Clifford's Tower on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
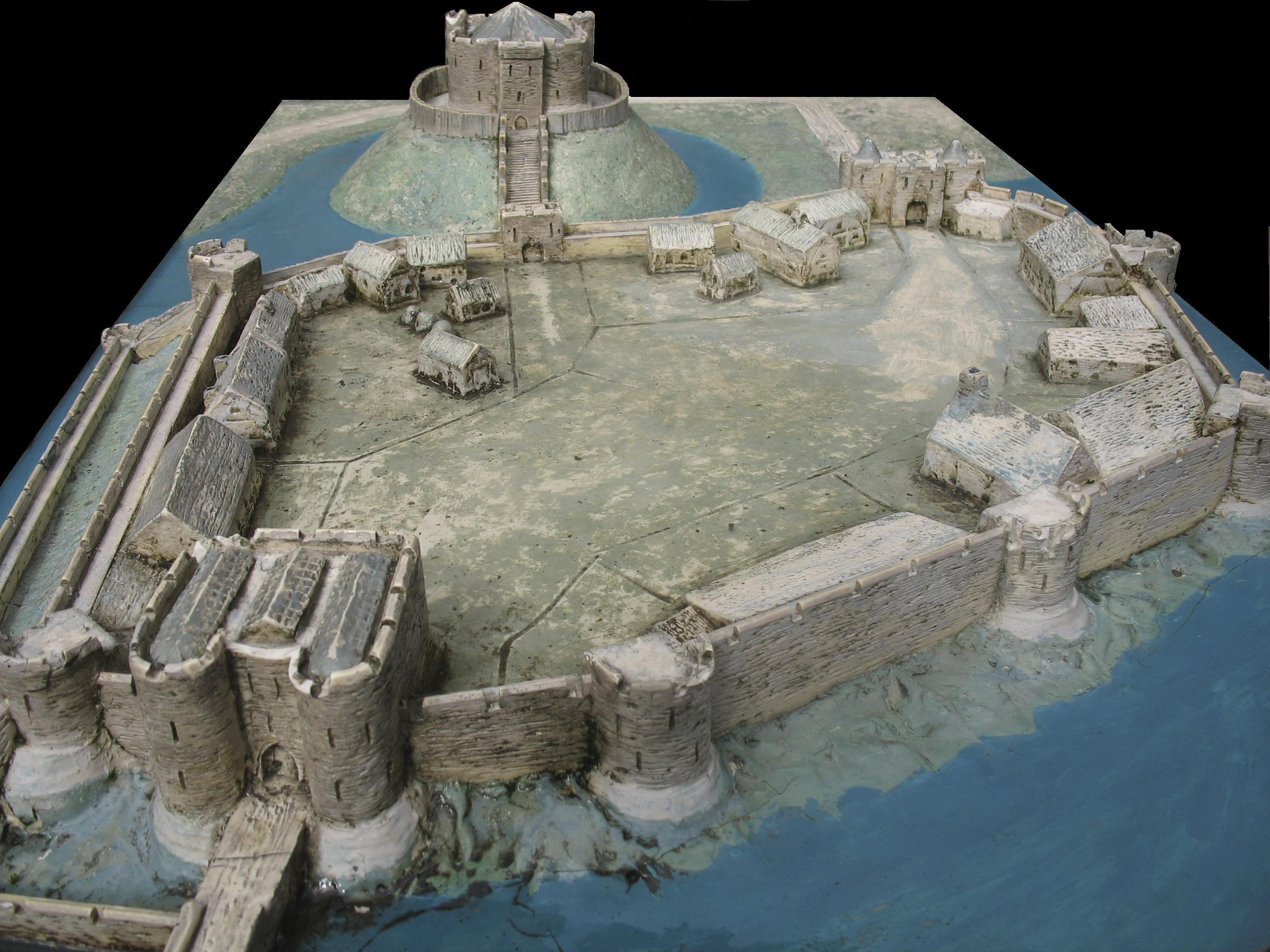
York Castle is a fortified complex in the city of
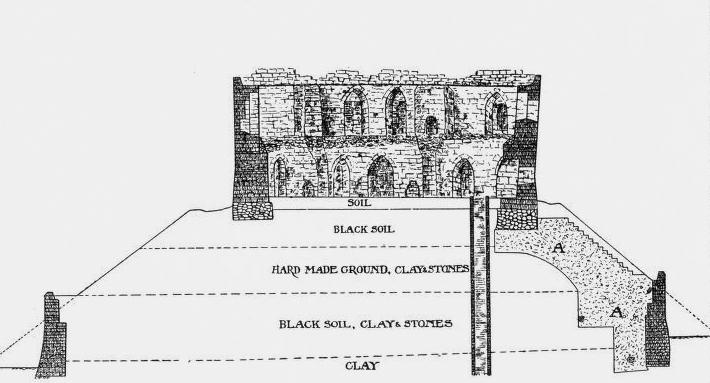
 King
King
 In the 15th century, York Castle, along with
In the 15th century, York Castle, along with
 Maintaining the castle was becoming increasingly expensive, and in 1614 King James sold the lease on Clifford's Tower and the surrounding land to John Babington and Edmund Duffield, a pair of property speculators. In turn, Babington and Duffield sold Clifford's Tower to a York merchant family. In 1642, however, the
Maintaining the castle was becoming increasingly expensive, and in 1614 King James sold the lease on Clifford's Tower and the surrounding land to John Babington and Edmund Duffield, a pair of property speculators. In turn, Babington and Duffield sold Clifford's Tower to a York merchant family. In 1642, however, the
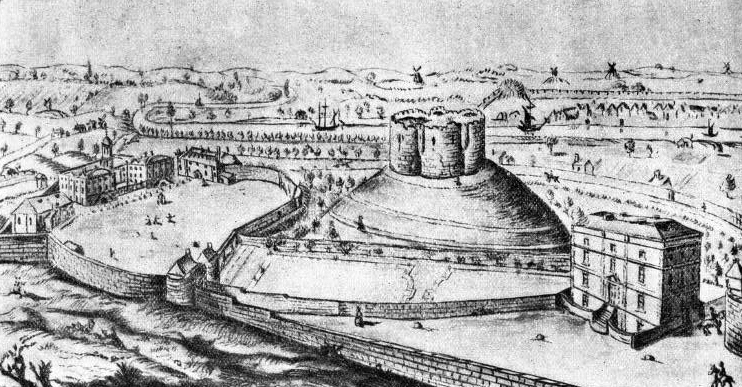 By 1701, the conditions of the county gaol had become scandalous and the decision was taken to redevelop the area occupied by the old bailey. A local tax helped to fund the development, and the king agreed for the ruins of St Mary's Abbey to be cannibalised for building stone. Three new buildings were erected to the south of Clifford's Tower. A new county gaol, built between 1701 and 1705 by William Wakefield, was placed on the south side, closely resembling the fashionable work of
By 1701, the conditions of the county gaol had become scandalous and the decision was taken to redevelop the area occupied by the old bailey. A local tax helped to fund the development, and the king agreed for the ruins of St Mary's Abbey to be cannibalised for building stone. Three new buildings were erected to the south of Clifford's Tower. A new county gaol, built between 1701 and 1705 by William Wakefield, was placed on the south side, closely resembling the fashionable work of
 Criticism of the castle prison increased at the end of the 18th century.Cooper, p.191. The facilities were felt to be inadequate and the crowds of spectators who gathered outside the prison to see inmates being taken into York for execution unseemly. Attempts were made to improve the way executions were carried out from 1803 onwards: the former castle courtyard, the Eye of the Ridings, was used for this purpose instead, although crowds still gathered outside the bailey to watch the slow deaths of the prisoners.Butler, p.23. By 1813 the execution process had been sped up by the introduction of the "
Criticism of the castle prison increased at the end of the 18th century.Cooper, p.191. The facilities were felt to be inadequate and the crowds of spectators who gathered outside the prison to see inmates being taken into York for execution unseemly. Attempts were made to improve the way executions were carried out from 1803 onwards: the former castle courtyard, the Eye of the Ridings, was used for this purpose instead, although crowds still gathered outside the bailey to watch the slow deaths of the prisoners.Butler, p.23. By 1813 the execution process had been sped up by the introduction of the " By the early 19th century, dredging and other improvements to the river Foss had made it possible to import flour into York by river, reducing the economic significance of the castle mills.Butler, p.8. In 1856, the castle mills were finally demolished as part of a further sequence of improvements to this part of the river. The King's Pool that formed part of the castle's water defences was drained. With the construction of several new bridges near the castle, the site became "surrounded by roads instead of moats". Some major trials took place at the Assizes (now Crown Court) building of York Castle in the 19th century, including that of Mary Fitzpatrick who was accused of murder.
By the early 19th century, dredging and other improvements to the river Foss had made it possible to import flour into York by river, reducing the economic significance of the castle mills.Butler, p.8. In 1856, the castle mills were finally demolished as part of a further sequence of improvements to this part of the river. The King's Pool that formed part of the castle's water defences was drained. With the construction of several new bridges near the castle, the site became "surrounded by roads instead of moats". Some major trials took place at the Assizes (now Crown Court) building of York Castle in the 19th century, including that of Mary Fitzpatrick who was accused of murder.
 York Prison finally closed in 1929, and the Tudor Gothic Victorian prison buildings were demolished in 1935. The Assize Courts building now houses the York
York Prison finally closed in 1929, and the Tudor Gothic Victorian prison buildings were demolished in 1935. The Assize Courts building now houses the York
English Heritage site for Clifford's TowerYork Castle Museum
{{authority control Grade I listed buildings in York Tourist attractions in York Castles in North Yorkshire Defunct prisons in North Yorkshire English Heritage sites in North Yorkshire Ruins in North Yorkshire Towers in North Yorkshire Jewish English history Grade I listed castles Grade I listed towers 11th-century establishments in England Scheduled monuments in York
York
York is a cathedral city in North Yorkshire, England, with Roman Britain, Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers River Ouse, Yorkshire, Ouse and River Foss, Foss. It has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a Yor ...
, England. It consists of a sequence of castles, prisons, law courts and other buildings, which were built over the last nine centuries on the north-west side of the River Foss
The River Foss is in North Yorkshire, England. It is a tributary of the River Ouse. It rises in the Foss Crooks Woods near Oulston Reservoir close to the village of Yearsley and runs south through the Vale of York to the Ouse in the centre of ...
.Cooper, p.149. The now ruined keep
A keep is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in castles that were fortified residen ...
of the medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
Norman castle
A castle is a type of fortification, fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by Military order (monastic society), military orders. Scholars usually consider a ''castle'' to be the private ...
is commonly referred to as Clifford's Tower. Built originally on the orders of William I William I may refer to:
Kings
* William the Conqueror (–1087), also known as William I, King of England
* William I of Sicily (died 1166)
* William I of Scotland (died 1214), known as William the Lion
* William I of the Netherlands and Luxembour ...
to dominate the former Viking
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9� ...
city of Jórvík
Scandinavian York or Viking York () is a term used by historians for what is now Yorkshire during the period of Scandinavian domination from late 9th century until it was annexed and integrated into England after the Norman Conquest; in parti ...
, the castle suffered a tumultuous early history before developing into a major fortification with extensive water defences. After a major explosion in 1684 rendered the remaining military defences uninhabitable, York Castle continued to be used as a gaol and prison until 1929.
The first motte and bailey
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively easy ...
castle on the site was built in 1068 following the Norman conquest of York. After the destruction of the castle by rebels and a Viking army in 1069, York Castle was rebuilt and reinforced with extensive water defences, including a moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch dug around a castle, fortification, building, or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. Moats can be dry or filled with water. In some places, moats evolved into more extensive water d ...
and an artificial lake. York Castle formed an important royal fortification in the north of England.
In 1190, 150 local Jews were murdered in a pogrom
A pogrom is a violent riot incited with the aim of Massacre, massacring or expelling an ethnic or religious group, particularly Jews. The term entered the English language from Russian to describe late 19th- and early 20th-century Anti-Jewis ...
in the timber castle keep; most of them committed suicide in order not to fall into the hands of the mob. Henry III rebuilt the castle in stone in the middle of the 13th century, creating a keep with a unique quatrefoil
A quatrefoil (anciently caterfoil) is a decorative element consisting of a symmetrical shape which forms the overall outline of four partially overlapping circles of the same diameter. It is found in art, architecture, heraldry and traditional ...
design, supported by an outer bailey wall and a substantial gatehouse
A gatehouse is a type of fortified gateway, an entry control point building, enclosing or accompanying a gateway for a town, religious house, castle, manor house, or other fortification building of importance. Gatehouses are typically the most ...
. During the Scottish wars between 1298 and 1338, York Castle was frequently used as the centre of royal administration across England, as well as an important military base of operations.
York Castle fell into disrepair by the 15th and 16th centuries, becoming used increasingly as a gaol for both local felons and political prisoners. By the time of Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudo ...
the castle was estimated to have lost all of its military value but was maintained as a centre of royal authority in York. The outbreak of the English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of th ...
in 1642 saw York Castle being repaired and refortified, playing a part in the Royalist
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of gove ...
defence of York in 1644 against Parliamentary
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
forces. York Castle continued to be garrisoned until 1684, when an explosion destroyed the interior of Clifford's Tower.
The castle bailey was redeveloped in a neoclassical style in the 18th century as a centre for county administration in Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ) is an area of Northern England which was History of Yorkshire, historically a county. Despite no longer being used for administration, Yorkshire retains a strong regional identity. The county was named after its county town, the ...
, and was used as a gaol and debtors' prison
A debtors' prison is a prison for people who are unable to pay debt. Until the mid-19th century, debtors' prisons (usually similar in form to locked workhouses) were a common way to deal with unpaid debt in Western Europe.Cory, Lucinda"A Histor ...
. Prison reform
Prison reform is the attempt to improve conditions inside prisons, improve the effectiveness of a penal system, reduce recidivism or implement alternatives to incarceration. It also focuses on ensuring the reinstatement of those whose lives are ...
in the 19th century led to the creation of a new prison built in a Tudor Gothic style on the castle site in 1825; used first as a county and then as a military prison
A military prison is a prison operated by a military. Military prisons are used variously to house prisoners of war, unlawful combatants, those whose freedom is deemed a national security risk by the military or national authorities, and members o ...
, this facility was demolished in 1935. By the 20th century the ruin of Clifford's Tower had become a well-known tourist destination and national monument; today the site is owned by English Heritage
English Heritage (officially the English Heritage Trust) is a charity that manages over 400 historic monuments, buildings and places. These include prehistoric sites, a battlefield, medieval castles, Roman forts, historic industrial sites, Lis ...
and open to the public. The other remaining buildings serve as the York Castle Museum
The York Castle Museum is a museum located in York, North Yorkshire, England, on the site of York Castle, which was originally built by William the Conqueror in 1068. The museum itself was founded by John L. Kirk in 1938, and is housed in pris ...
and the Crown Court
The Crown Court is the criminal trial court, court of first instance in England and Wales responsible for hearing all indictable offences, some Hybrid offence, either way offences and appeals of the decisions of magistrates' courts. It is ...
.
History
11th century
York was a Viking capital in the 10th century, and continued as an important northern city in the 11th century. In 1068, onWilliam the Conqueror
William the Conqueror (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), sometimes called William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England (as William I), reigning from 1066 until his death. A descendant of Rollo, he was D ...
's first northern expedition after the Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, French people, French, Flemish people, Flemish, and Bretons, Breton troops, all led by the Du ...
,Brown, p.32. he built a number of castles across the north-east of England, including one at York. This first castle at York was a basic wooden motte and bailey castle built between the rivers Ouse and Foss
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is software available under a license that grants users the right to use, modify, and distribute the software modified or not to everyone free of charge. FOSS is an inclusive umbrella term encompassing free ...
on the site of the present-day York Castle. It was built in haste; contemporary accounts imply it was constructed in only eight days, although this assertion has been challenged. The motte was originally around wide at the base.Cooper, p.14. As it was built in an urban environment, hundreds of houses had to be destroyed to make way for the development. William Malet, the sheriff of Yorkshire
The High Sheriff, Sheriff is the oldest secular office under the Crown. Formerly the Sheriff was the principal law enforcement officer in the county but over the centuries most of the responsibilities associated with the post have been transferr ...
, was placed in charge of the castle and successfully defended it against an immediate uprising by the local population.
In response to the worsening security situation, William conducted his second northern campaign in 1069. He built another castle in York, on what is now Baile Hill on the west bank of the Ouse opposite the first castle, in an effort to improve his control over the city. This second castle was also a motte and bailey design, with the Baile Hill motte probably reached by a horizontal bridge and steps cut up the side of the motte. Later that year, a Danish Viking fleet sailed up to York along the Humber
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal rivers River Ouse, Yorkshire, Ouse and River Trent, Trent. From there to the North Sea, it forms ...
and the Ouse, and attacked both castles with the assistance of Cospatrick of Northumbria and a number of local rebels.Hull, p.98. The Normans, attempting to drive the rebels back, set fire to some of the city's houses. The fire grew out of control and also set fire to York Minster
York Minster, formally the Cathedral and Metropolitical Church of Saint Peter in York, is an Anglicanism, Anglican cathedral in the city of York, North Yorkshire, England. The minster is the seat of the archbishop of York, the second-highest of ...
and, some argue, the castles as well. The castles were captured and partially dismantled, and Malet was taken hostage by the Danes
Danes (, ), or Danish people, are an ethnic group and nationality native to Denmark and a modern nation identified with the country of Denmark. This connection may be ancestral, legal, historical, or cultural.
History
Early history
Denmark ...
.
William conducted a widespread sequence of punitive operations across the north of England in the aftermath of the attacks in 1069 and 1070. This "Harrying of the North
The Harrying of the North was a series of military campaigns waged by William the Conqueror in the winter of 1069–1070 to subjugate Northern England, where the presence of the last House of Wessex, Wessex claimant, Edgar Ætheling, had encour ...
" restored sufficient order to allow the rebuilding of the two castles, again in wood. The bailey at York Castle was enlarged slightly in the process; buildings believed to have been inside the bailey at this time include "halls, kitchens, a chapel, barracks, stores, stables, forges ndworkshops". By the time the Domesday Book
Domesday Book ( ; the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book") is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by ...
was written in 1086, York Castle was also surrounded by a water-filled moat and a large artificial lake called the King's Pool, fed from the river Foss by a dam built for the purpose. More property, including two watermill
A watermill or water mill is a mill that uses hydropower. It is a structure that uses a water wheel or water turbine to drive a mechanical process such as mill (grinding), milling (grinding), rolling, or hammering. Such processes are needed in ...
s, had to be destroyed to make way for the water defences. Over time the Baile Hill site was abandoned in favour of the first castle site, leaving only the motte, which still exists.
12th century

Henry II
Henry II may refer to:
Kings
* Saint Henry II, Holy Roman Emperor (972–1024), crowned King of Germany in 1002, of Italy in 1004 and Emperor in 1014
*Henry II of England (1133–89), reigned from 1154
*Henry II of Jerusalem and Cyprus (1271–1 ...
visited York Castle four times during his reign.Cooper, p.23. The royal chambers at the time were inside the keep for safety, and Henry paid £15 for repairs to the keep. During his 1175 visit, Henry used the castle as the base for receiving the homage of William the Lion
William the Lion (), sometimes styled William I (; ) and also known by the nickname ; e.g. Annals of Ulster, s.a. 1214.6; Annals of Loch Cé, s.a. 1213.10. ( 1142 – 4 December 1214), reigned as King of Alba from 1165 to 1214. His almost 49 ...
of Scotland. Castle mills were built close by to support the garrison, and the military order of the Knights Templar
The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon, mainly known as the Knights Templar, was a Military order (religious society), military order of the Catholic Church, Catholic faith, and one of the most important military ord ...
was granted ownership of the mills in the mid-12th century.Pounds, p.193. The mills proved to be vulnerable to the flooding of the two rivers and had to be repeatedly repaired.
Massacre of Jews
In 1190, York Castle was the location of one of the worst pogroms in England during the medieval period. The Normans had introduced the first Jewish communities into England, where some occupied a special economic role as moneylenders, an essential but otherwise banned activity. English Jews were subject to considerable religious prejudice and primarily worked from towns and cities in which there was a local royal castle that could provide them with protection in the event of attacks from the majority Christian population. Royal protection was usually granted as the Norman and Angevin kings had determined that Jewish property and debts owed to Jews ultimately belonged to the crown, reverting to the king on a Jew's death.Richard I
Richard I (8 September 1157 – 6 April 1199), known as Richard the Lionheart or Richard Cœur de Lion () because of his reputation as a great military leader and warrior, was King of England from 1189 until his death in 1199. He also ru ...
was crowned king in 1189 and announced his intention to join the Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding t ...
; this inflamed anti-Jewish sentiment. Rumours began to spread that the king had ordered that the English Jews be attacked. In York, tensions broke out into violence the following year. Richard de Malbis, who owed money to the powerful Jewish merchant Aaron of Lincoln, exploited an accidental house fire to incite a local mob to attack the home and family of a recently deceased Jewish employee of Aaron in York. Josce of York, the leader of the Jewish community, led the local Jewish families into the royal castle, where they took refuge in the wooden keep.Butler, p.14. The mob surrounded the castle, and when the constable
A constable is a person holding a particular office, most commonly in law enforcement. The office of constable can vary significantly in different jurisdictions. ''Constable'' is commonly the rank of an officer within a police service. Other peo ...
left the castle to discuss the situation, the Jews, fearing the entry of the mob or being handed over to the sheriff, refused to allow him back in. The constable appealed to the sheriff, who called out his own men and laid siege to the keep. The siege continued until 16 March when the Jews' position became untenable. Their religious leader, Rabbi Yomtob, proposed an act of collective suicide to avoid being killed by the mob, and the castle was set on fire to prevent their bodies being mutilated after their deaths. Several Jews perished in the flames but the majority took their own lives rather than give themselves up to the mob.Hull, p.99. However, a handful of Jews did surrender, promising to convert to Christianity, but they were killed by the angry crowd. Around 150 Jews died in total in the massacre. The keep was rebuilt, again in wood, on the motte, which was raised in height by at a cost of £207.
13th and 14th centuries
John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second E ...
used York Castle extensively during his reign, using the keep as his personal quarters for his own security. The castle was kept in good repair during that time. During this period, the first records of the use of the castle as a gaol appeared, with references to prisoners taken during John's Irish campaigns being held at York Castle. By the 13th century there was a well-established system of castle-guard
Castle-guard was an arrangement under the feudal system, by which the duty of finding knights to guard royal castles was imposed on certain manors, knight's fees or baronies. The greater barons provided for the guard of their castles by exacti ...
s in place, under which various lands around York were granted in return for the provision of knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of a knighthood by a head of state (including the pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church, or the country, especially in a military capacity.
The concept of a knighthood ...
s and crossbow
A crossbow is a ranged weapon using an Elasticity (physics), elastic launching device consisting of a Bow and arrow, bow-like assembly called a ''prod'', mounted horizontally on a main frame called a ''tiller'', which is hand-held in a similar f ...
men to assist in protecting the castle.
Henry III also made extensive use of the castle, but during his visit at Christmas 1228 a gale destroyed the wooden keep on the motte. The keep was apparently not repaired, and a building for the king's use was built in the bailey instead. In 1244, when the Scots threatened to invade England, King Henry III visited the castle and ordered it to be rebuilt in white limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
, at a cost of about £2,600. The work was carried out between 1245 and 1270, and included the construction of a towered curtain wall, a gatehouse of considerable size with two large towers, two smaller gatehouses, a small watergate
The Watergate scandal was a major political scandal in the United States involving the administration of President Richard Nixon. The scandal began in 1972 and ultimately led to Nixon's resignation in 1974, in August of that year. It revol ...
, a small gateway into the city, a chapel, and a new stone keep, first known as the King's, later Clifford's, Tower.
Clifford's Tower is of an unusual design. The two-storey tower has a quatrefoil plan with four circular lobes. Each lobe measures across, with walls thick; at its widest, the tower is across.Clark, p.256. A square gatehouse, wide, protected the entrance on the south side between two of the lobes. There are defensive turrets between the other lobes. Large corbel
In architecture, a corbel is a structural piece of stone, wood or metal keyed into and projecting from a wall to carry a wikt:superincumbent, bearing weight, a type of bracket (architecture), bracket. A corbel is a solid piece of material in t ...
s and a central pier
A pier is a raised structure that rises above a body of water and usually juts out from its shore, typically supported by piling, piles or column, pillars, and provides above-water access to offshore areas. Frequent pier uses include fishing, b ...
supported the huge weight of stone and the first floor. Loopholes of a design unique to York Castle provided firing points. A chapel was built over the entrance, measuring doubling as a portcullis
A portcullis () is a heavy, vertically closing gate typically found in medieval fortifications. It consists of a latticed Grille (architecture), grille made of wood and/or metal, which slides down grooves inset within each jamb of the gateway.
...
chamber as at Harlech
Harlech () is a seaside resort and community (Wales), community in Gwynedd, North Wales, and formerly in the Historic counties of Wales, historic county of Merionethshire. It lies on Tremadog Bay in the Snowdonia National Park. Before 1966, it ...
and Chepstow Castle
Chepstow Castle () at Chepstow, Monmouthshire, Wales, is the oldest surviving post-Roman stone fortification in Britain. Located above cliffs on the River Wye, construction began in 1067 under the instruction of the Normans, Norman Lord William ...
s. The tower is believed to be an experiment in improving flanking fire by making more ground visible from the summit of the keep. Although unique in England, the design of the tower closely resembles that at Étampes
Étampes () is a Communes of France, commune in the functional area (France), metropolitan area of Paris, France. It is located south-southwest from the Kilometre zero#France, center of Paris (as the crow flies). Étampes is a Subprefectures in ...
in France, and may have influenced the design of the future keep of Pontefract Castle
Pontefract (or Pomfret) Castle is a castle ruin in the town of Pontefract, in West Yorkshire, England. King Richard II of England, Richard II is thought to have died there. It was the site of a series of famous sieges during the 17th-cent ...
. Henry employed master mason Henry de Rayns and chief carpenter Simon of Northampton for the project, and the cost of the tower accounted for the majority of the overall expenditure on the castle during this period of work.
The new castle needed constant investment to maintain its quality as a military fortification. Winter floods in 1315–16 damaged the soil at the base of the motte, requiring immediate repairs. Around 1358–60, the heavy stone keep again suffered from subsidence and the south-eastern lobe cracked from top to bottom. Royal officials recommended that the keep be completely rebuilt, but, instead, the lobe was repaired at a cost of £200.
Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots (Latin: Malleus Scotorum), was King of England from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he was Lord of Ireland, and from 125 ...
gave wide-reaching powers to the sheriff of Yorkshire for enforcing law and order in the city of York, and the sheriffs established their headquarters in Clifford's Tower. During the wars against the Scots under both Edward and his son, York Castle also formed the centre of royal administration in England for almost half the years between 1298 and 1338.Musson, p.164. Many Westminster
Westminster is the main settlement of the City of Westminster in Central London, Central London, England. It extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street and has many famous landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, Buckingham Palace, ...
institutions followed the king north to York, basing themselves in the castle compound. The existing castle buildings were insufficient to house all the administrative institutions; a temporary building inside the castle was built for the Court of Common Pleas at the beginning of the period, and rebuilt on a larger scale during 1319–20. The Exchequer
In the Civil Service (United Kingdom), civil service of the United Kingdom, His Majesty's Exchequer, or just the Exchequer, is the accounting process of central government and the government's ''Transaction account, current account'' (i.e., mon ...
took over Clifford's Tower. Other buildings around the city had to be commandeered to absorb the overflow from the castle itself. As a result of the extended use of the castle for these purposes, the law courts at York Castle began to compete with those in London, a pattern that lasted into the 1360s. The castle eventually acquired its own mint
Mint or The Mint may refer to:
Plants
* Lamiaceae, the mint family
** ''Mentha'', the genus of plants commonly known as "mint"
Coins and collectibles
* Mint (facility), a facility for manufacturing coins
* Mint condition, a state of like-new ...
in 1344, when Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring royal authority after t ...
decided to create a permanent mint in York Castle to produce gold and silver coins to serve the needs of the north of England.Cooper, p.151. European coiners were brought to York to establish the facility.
Henry III extended the castle's role as a gaol for holding a wide range of prisoners.Twyford, p.45. The sheriff was responsible for the gaol at this time, and his deputy usually took the role of a full-time gaoler.Cooper, p.98. Up to three hundred and ten prisoners were held in the castle at any one time. The conditions in which prisoners were held were "appalling", and led to the widespread loss of life amongst detainees. Prison escapes were relatively common, and many of them, such as the break-out by 28 prisoners in 1298, were successful. When the Military Order of the Knights Templar
The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon, mainly known as the Knights Templar, was a Military order (religious society), military order of the Catholic Church, Catholic faith, and one of the most important military ord ...
was dissolved in England in 1307, York Castle was used to hold many of the arrested knights. The castle mills, as former Templar property, returned to royal control at the same time.Cooper, p.126. Edward II
Edward II (25 April 1284 – 21 September 1327), also known as Edward of Caernarfon or Caernarvon, was King of England from 1307 until he was deposed in January 1327. The fourth son of Edward I, Edward became the heir to the throne follo ...
also used the castle as a gaol in his campaign against his rebellious barons in 1322, and after the Battle of Boroughbridge
The Battle of Boroughbridge was fought on 16 March 1322 in England between a group of rebellious barons and the forces of King Edward II, near Boroughbridge, north-west of York. The culmination of a long period of antagonism between the King a ...
many of the defeated rebel leaders were executed at York Castle.
By the end of the 14th century, the castle bailey was primarily occupied by the local county administration. It was used extensively as a gaol, with prisoners being kept in the various towers around the bailey. The old castle-guard system for securing the castle had changed into a system whereby the crown used rents from local royal lands to hire local guards for the castle. Increasingly, royalty preferred to stay at the Franciscan friary, between the castle and King's Staith on the Ouse, while their staff resided at St Mary's Abbey and St Andrew's Priory in the Fishergate
Fishergate is a street and surrounding area of York, England.
History
Fishergate runs along a strip of slightly raised ground, east of the River Ouse. Archaeological investigations have found evidence of prehistoric occupation, before the ...
area.Butler, p.17.
15th and 16th centuries
 In the 15th century, York Castle, along with
In the 15th century, York Castle, along with Nottingham Castle
Nottingham Castle is a Stuart Restoration-era ducal mansion in Nottingham, England, built on the site of a Normans, Norman castle built starting in 1068, and added to extensively through the medieval period, when it was an important royal fortr ...
, was considered a key security asset in the north of England, but investment even in these castles diminished. Repairs to York Castle grew infrequent from 1400 onwards, and it fell into increasing disrepair. Richard III
Richard III (2 October 1452 – 22 August 1485) was King of England from 26 June 1483 until his death in 1485. He was the last king of the Plantagenet dynasty and its cadet branch the House of York. His defeat and death at the Battle of Boswor ...
recognised the issue and in 1483 had some of the most decrepit structures removed, but he died at the Battle of Bosworth
The Battle of Bosworth or Bosworth Field ( ) was the last significant battle of the Wars of the Roses, the civil war between the houses of Lancaster and York that extended across England in the latter half of the 15th century. Fought on 22 ...
before replacement work could commence. By the reign of Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
, the antiquary
An antiquarian or antiquary () is an aficionado or student of antiquities or things of the past. More specifically, the term is used for those who study history with particular attention to ancient artefacts, archaeological and historic sit ...
John Leland reported that the castle was in considerable disrepair; nonetheless the water defences remained intact, unlike those of many other castles of the period. As a result of the deterioration, Henry had to be advised that the king's councillors no longer had any official residence in which to stay and work when they were in York.Cooper, p.148. The castle mint was shut down after the death of Edward VI
Edward VI (12 October 1537 – 6 July 1553) was King of England and King of Ireland, Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death in 1553. He was crowned on 20 February 1547 at the age of nine. The only surviving son of Henry VIII by his thi ...
in 1553, and the castle mills were given to a local charitable hospital in 1464. The hospital was then closed during the Reformation, and the mills passed into private ownership once again.
The castle continued to be used as a gaol, increasingly for local felons, and a location for political executions. By the 16th century it had become traditional to execute traitors by hanging them from the top of Clifford's Tower, rather than killing them at Micklegate Bar
York has, since Roman times, been defended by walls of one form or another. To this day, substantial portions of the walls remain, and York has more miles of intact wall than any other city in England. They are known variously as York City W ...
, the usual previous location for capital punishment in York.Cooper, p.158. In 1536, for example, the political leader Robert Aske was executed at York Castle on the orders of Henry VIII, following the failure of Aske's Pilgrimage of Grace
The Pilgrimage of Grace was an English Catholic popular revolt beginning in Yorkshire in October 1536 before spreading to other parts of Northern England, including Cumberland, Northumberland, Durham and north Lancashire. The protests occurre ...
protest against the dissolution of the monasteries. For most of the period the sheriffs of Yorkshire remained in control of the castle, although there were some notable exceptions such as the appointment of the royal favourite Sir Robert Ryther by Edward IV
Edward IV (28 April 1442 – 9 April 1483) was King of England from 4 March 1461 to 3 October 1470, then again from 11 April 1471 until his death in 1483. He was a central figure in the Wars of the Roses, a series of civil wars in England ...
in 1478. At the end of the 16th century, however, the Clifford family ( Earls of Cumberland), became the hereditary constables of the castle, and Clifford's Tower took its name from the family at around this time.Butler, p.4.
The deterioration of the castle continued into the reign of Elizabeth I, who was advised that it no longer had any military utility.Cooper, p.149. Robert Redhead, the tower keeper, became infamous at the time for taking parts of the castle to pieces and selling off the stonework for his own profit. Despite numerous attempts by local city and crown officials to halt this, Redhead continued to cause considerable damage before being forced to stop. Proposals were made to pull down Clifford's Tower altogether in 1596, but were turned down because of the strength of local feeling.
17th century
 Maintaining the castle was becoming increasingly expensive, and in 1614 King James sold the lease on Clifford's Tower and the surrounding land to John Babington and Edmund Duffield, a pair of property speculators. In turn, Babington and Duffield sold Clifford's Tower to a York merchant family. In 1642, however, the
Maintaining the castle was becoming increasingly expensive, and in 1614 King James sold the lease on Clifford's Tower and the surrounding land to John Babington and Edmund Duffield, a pair of property speculators. In turn, Babington and Duffield sold Clifford's Tower to a York merchant family. In 1642, however, the English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of th ...
broke out between the rival factions of the Royalists
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of gover ...
and Parliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
. Forces loyal to Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
, under the command of Henry Clifford, garrisoned York Castle and the surrounding city in 1643. York effectively became the "northern capital" for the Royalist cause. Clifford repaired the castle and strengthened the walls to permit them to support cannon
A cannon is a large-caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder during th ...
, placing his arms alongside those of the king above the entrance.Timbs and Gunn, p.170. Clifford's Tower's gatehouse was substantially remodelled, losing its original medieval appearance. Baile Hill, on the other side of the river, became a gun emplacement. The castle mint was reopened to supply the king's forces with coins.
The war turned against the Royalist factions, and on 23 April 1644 Parliamentary forces commenced the siege of York
The siege of York in 1644 was a prolonged contest for York during the First English Civil War, between the Scottish Covenanter army and the Parliamentarian armies of the Northern Association and Eastern Association, and the Royalist Ar ...
. A Scottish army under Alexander Leslie
Alexander Leslie, 1st Earl of Leven (4 April 1661) was a Scottish army officer. Born illegitimate and raised as a foster child, he subsequently advanced to the rank of field marshal in Swedish Army, and in Scotland became Lord General in comma ...
came from the south, while a Parliamentary force under Ferdinando Fairfax came from the east. Six weeks later, Edward Montagu brought a third contingent to York, bringing the number of forces besieging the city to over 30,000 men. William Cavendish commanded the city during the siege, while Colonel Sir Francis Cobb was appointed the governor of the castle. Despite bombardment, attempts to undermine the walls and attacks on the gates, the city held out through May and June. Prince Rupert
Prince Rupert of the Rhine, Duke of Cumberland, (17 December 1619 ( O.S.) 7 December 1619 (N.S.)– 29 November 1682 (O.S.) December 1682 (N.S) was an English-German army officer, admiral, scientist, and colonial governor. He first rose to ...
, sent to relieve York, approached with reinforcements, and through clever manoeuvring was able to force the besiegers to withdraw, lifting the siege on 1 July. The next day, Parliamentary forces defeated Rupert at the Battle of Marston Moor
The Battle of Marston Moor was fought on 2 July 1644, during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms of 1639–1653. The combined forces of the English Parliamentarians under Lord Fairfax and the Earl of Manchester and the Scottish Covenanters unde ...
, six miles west of York, making the surrender of York and the castle inevitable. On 14 July the city and castle surrendered to the Parliamentary forces, who permitted the Royalists to march out with full honours.
Parliament then appointed Thomas Dickenson, the local mayor, as the governor of Clifford's Tower. Control of the castle rested with the post of mayor until the Restoration. Efforts were made to separate the structures of Clifford's Tower, which Parliament used as a garrison, from the buildings of the bailey, which continued to be used as a prison.Cooper, p.173. Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English statesman, politician and soldier, widely regarded as one of the most important figures in British history. He came to prominence during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, initially ...
visited Clifford's Tower in 1650, and received a salute from the guns stationed on top of it. The cost of the garrison was levied on the city of York.
After the Restoration of Charles II, the pre-war owners of the property laid claim to Clifford's Tower, eventually being granted ownership. A garrison continued to be stationed there, however, which prevented the owners from actually occupying or using the property.Clarke, p.261. Repairs were made to the tower, and it became a magazine
A magazine is a periodical literature, periodical publication, print or digital, produced on a regular schedule, that contains any of a variety of subject-oriented textual and visual content (media), content forms. Magazines are generally fin ...
for storing gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, charcoal (which is mostly carbon), and potassium nitrate, potassium ni ...
and shot. Attempts were made to restore the condition of the moat, which had become badly silted. Some political prisoners continued to be held at the castle during the Restoration period, including George Fox
George Fox (July 1624 Old Style and New Style dates, O.S. – 13 January 1691 Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.) was an English Dissenters, English Dissenter, who was a founder of the Quakers, Religious Society of Friends, commonly known as t ...
, the founder of the Society of Friends
Quakers are people who belong to the Religious Society of Friends, a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations. Members refer to each other as Friends after in the Bible, and originally, others referred to them as Quakers ...
.
The county facilities in the bailey were expanded during these years, with improvements to the Grand Jury House and the Common Hall, but by the 1680s the role of the military garrison at York Castle was being called into question.Butler, p.20. Sir Christopher Musgrave produced a report for the Crown in 1682; he argued that it would cost at least £30,000 to turn the castle into a modern fortification, producing a proposal for the six bastion
A bastion is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fire from the ...
s that such a star fort
A bastion fort or ''trace italienne'' (a phrase derived from non-standard French, meaning 'Italian outline') is a fortification in a style developed during the early modern period in response to the ascendancy of gunpowder weapons such as c ...
would require. This work was never carried out. Meanwhile, the garrison and the castle had become extremely unpopular with the people of York, who disliked both the cost and the imposition of external authority.
On St George's Day
Saint George's Day is the Calendar of saints, feast day of Saint George, celebrated by Christian churches, countries, regions, and cities of which he is the Patronages of Saint George, patron saint, including Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bu ...
in 1684 at around 10 pm, an explosion in the magazine destroyed the interior of Clifford's Tower entirely. The official explanation was that the celebratory salute from the guns on the roof had set fire to parts of the woodwork, which later ignited the magazine. Most historians, however, believe the explosion was not accidental. At the time, it was common in the city to toast the potential demolition of the "Minced Pie", as the castle was known to locals; suspiciously, some members of the garrison had moved their personal belongings to safety just before the explosion, and no-one from the garrison was injured by the event. The heat of the fire turned the limestone of the tower to its current, slightly pink, colour. The now-ruined tower was returned fully to private ownership, eventually forming part of the lands of the neighbouring house and gardens belonging to Samuel Waud.
18th century
 By 1701, the conditions of the county gaol had become scandalous and the decision was taken to redevelop the area occupied by the old bailey. A local tax helped to fund the development, and the king agreed for the ruins of St Mary's Abbey to be cannibalised for building stone. Three new buildings were erected to the south of Clifford's Tower. A new county gaol, built between 1701 and 1705 by William Wakefield, was placed on the south side, closely resembling the fashionable work of
By 1701, the conditions of the county gaol had become scandalous and the decision was taken to redevelop the area occupied by the old bailey. A local tax helped to fund the development, and the king agreed for the ruins of St Mary's Abbey to be cannibalised for building stone. Three new buildings were erected to the south of Clifford's Tower. A new county gaol, built between 1701 and 1705 by William Wakefield, was placed on the south side, closely resembling the fashionable work of John Vanbrugh
Sir John Vanbrugh (; 24 January 1664 (baptised) – 26 March 1726) was an English architect, dramatist and herald, perhaps best known as the designer of Blenheim Palace and Castle Howard. He wrote two argumentative and outspoken Restor ...
. The local architect John Carr then built the Assize Courts
The assizes (), or courts of assize, were periodic courts held around England and Wales until 1972, when together with the quarter sessions they were abolished by the Courts Act 1971 and replaced by a single permanent Crown Court. The assizes ex ...
on the site of the old Jury House between 1773 and 1777 on the west side, and oversaw the replacement of the Sessions House and Common Hall by the Female Prison between 1780 and 1783 on the east side. The Female Prison and county gaol were later combined to become the Debtors' Prison. Both of Carr's buildings were designed in a distinctive neoclassical style; the Assize Court building was particularly praised at the time as being "a superb building of the Ionic order". The castle courtyard was grassed over to form a circle in 1777 and became known as the "Eye of the Ridings" because it was used for the election of members of parliament for York.Butler, p.23.
Visits by the prison reformer John Howard
John Winston Howard (born 26 July 1939) is an Australian former politician who served as the 25th prime minister of Australia from 1996 to 2007. He held office as leader of the Liberal Party of Australia. His eleven-year tenure as prime min ...
as part of the research for his book ''The State of the Prisons'' found these prisons flawed, but in relatively good condition compared to others at the time. The Debtors' Prison as a whole was an "honour to the county" of York, with "airy and healthy" rooms, but the felon
A felony is traditionally considered a crime of high seriousness, whereas a misdemeanor is regarded as less serious. The term "felony" originated from English common law (from the French medieval word "''félonie''") to describe an offense that ...
s' wing of the prison attracted some criticism.Howard, quoted Twyford p.47. The felons' wing was "too small" and had "no water" for the inmates; felons were forced to sleep on piles of straw on the floor. Indeed, conditions were so bad in the felons' wing that nine prisoners suffocated in one night during 1739.
Just outside the main walls, the castle mills had become increasingly ineffective from the 16th century onwards because of a reduction in the flow of the rivers driving the water-wheels. As a result, in 1778 they were rebuilt with a new steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs Work (physics), mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a Cylinder (locomotive), cyl ...
to drive the machinery; this steam engine caused considerable discomfort to the prisoners affected by the smoke and noise.
19th century
 Criticism of the castle prison increased at the end of the 18th century.Cooper, p.191. The facilities were felt to be inadequate and the crowds of spectators who gathered outside the prison to see inmates being taken into York for execution unseemly. Attempts were made to improve the way executions were carried out from 1803 onwards: the former castle courtyard, the Eye of the Ridings, was used for this purpose instead, although crowds still gathered outside the bailey to watch the slow deaths of the prisoners.Butler, p.23. By 1813 the execution process had been sped up by the introduction of the "
Criticism of the castle prison increased at the end of the 18th century.Cooper, p.191. The facilities were felt to be inadequate and the crowds of spectators who gathered outside the prison to see inmates being taken into York for execution unseemly. Attempts were made to improve the way executions were carried out from 1803 onwards: the former castle courtyard, the Eye of the Ridings, was used for this purpose instead, although crowds still gathered outside the bailey to watch the slow deaths of the prisoners.Butler, p.23. By 1813 the execution process had been sped up by the introduction of the "short drop
Short may refer to:
Places
* Short (crater), a lunar impact crater on the near side of the Moon
* Short, Mississippi, an unincorporated community
* Short, Oklahoma, a census-designated place
People
* Short (surname)
* List of people known ...
" method of hanging, allowing the unusually rapid execution of fourteen Luddite
The Luddites were members of a 19th-century movement of English textile workers who opposed the use of certain types of automated machinery due to concerns relating to worker pay and output quality. They often destroyed the machines in organ ...
agitators at the castle in 1814. Overcrowding in the jail was now also a problem, with up to 114 prisoners being held at any one time; occasionally, around forty prisoners awaiting trial had to be kept in the jail yard for lack of space elsewhere. Other radicals imprisoned there included Joshua Hobson and Alice Mann in 1836.
The suitability of the prison was finally brought to a head at the 1821 assizes
The assizes (), or courts of assize, were periodic courts held around England and Wales until 1972, when together with the quarter sessions they were abolished by the Courts Act 1971 and replaced by a single permanent Crown Court. The assizes ex ...
in York, when an official complaint was made and an investigation begun. The decision was taken to purchase Clifford's Tower and the Waud house, with the aim of demolishing them both to make room for a new, more modern prison. Sydney Smith
Sydney Smith (3 June 1771 – 22 February 1845) was an English wit, writer, and Anglican cleric. Besides his energetic parochial work, he was known for his writing and philosophy, founding the ''Edinburgh Review'', lecturing at the Royal Inst ...
, the famous wit, writer and vicar
A vicar (; Latin: '' vicarius'') is a representative, deputy or substitute; anyone acting "in the person of" or agent for a superior (compare "vicarious" in the sense of "at second hand"). Linguistically, ''vicar'' is cognate with the English p ...
of Foston-le-Clay, successfully led a campaign to save Clifford's Tower, emphasising the historic importance of the location for the surrounding city. An alternative proposal, put forward by architect Robert Wallace, would have seen the conversion of Clifford's Tower back into a habitable building to form the hub of a radial
Radial is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Mathematics and Direction
* Vector (geometric), a line
* Radius, adjective form of
* Radial distance (geometry), a directional coordinate in a polar coordinate system
* Radial set
* A ...
prison design, but this was turned down.
In 1825, Clifford's Tower and the Waud house were purchased by the county of Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ) is an area of Northern England which was History of Yorkshire, historically a county. Despite no longer being used for administration, Yorkshire retains a strong regional identity. The county was named after its county town, the ...
at the cost of £8,800 () The new prison buildings, designed by architects P. F. Robinson and G. T. Andrews, were constructed in a Tudor Gothic style, including a gatehouse high and a radial prison block, protected by a long, high stone wall. The prison, considered to be the strongest such building in England, was built entirely of stone to be both secure and fireproof. Dark grey gritstone
Gritstone or grit is a hard, coarse-grained, siliceous sandstone. This term is especially applied to such sandstones that are quarried for building material. British gritstone was used for millstones to mill flour, to grind wood into pulp for ...
was used in the construction to produce a forbidding appearance, although the prison itself was considered healthy and well ventilated.
Clifford's Tower played no part in the formal design of the prison, although the talus, or sloping edge of the motte, was cut away and replaced by a retaining wall to allow more space for the new prison building. The backyard of the Female Prison, concealed from public view by the new wall, was used for hangings from 1868 onwards.
The Prison Act, 1877, reformed the English prison system, and York Castle gaol was passed into the control of central government the following year.Cooper, p.196. It was used as the county prison until 1900, when the remaining prisoners were transferred to Wakefield Prison
His Majesty's Prison Wakefield is a Category A men's prison in Wakefield, West Yorkshire, England, operated by His Majesty's Prison Service. The prison has been nicknamed the "Monster Mansion" along with HM Prison Frankland due to the large num ...
, and from then onwards the facility was used as a military prison
A military prison is a prison operated by a military. Military prisons are used variously to house prisoners of war, unlawful combatants, those whose freedom is deemed a national security risk by the military or national authorities, and members o ...
instead.Butler, p.24.
 By the early 19th century, dredging and other improvements to the river Foss had made it possible to import flour into York by river, reducing the economic significance of the castle mills.Butler, p.8. In 1856, the castle mills were finally demolished as part of a further sequence of improvements to this part of the river. The King's Pool that formed part of the castle's water defences was drained. With the construction of several new bridges near the castle, the site became "surrounded by roads instead of moats". Some major trials took place at the Assizes (now Crown Court) building of York Castle in the 19th century, including that of Mary Fitzpatrick who was accused of murder.
By the early 19th century, dredging and other improvements to the river Foss had made it possible to import flour into York by river, reducing the economic significance of the castle mills.Butler, p.8. In 1856, the castle mills were finally demolished as part of a further sequence of improvements to this part of the river. The King's Pool that formed part of the castle's water defences was drained. With the construction of several new bridges near the castle, the site became "surrounded by roads instead of moats". Some major trials took place at the Assizes (now Crown Court) building of York Castle in the 19th century, including that of Mary Fitzpatrick who was accused of murder.
20th century
In 1890 the Prison Commissioners agreed to declare Clifford's Tower a national monument and to conserve it as a historic location. In 1902 Clifford's Tower was given to the York Corporation, together with a grant of £3,000 () arranged by Lord Wenlock for conservation and repairs. The removal of the talus and the damage to the castle stonework in the 16th century had put excessive pressure on the supporting motte, causing a recurrence of the 14th-century subsidence. Sir Basil Mott, a leading Victorian engineer, installed concrete underpinnings to stabilise the structure beneath the gatehouse. By the early 20th century, Clifford's Tower was regularly open to visitors, and in 1915 it was passed to theOffice of Works
The Office of Works was an organisation responsible for structures and exterior spaces, first established as part of the English royal household in 1378 to oversee the building and maintenance of the royal castles and residences.
In 1832 it be ...
as a national monument. The castle was historically excluded from York's municipal boundaries; it was formally absorbed into the city in 1968.
Today
 York Prison finally closed in 1929, and the Tudor Gothic Victorian prison buildings were demolished in 1935. The Assize Courts building now houses the York
York Prison finally closed in 1929, and the Tudor Gothic Victorian prison buildings were demolished in 1935. The Assize Courts building now houses the York Crown Court
The Crown Court is the criminal trial court, court of first instance in England and Wales responsible for hearing all indictable offences, some Hybrid offence, either way offences and appeals of the decisions of magistrates' courts. It is ...
, while the former Debtors' Prison and Female Prison, together with a modern entrance area, are now the Castle Museum. The circular grassed area between these buildings that was once known as the "Eye of the Ridings" is now known as Castle Green, or the "Eye of York". Clifford's Tower is the most prominent surviving part of the original medieval fortification, although the stone steps up the side of the motte are modern. Fragments of the bailey wall, parts of the south gatehouse and one of the corner towers also survive.
The castle is classed as a Grade I listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building is a structure of particular architectural or historic interest deserving of special protection. Such buildings are placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Hi ...
and a scheduled monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorised change.
The various pieces of legislation that legally protect heritage assets from damage, visu ...
. The site, managed by English Heritage
English Heritage (officially the English Heritage Trust) is a charity that manages over 400 historic monuments, buildings and places. These include prehistoric sites, a battlefield, medieval castles, Roman forts, historic industrial sites, Lis ...
, is open to the public. Until the 1970s, the pogrom
A pogrom is a violent riot incited with the aim of Massacre, massacring or expelling an ethnic or religious group, particularly Jews. The term entered the English language from Russian to describe late 19th- and early 20th-century Anti-Jewis ...
of 1190 was often underplayed by official histories of the castle; early official guides to the castle made no reference to it. In 1978, however, the first memorial tablet to the victims was laid at the base of Clifford's Tower, and in 1990 the 800th anniversary of the killings was commemorated at the tower. Recently, commercial interests have sought to introduce retail development to the area surrounding it. Citizens, visitors, academics, environmentalists, local businesspeople and Jewish groups have opposed the development with some success, winning a lengthy and bitter public inquiry in 2003.
In March 2022 an English Heritage conservation project, including work on the limestone fabric of the tower and care of the chapel roof, was completed. New internal access stairways of gluelam timber leading to a new roof deck allow visitors a close view of some original features of the building and less-crowded viewpoints over the city.
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * *Hull, Lise E. (2006) ''Britain's Medieval Castles.'' Westport: Praeger. . *McLynn, Frank. (2007) ''Lionheart and Lackland: King Richard, King John and the Wars of Conquest.'' London: Vintage. . * *Pounds, Norman John Greville. (1990) ''The Medieval Castle in England and Wales: a Social and Political History.'' Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. . * *Sears, Robert. (1847) ''A New and Popular Pictorial Description of England, Scotland, Ireland, Wales and the British Islands.'' New York: Robert Sears. . * *Stenton, Doris Mary. (1976) ''English Society in the Early Middle Ages (1066–1307).'' Harmondsworth, UK: Penguin. . * *Toy, Sidney. (1985) ''Castles: Their Construction and History.'' New York: Dover Publications. . *Twyford, Anthony William. (2010) ''Records of York Castle – Fortress, Courthouse and Prison.'' Alcester, UK: Read Books. . *Further reading
*Renn, D. F. (1971) ''Clifford's Tower and the castles of York.'' London : Her Majesty's Stationery Office. .External links
English Heritage site for Clifford's Tower
{{authority control Grade I listed buildings in York Tourist attractions in York Castles in North Yorkshire Defunct prisons in North Yorkshire English Heritage sites in North Yorkshire Ruins in North Yorkshire Towers in North Yorkshire Jewish English history Grade I listed castles Grade I listed towers 11th-century establishments in England Scheduled monuments in York