign and can be confirmed by molecular genetic testing of the causative genes. Recent studies revealed that fifth finger nail/distal phalanx hypoplasia or aplasia is not a mandatory finding.
Typically, lab work will be done to rule out other conditions and genetic testing will also be performed to get the official diagnosis.
Treatment
There is no known cure or standard for treatment. Treatment is based on symptoms and may include physical, occupational and speech therapy and educational services as well.References
External links
Coffin–Siris syndrome
on
Orphanet
Orphanet is a knowledge base dedicated to rare diseases as well as corresponding diagnosis, orphan drugs, clinical trials and expert networks
The website is managed by a network of academic establishments from 40 countries, led by Inserm.
It c ...
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Coffin-Siris syndrome
Syndromes with intellectual disability
Genetic disorders with OMIM but no gene
Syndromes affecting the nervous system