Chlorphenamine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Chlorphenamine (CP, CPM), also known as chlorpheniramine, is an
 A second method boom starts from
A second method boom starts from 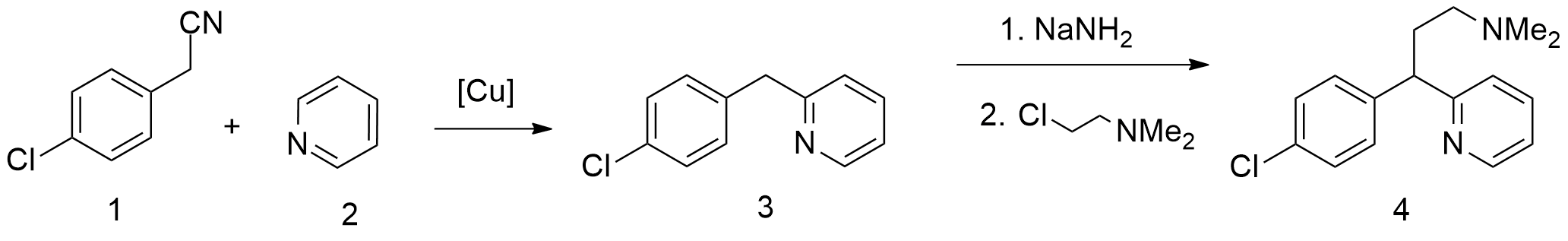
antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides ...
used to treat the symptoms of allergic conditions such as allergic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis, of which the seasonal type is called hay fever, is a type of inflammation in the nose that occurs when the immune system overreacts to allergens in the air. It is classified as a type I hypersensitivity reaction. Signs a ...
(hay fever). It is taken orally (by mouth). The medication takes effect within two hours and lasts for about 4–6 hours. It is a first-generation antihistamine
H1 antagonists, also called H1 blockers, are a class of medications that block the action of histamine at the H1 receptor, helping to relieve allergic reactions. Agents where the main therapeutic effect is mediated by negative modulation of his ...
and works by blocking the histamine H1 receptor.
Common side effects include sleepiness, restlessness, and weakness. Other side effects may include dry mouth
Xerostomia, also known as dry mouth, is a subjective complaint of dryness in the mouth, which may be associated with a change in the composition of saliva, reduced salivary flow, or have no identifiable cause.
This symptom is very common and is o ...
and wheeziness.
Chlorpheniramine was patented in 1948 and came into medical use in 1949. It is available as a generic medication
A generic drug is a pharmaceutical drug that contains the same chemical substance as a drug that was originally protected by chemical patents. Generic drugs are allowed for sale after the patents on the original drugs expire. Because the active ch ...
and over the counter
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are medicines sold directly to a consumer without a requirement for a prescription from a healthcare professional, as opposed to prescription drugs, which may be supplied only to consumers possessing a valid pres ...
.
In 2022, it was the 291st most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 400,000 prescriptions.
Medical uses
Combination products
Chlorphenamine is often combined withphenylpropanolamine
Phenylpropanolamine (PPA), sold under many brand names, is a sympathomimetic agent used as a decongestant and appetite suppressant. It was once common in prescription and over-the-counter cough and cold preparations. The medication is taken ...
to form an allergy
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include Allergic rhinitis, hay fever, Food allergy, food al ...
medication with both antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides ...
and decongestant
A decongestant, or nasal decongestant, is a type of pharmaceutical drug that is used to relieve nasal congestion in the upper respiratory tract. The active ingredient in most decongestants is either pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine (the latter o ...
properties, although phenylpropanolamine was removed from the U.S. market per studies concluding that it increased the risk of stroke in young women. Vernate was a trade name of one such product available in the U.S. prior to the FDA ban; it was manufactured by Tutag and was among the medications prescribed to Elvis Presley
Elvis Aaron Presley (January 8, 1935 – August 16, 1977) was an American singer and actor. Referred to as the "King of Rock and Roll", he is regarded as Cultural impact of Elvis Presley, one of the most significant cultural figures of the ...
.
In the drug Coricidin, chlorphenamine is combined with the cough suppressant dextromethorphan
Dextromethorphan, sold under the brand name Robitussin among others, is a cough suppressant used in many cough and Common cold, cold medicines. In 2022, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the combination dextromethorphan/bupropi ...
. In the drug Cêgripe, chlorphenamine is combined with the analgesic paracetamol
Paracetamol, or acetaminophen, is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic agent used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. It is a widely available over-the-counter drug sold under various brand names, including Tylenol and Panadol.
Parac ...
(also known as acetaminophen, sold as ''Tylenol'').
Side effects
The adverse effects include drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, constipation, anxiety, nausea, blurred vision, restlessness, decreased coordination, dry mouth, shallow breathing, hallucinations, irritability, problems with memory or concentration, tinnitus and trouble urinating. Chlorphenamine produces lesssedation
Sedation is the reduction of irritability or agitation by administration of sedative drugs, generally to facilitate a medical procedure or diagnostic procedure. Examples of drugs which can be used for sedation include isoflurane, diethyl ether, ...
than other first-generation antihistamine
H1 antagonists, also called H1 blockers, are a class of medications that block the action of histamine at the H1 receptor, helping to relieve allergic reactions. Agents where the main therapeutic effect is mediated by negative modulation of his ...
s.
A large study on people 65 years old or older linked the development of Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit ...
and other forms of dementia to the "higher cumulative" use of chlorphenamine and other first-generation antihistamines, due to their anticholinergic
Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the acetylcholine (ACh) neurotransmitter at synapses in the central nervous system, central and peripheral nervous system.
These agents inhibit the parasympatheti ...
properties. Chlorphenamine is rated as a "high burden" anticholinergic by experts on a semi-subjective scale. This is inconsistent with the ''in vitro'' experiments showing low affinity to muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (see below).
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Chlorphenamine acts primarily as a potent H1antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides ...
. It is specifically a potent inverse agonist
In pharmacology, an inverse agonist is a drug that binds to the same receptor as an agonist but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist.
A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agonist or inverse agon ...
of the histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses communication, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Discovered in 19 ...
H1 receptor. The drug is also commonly described as possessing weak anticholinergic
Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the acetylcholine (ACh) neurotransmitter at synapses in the central nervous system, central and peripheral nervous system.
These agents inhibit the parasympatheti ...
activity by acting as an antagonist
An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the main enemy or rival of the protagonist and is often depicted as a villain.muscarinic acetylcholine receptor
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) are acetylcholine receptors that form G protein-coupled receptor, G protein-coupled receptor complexes in the cell membranes of certain neurons and other Cell (biology), cells. They play several role ...
s. The dextrorotatory
Optical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it travels through certain materials. Circul ...
stereoisomer
In stereochemistry, stereoisomerism, or spatial isomerism, is a form of isomerism in which molecules have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in ...
, dexchlorpheniramine, has been reported to possess Kd values of 15 nM for the H1 receptor and 1,300 nM for the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in human brain tissue. The smaller the Kd value, the greater the binding affinity of the ligand for its target.
In addition to acting as an inverse agonist
In pharmacology, an inverse agonist is a drug that binds to the same receptor as an agonist but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist.
A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agonist or inverse agon ...
at the H1 receptor, chlorphenamine has been found to act as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor
A serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI) is a type of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor of the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, or 5-HT) by blocking the drug action, action of the serotonin transporter (SERT). This in turn lea ...
(Kd = 15.2 nM for the serotonin transporter
The serotonin transporter (SERT or 5-HTT) also known as the sodium-dependent serotonin transporter and solute carrier family 6 member 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC6A4 gene. SERT is a type of monoamine transporter protein t ...
). It has only weak affinity for the norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
and dopamine transporter
The dopamine transporter (DAT, also sodium-dependent dopamine transporter) is a membrane-spanning protein coded for in humans by the ''SLC6A3'' gene (also known as ''DAT1''), that pumps the neurotransmitter dopamine out of the synaptic cleft ba ...
s (Kd = 1,440 nM and 1,060 nM, respectively).
A study found that dexchlorphenamine had Ki values for the human cloned H1 receptor of 2.67 to 4.81 nM while levchlorphenamine had Ki values of 211 to 361 nM for this receptor, indicating that dexchlorphenamine is the active enantiomer. Another study found that dexchlorphenamine had a Ki value of 20 to 30 μM for the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) are acetylcholine receptors that form G protein-coupled receptor, G protein-coupled receptor complexes in the cell membranes of certain neurons and other Cell (biology), cells. They play several role ...
using rat brain tissue while levchlorphenamine had a Ki value of 40 to 50 μM for this receptor, indicating that both enantiomers have very low affinity for it.
Pharmacokinetics
Theelimination half-life
Biological half-life (elimination half-life, pharmacological half-life) is the time taken for concentration of a biological substance (such as a medication) to decrease from its maximum concentration ( Cmax) to half of Cmax in the blood plasma. ...
of chlorphenamine has variously ranged between 13.9 and 43.4 hours in adults following a single dose in clinical studies.
Chemistry
Chlorphenamine is an alkylamine and is a part of a series of antihistamines including pheniramine (Naphcon) and itshalogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and the radioactive elements astatine (At) and tennessine (Ts), though some authors would ...
ated derivatives including fluorpheniramine, dexchlorphenamine (Polaramine), brompheniramine
Brompheniramine, sold under the brand name Dimetapp among others, is a first-generation antihistamine drug of the propylamine (alkylamine) class. It is indicated for the treatment of the symptoms of the common cold and allergic rhinitis, such ...
(Dimetapp), dexbrompheniramine (Drixoral), deschlorpheniramine, and iodopheniramine. The halogenated alkylamine antihistamines all exhibit optical isomerism
In chemistry, an enantiomer (Help:IPA/English, /ɪˈnænti.əmər, ɛ-, -oʊ-/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''ih-NAN-tee-ə-mər''), also known as an optical isomer, antipode, or optical antipode, is one of a pair of molecular entities whi ...
, and chlorphenamine in the indicated products is racemic chlorphenamine maleate
Maleic acid or ''cis''-butenedioic acid is an organic compound that is a dicarboxylic acid, a molecule with two carboxyl groups. Its chemical formula is HO2CCH=CHCO2H. Maleic acid is the ''cis'' isomer of butenedioic acid, whereas fumaric acid ...
, whereas dexchlorphenamine is the dextrorotary stereoisomer.
Synthesis
There are several patented methods for thesynthesis
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to:
Science Chemistry and biochemistry
*Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors
**Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organi ...
of chlorphenamine. In one example, 4-chlorophenylacetonitrile is reacted with 2-chloropyridine
2-Chloropyridine is an aryl chloride with the formula C5H4ClN. It is a colorless liquid that is mainly used to generate fungicides and insecticides in industry. It also serves to generate antihistamines and antiarrythymics for pharmaceutical purpo ...
in the presence of sodium amide
Sodium amide, commonly called sodamide (systematic name sodium azanide), is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a salt composed of the sodium cation and the azanide anion. This solid, which is dangerously reactive toward water, is whit ...
to form 4-chlorophenyl(2-pyridyl)acetonitrile. Alkylating this with 2-dimethylaminoethylchloride in the presence of sodium amide
Sodium amide, commonly called sodamide (systematic name sodium azanide), is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a salt composed of the sodium cation and the azanide anion. This solid, which is dangerously reactive toward water, is whit ...
gives γ-(4-chlorphenyl)-γ-cyano-''N'',''N''-dimethyl-2-pyridinepropanamine, the hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
and decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO2). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is ...
of which lead to chlorphenamine.
 A second method boom starts from
A second method boom starts from pyridine
Pyridine is a basic (chemistry), basic heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom . It is a highly flammable, weak ...
, which undergoes alkylation by 4-chlorophenylacetonitrile, giving 2-(4-chlorobenzyl)pyridine. Alkylating this with 2-dimethylaminoethylchloride in the presence of sodium amide gives chlorphenamine.

Society and culture
Names
''Chlorphenamine'' is the while ''chlorpheniramine'' is the and former . Brand names include Chlor-Trimeton, Demazin, Allerest 12 Hour, Piriton, Chlorphen-12, Tylenol Cold/Allergy, and numerous others according to country.References
{{Portal bar, Medicine Antidepressants Anxiolytics 4-Chlorophenyl compounds CYP2D6 inhibitors H1 receptor antagonists Local anesthetics Muscarinic antagonists 2-Pyridyl compounds Serotonin reuptake inhibitors Sigma receptor modulators Sodium channel blockers Dimethylamino compounds