Coal power plant on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A coal-fired power station or coal power plant is a thermal power station which burns
A coal-fired power station or coal power plant is a thermal power station which burns
 As a type of thermal power station, a coal-fired power station converts chemical energy stored in coal successively into
As a type of thermal power station, a coal-fired power station converts chemical energy stored in coal successively into
 two-thirds of coal burned is to generate electricity. In 2020 coal was the largest source of electricity at 34%. Over half of global coal-fired generation in 2020 occurred in China, and coal provided approximately 60% of electricity in China, India and Indonesia.
Globally in 2020, 2,059 GW of coal-fired capacity was operational, with 50 GW newly commissioned and 25 GW under construction (primarily in China), while 38 GW was retired (mainly in the US and EU).
By 2023, global coal power capacity had increased to 2,130 GW, largely due to 47.4 GW of additions in China.
While some nations pledged to transition away from coal power at the 2021 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP26) through the ''Global Coal to Clean Power Transition Statement'', significant challenges persist, especially in developing countries such as Indonesia and Vietnam.
two-thirds of coal burned is to generate electricity. In 2020 coal was the largest source of electricity at 34%. Over half of global coal-fired generation in 2020 occurred in China, and coal provided approximately 60% of electricity in China, India and Indonesia.
Globally in 2020, 2,059 GW of coal-fired capacity was operational, with 50 GW newly commissioned and 25 GW under construction (primarily in China), while 38 GW was retired (mainly in the US and EU).
By 2023, global coal power capacity had increased to 2,130 GW, largely due to 47.4 GW of additions in China.
While some nations pledged to transition away from coal power at the 2021 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP26) through the ''Global Coal to Clean Power Transition Statement'', significant challenges persist, especially in developing countries such as Indonesia and Vietnam.
 As coal is mainly
As coal is mainly
 Coal burning power plants kill many thousands of people every year with their emissions of
Coal burning power plants kill many thousands of people every year with their emissions of
 In May 2021, the G7 committed to end support for coal-fired power stations within the year. The G7's commitment to end coal support is significant as their coal capacity decreased from 23% (443 GW) in 2015 to 15% (310 GW) in 2023, reflecting a shift towards greener policies. This contrasts with China and India, where coal remains central to energy policy.
As of 2023, the Group of Twenty (G20) holds 92% of the world's operating coal capacity (1,968 GW) and 88% of pre-construction capacity (336 GW).
The energy policy of China regarding coal and coal in China are the most important factors regarding the future of coal-fired power stations, because the country has so many. According to one analysis local officials overinvested in coal-fired power in the mid-2010s because central government guaranteed operating hours and set a high wholesale electricity price.
In democracies coal power investment follows an environmental Kuznets curve. The energy policy of India about coal is an issue in the politics of India.
In May 2021, the G7 committed to end support for coal-fired power stations within the year. The G7's commitment to end coal support is significant as their coal capacity decreased from 23% (443 GW) in 2015 to 15% (310 GW) in 2023, reflecting a shift towards greener policies. This contrasts with China and India, where coal remains central to energy policy.
As of 2023, the Group of Twenty (G20) holds 92% of the world's operating coal capacity (1,968 GW) and 88% of pre-construction capacity (336 GW).
The energy policy of China regarding coal and coal in China are the most important factors regarding the future of coal-fired power stations, because the country has so many. According to one analysis local officials overinvested in coal-fired power in the mid-2010s because central government guaranteed operating hours and set a high wholesale electricity price.
In democracies coal power investment follows an environmental Kuznets curve. The energy policy of India about coal is an issue in the politics of India.
Coal fired power plant
Energy Education by the
How a coal plant works video
by the Tennessee Valley Authority
How a coal plant works video
by
Electricity from coal
by the World Coal Association
World's coal power plants mapped
by Carbon Brief * by various environmental, social justice and health advocates
Coal-fired power
by the
Economics of coal
by Carbon Tracker
Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air
{{Authority control Greenhouse gas emissions Subsidies
coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
to generate electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
. Worldwide there are about 2,500 coal-fired power stations, on average capable of generating a gigawatt each. They generate about a third of the world's electricity, but cause many illnesses and the most early deaths per unit of energy produced, mainly from air pollution
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the Atmosphere of Earth, air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be Gas, gases like Ground-level ozone, ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles li ...
. World installed capacity doubled from 2000 to 2023 and increased 2% in 2023.
A coal-fired power station is a type of fossil fuel power station. The coal is usually pulverized and then burned in a pulverized coal-fired boiler. The furnace heat converts boiler water to steam
Steam is water vapor, often mixed with air or an aerosol of liquid water droplets. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization. Saturated or superheated steam is inv ...
, which is then used to spin turbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced can be used for generating electrical ...
s that turn generators. Thus chemical energy stored in coal is converted successively into thermal energy
The term "thermal energy" is often used ambiguously in physics and engineering. It can denote several different physical concepts, including:
* Internal energy: The energy contained within a body of matter or radiation, excluding the potential en ...
, mechanical energy and, finally, electrical energy
Electrical energy is the energy transferred as electric charges move between points with different electric potential, that is, as they move across a voltage, potential difference. As electric potential is lost or gained, work is done changing the ...
.
Coal-fired power stations are the largest single contributor to climate change, releasing approximately 12 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
annually, about one-fifth of global greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate chan ...
. China accounts for over half of global coal-fired electricity generation. While the total number of operational coal plants began declining in 2020, due to retirements in Europe and the Americas, construction continues in Asia, primarily in China. The profitability of some plants is maintained by externalities, as the health and environmental costs of coal production and use are not fully reflected in electricity prices. However, newer plants face the risk of becoming stranded assets. The UN Secretary General has called for OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
nations to phase out coal-fired generation by 2030, and the rest of the world by 2040.
History
The first coal-fired power stations were built in the late 19th century and usedreciprocating engine
A reciprocating engine, more often known as a piston engine, is a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of al ...
s to generate direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional electric current, flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor (material), conductor such as a wire, but can also flow throug ...
. Steam turbines allowed much larger plants to be built in the early 20th century and alternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in w ...
was used to serve wider areas.
Transport and delivery of coal
Coal is delivered by highway truck, rail,barge
A barge is typically a flat-bottomed boat, flat-bottomed vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. Original use was on inland waterways, while modern use is on both inland and ocean, marine water environments. The firs ...
, collier ship or coal slurry pipeline. Generating stations are sometimes built next to a mine; especially one mining coal, such as lignite, which is not valuable enough to transport long-distance; so may receive coal by conveyor belt or massive diesel-electric-drive trucks
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport freight, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame construction ...
. A large coal train called a "unit train" may be 2 km long, containing 130-140 cars with around 100 tonnes of coal in each one, for a total load of over 10,000 tonnes. A large plant under full load requires at least one coal delivery this size every day. Plants may get as many as three to five trains a day, especially in "peak season" during the hottest summer or coldest winter months (depending on local climate) when power consumption is high.
Modern unloaders use rotary dump devices, which eliminate problems with coal freezing in bottom dump cars. The unloader includes a train positioner arm that pulls the entire train to position each car over a coal hopper. The dumper clamps an individual car against a platform that swivels the car upside down to dump the coal. Swiveling couplers enable the entire operation to occur while the cars are still coupled together. Unloading a unit train takes about three hours.
Shorter trains may use railcars with an "air-dump", which relies on air pressure from the engine plus a "hot shoe" on each car. This "hot shoe" when it comes into contact with a "hot rail" at the unloading trestle, shoots an electric charge through the air dump apparatus and causes the doors on the bottom of the car to open, dumping the coal through the opening in the trestle. Unloading one of these trains takes anywhere from an hour to an hour and a half. Older unloaders may still use manually operated bottom-dump rail cars and a "shaker" attached to dump the coal.
A collier (cargo ship carrying coal) may hold of coal and takes several days to unload. Some colliers carry their own conveying equipment to unload their own bunkers; others depend on equipment at the plant. For transporting coal in calmer waters, such as rivers and lakes, flat-bottomed barge
A barge is typically a flat-bottomed boat, flat-bottomed vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. Original use was on inland waterways, while modern use is on both inland and ocean, marine water environments. The firs ...
s are often used. Barges are usually unpowered and must be moved by tugboat
A tugboat or tug is a marine vessel that manoeuvres other vessels by pushing or pulling them, with direct contact or a tow line. These boats typically tug ships in circumstances where they cannot or should not move under their own power, suc ...
s or towboats.
For start up or auxiliary purposes, the plant may use fuel oil as well. Fuel oil can be delivered to plants by pipeline
A pipeline is a system of Pipe (fluid conveyance), pipes for long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas, typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than of pipeline in 120 countries ...
, tanker, tank car or truck. Oil is stored in vertical cylindrical steel tanks with capacities as high as . The heavier no. 5 "bunker" and no. 6 fuels are typically steam-heated before pumping in cold climates.
Operation
thermal energy
The term "thermal energy" is often used ambiguously in physics and engineering. It can denote several different physical concepts, including:
* Internal energy: The energy contained within a body of matter or radiation, excluding the potential en ...
, mechanical energy and, finally, electrical energy
Electrical energy is the energy transferred as electric charges move between points with different electric potential, that is, as they move across a voltage, potential difference. As electric potential is lost or gained, work is done changing the ...
. The coal is usually pulverized and then burned in a pulverized coal-fired boiler. The heat from the burning pulverized coal converts boiler water to steam
Steam is water vapor, often mixed with air or an aerosol of liquid water droplets. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization. Saturated or superheated steam is inv ...
, which is then used to spin turbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced can be used for generating electrical ...
s that turn generators. Compared to a thermal power station burning other fuel types, coal specific fuel processing and ash disposal is required.
For units over about 200 MW capacity, redundancy of key components is provided by installing duplicates of the forced and induced draft fans, air preheaters, and fly ash collectors. On some units of about 60 MW, two boilers per unit may instead be provided. The hundred largest coal power stations range in size from 3,000 MW to 6,700 MW.
Coal processing
Coal is prepared for use by crushing the rough coal to pieces less than in size. The coal is then transported from the storage yard to in-plant storage silos by conveyor belts at rates up to 4,000 tonnes per hour. In plants that burn pulverized coal, silos feed coal to pulverizers (coal mills) that take the larger 5 cm pieces, grind them to the consistency of talcum powder, sort them, and mix them with primary combustion air, which transports the coal to the boiler furnace and preheats the coal in order to drive off excess moisture content. A 500 MWe plant may have six such pulverizers, five of which can supply coal to the furnace at 250 tonnes per hour under full load. In plants that do not burn pulverized coal, the larger 5 cm pieces may be directly fed into the silos which then feed either mechanical distributors that drop the coal on a traveling grate or the cyclone burners, a specific kind of combustor that can efficiently burn larger pieces of fuel.Boiler operation
Plants designed for lignite (brown coal) are used in locations as varied as Germany,Victoria, Australia
Victoria, commonly abbreviated as Vic, is a state in southeastern Australia. It is the second-smallest state (after Tasmania), with a land area of ; the second-most-populated state (after New South Wales), with a population of over 7 million; ...
, and North Dakota
North Dakota ( ) is a U.S. state in the Upper Midwest, named after the indigenous Dakota people, Dakota and Sioux peoples. It is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba to the north and by the U.S. states of Minneso ...
. Lignite is a much younger form of coal than black coal. It has a lower energy density than black coal and requires a much larger furnace for equivalent heat output. Such coals may contain up to 70% water and ash, yielding lower furnace temperatures and requiring larger induced-draft fans. The firing systems also differ from black coal and typically draw hot gas from the furnace-exit level and mix it with the incoming coal in fan-type mills that inject the pulverized coal and hot gas mixture into the boiler.
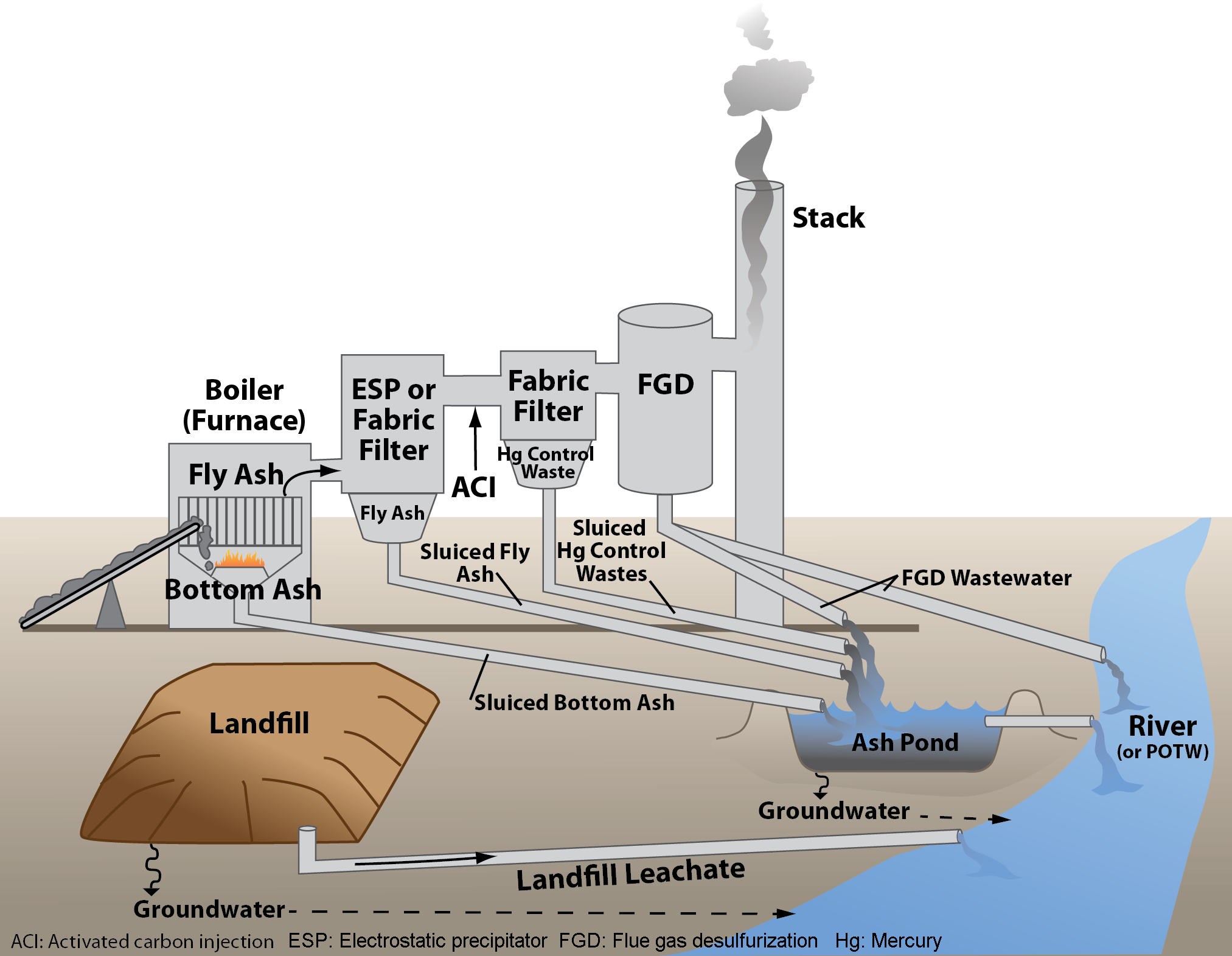
Ash disposal
The ash is often stored in ash ponds. Although the use of ash ponds in combination with air pollution controls (such as wet scrubbers) decreases the amount of airborne pollutants, the structures pose serious health risks for the surrounding environment. Power utility companies have often built the ponds without liners, especially in the United States, and therefore chemicals in the ash can leach intogroundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
and surface waters.
Since the 1990s, power utilities in the U.S. have designed many of their new plants with dry ash handling systems. The dry ash is disposed in landfills, which typically include liners and groundwater monitoring systems. Dry ash may also be recycled into products such as concrete, structural fills for road construction and grout.
Fly ash collection
Fly ash
Coal combustion products (CCPs), also called coal combustion wastes (CCWs) or coal combustion residuals (CCRs), are byproducts of burning coal. They are categorized in four groups, each based on physical and chemical forms derived from coal combust ...
is captured and removed from the flue gas by electrostatic precipitators or fabric bag filters (or sometimes both) located at the outlet of the furnace and before the induced draft fan. The fly ash is periodically removed from the collection hoppers below the precipitators or bag filters. Generally, the fly ash is pneumatically transported to storage silos and stored on site in ash ponds, or transported by trucks or railroad cars to landfill
A landfill is a site for the disposal of waste materials. It is the oldest and most common form of waste disposal, although the systematic burial of waste with daily, intermediate and final covers only began in the 1940s. In the past, waste was ...
s.
Bottom ash collection and disposal
At the bottom of the furnace, there is a hopper for collection ofbottom ash
Bottom ash is part of the non- combustible residue of combustion in a power plant, boiler, furnace, or incinerator. In an industrial context, it has traditionally referred to coal combustion and comprises traces of combustibles embedded in for ...
. This hopper is kept filled with water to quench the ash and clinkers falling down from the furnace. Arrangements are included to crush the clinkers and convey the crushed clinkers and bottom ash to on-site ash ponds, or off-site to landfills. Ash extractors are used to discharge ash from municipal solid waste–fired boilers.
Flexibility
Effectiveenergy policy
Energy policies are the government's strategies and decisions regarding the Energy production, production, Energy distribution, distribution, and World energy supply and consumption, consumption of energy within a specific jurisdiction. Energy ...
, law and electricity market
An electricity market is a system that enables the exchange of electrical energy, through an electrical grid. Historically, electricity has been primarily sold by companies that operate electric generators, and purchased by consumers or electr ...
s are essential for grid flexibility. While the flexibility of some coal-fired power stations can be enhanced, they generally offer less dispatchable generation than most gas-fired power plants. A key aspect of flexibility is low minimum load; however, certain flexibility upgrades for coal plants may be more costly than deploying renewable energy
Renewable energy (also called green energy) is energy made from renewable resource, renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human lifetime, human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind pow ...
sources with battery storage.
Coal power generation
 two-thirds of coal burned is to generate electricity. In 2020 coal was the largest source of electricity at 34%. Over half of global coal-fired generation in 2020 occurred in China, and coal provided approximately 60% of electricity in China, India and Indonesia.
Globally in 2020, 2,059 GW of coal-fired capacity was operational, with 50 GW newly commissioned and 25 GW under construction (primarily in China), while 38 GW was retired (mainly in the US and EU).
By 2023, global coal power capacity had increased to 2,130 GW, largely due to 47.4 GW of additions in China.
While some nations pledged to transition away from coal power at the 2021 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP26) through the ''Global Coal to Clean Power Transition Statement'', significant challenges persist, especially in developing countries such as Indonesia and Vietnam.
two-thirds of coal burned is to generate electricity. In 2020 coal was the largest source of electricity at 34%. Over half of global coal-fired generation in 2020 occurred in China, and coal provided approximately 60% of electricity in China, India and Indonesia.
Globally in 2020, 2,059 GW of coal-fired capacity was operational, with 50 GW newly commissioned and 25 GW under construction (primarily in China), while 38 GW was retired (mainly in the US and EU).
By 2023, global coal power capacity had increased to 2,130 GW, largely due to 47.4 GW of additions in China.
While some nations pledged to transition away from coal power at the 2021 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP26) through the ''Global Coal to Clean Power Transition Statement'', significant challenges persist, especially in developing countries such as Indonesia and Vietnam.
Efficiency
There are 4 main types of coal-fired power station in increasing order of efficiency are: subcritical, supercritical, ultra-supercritical and cogeneration (also called combined heat and power or CHP). Subcritical is the least efficient type, however recent innovations have allowed retrofits to older subcritical plants to meet or even exceed efficiency of supercritical plants.Integrated gasification combined cycle design
Integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) is a coal-based power generation technology that uses a high-pressure gasifier to convert coal (or other carbon-based fuels) into pressurized synthesis gas (syngas). The gasification process allows the use of a combined cycle generator, typically achieving higher efficiency. IGCC also facilitates removal of certain pollutants from the syngas before power generation. However, this technology is more expensive than conventional coal-fired power stations.Carbon dioxide emissions
 As coal is mainly
As coal is mainly carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
, coal-fired power stations have a high carbon intensity. On average, coal power stations emit far more greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
per unit electricity generated compared with other energy sources (see also life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources). In 2018 coal burnt to generate electricity emitted over 10 Gt of the 34 Gt total from fuel combustion (the overall total greenhouse gas emissions for 2018 was 55 Gt e).
Mitigation
Phase out
From 2015 to 2020, although coal generation hardly fell in absolute terms, some of its market share was taken by wind and solar. In 2020 only China increased coal power generation, and globally it fell by 4%. However, in 2021, China declared that it limited coal generation until 2025 and subsequently phase it out over time. The UN Secretary General has said thatOECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
countries should stop generating electricity from coal by 2030 and the rest of the world by 2040, otherwise limiting global warming to 1.5 °C, a target of the Paris Agreement, would be extremely difficult. A 2024 analysis by The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British newspaper published weekly in printed magazine format and daily on Electronic publishing, digital platforms. It publishes stories on topics that include economics, business, geopolitics, technology and culture. M ...
concluded that financing phase-out would be cheaper than carbon offsets. However phasing out in Asia can be a financial challenge as plants there are relatively young: in China the co-benefits of closing a plant vary greatly depending on its location. Vietnam is among the few coal-dependent fast developing countries that fully pledged to phase out unbated coal power by the 2040s or as soon as possible thereafter.
Ammonia co-firing
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
has a high hydrogen density and is easy to handle. It can be used as storing carbon-free fuel in gas turbine power generation and help significantly reduce CO₂ emissions as a fuel.
In Japan, the first major four-year test project was started in June 2021 to develop technology to enable co-firing a significant amount of ammonia at a large-scale commercial coal-fired plant. However low-carbon hydrogen and ammonia is in demand for sustainable shipping, which unlike electricity generation, has few other clean options.
Conversion
Some power stations are being converted to burn gas,biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how ...
or waste, and conversion to thermal storage will be trialed in 2023.
Carbon capture
Retrofitting some existing coal-fired power stations with carbon capture and storage was being considered in China in 2020, but this is very expensive, reduces the energy output and for some plants is not technically feasible.Pollution
 Coal burning power plants kill many thousands of people every year with their emissions of
Coal burning power plants kill many thousands of people every year with their emissions of particulates
Particulate matter (PM) or particulates are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspension (chemistry), suspended in the atmosphere of Earth, air. An ''aerosol'' is a mixture of particulates and air, as opposed to the particulate ...
, microscopic air pollutants that enter human lungs and other human organs and induce a variety of adverse medical conditions, including asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
, heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina pectoris, angina, myocardial infarction, heart attack), heart failure, ...
, low birth weight and cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
s. In the U.S. alone, such particulates, known as PM2.5 (particulates with a diameter of 2.5 μm or less), caused at least 460,000 excess deaths over two decades.
In some countries pollution is somewhat controlled by best available techniques, for example those in the EU through its Industrial Emissions Directive. In the United States, coal-fired plants are governed at the national level by several air pollution regulations, including the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS) regulation, by effluent guidelines for water pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of Body of water, water bodies, with a negative impact on their uses. It is usually a result of human activities. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and ...
, and by solid waste regulations under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA).
Coal-fired power stations continue to pollute in lightly regulated countries: such as the Western Balkans, India, Russia and South Africa, causing over a hundred thousand early deaths each year.
Local air pollution
Damage to health fromparticulates
Particulate matter (PM) or particulates are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspension (chemistry), suspended in the atmosphere of Earth, air. An ''aerosol'' is a mixture of particulates and air, as opposed to the particulate ...
, sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is r ...
and nitrogen oxide occurs mainly in Asia and is often due to burning low quality coal, such as lignite, in plants lacking modern flue gas treatment. Early deaths due to air pollution have been estimated at 200 per GW-year, however they may be higher around power plants where scrubbers are not used or lower if they are far from cities. Evidence indicates that exposure to sulfur, sulfates, or PM2.5 from coal emissions may be associated with higher relative morbidity or mortality risk than that to other PM2.5 constituents or PM2.5 from other sources per unit concentration.
Water pollution
Pollutants such as heavy metals leaching into ground water from unlined coal ash storage ponds or landfills pollute water, possibly for decades or centuries. Pollutant discharges from ash ponds to rivers (or other surface water bodies) typically includearsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
, lead, mercury, selenium
Selenium is a chemical element; it has symbol (chemistry), symbol Se and atomic number 34. It has various physical appearances, including a brick-red powder, a vitreous black solid, and a grey metallic-looking form. It seldom occurs in this elem ...
, chromium, and cadmium.
Mercury emissions from coal-fired power plants can fall back onto the land and water in rain, and then be converted into methylmercury
Methylmercury is an organometallic cation with the formula . It is the simplest organomercury compound. Methylmercury is extremely toxic, and its derivatives are the major source of organic mercury for humans. It is a bioaccumulative environment ...
by bacteria. Through biomagnification, this mercury can then reach dangerously high levels in fish. More than half of atmospheric mercury comes from coal-fired power plants.
Coal-fired power plants also emit sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is r ...
and nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
. These emissions lead to acid rain
Acid rain is rain or any other form of Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation that is unusually acidic, meaning that it has elevated levels of hydrogen ions (low pH). Most water, including drinking water, has a neutral pH that exists b ...
, which can restructure food webs and lead to the collapse of fish and invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
populations.
Mitigation of local pollution
local pollution in China, which has by far the most coal-fired power stations, is forecast to be reduced further in the 2020s and 2030s, especially if small and low efficiency plants are retired early.Economics
Subsidies
Coal power plants tend to serve as base load technology, as they have high availability factors, and are relatively difficult and expensive to ramp up and down. As such, they perform poorly in real-time energy markets, where they are unable to respond to changes in the locational marginal price. In the United States, this has been especially true in light of the advent of cheap natural gas, which can serve as a fuel in dispatchable power plants that substitute the role of baseload on the grid. In 2020 the coal industry was subsidized $US18 billion.Finance
Coal financing is the financial support provided for coal-related projects, encompassing coal mining and coal-fired power stations. Its role in shaping the global energy landscape and its environmental and climate impacts have made it a subject of concern. The misalignment of coal financing with international climate objectives, particularly the Paris Agreement, has garnered attention. The Paris Agreement aims to restrictglobal warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes ...
to well below 2 degrees Celsius and ideally limit it to 1.5 degrees Celsius. Achieving these goals necessitates a substantial reduction in coal-related activities.
Studies, including finance-based accounting of coal emissions, have revealed a misalignment of coal financing with climate objectives. Major nations, such as China, Japan, and the U.S., have extended financial support to overseas coal power infrastructure. The largest backers are Chinese banks under the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). This support has led to significant long-term climate and financial risks and harms the objectives of reducing CO2 emissions set by the Paris Agreement, of which China, the United States and Japan are signatories. A substantial portion of the associated emissions is anticipated to occur after 2019.
Coal financing poses challenges to the global decarbonization of the power generation sector. As renewable energy
Renewable energy (also called green energy) is energy made from renewable resource, renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human lifetime, human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind pow ...
technologies become cost-competitive, the economic viability of coal projects diminishes, making past fossil fuel investments less attractive. To address these concerns and align with climate goals, there is a growing call for stricter policies regarding overseas coal financing. Countries, including Japan and the U.S., have faced criticism for permitting the financing of certain coal projects. Strengthening the policies, potentially by banning public financing of coal projects entirely, would enhance their climate efforts and credibility. In addition, Enhanced transparency in disclosing financing details is crucial for evaluating their environmental impacts.
Capacity factors
In India capacity factors are below 60%. In 2020 coal-fired power stations in the United States had an overall capacity factor of 40%; that is, they operated at a little less than half of their cumulative nameplate capacity.Stranded assets
If global warming is limited to well below 2 °C as specified in the Paris Agreement, coal plant stranded assets of over US$500 billion are forecast by 2050, mostly in China. In 2020 think tank Carbon Tracker estimated that 39% of coal-fired plants were already more expensive than new renewables and storage and that 73% would be by 2025. about half of China's coal power companies are losing money and old and small power plants "have no hope of making profits". India is keeping potential stranded assets operating by subsidizing them.Politics
 In May 2021, the G7 committed to end support for coal-fired power stations within the year. The G7's commitment to end coal support is significant as their coal capacity decreased from 23% (443 GW) in 2015 to 15% (310 GW) in 2023, reflecting a shift towards greener policies. This contrasts with China and India, where coal remains central to energy policy.
As of 2023, the Group of Twenty (G20) holds 92% of the world's operating coal capacity (1,968 GW) and 88% of pre-construction capacity (336 GW).
The energy policy of China regarding coal and coal in China are the most important factors regarding the future of coal-fired power stations, because the country has so many. According to one analysis local officials overinvested in coal-fired power in the mid-2010s because central government guaranteed operating hours and set a high wholesale electricity price.
In democracies coal power investment follows an environmental Kuznets curve. The energy policy of India about coal is an issue in the politics of India.
In May 2021, the G7 committed to end support for coal-fired power stations within the year. The G7's commitment to end coal support is significant as their coal capacity decreased from 23% (443 GW) in 2015 to 15% (310 GW) in 2023, reflecting a shift towards greener policies. This contrasts with China and India, where coal remains central to energy policy.
As of 2023, the Group of Twenty (G20) holds 92% of the world's operating coal capacity (1,968 GW) and 88% of pre-construction capacity (336 GW).
The energy policy of China regarding coal and coal in China are the most important factors regarding the future of coal-fired power stations, because the country has so many. According to one analysis local officials overinvested in coal-fired power in the mid-2010s because central government guaranteed operating hours and set a high wholesale electricity price.
In democracies coal power investment follows an environmental Kuznets curve. The energy policy of India about coal is an issue in the politics of India.
Protests
In the 21st century people have often protested against opencast mining, for example at Hambach Forest, Akbelen Forest and Ffos-y-fran; and at sites of proposed new plants, such as in Kenya and China.See also
* Powering Past Coal Alliance * Global Energy MonitorNotes
References
External links
Coal fired power plant
Energy Education by the
University of Calgary
{{Infobox university
, name = University of Calgary
, image = University of Calgary coat of arms without motto scroll.svg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of arms
, former ...
How a coal plant works video
by the Tennessee Valley Authority
How a coal plant works video
by
Ontario Power Generation
Ontario Power Generation Inc. (OPG) is a Crown corporations of Canada, Crown corporation and "government business enterprise" that is responsible for approximately half of the electricity generation in the province of Ontario, Canada. It is w ...
Electricity from coal
by the World Coal Association
World's coal power plants mapped
by Carbon Brief * by various environmental, social justice and health advocates
Coal-fired power
by the
International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency (IEA) is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organization, established in 1974, that provides policy recommendations, analysis and data on the global energy sector. The 31 member countries and 13 associatio ...
Economics of coal
by Carbon Tracker
Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air
{{Authority control Greenhouse gas emissions Subsidies