Chromosome Regions on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Several chromosome regions have been defined by convenience and convention in order to talk about gene loci. The largest regions on each chromosome are the short arm p and the long arm q, separated by a narrow region near the center called the
Several chromosome regions have been defined by convenience and convention in order to talk about gene loci. The largest regions on each chromosome are the short arm p and the long arm q, separated by a narrow region near the center called the
 Several chromosome regions have been defined by convenience and convention in order to talk about gene loci. The largest regions on each chromosome are the short arm p and the long arm q, separated by a narrow region near the center called the
Several chromosome regions have been defined by convenience and convention in order to talk about gene loci. The largest regions on each chromosome are the short arm p and the long arm q, separated by a narrow region near the center called the centromere
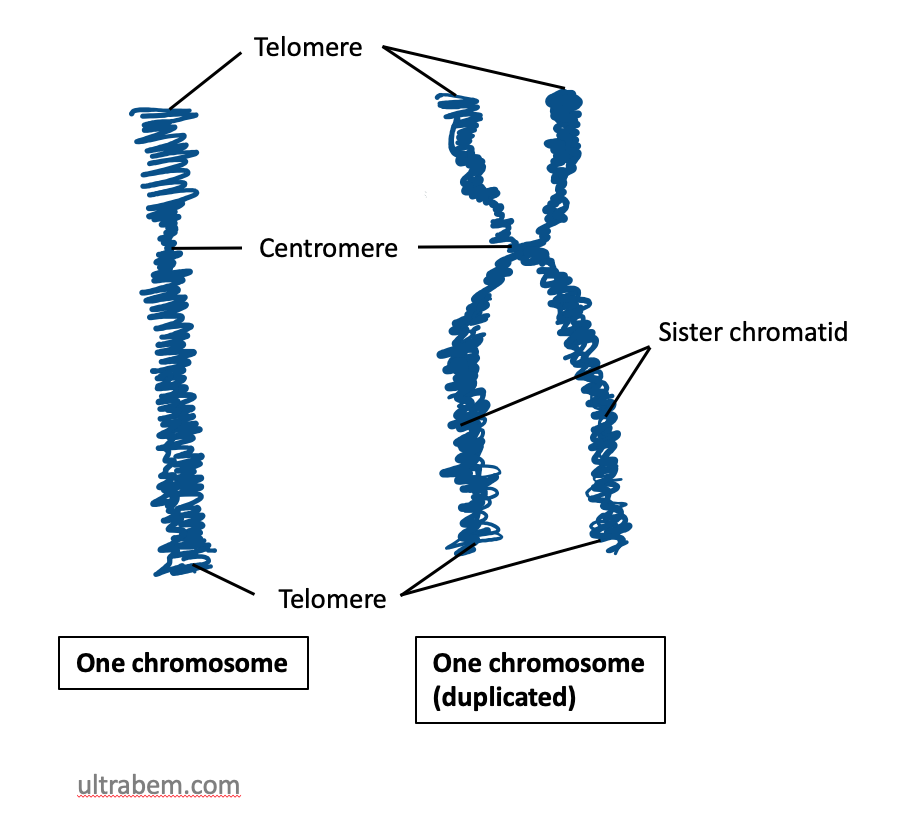
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fiber ...
. Other specific regions have also been defined, some of which are similarly found on every chromosome, while others are only present in certain chromosomes.
Named regions include:
* Arms (p and q)
* Centromere
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fiber ...
* Kinetochore
A kinetochore (, ) is a flared oblique-shaped protein structure associated with duplicated chromatids in eukaryotic cells where the spindle fibers, which can be thought of as the ropes pulling chromosomes apart, attach during cell division to ...
* Telomere
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes (see #Sequences, Sequences). Telomeres are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In ...
* Sub telomere
* satellite chromosome or trabant.
* NOR region
During cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell (biology), cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukar ...
, the molecules that compose chromosomes (DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
and protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s) undergo a condensation process (called the chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important r ...
reticulum condensation) that forms a compact and small complex called a chromatid. The complexes containing the duplicated DNA molecules, the sister chromatid
A chromatid (Greek ''khrōmat-'' 'color' + ''-id'') is one half of a duplicated chromosome. Before replication, one chromosome is composed of one DNA molecule. In replication, the DNA molecule is copied, and the two molecules are known as chrom ...
s, are attached to each other by the centromere
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fiber ...
(where the Kinetochore
A kinetochore (, ) is a flared oblique-shaped protein structure associated with duplicated chromatids in eukaryotic cells where the spindle fibers, which can be thought of as the ropes pulling chromosomes apart, attach during cell division to ...
assembles).
If the chromosome is a submetacentric chromosome (One arm big and the other arm small) then the centromere divides each chromosome into two regions: the smaller one, which is the p region, and the bigger one, the q region. The sister chromatids will be distributed to each daughter cell at the end of the cell division. Whereas if the chromosome is isobrachial (centromere at centre and arms of equal length), the p and q system is meaningless.
At either end of a chromosome is a telomere
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes (see #Sequences, Sequences). Telomeres are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In ...
, a cap of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
that protects the rest of the chromosome from damage. The telomere has repetitive junk DNA
Junk DNA (non-functional DNA) is a DNA sequence that has no known biological function. Most organisms have some junk DNA in their genomes—mostly pseudogenes and fragments of transposons and viruses—but it is possible that some organ ...
and hence any enzymatic damage will not affect the coded regions. The areas of the p and q regions close to the telomeres are the subtelomere
Subtelomeres are segments of DNA between telomeric caps and chromatin.
Structure
Telomeres are specialized protein–DNA constructs present at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes, which prevent them from degradation and end-to-end chromosomal fu ...
s, or subtelomeric regions. The areas closer to the centromere are the pericentronomic regions. Finally, the interstitial regions are the parts of the p and q regions that are close to neither the centromere nor the telomeres, but are roughly in the middle of p or q.
See also
* Satellite chromosomeReferences
Chromosomes {{genetics-stub