choroid plexus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The choroid plexus, or plica choroidea, is a plexus of cells that arises from the tela choroidea in each of the ventricles of the brain. Regions of the choroid plexus produce and secrete most of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the
 There is a choroid plexus in each of the four ventricles. In the lateral ventricles, it is found in the body, and continued in an enlarged amount in the atrium. There is no choroid plexus in the anterior horn. In the third ventricle, there is a small amount in the roof that is continuous with that in the body, via the interventricular foramina, the channels that connect the lateral ventricles with the third ventricle. A choroid plexus is in part of the roof of the fourth ventricle.
There is a choroid plexus in each of the four ventricles. In the lateral ventricles, it is found in the body, and continued in an enlarged amount in the atrium. There is no choroid plexus in the anterior horn. In the third ventricle, there is a small amount in the roof that is continuous with that in the body, via the interventricular foramina, the channels that connect the lateral ventricles with the third ventricle. A choroid plexus is in part of the roof of the fourth ventricle.
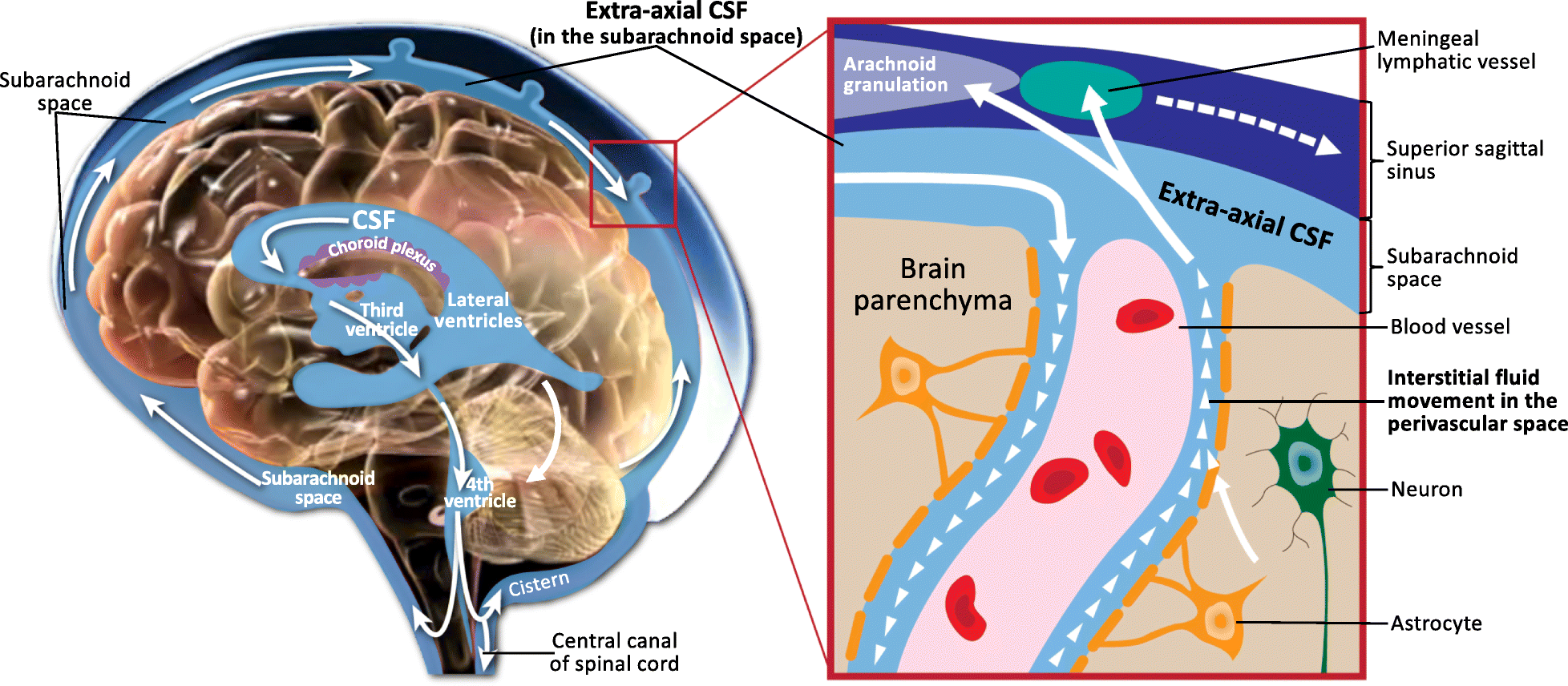 The choroid plexus regulates the production and composition of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), that provides the protective buoyancy for the brain. CSF acts as a medium for the glymphatic filtration system that facilitates the removal of metabolic waste from the brain, and the exchange of
The choroid plexus regulates the production and composition of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), that provides the protective buoyancy for the brain. CSF acts as a medium for the glymphatic filtration system that facilitates the removal of metabolic waste from the brain, and the exchange of
File:Gray749.png, Coronal section of inferior horn of lateral ventricle.
File:Choroid Plexus Histology 40x.png, Choroid plexus histology 40x
File:Slide2ff.JPG, Choroid plexus
File:Slide3oo.JPG, Choroid plexus
File:Choroid plexus.jpg, Choroid plexus
3-Dimensional images of choroid plexus (marked red)
*
Images of Choroid Plexus * More info a
BrainInfo
{{DEFAULTSORT:Choroid Plexus Meninges Ventricular system
central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
. The choroid plexus consists of modified ependymal cells surrounding a core of capillaries and loose connective tissue. Multiple cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proj ...
on the ependymal cells move to circulate the cerebrospinal fluid.
Structure
Location
Microanatomy
The choroid plexus consists of a layer of cuboidal epithelial cells surrounding a core of capillaries and loose connective tissue. Theepithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
of the choroid plexus is continuous with the ependymal cell layer (ventricular layer) that lines the ventricular system. Progenitor ependymal cells are monociliated but they differentiate into multiciliated ependymal cells. Unlike the ependyma, the choroid plexus epithelial layer has tight junctions between the cells on the side facing the ventricle (apical surface). These tight junctions prevent the majority of substances from crossing the cell layer into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF); thus the choroid plexus acts as a blood–CSF barrier. The choroid plexus folds into many villi around each capillary, creating frond-like processes that project into the ventricles. The villi, along with a brush border of microvilli, greatly increase the surface area of the choroid plexus. CSF is formed as plasma is filtered from the blood through the epithelial cells. Choroid plexus epithelial cells actively transport sodium ions into the ventricles and water follows the resulting osmotic gradient.
The choroid plexus consists of many capillaries, separated from the ventricles by choroid epithelial cells. Fluid filters through these cells from blood to become cerebrospinal fluid. There is also much active transport
In cellular biology, active transport is the movement of molecules or ions across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration—against the concentration gradient. Active transport requires cellula ...
of substances into, and out of, the CSF as it is made.
Function
 The choroid plexus regulates the production and composition of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), that provides the protective buoyancy for the brain. CSF acts as a medium for the glymphatic filtration system that facilitates the removal of metabolic waste from the brain, and the exchange of
The choroid plexus regulates the production and composition of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), that provides the protective buoyancy for the brain. CSF acts as a medium for the glymphatic filtration system that facilitates the removal of metabolic waste from the brain, and the exchange of biomolecules
A biomolecule or biological molecule is loosely defined as a molecule produced by a living organism and essential to one or more typically biological processes. Biomolecules include large macromolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipi ...
and xenobiotics into and out of the brain. In this way the choroid plexus has a very important role in helping to maintain the delicate extracellular environment required by the brain to function optimally.
The choroid plexus is also a major source of transferrin
Transferrins are glycoproteins found in vertebrates which bind and consequently mediate the transport of iron (Fe) through blood plasma. They are produced in the liver and contain binding sites for two Iron(III), Fe3+ ions. Human transferrin is ...
secretion that plays a part in iron homeostasis in the brain.
Blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier
The blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier (BCSFB) is a fluid–brain barrier that is composed of a pair of membranes that separate blood from CSF at the capillary level and CSF from brain tissue. The blood–CSF boundary at the choroid plexus is a membrane composed of epithelial cells and tight junctions that link them. There is a CSF-brain barrier at the level of the pia mater, but only in the embryo. Similar to the blood–brain barrier, the blood–CSF barrier functions to prevent the passage of most blood-borne substances into the brain, while selectively permitting the passage of specific substances (such as nutrients) into the brain and facilitating the removal of brain metabolites and metabolic products into the blood. Despite the similar function between the BBB and BCSFB, each facilitates the transport of different substances into the brain due to the distinctive structural characteristics of each of the two barrier systems. For a number of substances, the BCSFB is the primary site of entry into brain tissue. The blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier has also been shown to modulate the entry of leukocytes from the blood to the central nervous system. The choroid plexus cells secretecytokine
Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling.
Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes ...
s that recruit monocyte-derived macrophages, among other cells, to the brain. This cellular trafficking has implications both in normal brain homeostasis and in neuroinflammatory processes.
Clinical significance
Choroid plexus cysts
During fetal development, some choroid plexus cysts may form. These fluid-filled cysts can be detected by a detailed second trimester ultrasound. The finding is relatively common, with a prevalence of ~1%. Choroid plexus cysts are usually an isolated finding. The cysts typically disappear later during pregnancy, and are usually harmless. They have no effect on infant and early childhood development. Choroid plexus cysts are associated with a 1% risk of fetal aneuploidy. The risk of aneuploidy increases to 10.5-12% if other risk factors or ultrasound findings are noted. Size, location, disappearance or progression, and whether the cysts are found on both sides or not do not affect the risk of aneuploidy. 44-50% of Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18) cases will present with choroid plexus cysts, as well 1.4% of Down syndrome (trisomy 21) cases. ~75% of abnormal karyotypes associated with choroid plexus cysts are trisomy 18, while the remainder are trisomy 21.Other
There are three graded types of choroid plexus tumor that mainly affect young children. These types ofcancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
are rare.
Etymology
Choroid plexus translates from the Latin ,Suzuki, S., Katsumata, T., Ura, R. Fujita, T., Niizima, M. & Suzuki, H. (1936). Über die Nomina Anatomica Nova. ''Folia Anatomica Japonica, 14'', 507-536. which mirrorsAncient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
. The word ''chorion'' was used by Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus (; September 129 – AD), often Anglicization, anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Ancient Rome, Roman and Greeks, Greek physician, surgeon, and Philosophy, philosopher. Considered to be one o ...
to refer to the outer membrane enclosing the fetus. Both meanings of the word plexus are given as pleating, or braiding. As often happens language changes and the use of both ''choroid'' or ''chorioid'' is both accepted. Nomina Anatomica (now Terminologia Anatomica) reflected this dual usage.
Additional images
See also
* Choroid plexus papilloma * Tela choroideaReferences
Sources
* *External links
3-Dimensional images of choroid plexus (marked red)
*
Images of Choroid Plexus * More info a
BrainInfo
{{DEFAULTSORT:Choroid Plexus Meninges Ventricular system