Chinggisids on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A Borjigin, ; ; russian: Борджигин, Bordžigin; English plural: Borjigins or Borjigid (from
A Borjigin, ; ; russian: Борджигин, Bordžigin; English plural: Borjigins or Borjigid (from  is a member of the
is a member of the
 The Borjigin family ruled over the
The Borjigin family ruled over the
 After the breakup of the Golden Horde, the Khiyat continued to rule the
After the breakup of the Golden Horde, the Khiyat continued to rule the
 A Borjigin, ; ; russian: Борджигин, Bordžigin; English plural: Borjigins or Borjigid (from
A Borjigin, ; ; russian: Борджигин, Bordžigin; English plural: Borjigins or Borjigid (from Middle Mongolian
Middle Mongol or Middle Mongolian, was a Mongolic koiné language spoken in the Mongol Empire. Originating from Genghis Khan's home region of Northeastern Mongolia, it diversified into several Mongolic languages after the collapse of the empire ...
);''Histoire des campagnes de Gengis Khan'', p. 119. Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and Q ...
plural:  is a member of the
is a member of the Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
sub-clan, which started with Bodonchar Munkhag
Bodonchar Munkhag (Mongol: Бодончар Мөнх, ; died 10th Century CE.) was a renowned Mongol warlord and a direct ancestor of Genghis Khan as well as of the Barlas Mongols, the tribe of the Central Asian warlord Timur.
According to the ...
of the Kiyat clan. Yesugei's descendants were thus said to be Kiyat-Borjigin. The senior Borjigids provided ruling princes for Mongolia
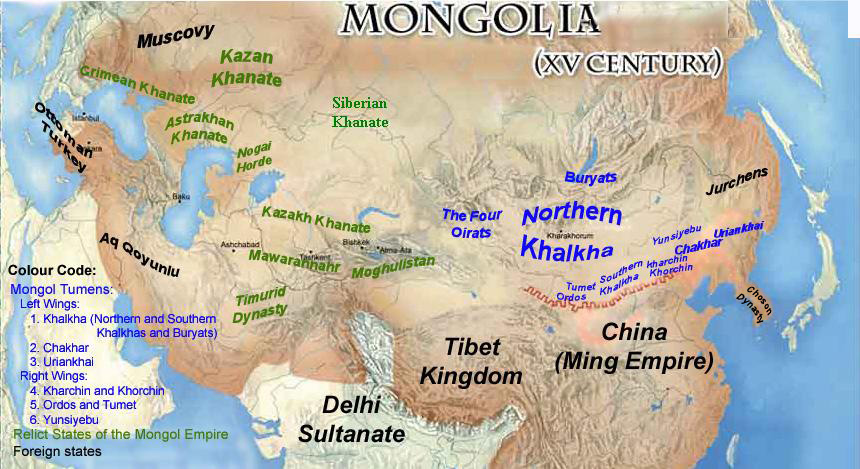
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 millio ...
and Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for ...
until the 20th century.Humphrey & Sneath, p. 27. The clan formed the ruling class
In sociology, the ruling class of a society is the social class who set and decide the political and economic agenda of society. In Marxist philosophy, the ruling class are the capitalist social class who own the means of production and by exte ...
among the Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
and some other peoples of Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former ...
and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, wh ...
. Today, the Borjigid are found in most of Mongolia, Inner Mongolia and Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
, and additionally genetic research has shown that descent from Genghis Khan
Descent from Genghis Khan in East Asia is well-documented by Chinese sources. His descent in West Asia and Europe was documented through the 14th century, in texts written by Rashid-al-Din Hamadani and other Muslim historians. With the advent of ...
and Amir Timur
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Temür'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Temür'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617–19 February 1405), later Timūr Gurkānī ( chg, ''Temür Kür ...
Barlas
The Barlas ( mn, Barulās, script=Latn;Grupper, S. M. ‘A Barulas Family Narrative in the Yuan Shih: Some Neglected Prosopographical and Institutional Sources on Timurid Origins.’ Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi 8 (1992–94): 11–97 Chagatay/ ...
is common throughout Central Asia and other regions.
Origin and name
The patrilineage began with Blue-greyWolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly u ...
(Börte Chino) and Fallow Doe (Gua Maral). According to ''The Secret History of the Mongols
''The Secret History of the Mongols'' (Middle Mongol: ''Mongɣol‑un niɣuca tobciyan''; Traditional Mongolian: , Khalkha Mongolian: , ; ) is the oldest surviving literary work in the Mongolian language. It was written for the Mongol royal fa ...
'', their 11th generation descendant Dobu Mergen's widow Alan Gua
Alan Gua ( mn, Алун гуа, ''Alun gua'', ''lit. "Alun the Beauty"''. ''Gua'' or ''Guva/Quwa'' means ''beauty'' in Mongolian) is a mythical figure from ''The Secret History of the Mongols'', eleven generations after the grey wolf and the whit ...
the Fair was impregnated by a ray of light. Her youngest son became the ancestor of the later Borjigid. He was Bodonchar Munkhag
Bodonchar Munkhag (Mongol: Бодончар Мөнх, ; died 10th Century CE.) was a renowned Mongol warlord and a direct ancestor of Genghis Khan as well as of the Barlas Mongols, the tribe of the Central Asian warlord Timur.
According to the ...
, who along with his brothers sired the entire Mongol nation. According to Rashid-al-Din Hamadani
Rashīd al-Dīn Ṭabīb ( fa, رشیدالدین طبیب; 1247–1318; also known as Rashīd al-Dīn Faḍlullāh Hamadānī, fa, links=no, رشیدالدین فضلالله همدانی) was a statesman, historian and physician in Il ...
, many of the older Mongolian clans were founded by members of the Borjigin — Barlas
The Barlas ( mn, Barulās, script=Latn;Grupper, S. M. ‘A Barulas Family Narrative in the Yuan Shih: Some Neglected Prosopographical and Institutional Sources on Timurid Origins.’ Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi 8 (1992–94): 11–97 Chagatay/ ...
, Urud, Manghud
The Mangghud, or Manghud ( mn, Мангуд, ''Mangud''), were a Mongol tribe of the Urud-Manghud federation. They established the Nogai Horde in the 14th century and the Manghit dynasty to rule the Emirate of Bukhara in 1785. They took the Is ...
, Taichiut, Chonos, Kiyat, etc. The first Khan of the Mongol was Bodonchar Munkhag's great-great-grandson Khaidu Khan. Khaidu's grandsons Khabul Khan
Khabul Khan ( mn, Хабул хан; ), also rendered as Qabul Khan, Kabul Khan and Khabul Khagan, (b. 1090s/1100 – d. 1130 CE.) was the founder and first known Khan of the Khamag Mongol confederation and great-grandfather of Genghis Khan. and ...
and Ambaghai
Ambaghai or Hambaqai Khan (; ) ( ? – died 1156) was a khan of the Khamag Mongol, one of the great grandsons of Khaidu Khan and the cousin and predecessor of Hotula Khan, he was the Leader of Taichud Clan one of sub-branch of Borjigid, and al ...
Khan (founder of the Taichiut clan) succeeded him. Thereafter, Khabul's sons, Hotula Khan and Yesugei
Yesugei Baghatur or Yesükhei ( Traditional Mongolian: ; Modern Mongolian: Есүхэй баатар, ''Yesukhei baatar'', ; ) (b. 1134 – d. 1171) was a major chief of the Khamag Mongol confederation and the father of Temüjin, later known a ...
, and Khabul's grandson Temujin (Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr /> Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent) Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin ...
, son of Yesugei) ruled the Khamag Mongol
Khamag Mongol ( mn, Хамаг монгол, Khamag mongol, lit=the whole Mongol; ) was a major Mongolic tribal confederation (khanlig) on the Mongolian Plateau in the 12th century. It is sometimes considered to be a predecessor state to the ...
. By the unification of the Mongols in 1206, virtually all of Temujin's uncles and first cousins had died, and from then on only the descendants of Yesugei Baghatur, his brother Daritai, and nephew Onggur formed the Borjigid.
According to Paul Pelliot
Paul Eugène Pelliot (28 May 187826 October 1945) was a French Sinologist and Orientalist best known for his explorations of Central Asia and his discovery of many important Chinese texts such as the Dunhuang manuscripts.
Early life and care ...
and Louis Hambis Louis may refer to:
* Louis (coin)
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
* HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy
See also
Derived or associated terms
* Lewis (d ...
, Rashid al-Din Hamadani
Rashīd al-Dīn Ṭabīb ( fa, رشیدالدین طبیب; 1247–1318; also known as Rashīd al-Dīn Faḍlullāh Hamadānī, fa, links=no, رشیدالدین فضلالله همدانی) was a statesman, historian and physician in Ilk ...
once explained that "''borčïqïn''" designated in the Turkic languages a man with dark-blue eyes ( ar, اشهل, translit=ašhal, label=none), and did so again without mentioning the said language, adding that Yesugei's children and the majority of their own children had had such eyes per coincidence, also recalling that the genie which had impregnated Alan Gua
Alan Gua ( mn, Алун гуа, ''Alun gua'', ''lit. "Alun the Beauty"''. ''Gua'' or ''Guva/Quwa'' means ''beauty'' in Mongolian) is a mythical figure from ''The Secret History of the Mongols'', eleven generations after the grey wolf and the whit ...
after her husband's death had had dark-blue eyes ("''ašhal čašm''"). Abu al-Ghazi Bahadur
Abu al-Ghazi Bahadur ( uz, Abulgʻozi Bahodirxon, Abulgazi, Ebulgazi, Abu-l-Ghazi, August 24, 1603 – 1663) was Khan of Khiva from 1643 to 1663. He spent ten years in Persia before becoming khan, and was very well educated, writing two historica ...
later paraphrased Hamadani by relating that Yesugei's eyes were dark-blue (" شهلا ''šahlā''"), that the Mongols ("''Moɣol''") called such eyes "''borǰïɣïn''" (بورجغن), that his sons and most of their descendants had dark-blue eyes ("''ašhal''"), and that one recognized thus in Yesugei's lineage the characteristic sign of the genie which had visited Alan Gua and had "''borǰïɣïn''" eyes, adding that the Arabs called "''ašhal''" a man whose iris ("''bübäčik''") was black, cornea white ("''aq''"), and whose limbal ring was red. This explanation was questioned by Paul Pelliot and Louis Hambis before. 14th century Arabic historian Shihab al-Umari
Shihab al-Din Abu al-Abbas Ahmad ibn Fadlallah al-Umari ( ar, شهاب الدين أبو العبّاس أحمد بن فضل الله العمري, Shihāb al-Dīn Abū al-ʿAbbās Aḥmad ibn Faḍlallāh al-ʿUmarī), commonly known as Ibn Fadlal ...
disputed Rashid al-Din's translation and claimed Alan Gua
Alan Gua ( mn, Алун гуа, ''Alun gua'', ''lit. "Alun the Beauty"''. ''Gua'' or ''Guva/Quwa'' means ''beauty'' in Mongolian) is a mythical figure from ''The Secret History of the Mongols'', eleven generations after the grey wolf and the whit ...
falsified the origin of her clan to escape death sentence. Historians such as Denise Aigle claimed that Rashid al-Din mythicized the origin of Genghis Khan ancestors (the Borjigin clan) through his own interpretations of The Secret History of the Mongols
''The Secret History of the Mongols'' (Middle Mongol: ''Mongɣol‑un niɣuca tobciyan''; Traditional Mongolian: , Khalkha Mongolian: , ; ) is the oldest surviving literary work in the Mongolian language. It was written for the Mongol royal fa ...
. Italian historian Igor de Rachewiltz
Igor de Rachewiltz (April 11, 1929 – July 30, 2016) was an Italian historian and philologist specializing in Mongol studies.
Igor de Rachewiltz was born in Rome, the son of Bruno Guido and Antonina Perosio, and brother of Boris de Rachewiltz. ...
claimed that the Mongol origins of the early ancestors of Genghis Khan were animals born from the blue-grey wolf (Borte Chino) and the fallow doe (Qo'ai Maral) that was described in the early legends, that their ancestors were animals.
History
 The Borjigin family ruled over the
The Borjigin family ruled over the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe ...
from the 13th to 14th century. The rise of Genghis (Chingis) narrowed the scope of the Borjigid-Kiyad clans sharply.Atwood, p. 45. This separation was emphasized by the intermarriage of Genghis's descendants with the Barlas
The Barlas ( mn, Barulās, script=Latn;Grupper, S. M. ‘A Barulas Family Narrative in the Yuan Shih: Some Neglected Prosopographical and Institutional Sources on Timurid Origins.’ Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi 8 (1992–94): 11–97 Chagatay/ ...
, Baarin, Manghud
The Mangghud, or Manghud ( mn, Мангуд, ''Mangud''), were a Mongol tribe of the Urud-Manghud federation. They established the Nogai Horde in the 14th century and the Manghit dynasty to rule the Emirate of Bukhara in 1785. They took the Is ...
and other branches of the original Borjigid. In the western regions of the Empire, the Jurkin and perhaps other lineages near to Genghis's lineage used the clan name Kiyad but did not share in the privileges of the Genghisids. The Borjigit clan had once dominated large lands stretching from Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
to Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
and from Indo-China
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
to Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( rus, links=no, Великий Новгород, t=Great Newtown, p=vʲɪˈlʲikʲɪj ˈnovɡərət), also known as just Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the o ...
. In 1335, with the disintegration of the Ilkhanate
The Ilkhanate, also spelled Il-khanate ( fa, ایل خانان, ''Ilxānān''), known to the Mongols as ''Hülegü Ulus'' (, ''Qulug-un Ulus''), was a khanate established from the southwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. The Ilkhanid realm, ...
in Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
, the first of numerous non-Borjigid-Kiyad dynasties appeared. Established by marriage partners of Genghisids, these included the Suldus Chupanids, Jalayirids
The Jalayirid Sultanate was a culturally Persianate, Mongol Jalayir dynasty which ruled over Iraq and western Persia after the breakup of the Ilkhanate, Mongol khanate of Persia in the 1330s.Bayne Fisher, William. ''The Cambridge History of Ira ...
in the Middle East, the Barulas dynasties in Chagatai Khanate
The Chagatai Khanate, or Chagatai Ulus ( xng, , translit=Čaɣatay-yin Ulus; mn, Цагаадайн улс, translit=Tsagaadain Uls; chg, , translit=Čağatāy Ulusi; fa, , translit=Xânât-e Joghatây) was a Mongol and later Turkicized kh ...
and India, the Manghud and Onggirat
The Khongirad ( Mongolian: ᠬᠣᠩᠭᠢᠷᠠᠳ; Хонгирад; Khonghirad; ), also known as Qongirat (Qoŋğırat/Қоңғырат), was one of the major divisions of the Mongol tribes. Variations on the name include Onggirat, Ongirat, Q ...
dynasties in the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragment ...
and Central Asia, and the Oirats
Oirats ( mn, Ойрад, ''Oirad'', or , Oird; xal-RU, Өөрд; zh, 瓦剌; in the past, also Eleuths) are the westernmost group of the Mongols whose ancestral home is in the Altai Mountains, Altai region of Siberia, Xinjiang and western M ...
in western Mongolia.
In 1368, during the reign of Toghun Temür (Emperor Huizong of Yuan), the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongols, Mongol-led Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Division of the M ...
was overthrown by the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
but members of the family continued to rule over northern China and the Mongolian Plateau into the 17th century, known as the Northern Yuan dynasty
The Northern Yuan () was a dynastic regime ruled by the Mongol Borjigin clan based in the Mongolian Plateau. It existed as a rump state after the collapse of the Yuan dynasty in 1368 and lasted until its conquest by the Jurchen-led Later ...
. Descendants of Genghis Khan's brothers, Hasar
Qasar (also spelled Hasar or Khasar, and also known as Jo'chi Qasar; Mongolian: Жочи Хасар) was one of Genghis Khan's three full brothers. According to the ''Jami' al-Tawarikh'', his given name was Jo'chi and he got the nickname Khasar ...
and Belgutei
Belgutei ( – ) was the son of Yesugei and Sochigel and half-brother to Genghis Khan. He also became general to Genghis Khan. Belgutei was considered a wise counselor and skilled diplomat, and was often used as a messenger by Genghis Khan. With ...
, surrendered to the Ming in the 1380s. By 1470 the Borjigin lines were severely weakened, and the Mongolian Plateau was almost in chaos.
Post-Mongol Empire
 After the breakup of the Golden Horde, the Khiyat continued to rule the
After the breakup of the Golden Horde, the Khiyat continued to rule the Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
and Kazan
Kazan ( ; rus, Казань, p=kɐˈzanʲ; tt-Cyrl, Казан, ''Qazan'', IPA: ɑzan is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Tatarstan in Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka rivers, covering ...
until the late 18th century. They were annexed by the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended th ...
and the Chinese. In Mongolia, the Kublaids reigned as Khagan
Khagan or Qaghan (Mongolian:; or ''Khagan''; otk, 𐰴𐰍𐰣 ), or , tr, Kağan or ; ug, قاغان, Qaghan, Mongolian Script: ; or ; fa, خاقان ''Khāqān'', alternatively spelled Kağan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan ...
of the Mongols, however, descendants of Ögedei and Ariq Böke
Ariq Böke (after 1219–1266), the components of his name also spelled Arigh, Arik and Bukha, Buka ( mn, Аригбөх, Arigböh, ; ), was the seventh and youngest son of Tolui and a grandson of Genghis Khan. After the death of his brother the ...
usurped the throne briefly.
Under Dayan Khan
Dayan Khan ( mn, Даян Хаан; Mongol script: ; ), born Batumöngke ( mn, Батмөнх; ), (1472–1517) was a khagan of the Northern Yuan dynasty, reigning from 1479 to 1517. During his rule, he reunited the Mongols under Chinggisid sup ...
(1480–1517) a broad Borjigid revival reestablished Borjigid supremacy among the Mongols proper. His descendants proliferated to become a new ruling class. The Borjigin clan was the strongest of the 49 Mongol banners
A banner can be a flag or another piece of cloth bearing a symbol, logo, slogan or another message. A flag whose design is the same as the shield in a coat of arms (but usually in a square or rectangular shape) is called a banner of arms. Also, ...
from which the Bontoi clan proper supported and fought for their Khan and for their honor. The eastern Khorchin
The Khorchin ( mn, Хорчин, ''Horçin''; ''Qorčin''; ) are a subgroup of the Mongols that speak the Khorchin dialect of Mongolian and predominantly live in northeastern Inner Mongolia of China.
History
The Ming dynasty gave Borjigin p ...
s were under the Hasarids, and the Ongnigud, Abagha Mongols were under the Belguteids and Temüge Odchigenids. A fragment of the Hasarids deported to Western Mongolia became the Khoshut
The Khoshut ( Mongolian: Хошууд,, qoşūd, ; literally "bannermen," from Middle Mongolian ''qosighu'' "flag, banner") are one of the four major tribes of the Oirat people. Originally, Khoshuuds were one of the Khorchin tribes in southeast ...
s.
The Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
respected the Borjigin family and the early emperors married the Hasarid Borjigids of the Khorchin. Even among the pro-Qing Mongols, traces of the alternative tradition survived. Aci Lomi, a banner general, wrote his ''History of the Borjigid Clan'' in 1732–35. The 18th century and 19th century Qing nobility was adorned by the descendants of the early Mongol adherents including the Borjigin.
Asian dynasties descended from Genghis Khan included the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongols, Mongol-led Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Division of the M ...
of China, the Ilkhanid
The Ilkhanate, also spelled Il-khanate ( fa, ایل خانان, ''Ilxānān''), known to the Mongols as ''Hülegü Ulus'' (, ''Qulug-un Ulus''), was a khanate established from the southwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. The Ilkhanid realm, ...
s of Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkme ...
, the Jochids
Descent from Genghis Khan in East Asia is well-documented by Chinese sources. His descent in West Asia and Europe was documented through the 14th century, in texts written by Rashid-al-Din Hamadani and other Muslim historians. With the advent of ...
of the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragment ...
, the Shaybanids
The Shibanids or Shaybanids ( fa, سلسله شیبانیان) or more accurately the Abu'l-Khayrid-Shibanids were a Persianized''Introduction: The Turko-Persian tradition'', Robert L. Canfield, Turko-Persia in Historical Perspective, ed. Robert L ...
of Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
, and the Astrakhanids of Central Asia. As a rule, the Genghisid descent played a crucial role in Tatar
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different politics. For instance,
 *Jochi
*Orda Khan
*
*Jochi
*Orda Khan
*
Image:YuanEmperorAlbumGenghisPortrait.jpg,
 Or in a different version (years of reign over the Northern Yuan dynasty [up to 1388] are given in brackets).
Or in a different version (years of reign over the Northern Yuan dynasty [up to 1388] are given in brackets).
''Histoire des campagnes de Gengis Khan''
(in French). E. J. Brill. * Humphrey, Caroline; Sneath, David. ''The End of Nomadism?''. * . * Kahn, Paul. ''The Secret History of the Mongols''. * Li, Gertraude Roth
''Manchu: A Textbook for Reading Documents''
* * Pegg, Carole. ''Mongolian Music, Dance & Oral Narrative''. * Perdue, Peter C. ''China Marches West''. * Sneath, David. ''Changing Inner Mongolia: Pastoral Mongolian Society and the Chinese State''. * Weatherford, Jack. ''Genghis Khan and the Making of the Modern World''. Three Rivers Press.
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different politics. For instance,
Mamai
Mamai ( Mongolian Cyrillic: Мамай, tt-Cyrl, Мамай, translit=Mamay; 1325?–1380/1381) was a powerful military commander of the Golden Horde. Contrary to popular misconception, he was not a khan (king), but a warlord and a kingmaker f ...
had to exercise his authority through a succession of puppet khans but could not assume the title of khan
Khan may refer to:
*Khan (inn), from Persian, a caravanserai or resting-place for a travelling caravan
* Khan (surname), including a list of people with the name
*Khan (title), a royal title for a ruler in Mongol and Turkic languages and used by ...
himself because he lacked Genghisid lineage.
The word "Chingisid" derives from the name of the Mongol conqueror Genghis (Chingis) Khan (c. 1162–1227 CE). Genghis and his successors created a vast empire stretching from the Sea of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it h ...
to the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, ...
.
* The ''Chingisid principle'', or golden lineage, was the rule of inheritance laid down in the (Yassa
Yassa (alternatively: ''Yasa'', ''Yasaq'', ''Jazag'', ''Zasag'', mn, Их засаг, ''Ikh Zasag'') was the oral law code of the Mongols declared in public in Bukhara by Genghis Khan'' de facto'' law of the Mongol Empire even though the "law" ...
), the legal code attributed to Genghis Khan.
* A ''Chingisid prince'' was one who could trace direct descent from Genghis Khan
Descent from Genghis Khan in East Asia is well-documented by Chinese sources. His descent in West Asia and Europe was documented through the 14th century, in texts written by Rashid-al-Din Hamadani and other Muslim historians. With the advent of ...
in the male line, and who could therefore claim high respect in the Mongol, Turkic
Turkic may refer to:
* anything related to the country of Turkey
* Turkic languages, a language family of at least thirty-five documented languages
** Turkic alphabets (disambiguation)
** Turkish language, the most widely spoken Turkic language
* ...
and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an ...
tic world.
* The ''Chingisid states'' were the successor states or Khanate
A khaganate or khanate was a polity ruled by a khan, khagan, khatun, or khanum. That political territory was typically found on the Eurasian Steppe and could be equivalent in status to tribal chiefdom, principality, kingdom or empire.
...
s after the Mongol empire broke up following the death of the Genghis Khan's sons and their successors.
* The term ''Chingisid people'' was used to describe the people of Genghis Khan's armies who came in contact with Europeans. It applied primarily the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragment ...
, led by Batu Khan
Batu Khan ( – 1255),, ''Bat haan'', tt-Cyrl, Бату хан; ; russian: хан Баты́й was a Mongol ruler and founder of the Golden Horde, a constituent of the Mongol Empire. Batu was a son of Jochi, thus a grandson of Genghis Khan. ...
, a grandson of Genghis. Members of the Horde were predominantly Oghuz — Turkic
Turkic may refer to:
* anything related to the country of Turkey
* Turkic languages, a language family of at least thirty-five documented languages
** Turkic alphabets (disambiguation)
** Turkish language, the most widely spoken Turkic language
* ...
-speaking people rather than Mongols. (Although the aristocracy was largely Mongol, Mongols were never more than a small minority in the armies and the lands they conquered.) Europeans often (incorrectly) called the people of the Golden Horde "Tartars
Tartary ( la, Tartaria, french: Tartarie, german: Tartarei, russian: Тартария, Tartariya) or Tatary (russian: Татария, Tatariya) was a blanket term used in Western European literature and cartography for a vast part of Asia bound ...
".
Babur
Babur ( fa, , lit= tiger, translit= Bābur; ; 14 February 148326 December 1530), born Mīrzā Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad, was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his ...
and Humayun
Nasir-ud-Din Muhammad ( fa, ) (; 6 March 1508 – 27 January 1556), better known by his regnal name, Humāyūn; (), was the second emperor of the Mughal Empire, who ruled over territory in what is now Eastern Afghanistan, Pakistan, Norther ...
, founders of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the ...
in India, asserted their authority as Chinggisids. Because they claimed descent through their maternal lineage, they had never used the clan name Borjigin.
The Genghisids also include such dynasties and houses as Giray, House of Siberia The House of Sibirsky ( Russian: Сибирский, Сибирские) was the foremost of many Genghisid ( Shaybanid) families formerly living in Russia. It traced its descent from Kuchum, the last of the Siberian khans.
History
Kuchum's ...
, Ar begs
Ar begs (in Russian chronicles "Арские князья") was a formation of Noqrat Tatars' nobility, served to Muscovy in 16th–17th century. In 14th–15th centuries they were rulers of semi-independent duchy in the middle Cheptsa, nowadays ...
, Yaushev family
Yaushev (russian: link=no, Яушевы, tt-Cyrl, Яушевлар, translit=Yawşevlar) are a Volga Tatars, Volga Tatar noble family.
Early history
The family is a branch of the Ar begs aristocratic clan and descents from Yaush (russian: link= ...
and other.
The last ruling monarch of Genghisid ancestry, Maqsud Shah (d. 1930), Khan of Kumul from 1908 to 1930.
Modern relevance
The Borjigin held power over Mongolia for many centuries (even duringQing period
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
) and only lost power when Communists
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a ...
took control in the 20th century. Aristocratic descent was something to be forgotten in the socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the ...
period. Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secreta ...
's associates executed some 30,000 Mongols including Borjigin nobles in a series of campaigns against their culture and religion. Clan association has lost its practical relevance in the 20th century, but is still considered a matter of honour and pride by many Mongolians
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
. In 1920s the communist regime banned the use of clan names. When the ban was lifted again in 1997, and people were told they had to have surnames, most families had lost knowledge about their clan association. Because of that, a disproportionate number of families registered the most prestigious clan name Borjigin, many of them without historic justification. The label Borjigin is used as a measure of cultural supremacy.
In Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for ...
, the Borjigid or Kiyad name became the basis for many Chinese surnames adopted by ethnic Inner Mongols. The Inner Mongolian Borjigin Taijis took the surname Bao
Baozi (), Pao-tsih or bao, is a type of yeast-leavened filled bun in various Chinese cuisines. There are many variations in fillings (meat or vegetarian) and preparations, though the buns are most often steamed. They are a variation of '' man ...
(, from Borjigid) and in Ordos Qi (, Qiyat). A genetic research
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar working i ...
has proposed that as many as 16 million men from populations as far apart as Hazaras
The Hazaras ( fa, , Həzārə; haz, , Āzərə) are an ethnic group and the principal component of the population of Afghanistan, native to, and primarily residing in the Hazaristan (Hazarajat) region in central Afghanistan and generally scat ...
in the West and Hezhe people
The Nanai people are a Tungusic people of East Asia who have traditionally lived along Heilongjiang (Amur), Songhuajiang (Sunggari) and Wusuli River on the Middle Amur Basin. The ancestors of the Nanai were the Jurchens of northernmost Manchur ...
to the east may have Borjigid-Kiyad ancestry. The Qiyat clan name is still found among the Kazakhs
The Kazakhs (also spelled Qazaqs; Kazakh: , , , , , ; the English name is transliterated from Russian; russian: казахи) are a Turkic-speaking ethnic group native to northern parts of Central Asia, chiefly Kazakhstan, but also part ...
, Uzbeks
The Uzbeks ( uz, , , , ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group native to the wider Central Asia, Central Asian region, being among the largest Turkic ethnic group in the area. They comprise the majority population of Uzbekistan, next to ...
and Karakalpaks
The Karakalpaks or Qaraqalpaqs (; kaa, Qaraqalpaqlar, Қарақалпақлар, قاراقلپقلر), are a Turkic ethnic group native to Karakalpakstan in Northwestern Uzbekistan. During the 18th century, they settled in the lower reache ...
.
Prominent Kiyads or Borjigins

Rulers of the
Khamag Mongol
Khamag Mongol ( mn, Хамаг монгол, Khamag mongol, lit=the whole Mongol; ) was a major Mongolic tribal confederation (khanlig) on the Mongolian Plateau in the 12th century. It is sometimes considered to be a predecessor state to the ...
(11th century – 1206)
* Khaidu
*Khabul Khan
Khabul Khan ( mn, Хабул хан; ), also rendered as Qabul Khan, Kabul Khan and Khabul Khagan, (b. 1090s/1100 – d. 1130 CE.) was the founder and first known Khan of the Khamag Mongol confederation and great-grandfather of Genghis Khan. and ...
*Yesugei
Yesugei Baghatur or Yesükhei ( Traditional Mongolian: ; Modern Mongolian: Есүхэй баатар, ''Yesukhei baatar'', ; ) (b. 1134 – d. 1171) was a major chief of the Khamag Mongol confederation and the father of Temüjin, later known a ...
Emperors and rulers of the
Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe ...
(1206–1368)
*Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr /> Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent) Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin ...
*Tolui
Tolui (also Toluy, Tului; , meaning: "the mirror"; – 1232) was a Mongol khan, the fourth son of Genghis Khan by his chief khatun, Börte. At his father's death in 1227, his '' ulus'', or territorial inheritance, was the Mongol homelands on ...
Khan (title), Khan
*Ögedei Khan
*Güyük Khan
*Möngke Khan
*Kublai Khan
Genghis Khan's brothers
*Hasar
Qasar (also spelled Hasar or Khasar, and also known as Jo'chi Qasar; Mongolian: Жочи Хасар) was one of Genghis Khan's three full brothers. According to the ''Jami' al-Tawarikh'', his given name was Jo'chi and he got the nickname Khasar ...
*Belgutei
Belgutei ( – ) was the son of Yesugei and Sochigel and half-brother to Genghis Khan. He also became general to Genghis Khan. Belgutei was considered a wise counselor and skilled diplomat, and was often used as a messenger by Genghis Khan. With ...
*Temüge
Rulers of the Khanates
=
Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongols, Mongol-led Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Division of the M ...
=
*Kublai Khan
*Temür Khan
*Toghon Temür Khan (title), Khan
=
Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragment ...
=
 *Jochi
*Orda Khan
*
*Jochi
*Orda Khan
*Batu Khan
Batu Khan ( – 1255),, ''Bat haan'', tt-Cyrl, Бату хан; ; russian: хан Баты́й was a Mongol ruler and founder of the Golden Horde, a constituent of the Mongol Empire. Batu was a son of Jochi, thus a grandson of Genghis Khan. ...
*Sartaq
*Berke
*Shiban
*Toqta
*Uzbeg Khan
=
Ilkhanate
The Ilkhanate, also spelled Il-khanate ( fa, ایل خانان, ''Ilxānān''), known to the Mongols as ''Hülegü Ulus'' (, ''Qulug-un Ulus''), was a khanate established from the southwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. The Ilkhanid realm, ...
=
*Hulagu
*Abaqa
*Ghazan
=
Chagatai Khanate
The Chagatai Khanate, or Chagatai Ulus ( xng, , translit=Čaɣatay-yin Ulus; mn, Цагаадайн улс, translit=Tsagaadain Uls; chg, , translit=Čağatāy Ulusi; fa, , translit=Xânât-e Joghatây) was a Mongol and later Turkicized kh ...
=
*Chagatai Khan
*Kaidu
*Duwa
*Esen Buqa I
*Kebek
*Tarmashirin
Post-Mongol Empire
Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragment ...
(1360–1502)
*Urus Khan
*Toqtamish
*Mamai
Mamai ( Mongolian Cyrillic: Мамай, tt-Cyrl, Мамай, translit=Mamay; 1325?–1380/1381) was a powerful military commander of the Golden Horde. Contrary to popular misconception, he was not a khan (king), but a warlord and a kingmaker f ...
*Olug Moxammat
Crimean Khanate (1441–1783)
*Mengli GirayKazan Khanate (1438–1552)
*Olug MoxammatUzbek Khanate (1428–1471)
*Abu'l-Khayr KhanKazakh Khanate (1456–1847)
*Janybek Khan
Northern Yuan dynasty
The Northern Yuan () was a dynastic regime ruled by the Mongol Borjigin clan based in the Mongolian Plateau. It existed as a rump state after the collapse of the Yuan dynasty in 1368 and lasted until its conquest by the Jurchen-led Later ...
(1368–1635)
*Öljei Temür Khan
*Dayan Khan
Dayan Khan ( mn, Даян Хаан; Mongol script: ; ), born Batumöngke ( mn, Батмөнх; ), (1472–1517) was a khagan of the Northern Yuan dynasty, reigning from 1479 to 1517. During his rule, he reunited the Mongols under Chinggisid sup ...
*Ligdan Khan
*Ejei Khan
Ruler of the Tumed
*Altan KhanKhalkha
*ZanabazarGallery
Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr /> Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent) Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin ...
Image:CoronationOfOgodei1229.jpg, Ögedei Khan
Image:TuluiWithQueenSorgaqtani.jpg, Tolui
Tolui (also Toluy, Tului; , meaning: "the mirror"; – 1232) was a Mongol khan, the fourth son of Genghis Khan by his chief khatun, Börte. At his father's death in 1227, his '' ulus'', or territorial inheritance, was the Mongol homelands on ...
with his wife Sorghaghtani Beki
Image:Mengli bayezid.jpg, Mengli Giray at the court of Bayezid II
Image:Altan Khan.jpg, Altan Khan
Image:Imperial Portrait of Empress Xiao Zhuang Wen.jpg, Empress Dowager Xiaozhuang
File:Facial Chronicle - b.10, p.049 - Tokhtamysh at Moscow.jpg, Tokhtamysh
Yuan dynasty family tree
Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr /> Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent) Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin ...
founded the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe ...
in 1206. His grandson, Kublai Khan, after defeating his younger brother and rival claimant to the throne Ariq Böke
Ariq Böke (after 1219–1266), the components of his name also spelled Arigh, Arik and Bukha, Buka ( mn, Аригбөх, Arigböh, ; ), was the seventh and youngest son of Tolui and a grandson of Genghis Khan. After the death of his brother the ...
, founded the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongols, Mongol-led Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Division of the M ...
of China in 1271. The dynasty was overthrown by the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
during the reign of Toghon Temür in 1368, but it survived in the Mongolian Plateau, known as the Northern Yuan dynasty
The Northern Yuan () was a dynastic regime ruled by the Mongol Borjigin clan based in the Mongolian Plateau. It existed as a rump state after the collapse of the Yuan dynasty in 1368 and lasted until its conquest by the Jurchen-led Later ...
. Although the throne was usurped by Esen Taishi of the Oirats
Oirats ( mn, Ойрад, ''Oirad'', or , Oird; xal-RU, Өөрд; zh, 瓦剌; in the past, also Eleuths) are the westernmost group of the Mongols whose ancestral home is in the Altai Mountains, Altai region of Siberia, Xinjiang and western M ...
in 1453, he was overthrown in the next year. A recovery of the khaganate was achieved by Dayan Khan
Dayan Khan ( mn, Даян Хаан; Mongol script: ; ), born Batumöngke ( mn, Батмөнх; ), (1472–1517) was a khagan of the Northern Yuan dynasty, reigning from 1479 to 1517. During his rule, he reunited the Mongols under Chinggisid sup ...
, but the territory was segmented by his descendants. The last khan (title), khan Ligden Khan, Ligden died in 1634 and his son Ejei Khan, Ejei Khongor submitted himself to Hong Taiji the next year, ending the Northern Yuan regime. However, the Borjigin nobles continued to rule their subjects until the 20th century under the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
.Sneath, p. 21.
 Or in a different version (years of reign over the Northern Yuan dynasty [up to 1388] are given in brackets).
Or in a different version (years of reign over the Northern Yuan dynasty [up to 1388] are given in brackets).
See also
*Family tree of Genghis Khan *History of Mongolia *Mongolian name *List of medieval Mongolian tribes and clans *Turco-MongolNotes
References
Citations
Sources
* Atwood, C. P. ''Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire''. * Crossley, Pamela Kyle. ''A Translucent Mirror''. * Franke, Herbert; Twitchett, Denis; Fairbank, John King. ''The Cambridge History of China: Alien Regimes and Border States, 907-1368''. * "The Genetic Legacy of the Mongols". ''American Journal of Human Genetics'', 72. * Halperin, Charles J. (1985). ''Russia and the Golden Horde: The Mongol Impact on Medieval Russian History''. Indiana University Press. . . * Heirman, Ann; Bumbacher, Stephan Peter. ''The Spread of Buddhism''.''Histoire des campagnes de Gengis Khan''
(in French). E. J. Brill. * Humphrey, Caroline; Sneath, David. ''The End of Nomadism?''. * . * Kahn, Paul. ''The Secret History of the Mongols''. * Li, Gertraude Roth
''Manchu: A Textbook for Reading Documents''
* * Pegg, Carole. ''Mongolian Music, Dance & Oral Narrative''. * Perdue, Peter C. ''China Marches West''. * Sneath, David. ''Changing Inner Mongolia: Pastoral Mongolian Society and the Chinese State''. * Weatherford, Jack. ''Genghis Khan and the Making of the Modern World''. Three Rivers Press.
Further reading
*Wada Sei 和田清. ''Tōashi Kenkyū (Mōko Hen)'' 東亜史研究 (蒙古編). Tokyo, 1959. *Honda Minobu 本田實信. ''On the genealogy of the early Northern Yüan'', Ural-Altaische Jahrbücher, XXX-314, 1958. *Okada Hidehiro 岡田英弘. ''Dayan Hagan no nendai'' ダヤン・ハガンの年代. Tōyō Gakuhō, Vol. 48, No. 3 pp. 1–26 and No. 4 pp. 40–61, 1965. *Okada Hidehiro 岡田英弘. ''Dayan Hagan no sensei'' ダヤン・ハガンの先世. Shigaku Zasshi. Vol. 75, No. 5, pp. 1–38, 1966. , - , - , - , - , - , - {{Authority control Borjigin, 900 establishments Mongolian nobility Mongol Empire people, *01 Yuan dynasty emperors Mongol Empire Yuan dynasty Ethnic groups in Mongolia Individual Chinese surnames Plain Yellow Banner