Chinese Revolution (1946−1952) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Chinese Civil War was fought between the
File:Nationalist China 1929 - 1937.PNG, The situation in China in 1929: After the
File:Situation at the End of World War Two.PNG, Japanese occupation (red) of eastern China near the end of the war, and Communist bases (striped)
 In the last month of World War II in East Asia, Soviet forces launched the huge
In the last month of World War II in East Asia, Soviet forces launched the huge
File:Manchuria Operation map-es.svg, The Soviet
 After the war with the Japanese ended, Chiang Kai-shek quickly moved KMT troops to newly liberated areas to prevent Communist forces from receiving the Japanese surrender. The US airlifted many KMT troops from central China to the
After the war with the Japanese ended, Chiang Kai-shek quickly moved KMT troops to newly liberated areas to prevent Communist forces from receiving the Japanese surrender. The US airlifted many KMT troops from central China to the
File:Chaing Kai-shek's Strategy 1947.PNG, Situation in 1947
File:Communist Offensives September through November 1948.PNG, Situation in the fall of 1948
File:Communist Offensives November 1948 - January 1949.PNG, Situation in the winter of 1948 and 1949
File:Communist Offensives April - October 1949.PNG, Situation in April to October 1949
As postwar negotiations between the Nationalist government and the CCP failed, the civil war between these two parties resumed. This stage of war is referred to in  After achieving decisive victory through the Liaoshen, Huaihai, and Pingjin campaigns, the CCP destroyed 144 regular and 29 irregular KMT divisions, including 1.54 million
After achieving decisive victory through the Liaoshen, Huaihai, and Pingjin campaigns, the CCP destroyed 144 regular and 29 irregular KMT divisions, including 1.54 million
 A PRC attempt to take the ROC-controlled island of
A PRC attempt to take the ROC-controlled island of
 In June 1949, the ROC declared a "closure" of all mainland China ports and its navy attempted to intercept all foreign ships. The closure was from a point north of the mouth of Min River in
In June 1949, the ROC declared a "closure" of all mainland China ports and its navy attempted to intercept all foreign ships. The closure was from a point north of the mouth of Min River in 
 On 25 October 1971, the
On 25 October 1971, the
Summary of Chinese Civil War 1946–1949
Topographic maps of China Series L500, U.S. Army Map Service, 1954–
Operational Art in the Chinese PLA's Huai Hai Campaign
{{Authority control 20th-century conflicts Aftermath of World War II Civil wars in China Cross-strait conflict Interwar period Military history of the Republic of China (1912–1949) Proxy wars Revolutions in China Revolution-based civil wars Wars involving the Republic of China Wars involving the People's Republic of China
Kuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT) is a major political party in the Republic of China (Taiwan). It was the one party state, sole ruling party of the country Republic of China (1912-1949), during its rule from 1927 to 1949 in Mainland China until Retreat ...
-led government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive (government), execu ...
of the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
and the forces of the Chinese Communist Party
The Communist Party of China (CPC), also translated into English as Chinese Communist Party (CCP), is the founding and One-party state, sole ruling party of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Founded in 1921, the CCP emerged victorious in the ...
(CCP). Armed conflict continued intermittently from 1 August 1927 until Communist victory resulted in their total control over mainland China
"Mainland China", also referred to as "the Chinese mainland", is a Geopolitics, geopolitical term defined as the territory under direct administration of the People's Republic of China (PRC) in the aftermath of the Chinese Civil War. In addit ...
on 7 December 1949.
The war is generally divided into two phases with an interlude: from August 1927 to 1937, the First United Front
The First United Front , also known as the KMT–CCP Alliance, of the Kuomintang (KMT) and the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), was formed in 1924 as an alliance to end Warlord Era, warlordism in China. Together they formed the National Revolution ...
alliance of the KMT and CCP collapsed during the Northern Expedition
The Northern Expedition was a military campaign launched by the National Revolutionary Army (NRA) of the Kuomintang (KMT) against the Beiyang government and other regional warlords in 1926. The purpose of the campaign was to reunify China prop ...
, and the Nationalists controlled most of China. From 1937 to 1945, hostilities were mostly put on hold as the Second United Front
The Second United Front ( zh, t=第二次國共合作 , s=第二次国共合作 , first=t , l=Second Nationalist-Communist Cooperation, p=dì èr cì guógòng hézuò ) was the alliance between the ruling Kuomintang (KMT) and the Chinese Co ...
fought the Japanese invasion of China with eventual help from the Allies of World War II
The Allies, formally referred to as the United Nations from 1942, were an international Coalition#Military, military coalition formed during World War II (1939–1945) to oppose the Axis powers. Its principal members were the "Four Policeme ...
. However, armed clashes between the groups remained common. Exacerbating the divisions within China further was the formation of the Wang Jingwei regime
The Reorganized National Government of the Republic of China, commonly described as the Wang Jingwei regime, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in eastern China. It existed coterminous with the Nationalist government of the Republic of ...
, a Japan-sponsored puppet government led by Wang Jingwei
Wang Zhaoming (4 May 188310 November 1944), widely known by his pen name Wang Jingwei, was a Chinese politician who was president of the Reorganized National Government of the Republic of China, a puppet state of the Empire of Japan. He was in ...
, which was established to nominally govern the regions of China that came under Japanese occupation.
The civil war resumed as soon as it became apparent that Japanese defeat was imminent, with the communists gaining the upper hand in the second phase of the war from 1945 to 1949, generally referred to as the Chinese Communist Revolution
The Chinese Communist Revolution was a social revolution, social and political revolution in China that began in 1927 and culminated with the proclamation of the People's Republic of China (PRC) in 1949. The revolution was led by the Chinese C ...
. The Communists gained control of mainland China and proclaimed the People's Republic of China in 1949, forcing the leadership of the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
to retreat to the island of Taiwan. Starting in the 1950s, a lasting political and military stand-off between the two sides of the Taiwan Strait
The Taiwan Strait is a strait separating the island of Taiwan and the Asian continent. The strait is part of the South China Sea and connects to the East China Sea to the north. The narrowest part is wide.
Names
Former names of the Tai ...
has ensued, with the ROC in Taiwan and the PRC on the mainland both claiming to be the legitimate government of all China. After the Second Taiwan Strait Crisis
The Second Taiwan Strait Crisis, also known as the 1958 Taiwan Strait Crisis, was a conflict between the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the Taiwan, Republic of China (ROC). The PRC shelled the islands of Kinmen (Quemoy) and the Matsu Is ...
, both tacitly ceased to engage in open conflict in 1979; however, no armistice
An armistice is a formal agreement of warring parties to stop fighting. It is not necessarily the end of a war, as it may constitute only a cessation of hostilities while an attempt is made to negotiate a lasting peace. It is derived from t ...
or peace treaty
A peace treaty is an treaty, agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually country, countries or governments, which formally ends a declaration of war, state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an ag ...
has ever been signed.
Background
Following the collapse of theQing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
and the 1911 Revolution
The 1911 Revolution, also known as the Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, ended China's last imperial dynasty, the Qing dynasty, and led to the establishment of the Republic of China (ROC). The revolution was the culmination of a decade ...
, Sun Yat-sen
Sun Yat-senUsually known as Sun Zhongshan () in Chinese; also known by Names of Sun Yat-sen, several other names. (; 12 November 186612 March 1925) was a Chinese physician, revolutionary, statesman, and political philosopher who founded the Republ ...
assumed the presidency
A presidency is an administration or the executive, the collective administrative and governmental entity that exists around an office of president of a state or nation. Although often the executive branch of government, and often personified b ...
of the newly formed Republic of China, and was shortly thereafter succeeded by Yuan Shikai
Yuan Shikai (; 16 September 18596 June 1916) was a Chinese general and statesman who served as the second provisional president and the first official president of the Republic of China, head of the Beiyang government from 1912 to 1916 and ...
. Yuan failed in a short-lived attempt to declare by himself emperor, and China fell into power struggle
A power struggle is situation where two or more people or groups fight to gain dominance over each other. The term is most commonly used in a political context, when parties contend for power or leadership positions, but can also be applied to a ...
after his death in 1916.
The Kuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT) is a major political party in the Republic of China (Taiwan). It was the one party state, sole ruling party of the country Republic of China (1912-1949), during its rule from 1927 to 1949 in Mainland China until Retreat ...
(KMT), led by Sun Yat-sen, created a new government in Guangzhou
Guangzhou, Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Canton or Kwangchow, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Guangdong Provinces of China, province in South China, southern China. Located on the Pearl River about nor ...
to rival the warlords who ruled over large swathes of China and prevented the formation of a solid central government. After Sun's efforts to obtain aid from Western countries were ignored, he turned to the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
. In 1923, Sun and Soviet representative Adolph Joffe
Adolph Abramovich Joffe (; alternatively transliterated as Adolf Ioffe or Yoffe; 10 October 1883 – 16 November 1927) was a Russian revolutionary, Bolshevik politician and Soviet diplomat of Karaite descent.
Biography Revolutionary career ...
in Shanghai
Shanghai, Shanghainese: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: is a direct-administered municipality and the most populous urban area in China. The city is located on the Chinese shoreline on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the ...
pledged Soviet assistance to China's unification in the Sun–Joffe Manifesto, a declaration of cooperation among the Comintern
The Communist International, abbreviated as Comintern and also known as the Third International, was a political international which existed from 1919 to 1943 and advocated world communism. Emerging from the collapse of the Second Internatio ...
, KMT, and the Chinese Communist Party
The Communist Party of China (CPC), also translated into English as Chinese Communist Party (CCP), is the founding and One-party state, sole ruling party of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Founded in 1921, the CCP emerged victorious in the ...
(CCP). Comintern agent Mikhail Borodin
Mikhail Markovich Gruzenberg, known by the alias Borodin (9 July 1884 – 29 May 1951), was a Bolshevik revolutionary and Communist International (Comintern) agent. He was an advisor to Sun Yat-sen and the Kuomintang (KMT) in China during the ...
arrived in 1923 to aid in the reorganization and consolidation of both the CCP and the KMT along the lines of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union
The Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU),. Abbreviated in Russian as КПСС, ''KPSS''. at some points known as the Russian Communist Party (RCP), All-Union Communist Party and Bolshevik Party, and sometimes referred to as the Soviet ...
. The CCP, which was initially a study group, and the KMT jointly formed the First United Front
The First United Front , also known as the KMT–CCP Alliance, of the Kuomintang (KMT) and the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), was formed in 1924 as an alliance to end Warlord Era, warlordism in China. Together they formed the National Revolution ...
.March, G. Patrick. ''Eastern Destiny: Russia in Asia and the North Pacific''. (1996). Greenwood. . p. 205.
In 1923, Sun sent Chiang Kai-shek, one of his lieutenants, for several months of military and political study in Moscow.H. H. Chang, ''Chiang Kai Shek: Asia's Man of Destiny'' (Doubleday, 1944; reprint 2007 ). p. 126. Chiang then became the head of the Whampoa Military Academy
The Republic of China Military Academy ( zh, t=中華民國陸軍軍官學校, p=Zhōnghúa Mīngúo Lùjūn Jūnguān Xúexiào, poj=Tiong-hôa Bîn-kok Lio̍k-kun Kun-koaⁿ Ha̍k-hāu), also known as the Chinese Military Academy (CMA), is ...
that trained the next generation of military leaders. The Soviets provided the academy with teaching material, organization, and equipment, including munitions. They also provided education in many of the techniques for mass mobilization. With this aid, Sun raised a dedicated "army of the party", with which he hoped to defeat the warlords militarily. CCP members were also present in the academy, and many of them became instructors, including Zhou Enlai
Zhou Enlai ( zh, s=周恩来, p=Zhōu Ēnlái, w=Chou1 Ên1-lai2; 5 March 1898 – 8 January 1976) was a Chinese statesman, diplomat, and revolutionary who served as the first Premier of the People's Republic of China from September 1954 unti ...
, who was made a political instructor.
Communist members were allowed to join the KMT on an individual basis. The CCP itself was still small at the time, having a membership of 300 in 1922 and only 1,500 by 1925.Fairbank, John King. (1994). ''China: A New History''. Harvard University Press. . As of 1923, the KMT had 50,000 members.
However, after Sun died in 1925, the KMT split into left- and right-wing movements. KMT members worried that the Soviets were trying to destroy the KMT from inside using the CCP. The CCP then began movements in opposition of the Northern Expedition
The Northern Expedition was a military campaign launched by the National Revolutionary Army (NRA) of the Kuomintang (KMT) against the Beiyang government and other regional warlords in 1926. The purpose of the campaign was to reunify China prop ...
, passing a resolution against it at a party meeting.
Then, in March 1927, the KMT held its second party meeting where the Soviets helped pass resolutions against the Expedition and curbing Chiang's power. Soon, the KMT would be clearly divided.
Throughout this time, the Soviet Union sent money and spies to support the CCP. Without their support, the CCP likely would have failed. This is evidenced by documents showing other communist parties in China at the time, one with as many as 10,000 members, which all failed without support from the Soviet Union.
Shanghai massacre and Northern Expedition (1927)
In early 1927, the KMT–CCP rivalry led to a split in the revolutionary ranks. The CCP and the left wing of the KMT decided to move the seat of the KMT government from Guangzhou toWuhan
Wuhan; is the capital of Hubei, China. With a population of over eleven million, it is the most populous city in Hubei and the List of cities in China by population, eighth-most-populous city in China. It is also one of the nine National cent ...
, where communist influence was strong. However, Chiang and Li Zongren
Li Zongren ( zh, c=李宗仁, p=Lǐ Zōngrén; 13 August 1890 – 30 January 1969), also known as Li Tsung-jen, courtesy name Delin (Te-lin; zh, p=Délín), was a Chinese warlord, military commander and politician. He was vice-president an ...
, whose armies defeated the warlord Sun Chuanfang
Sun Chuanfang () (April 17, 1885 – November 13, 1935) was a Chinese warlord in the Zhili clique and protégé of the "Jade Marshal" Wu Peifu.
Early life and education
Sun Chuanfang was born in Licheng District, Jinan, Licheng, Shandong ...
, moved eastward toward Jiangxi
; Gan: )
, translit_lang1_type2 =
, translit_lang1_info2 =
, translit_lang1_type3 =
, translit_lang1_info3 =
, image_map = Jiangxi in China (+all claims hatched).svg
, mapsize = 275px
, map_caption = Location ...
. The leftists rejected Chiang's demand to eliminate Communist influence within KMT, and Chiang denounced them for betraying Sun Yat-sen's Three Principles of the People
The Three Principles of the People (), also known as the Three People's Principles, San-min Doctrine, San Min Chu-i, or Tridemism is a political philosophy developed by Sun Yat-sen as part of a philosophy to improve China during the Republi ...
by taking orders from the Soviet Union. According to Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; traditionally Romanization of Chinese, romanised as Mao Tse-tung. (26December 18939September 1976) was a Chinese politician, revolutionary, and political theorist who founded the People's Republic of China (PRC) in ...
, Chiang's tolerance of the CCP in the KMT camp decreased as his power increased.
On 7 April, Chiang and several other KMT leaders held a meeting, during which they proposed that Communist activities were socially and economically disruptive and had to be undone for the Nationalist revolution to proceed. On 12 April, many communists within the KMT were purged in Shanghai through hundreds of arrests and executions on the orders of General Bai Chongxi
Bai Chongxi (18 March 1893 – 2 December 1966; , , Xiao'erjing: ) was a Chinese general in the National Revolutionary Army of the Republic of China (ROC) and a prominent leader of the Kuomintang. He was of Hui ethnicity and of the Muslim faith ...
. The CCP referred to this as the ''12 April Incident'', the White Terror, or the Shanghai massacre
The Shanghai massacre of 12 April 1927, the April 12 Purge or the April 12 Incident as it is commonly known in China, was the violent suppression of Chinese Communist Party (CCP) organizations and leftist elements in Shanghai by forces support ...
. This incident widened the rift between Chiang and Wang Jingwei
Wang Zhaoming (4 May 188310 November 1944), widely known by his pen name Wang Jingwei, was a Chinese politician who was president of the Reorganized National Government of the Republic of China, a puppet state of the Empire of Japan. He was in ...
, the leader of the left wing faction of the KMT. The left wing of the KMT also expelled CCP members from the Wuhan Government
The Wuhan Nationalist government (), also known as the Wuhan government, Wuhan regime, or Hankow government, was a government dominated by the left-wing of the Nationalist or Kuomintang (KMT) Party of China that was based in Wuhan from 5 Decembe ...
, which in turn was toppled by Chiang Kai-shek. The KMT resumed its campaign against the warlords and captured Beijing in June 1928. Soon, most of eastern China
East China () is a geographical region in the People’s Republic of China, mainly consisting of seven province-level administrative divisions, namely the provinces (from north to south) Shandong, Jiangsu, Anhui, Zhejiang, Jiangxi, Fujian, a ...
was under the control of the Nanjing central government, which received prompt international recognition as the sole legitimate government of China. The KMT government announced, in conformity with Sun Yat-sen, the formula for the three stages of revolution: military unification, political tutelage, and constitutional democracy.
Communist insurgency (1927–1937)
On 1 August 1927, the CCP launched an uprising in Nanchang against the Nationalist government inWuhan
Wuhan; is the capital of Hubei, China. With a population of over eleven million, it is the most populous city in Hubei and the List of cities in China by population, eighth-most-populous city in China. It is also one of the nine National cent ...
. This conflict led to the creation of the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
.Lee, Lai to. Trade Unions in China: 1949 To the Present. (1986). National University of Singapore Press. . On 4 August, the main forces of the Red Army left Nanchang and headed southwards for an assault on Guangdong. Nationalist forces quickly reoccupied Nanchang while the remaining members of the CCP in Nanchang went into hiding. A CCP meeting on 7 August confirmed the objective of the party was to seize political power by force, but the CCP was quickly suppressed the next day by the Nationalist government in Wuhan, led by Wang Jingwei. On 14 August, Chiang Kai-shek announced his temporary retirement, as the Wuhan faction and Nanjing faction of the Kuomintang were allied once again with common goal of suppressing the CCP after the earlier split. Wang Jingwei took the leadership of KMT after Chiang.
Attempts were later made by the CCP to take the cities of Changsha
Changsha is the capital of Hunan, China. It is the 15th most populous city in China with a population of 10,513,100, the Central China#Cities with urban area over one million in population, third-most populous city in Central China, and the ...
, Shantou
Shantou, Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanization of Chinese, romanized as Swatow and sometimes known as Santow, is a prefecture-level city on the eastern coast of Guangdong, China, with a total population of 5,502,031 as of the 20 ...
and Guangzhou. The Red Army consisting of mutinous former National Revolutionary Army (NRA) soldiers as well as armed peasants established control over several areas in southern China
Northern China () and Southern China () are two approximate regions that display certain differences in terms of their geography, demographics, economy, and culture.
Extent
The Qinling–Daba Mountains serve as the transition zone between ...
. KMT forces continued to attempt to suppress the rebellions. Then, in September, Wang Jingwei was forced out of Wuhan. September also saw an unsuccessful armed rural insurrection, known as the Autumn Harvest Uprising
The Autumn Harvest Uprising was an insurrection that took place in Hunan and Jiangxi provinces of China, on September 7, 1927, led by Mao Zedong, who established a short-lived Hunan Soviet.
After initial success, the uprising was brutally ...
, led by Mao Zedong. Borodin then returned to the Soviet Union in October via Mongolia. In November, Chiang Kai-shek went to Shanghai and invited Wang to join him. On 11 December, the CCP started the Guangzhou Uprising
The Guangzhou Uprising, Canton Uprising or Canton Riots of 1927 was a failed communist uprising in the city of Guangzhou (Canton) in southern China.
Background
The Chinese Communist Party (CCP)'s Guangdong Provincial Committee had been pre ...
, establishing a soviet there the next day, but lost the city by 13 December to a counter-attack under the orders of General Zhang Fakui
Zhang Fakui (2 September 1896 – 10 March 1980) was a Chinese Nationalist general who fought against northern warlords, the Imperial Japanese Army and Chinese Communist forces in his military career. He served as commander-in-chief of the ...
. On 16 December, Wang Jingwei fled to France. There were now three capitals in China: the internationally recognized republic capital in Beijing
Beijing, Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Peking, is the capital city of China. With more than 22 million residents, it is the world's List of national capitals by population, most populous national capital city as well as ...
, the CCP and left-wing
Left-wing politics describes the range of Ideology#Political ideologies, political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy either as a whole or of certain social ...
KMT at Wuhan and the right-wing KMT regime at Nanjing
Nanjing or Nanking is the capital of Jiangsu, a province in East China. The city, which is located in the southwestern corner of the province, has 11 districts, an administrative area of , and a population of 9,423,400.
Situated in the Yang ...
, which would remain the KMT capital for the next decade.
This marked the beginning of a ten-year armed struggle, known in mainland China as the "Ten-Year Civil War" (十年内战) which ended with the Xi'an Incident
The Xi'an Incident was a Chinese political crisis that lasted from 12 to 26 December 1936. Chiang Kai-shek, the leader of the Nationalist government of China, was arrested in Xi'an by soldiers of the Northeastern Army under the command of Ge ...
, when Chiang Kai-shek was forced to form the Second United Front
The Second United Front ( zh, t=第二次國共合作 , s=第二次国共合作 , first=t , l=Second Nationalist-Communist Cooperation, p=dì èr cì guógòng hézuò ) was the alliance between the ruling Kuomintang (KMT) and the Chinese Co ...
against invading forces from the Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From Japan–Kor ...
. In 1930, the Central Plains War
The Central Plains War () was a series of military campaigns in 1929 and 1930 that constituted a Chinese civil war between the Nationalist Kuomintang government in Nanjing led by Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek and several regional military command ...
broke out as an internal conflict of the KMT; launched by Feng Yuxiang
Feng Yuxiang (; ; 6 November 1882 – 1 September 1948), courtesy name Huanzhang (焕章), was a Chinese warlord and later general in the National Revolutionary Army. He served as Vice Premier of the Republic of China from 1928 to 1930.
A ...
, Yan Xishan
Yan Xishan (; 8 October 1883 – 22 July 1960; also romanized as Yen Hsi-shan) was a Chinese warlord who served in the government of the Republic of China from June 1949 to March 1950 as its last premier in mainland China and first premi ...
, and Wang Jingwei. The attention was turned to root out remaining pockets of CCP activity in a series of five encirclement campaigns
The encirclement campaigns of the Chinese Civil War were Republic of China (ROC) offensives against Chinese Communist Party (CCP) revolutionary base areas in China from the late-1920s to 1934 during the Chinese Civil War.
The climax were the fiv ...
. The first
First most commonly refers to:
* First, the ordinal form of the number 1
First or 1st may also refer to:
Acronyms
* Faint Images of the Radio Sky at Twenty-Centimeters, an astronomical survey carried out by the Very Large Array
* Far Infrared a ...
and second
The second (symbol: s) is a unit of time derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes, and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of U ...
campaigns failed, and the third
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* 1⁄60 of a ''second'', i.e., the third in a series of fractional parts in a sexagesimal number system
Places
* 3rd Street (di ...
was aborted due to the Mukden Incident. The fourth campaign (1932–1933) achieved some early successes, but Chiang's armies were badly mauled when they tried to penetrate into the heart of Mao's Soviet Chinese Republic. During these campaigns, KMT columns struck swiftly into CCP areas, but were easily engulfed by the vast countryside and were not able to consolidate their foothold.
Finally, in late 1934, Chiang launched a fifth campaign that involved the systematic encirclement of the Jiangxi Soviet
The Jiangxi Soviet, sometimes referred to as the Jiangxi-Fujian Soviet, was a soviet area that existed between 1931 and 1934, governed by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). It was the largest component of the Chinese Soviet Republic and hom ...
region with fortified blockhouse
A blockhouse is a small fortification, usually consisting of one or more rooms with loopholes, allowing its defenders to fire in various directions. It is usually an isolated fort in the form of a single building, serving as a defensive stro ...
s.Manwaring, Max G. Joes, Anthony James. (2000). ''Beyond Declaring Victory and Coming Home: The Challenges of Peace and Stability operations''. Greenwood. . p. 58. The blockhouse strategy was devised and implemented in part by newly hired Nazi
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During H ...
advisors. Unlike previous campaigns in which they penetrated deeply in a single strike, this time the KMT troops patiently built blockhouses, each separated by about , to surround the Communist areas and cut off their supplies and food sources.
In October 1934, the CCP took advantage of gaps in the ring of blockhouses (manned by the forces of a warlord ally of Chiang Kai-shek's, rather than regular KMT troops) and broke out of the encirclement. The warlord armies were reluctant to challenge Communist forces for fear of losing their own men and did not pursue the CCP with much fervor. In addition, the main KMT forces were preoccupied with annihilating Zhang Guotao
Zhang Guotao (November 26, 1897 – December 3, 1979) was a Chinese revolutionary who was a founding member of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and rival to Mao Zedong. During the 1920s he studied in the Soviet Union and became a key contact ...
's army, which was much larger than Mao's. The massive military retreat of Communist forces lasted a year and covered what Mao estimated as 12,500 km (25,000 Li); it became known as the Long March
The Long March ( zh, s=长征, p=Chángzhēng, l=Long Expedition) was a military retreat by the Chinese Red Army and Chinese Communist Party (CCP) from advancing Kuomintang forces during the Chinese Civil War, occurring between October 1934 and ...
.Zhang, Chunhou. Vaughan, C. Edwin. (2002). ''Mao Zedong as Poet and Revolutionary Leader: Social and Historical Perspectives''. Lexington books. . pp. 58, 65.
This military retreat was undertaken by the Chinese Communist Party, led by Mao Zedong, to evade the pursuit or attack of the Kuomintang army. It consisted of a series of marches, during which numerous Communist armies in the south escaped to the north and west. Over the course of the march from Jiangxi the First Front Army, led by an inexperienced military commission, was on the brink of annihilation by Chiang Kai-Shek's troops as their stronghold was in Jiangxi. The Communists, under the command of Mao Zedong and Zhou Enlai, "escaped in a circling retreat to the west and north, which reportedly traversed over 9,000 kilometers over 370 days." The route passed through some of the most difficult terrain of western China by traveling west, and then northwards towards Shaanxi. "In November 1935, shortly after settling in northern Shaanxi, Mao officially took over Zhou Enlai's leading position in the Red Army. Following a major reshuffling of official roles, Mao became the chairman of the Military Commission, with Zhou and Deng Xiaoping as vice-chairmen." This marked Mao's position as the pre-eminent leader of the CCP, with Zhou in second position to him.
The march ended when the CCP reached the interior of Shaanxi
Shaanxi is a Provinces of China, province in north Northwestern China. It borders the province-level divisions of Inner Mongolia to the north; Shanxi and Henan to the east; Hubei, Chongqing, and Sichuan to the south; and Gansu and Ningxia to t ...
. Zhang Guotao
Zhang Guotao (November 26, 1897 – December 3, 1979) was a Chinese revolutionary who was a founding member of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and rival to Mao Zedong. During the 1920s he studied in the Soviet Union and became a key contact ...
's army (Red 4th Front Army), which took a different route through northwest China, was largely destroyed by the forces of Chiang Kai-shek and his Chinese Muslim
Islam has been practiced in China since the 7th century CE.. There are an estimated 17–25 million Muslims in China, less than 2 percent of the total population. Though Hui Muslims are the most numerous group, the greatest concentration of Mu ...
allies, the Ma clique
The Ma clique or Ma family warlords is a collective name for a group of Hui (Muslim Chinese) warlords in Northwestern China who ruled the Chinese provinces of Qinghai, Gansu and Ningxia for 10 years from 1919 until 1928. Following the colla ...
. Along the way, the Communist army confiscated property and weapons from local warlords and landlords, while recruiting peasants and the poor, solidifying its appeal to the masses. Of the 90,000–100,000 people who began the Long March from the Soviet Chinese Republic, only around 7,000–8,000 made it to Shaanxi. The remnants of Zhang's forces eventually joined Mao in Shaanxi, but with his army destroyed, Zhang, even as a founding member of the CCP, was never able to challenge Mao's authority. Essentially, the great retreat made Mao the undisputed leader of the Chinese Communist Party.
The Kuomintang used Kham
Kham (; ) is one of the three traditional Tibet, Tibetan regions, the others being Domey also known as Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The official name of this Tibetan region/province is Dotoe (). The original residents of ...
pa troopswho were former banditsto battle the Communist Red Army as it advanced and to undermine local warlords who often refused to fight Communist forces to conserve their own strength. The KMT enlisted 300 "Khampa bandits" into its Consolatory Commission military in Sichuan, where they were part of the effort of the central government to penetrate and destabilize local Han warlords such as Liu Wenhui
Liu Wenhui (; 10 January 1895 – 24 June 1976) was a Chinese general and warlord of Sichuan province ( Sichuan clique). At the beginning of his career, he was aligned with the Kuomintang (KMT), commanding the Sichuan-Xikang Defence Force from 1 ...
. The government was seeking to exert full control over frontier areas against the warlords. Liu had refused to battle the Communists in order to conserve his army. The Consolatory Commission forces were used to battle the Red Army, but they were defeated when their religious leader was captured by the Communists.
Northern Expedition
The Northern Expedition was a military campaign launched by the National Revolutionary Army (NRA) of the Kuomintang (KMT) against the Beiyang government and other regional warlords in 1926. The purpose of the campaign was to reunify China prop ...
, the KMT had direct control over east and central China, while the rest of China proper as well as Manchuria was under the control of warlords loyal to the Nationalist government.
File:China Soviet Zones.png, Map showing the communist-controlled Soviet Zones of China during and after the encirclement campaigns
File:The Long March 1934 - 1935.PNG, Route(s) taken by Communist forces during the Long March
File:Long-march.jpg, A Communist leader addressing survivors of the Long March
File:Chiang1926.jpg, Generalissimo
''Generalissimo'' ( ), also generalissimus, is a military rank of the highest degree, superior to field marshal and other five-star ranks in the states where they are used.
Usage
The word (), an Italian term, is the absolute superlative ...
Chiang Kai-shek, Commander-in-Chief of the National Revolutionary Army
The National Revolutionary Army (NRA; zh, labels=no, t=國民革命軍) served as the military arm of the Kuomintang, Chinese Nationalist Party (Kuomintang, or KMT) from 1924 until 1947.
From 1928, it functioned as the regular army, de facto ...
, emerged from the Northern Expedition
The Northern Expedition was a military campaign launched by the National Revolutionary Army (NRA) of the Kuomintang (KMT) against the Beiyang government and other regional warlords in 1926. The purpose of the campaign was to reunify China prop ...
as the leader of the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
File:National Revolutionary Army troops.png, NRA soldiers marching
File:National Revolutionary Army artillery.png, NRA troops firing artillery at Communist forces
Negotiations and the Xi'an Incident
In the late 1935, Chiang Kai-shek started secret negotiations with the Soviet Union in the hopes of gaining material assistance if war broke out between China and Japan. As a precondition for an agreement, the Soviets wanted Chiang to negotiate a ceasefire with the CCP. Although reluctant to engage with a group he saw as a rebels, Chiang cautiously sought to establish contact with the CCP. The CCP Central Committee told them that the CCP was interested in a united anti-Japanese army under a government of national defense. Given the wide gap between the CCP and KMT's conditions, further negotiations did not take place during the first half of 1936. Meanwhile, the CCP opened up separate negotiations with the Nationalist forces besieging them in northwest China. They managed to sign secret ceasefire agreements withZhang Xueliang
Zhang Xueliang ( zh, t=張學良; June 3, 1901 – October 15, 2001), also commonly known by his nickname "the Young Marshal", was a Chinese general who in 1928 succeeded his father Zhang Zuolin as the commander of the Northeastern Army. He is bes ...
, leader of the Northeastern Army
The Northeastern Army, also known as the Fengtian Army (see #Terminology, terminology), was a Chinese army that existed from 1911 to 1937. General Zhang Zuolin developed it as an independent fighting force during the Warlord Era. He used the a ...
, and Yang Hucheng
Yang Hucheng () (26 November 1893 – 6 September 1949) was a Chinese general during the Warlord Era of Republican China and Kuomintang (KMT) general during the Chinese Civil War.
Warlord years
Yang Hucheng joined the Xinhai Revolution in ...
, leader of the Northwestern Army. These generals were frustrated that Chiang' was prioritizing Civil War over resistance to Japan. Yan Xishan, another neighboring warlord, also signed a secret agreement with the Communists, although he was not as closely aligned with them as Zhang or Yang. The members of this northwestern alliance were united by their desire to resist Japan, but they differed over the details of how this could best be accomplished. The Communists supported a plan to use Soviet support to take over Shaanxi
Shaanxi is a Provinces of China, province in north Northwestern China. It borders the province-level divisions of Inner Mongolia to the north; Shanxi and Henan to the east; Hubei, Chongqing, and Sichuan to the south; and Gansu and Ningxia to t ...
, Gansu
Gansu is a provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeastern part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan Plateau, Ti ...
, Ningxia
Ningxia, officially the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region in Northwestern China. Formerly a province, Ningxia was incorporated into Gansu in 1954 but was later separated from Gansu in 1958 and reconstituted as an autonomous ...
, Qinghai
Qinghai is an inland Provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. It is the largest provinces of China, province of China (excluding autonomous regions) by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xin ...
, and Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People' ...
and turn northwest China into a base under Zhang's command to resist Japan and oppose Chiang. Zhang, Yang, and Yan were still committed to convincing Chiang to lead the anti-Japanese resistance. As they continued to negotiate, they kept their alliance secret and even staged fake military battles to allay the suspicions of the Nanjing government.
Negotiations between Chiang and the CCP began in earnest in late 1936. Chiang continued to try to resolve the civil war militarily; he continued to consider a negotiated settlement with the CCP to be a last resort. He was encouraged by the results of the Ningxia campaign in mid-to-late October. In that campaign, the Second and Fourth Corps of the Red Army marched north to pick up supplies dropped in Mongolia by the Soviet Union, but found themselves trapped on the wrong side of the Yellow River. They were cut to pieces by the Hui cavalry allied with the Nationalists. Chiang began making preparations for a sixth encirclement campaign, and instructed Zhang and Yang to participate. In early November, Chen Lifu presented Pan Hannian with a set of extremely harsh conditions for a deal. Pan balked, calling them "conditions for surrender". In late November, Chiang ordered the Northeastern Army and forces from the central Nationalist Army, Hu Zongnan
Hu Zongnan (; 16 May 1896 – 14 February 1962), courtesy name Shoushan (壽山), was a Chinese general in the National Revolutionary Army and then the Republic of China Army. Together with Chen Cheng and Tang Enbo, Hu, a native of Zhe ...
's Right Route Army, to attack towards the Communist capital at Bao'an. At the resulting Battle of Shanchengbao, the Northeastern Army withheld most of its forces from the attack. This allowed the Red Army to ambush and nearly wipe out Hu's 78th regiment. This reversed the diplomatic situation: Chen Lifu moderated his conditions, but the CCP recalled Pan Hannian from Nanjing on December 10.
In late 1936, Zhang Xueliang decided that his repeated attempts to persuade Chiang to create a united front with the Communists were not going to be enough. To Zhang, Chiang appeared dead-set on continuing the Civil War even as the threat of Japanese invasion loomed ever larger. Following Yang Hucheng's advice, he decided to resort to drastic measures. On 12 December 1936, the disgruntled Zhang and Yang conspired to kidnap Chiang and force him into a truce with the CCP. The incident became known as the Xi'an Incident.Ye, Zhaoyan Ye, Berry, Michael. (2003). ''Nanjing 1937: A Love Story''. Columbia University Press. . Both parties suspended fighting to form a Second United Front to focus their energies and fight the Japanese.
Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945)
In 1937, Japan launched its full-scale invasion of China and its well-equipped troops overran KMT defenders in northern and coastal China. The alliance of CCP and KMT was in name only.Buss, Claude Albert. (1972). Stanford Alumni Association. ''The People's Republic of China and Richard Nixon. United States''. Unlike the KMT forces, CCP troops shunnedconventional warfare
Conventional warfare is a form of warfare conducted by using conventional weapons and battlefield tactics between two or more sovereign state, states in open confrontation. The forces on each side are well-defined and fight by using weapons that ...
and instead waged guerrilla warfare
Guerrilla warfare is a form of unconventional warfare in which small groups of irregular military, such as rebels, partisans, paramilitary personnel or armed civilians, which may include recruited children, use ambushes, sabotage, terrori ...
against the Japanese. The level of actual cooperation and coordination between the CCP and KMT during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
was minimal. In the midst of the Second United Front, the CCP and the KMT were still vying for territorial advantage in " Free China" (i.e., areas not occupied by the Japanese or ruled by Japanese puppet governments such as Manchukuo and the Reorganized National Government of China
The Reorganized National Government of the Republic of China, commonly described as the Wang Jingwei regime, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in eastern China. It existed coterminous with the Nationalist government of the Republic of ...
).
The situation came to a head in late 1940 and early 1941 when clashes between Communist and KMT forces intensified. Chiang demanded in December 1940 that the CCP's New Fourth Army
The New Fourth Army (N4A) () was a military unit nominally under the banner of the National Revolutionary Army (NRA) of the Republic of China, established in 1937 as part of the Second United Front against Japan.
However, in practice, the New ...
evacuate Anhui
Anhui is an inland Provinces of China, province located in East China. Its provincial capital and largest city is Hefei. The province is located across the basins of the Yangtze and Huai rivers, bordering Jiangsu and Zhejiang to the east, Jiang ...
and Jiangsu
Jiangsu is a coastal Provinces of the People's Republic of China, province in East China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with its capital in Nanjing. Jiangsu is the List of Chinese administra ...
Provinces, due to its provocation and harassment of KMT forces in this area. Under intense pressure, the New Fourth Army commanders complied. The following year they were ambushed by KMT forces during their evacuation, which led to several thousand deaths.Schoppa, R. Keith. (2000). ''The Columbia Guide to Modern Chinese History''. Columbia University Press. . It also ended the Second United Front, formed earlier to fight the Japanese.
As clashes between the CCP and KMT intensified, countries such as the United States and the Soviet Union attempted to prevent a disastrous civil war. After the New Fourth Army incident, US President Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
sent special envoy
Diplomatic rank is a system of professional and social rank used in the world of diplomacy and international relations. A diplomat's rank determines many ceremonial details, such as the order of precedence at official processions, table seating ...
Lauchlin Currie
Lauchlin Bernard Currie (8 October 1902 – 23 December 1993) was a Canadian economist best known for being President Franklin Roosevelt's chief economic advisor during World War II.
After Roosevelt's death, he led the first World Bank survey ...
to talk with Chiang Kai-shek and KMT party leaders to express their concern regarding the hostility between the two parties, with Currie stating that the only ones to benefit from a civil war would be the Japanese. The Soviet Union, allied more closely with the CCP, sent an imperative telegram to Mao in 1941, warning that civil war would also make the situation easier for the Japanese military. Due to the international community's efforts, there was a temporary and superficial peace. Chiang criticized the CCP in 1943 with the propaganda piece ''China's Destiny'', which questioned the CCP's power after the war, while the CCP strongly opposed Chiang's leadership and referred to his regime as fascist in an attempt to generate a negative public image. Both leaders knew that a deadly battle had begun between themselves.
In general, developments in the Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War was fought between the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China and the Empire of Japan between 1937 and 1945, following a period of war localized to Manchuria that started in 1931. It is considered part ...
were to the advantage of the CCP, as its guerrilla war tactics had won them popular support within the Japanese-occupied areas. In occupied areas, the Communists established military and political bases from which it carried out guerilla warfare. The Communists built popular support in these areas, returning land to poor peasants, reducing peasant's rent, and arming the people. By Spring 1945, there were 19 Communist-governed areas in China in which 95 million people lived. In Fall 1945, the Communist armies had 1.27 million men and were supported by 2.68 million militia members. The KMT had to defend the country against the main Japanese campaigns, since it was the legal Chinese government, a factor which proved costly to Chiang Kai-shek and his troops. Japan launched its last major offensive against the KMT, Operation Ichi-Go
Operation Ichi-Go () was a campaign of a series of major battles between the Imperial Japanese Army forces and the National Revolutionary Army of the Republic of China, fought from April to December 1944. It consisted of three separate battles in ...
, in 1944, which resulted in the severe weakening of Chiang's forces. The CCP also suffered fewer losses through its guerrilla tactics.
Immediate post-war clashes (1945–1946)
Under the terms of the Japaneseunconditional surrender
An unconditional surrender is a surrender in which no guarantees, reassurances, or promises (i.e., conditions) are given to the surrendering party. It is often demanded with the threat of complete destruction, extermination or annihilation.
Anno ...
dictated by the Allies, Japanese troops were to surrender to KMT troops but not to the CCP, which was present in some of the occupied areas as well.Zarrow, Peter Gue. (2005). ''China in War and Revolution, 1895–1949''. Routledge. . p. 338. In Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical region in northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day northeast China and parts of the modern-day Russian Far East south of the Uda (Khabarovsk Krai), Uda River and the Tukuringra-Dzhagdy Ranges. The exact ...
, however, where the KMT had no forces, the Japanese surrendered to the Soviet Union. Chiang Kai-shek reminded Japanese troops to remain at their posts to receive the KMT, but Communist forces soon began taking surrenders from the Japanese and fighting those who resisted. General Wedemeyer of the United States Army became alarmed at these developments and wanted seven American divisions to be sent to China, but General Marshall replied that it should not be given priority over Japan and Korea.
The first post-war peace negotiation, attended by both Chiang Kai-shek and Mao Zedong, was in Chongqing
ChongqingPostal Romanization, Previously romanized as Chungking ();. is a direct-administered municipality in Southwestern China. Chongqing is one of the four direct-administered municipalities under the State Council of the People's Republi ...
from 28 August to 10 October 1945. Chiang entered the meeting at an advantage because he had recently signed a friendly treaty with the Soviet Union while the Communists were still forcing the Japanese to surrender in some places. Mao was accompanied by American ambassador Patrick J. Hurley
Patrick Jay Hurley (January 8, 1883July 30, 1963) was an American attorney, Republican Party politician, military officer, and diplomat. He was the 51st United States Secretary of War from 1929 to 1933 in the cabinet of Herbert Hoover and a ke ...
, who was devoted to Chiang but also wanted to ensure Mao's safety in light of the past history between the two Chinese leaders. It concluded with the signing of the Double Tenth Agreement
The Double Tenth Agreement, formally known as the Summary of Conversations Between the Government and Representatives of the Communist Party of China, was an agreement between the Kuomintang (KMT) and the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) that was ...
.Xu, Guangqiu. (2001). ''War Wings: The United States and Chinese Military Aviation, 1929–1949''. Greenwood. . p. 201. Both sides stressed the importance of a peaceful reconstruction, but the conference did not produce any concrete results. Battles between the two sides continued even as peace negotiations were in progress, until the agreement was reached in January 1946. However, large campaigns and full-scale confrontations between the CCP and Chiang's troops were temporarily avoided. On 26 November 1945, Hurley resigned, viewing Chiang as having gone against his agreement with the Communists. In December 1945, Hurley's former position was filled by Marshall.
 In the last month of World War II in East Asia, Soviet forces launched the huge
In the last month of World War II in East Asia, Soviet forces launched the huge Manchurian Strategic Offensive Operation
The Soviet invasion of Manchuria, formally known as the Manchurian Strategic Offensive Operation or simply the Manchurian Operation () and sometimes Operation August Storm, began on 9 August 1945 with the Soviet invasion of the Empire of Japan's ...
against the Japanese Kwantung Army
The Kwantung Army (Japanese language, Japanese: 関東軍, ''Kantō-gun'') was a Armies of the Imperial Japanese Army, general army of the Imperial Japanese Army from 1919 to 1945.
The Kwantung Army was formed in 1906 as a security force for th ...
in Manchuria and along the Chinese-Mongolian border. This operation destroyed the Kwantung Army in just three weeks and left the USSR occupying all of Manchuria by the end of the war in a total power vacuum of local Chinese forces. Consequently, the 700,000 Japanese troops stationed in the region surrendered. Later in the year Chiang Kai-shek realized that he lacked the resources to prevent a CCP takeover of Manchuria following the scheduled Soviet departure.Lilley, James. ''China hands: nine decades of adventure, espionage, and diplomacy in Asia''. PublicAffairs, New York, 2004 He therefore made a deal with the Soviets to delay their withdrawal until he had moved enough of his best-trained men and modern materiel
Materiel or matériel (; ) is supplies, equipment, and weapons in military supply-chain management, and typically supplies and equipment in a commerce, commercial supply chain management, supply chain context.
Military
In a military context, ...
into the region. However, the Soviets refused permission for the Nationalist troops to traverse its territory and spent the extra time systematically dismantling the extensive Manchurian industrial base (worth up to $2 billion) and shipping it back to their war-ravaged country. KMT troops were then airlifted by the US to occupy key cities in North China, while the countryside was already dominated by the CCP. On 15 November 1945, the KMT began a campaign to prevent the CCP from strengthening its already strong base. At the same time, however, the return of the KMT also brought widespread graft and corruption, with an OSS
OSS or Oss may refer to:
Places
* Oss, a city and municipality in the Netherlands
* Osh Airport, IATA code OSS
People with the name
* Oss (surname), a surname
Arts and entertainment
* ''O.S.S.'' (film), a 1946 World War II spy film about ...
officer remarking that the only winners were the Communists.
In the winter of 1945–1946, Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
commanded Marshal Rodion Malinovsky
Rodion Yakovlevich Malinovsky (; ; – 31 March 1967) was a Soviet military commander and Marshal of the Soviet Union. He served as Minister of Defence of the Soviet Union from 1957 to 1967, during which he oversaw the strengthening of the Sov ...
to give Mao Zedong most Imperial Japanese Army
The Imperial Japanese Army (IJA; , ''Dai-Nippon Teikoku Rikugun'', "Army of the Greater Japanese Empire") was the principal ground force of the Empire of Japan from 1871 to 1945. It played a central role in Japan’s rapid modernization during th ...
weapons that were captured.
Chiang Kai-shek's forces pushed as far as Jinzhou
Jinzhou (, zh, s= , t=錦州 , p=Jǐnzhōu), formerly Chinchow, is a coastal prefecture-level city in central-west Liaoning province, China. It is a geographically strategic city located in the Liaoxi Corridor, which connects most of the la ...
by 26 November 1945, meeting with little resistance. This was followed by a Communist offensive on the Shandong Peninsula
The Shandong Peninsula or Jiaodong (tsiaotung) Peninsula is a peninsula in Shandong in eastern China, between the Bohai Sea to the north and the Yellow Sea to the south. The latter name refers to the east and Jiaozhou.
Geography
The waters ...
that was largely successful, as all of the peninsula, except what was controlled by the US, fell to the Communists. The truce fell apart in June 1946 when full-scale war between CCP and KMT forces broke out on 26 June 1946. China then entered a state of civil war that lasted more than three years.
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
invaded Manchuria in August 1945.
File:Chinese Communist troops marched north(1945) 03.jpg, Chinese Communist soldiers march north to occupy rural Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical region in northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day northeast China and parts of the modern-day Russian Far East south of the Uda (Khabarovsk Krai), Uda River and the Tukuringra-Dzhagdy Ranges. The exact ...
, 1945.
Resumed fighting (1946–1949)
Background and disposition of forces
By the end of the Second Sino-Japanese War, the power of the Chinese Communist Party grew considerably. Their main force grew to 1.2 million troops, backed with additional militia of 2 million, totalling 3.2 million troops. Their "Liberated Zone" in 1945 contained 19 base areas, including one-quarter of the country's territory and one-third of its population; this included many important towns and cities. Moreover, the Soviet Union turned over all of its captured Japanese weapons and a substantial amount of their own supplies to the Communists, who received Northeastern China from the Soviets as well. In March 1946, despite repeated requests from Chiang, theSoviet Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of Peop ...
under the command of Marshal Rodion Malinovsky continued to delay pulling out of Manchuria, while Malinovsky secretly told the CCP forces to move in behind them, which led to full-scale war for the control of the Northeast. These favorable conditions also facilitated many changes inside the Communist leadership: the more radical hard-line faction who wanted a complete military take-over of China finally gained the upper hand and defeated the careful opportunists. Before giving control to Communist leaders, on 27 March, Soviet diplomats requested a joint venture of industrial development with the Nationalist Party in Manchuria.
Although General Marshall stated that he knew of no evidence that the CCP was being supplied by the Soviet Union, the CCP was able to utilize a large number of weapons abandoned by the Japanese, including some tanks. When large numbers of well-trained KMT troops began to defect to the Communist forces, the CCP was finally able to achieve material superiority. The CCP's most effective political reform was its land reform policy. This drew the massive number of landless and starving peasants in the countryside into the Communist cause. This strategy enabled the CCP to access an extensive supply of manpower for both combat and logistical purposes; despite suffering heavy casualties throughout many of the war's campaigns, manpower continued to grow. For example, during the Huaihai Campaign alone the CCP was able to mobilize 5,430,000 peasants to fight against the KMT forces.
 After the war with the Japanese ended, Chiang Kai-shek quickly moved KMT troops to newly liberated areas to prevent Communist forces from receiving the Japanese surrender. The US airlifted many KMT troops from central China to the
After the war with the Japanese ended, Chiang Kai-shek quickly moved KMT troops to newly liberated areas to prevent Communist forces from receiving the Japanese surrender. The US airlifted many KMT troops from central China to the Northeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A '' compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—eac ...
(Manchuria). President Harry S. Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. As the 34th vice president in 1945, he assumed the presidency upon the death of Franklin D. Roosevelt that year. Subsequen ...
was very clear about what he described as "using the Japanese to hold off the Communists". In his memoirs he writes:
Using the pretext of "receiving the Japanese surrender", business interests within the KMT government occupied most of the banks, factories and commercial properties, which had previously been seized by the Imperial Japanese Army. They also conscripted troops at an accelerated pace from the civilian population and hoarded supplies, preparing for a resumption of war with the Communists. These hasty and harsh preparations caused great hardship for the residents of cities such as Shanghai, where the unemployment rate rose dramatically to 37.5%.
Hyperinflation
In economics, hyperinflation is a very high and typically accelerating inflation. It quickly erodes the real versus nominal value (economics), real value of the local currency, as the prices of all goods increase. This causes people to minimiz ...
meant those employed in the Kuomintang forces lost the purchasing power of their pay. This resulted in corruption and the embezzlement of supplies which disappeared into the barter economy. Ordinary Kuomintang soldiers were often malnourished and desertion was common.
The US strongly supported the Kuomintang forces. About 50,000 US soldiers were sent to guard strategic sites in Hebei and Shandong in Operation Beleaguer
Operation Beleaguer was the codename for the United States Marine Corps' occupation of northeastern China's Hebei and Shandong provinces from 1945 until 1949. The Marines were tasked with overseeing the repatriation of more than 600,000 Japanes ...
. The US equipped and trained KMT troops, and transported Japanese and Koreans back to help KMT forces to occupy liberated zones as well as to contain Communist-controlled areas. According to William Blum, American aid included substantial amounts of mostly surplus military supplies, and loans were made to the KMT. Within less than two years after the Sino-Japanese War, the KMT had received $4.43 billion from the USmost of which was military aid. Highlighting the aid provided by the US to the KMT, the Communists' position was that the US was stirring domestic warfare and characterized the civil war as both a national revolution against the KMT and a revolution against US colonization and aggression.
Outbreak of war
mainland China
"Mainland China", also referred to as "the Chinese mainland", is a Geopolitics, geopolitical term defined as the territory under direct administration of the People's Republic of China (PRC) in the aftermath of the Chinese Civil War. In addit ...
and Communist historiography as the "War of Liberation" (). On 20 July 1946, Chiang Kai-shek launched a large-scale assault on Communist territory in North China
North China () is a list of regions of China, geographical region of the People's Republic of China, consisting of five province-level divisions of China, provincial-level administrative divisions, namely the direct-administered municipalities ...
with 113 brigades (a total of 1.6 million troops).
Knowing their disadvantages in manpower and equipment, the CCP executed a "passive defense" strategy. It avoided the strong points of the KMT army and was prepared to abandon territory in order to preserve its forces. In most cases the surrounding countryside and small towns had come under Communist influence long before the cities. The CCP also attempted to wear out the KMT forces as much as possible. This tactic seemed to be successful; after a year, the power balance became more favorable to the CCP. They wiped out 1.12 million KMT troops, while their strength grew to about two million men.
In March 1947, the KMT achieved a symbolic victory by seizing Yan'an, the capital of the Yan'an Soviet
The Yan'an Soviet was a soviet governed by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) during the 1930s and 1940s. In October 1936 it became the final destination of the Long March, and served as the CCP's main base until after the Second Sino-Japanese War ...
. The Communists counterattacked soon afterwards. With KMT efforts for an all-out offensive failing, the Nationalists changed strategy from broad assaults to concentrating on key targets, including Communist-controlled areas in Shandong and Shaanxi. This approach also failed.
From June to September 1947, the Communists launched offensives and Nationalist-controlled areas became the primary battlefields. On 30 June 1947, CCP troops crossed the Yellow River and moved to the Dabie Mountains
The Dabie Mountains () are a major mountain range located in central China. Running northwest-to-southeast, they form the main watershed between the Huai River, Huai and Yangtze rivers. The range also marks the boundary between Hubei Province (n ...
area, restored and developed the Central Plain. At the same time, Communist forces also began to counterattack in Northeastern China, North China and East China.
The period of August 1948 through October 1949 included the three most significant Communist military campaigns of the civil war: the Liaoshen Campaign (northeast China), Huaihai Campaign (east China), and Pingjin Campaign (Beijing-Tianjin).
The Liaoshen campaign was launched on 12 September 1948 and led by Lin Biao
Lin Biao ( zh, 林彪; 5 December 1907 – 13 September 1971) was a Chinese politician and Marshal of the People's Republic of China who was pivotal in the Chinese Communist Party, Communist Chinese Communist Revolution, victory during the Chines ...
. The main focus of the campaign was Jinzhou. On 14 October, the Communists launched an all-out assault and captured the city in 24 hours. Most of the 90,000 Nationalists casualties in this battle were incorporated into the Communist ranks. The siege of Changchun ended on 19 October when the Nationalist garrison surrendered. On 1 November, the Communists captured Shenyang
Shenyang,; ; Mandarin pronunciation: ; formerly known as Fengtian formerly known by its Manchu language, Manchu name Mukden, is a sub-provincial city in China and the list of capitals in China#Province capitals, provincial capital of Liaonin ...
. By late 1948, the CCP had taken control of the Northeast through the decisive Liaoshen Campaign.Westad, Odd Arne. (2003). ''Decisive Encounters: The Chinese Civil War, 1946–1950''. Stanford University Press. . pp. 192–193.
The capture of large KMT units provided the CCP with the tanks, heavy artillery and other combined-arms assets needed to execute offensive operations south of the Great Wall. By April 1948, the city of Luoyang fell, cutting the KMT army off from Xi'an.Elleman, Bruce A. Modern Chinese Warfare, 1795–1989. Routledge. . Following a fierce battle, the CCP captured Jinan
Jinan is the capital of the province of Shandong in East China. With a population of 9.2 million, it is one of the largest cities in Shandong in terms of population. The area of present-day Jinan has played an important role in the history of ...
and Shandong province on 24 September 1948. During this period, Battle of Weixian took place, which was an important battle for the CCP to liberate Shandong. Through the Weixian Campaign, the CCP controlled the Jiaoji Railway and cut off the connection between Jinan and Qingdao.
The Huaihai Campaign of late 1948 and early 1949 secured east-central China for the CCP. It was the largest military operation of the civil war. A large number of KMT troops deserted and changed sides in these conflicts. The outcome of these encounters were decisive for the military outcome of the civil war.
The Pingjin campaign lasted 64 days, from 21 November 1948 to 31 January 1949.Finkelstein, David Michael. Ryan, Mark A. McDevitt, Michael. (2003). ''Chinese Warfighting: The PLA Experience Since 1949''. M. E. Sharpe. China. . p. 63. The PLA suffered heavy casualties while securing Zhangjiakou
Zhangjiakou (), also known as Kalgan and by several other names, is a prefecture-level city in northwestern Hebei province in Northern China, bordering Beijing to the southeast, Inner Mongolia to the north and west, and Shanxi to the southwest ...
, Tianjin along with its port and garrison at Dagu and Beiping
"Beijing" is from pinyin ''Běijīng,'' which is romanized from , the Chinese name for this city. The pinyin system of transliteration was approved by the Chinese government in 1958, but little used until 1979. It was gradually adopted by various ...
. The CCP brought 890,000 troops from the northeast to oppose some 600,000 KMT troops. There were 40,000 CCP casualties at Zhangjiakou alone. They in turn killed, wounded or captured some 520,000 KMT during the campaign. The KMT's defeat in the Pingjin campaign ended its ability to be an effective fighting force on the mainland.
veteran
A veteran () is a person who has significant experience (and is usually adept and esteemed) and expertise in an job, occupation or Craft, field.
A military veteran is a person who is no longer serving in the military, armed forces.
A topic o ...
KMT troops.
Stalin initially favored a coalition government
A coalition government, or coalition cabinet, is a government by political parties that enter into a power-sharing arrangement of the executive. Coalition governments usually occur when no single party has achieved an absolute majority after an ...
in postwar China, and tried to persuade Mao to stop the CCP from crossing the Yangtze and attacking the KMT positions south of the river. Mao rejected Stalin's position and on 21 April, began the Yangtze River Crossing Campaign. On 23 April, they captured the KMT's capital, Nanjing. The KMT government retreated to Canton (Guangzhou) until 15 October, Chongqing
ChongqingPostal Romanization, Previously romanized as Chungking ();. is a direct-administered municipality in Southwestern China. Chongqing is one of the four direct-administered municipalities under the State Council of the People's Republi ...
until 25 November, and then Chengdu before retreating to Taiwan on 7 December. By late 1949, the People's Liberation Army was pursuing remnants of KMT forces southwards in southern China, and only Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
was left. A Chinese Muslim Hui cavalry regiment, the 14th Tungan Cavalry, was sent by the Kuomintang to attack Mongol and Soviet positions along the border during the Pei-ta-shan Incident.
The Kuomintang made several last-ditch attempts to use Kham
Kham (; ) is one of the three traditional Tibet, Tibetan regions, the others being Domey also known as Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The official name of this Tibetan region/province is Dotoe (). The original residents of ...
pa troops against the Communists in southwest China. The Kuomintang formulated a plan in which three Khampa divisions would be assisted by the Panchen Lama
The Panchen Lama () is a tulku of the Gelug school of Tibetan Buddhism. The Panchen Lama is one of the most important figures in the Gelug tradition, with its spiritual authority second only to the Dalai Lama. Along with the council of high la ...
to oppose the Communists. Kuomintang intelligence reported that some Tibetan tusi chiefs and the Khampa Su Yonghe controlled 80,000 troops in Sichuan, Qinghai and Tibet. They hoped to use them against the Communist army.
Pushing south
On 1 October 1949, Mao Zedong officially proclaimed the People's Republic of China with its capital at Beiping, which was returned to the former name Beijing. Chiang Kai-shek and approximately two million Nationalist soldiers retreated from mainland China to theisland of Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The island of Taiwan, formerly known to Westerners as Formosa, has an area of and makes up 99% of the land under ROC control. It lies about across the Taiwan Strait f ...
in December after the PLA advanced into Sichuan province. Isolated Nationalist pockets of resistance remained in the area, but the majority of the resistance collapsed after the fall of Chengdu on 10 December 1949, with some resistance continuing in the far south.
 A PRC attempt to take the ROC-controlled island of
A PRC attempt to take the ROC-controlled island of Quemoy
Kinmen, alternatively known as Quemoy, is a group of islands governed as a county by the Republic of China (Taiwan), only east from the city of Xiamen in Fujian, located at the southeastern coast of the People's Republic of China, from which ...
was thwarted in the Battle of Kuningtou
The Battle of Kinmen ( zh, t=金門戰役), also known as the Battle of Kuningtou ( zh, t=古寧頭之役) or the Battle of Guningtou, was fought in October 1949 on the island of Kinmen (Quemoy), located in the Taiwan Strait, during the final ...
, halting the PLA advance towards Taiwan. In December 1949, Chiang proclaimed Taipei the temporary capital
A temporary capital or a provisional capital is a city or town chosen by a government as an interim base of operations due to some difficulty in retaining or establishing control of a different metropolitan area. The most common circumstances leadi ...
of the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
and continued to assert his government as the sole legitimate authority in China.
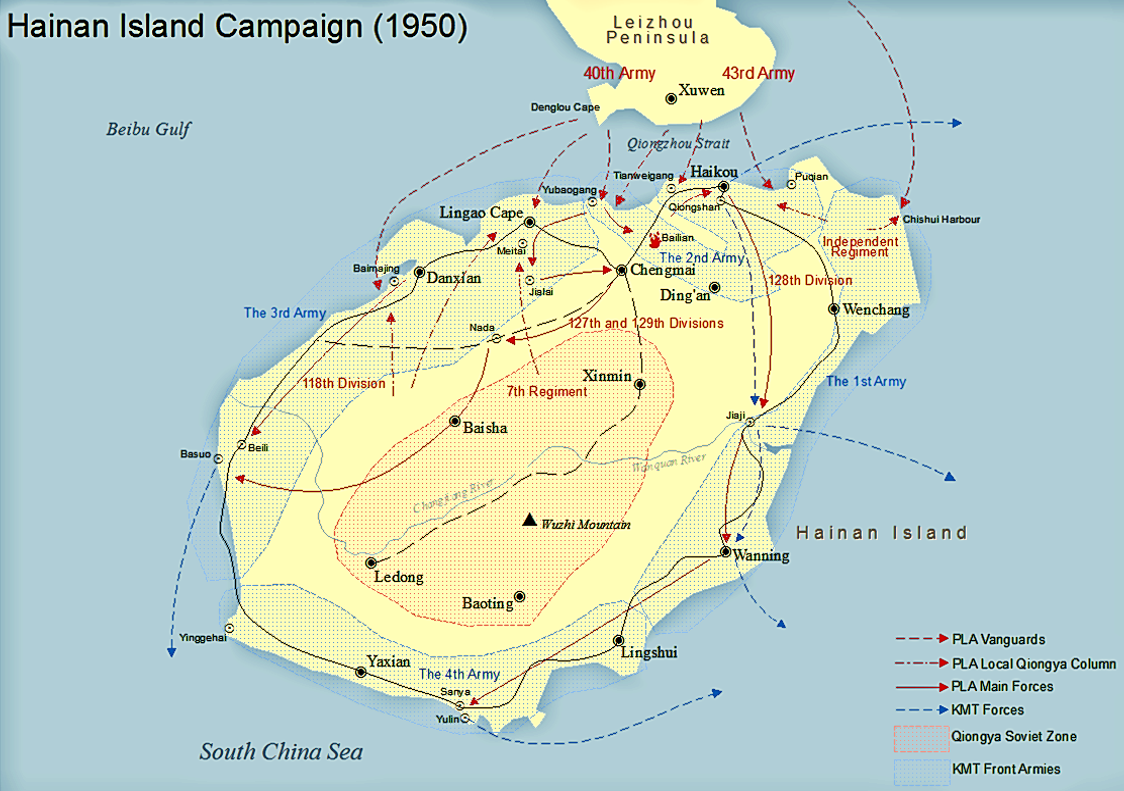
The Communists' other amphibious operations of 1950 were more successful: they led to the Communist conquest of Hainan Island in April 1950, the Wanshan Islands Wanshan may refer to:
*Wanshan Archipelago, in Guangdong, China
*Wanshan District
Wanshan District () is a district of the city of Tongren, Guizhou province, China, bordering Hunan province to the southeast and east. Wanshan was known as Wanshan ...
off the Guangdong coast (May–August 1950), and Zhoushan Island
Zhoushan Island is the principal and namesake island in the Zhoushan Islands, formerly romanized as the ChusanIslands, an archipelago administered by Zhoushan Prefecture in Zhejiang Province in the People's Republic of China. It is the provinc ...
off Zhejiang (May 1950).
Aftermath
Most observers expected Chiang's government to eventually fall to the imminent invasion of Taiwan by the People's Liberation Army, and the US was initially reluctant in offering full support for Chiang in their final stand. US PresidentHarry S. Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. As the 34th vice president in 1945, he assumed the presidency upon the death of Franklin D. Roosevelt that year. Subsequen ...
announced on 5 January 1950 that the United States would not engage in any dispute involving the Taiwan Strait, and that he would not intervene in the event of an attack by the PRC. Truman, seeking to exploit the possibility of a Titoist-style Sino-Soviet split
The Sino-Soviet split was the gradual worsening of relations between the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) during the Cold War. This was primarily caused by divergences that arose from their ...
, announced in his United States Policy toward Formosa that the US would obey the Cairo Declaration's designation of Taiwan as Chinese territory and would not assist the Nationalists. However, the Communist leadership was not aware of this change of policy, instead becoming increasingly hostile to the US. The situation quickly changed after the sudden onset of the Korean War
The Korean War (25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953) was an armed conflict on the Korean Peninsula fought between North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea; DPRK) and South Korea (Republic of Korea; ROK) and their allies. North Korea was s ...
in June 1950. This led to changing political climate in the US, and President Truman ordered the United States Seventh Fleet
The Seventh Fleet is a numbered fleet of the United States Navy. It is headquartered at U.S. Fleet Activities Yokosuka, in Yokosuka, Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan. It is part of the United States Pacific Fleet. At present, it is the largest of the ...
to sail to the Taiwan Strait
The Taiwan Strait is a strait separating the island of Taiwan and the Asian continent. The strait is part of the South China Sea and connects to the East China Sea to the north. The narrowest part is wide.
Names
Former names of the Tai ...
as part of the containment
Containment was a Geopolitics, geopolitical strategic foreign policy pursued by the United States during the Cold War to prevent the spread of communism after the end of World War II. The name was loosely related to the term ''Cordon sanitaire ...
policy against potential Communist advance.
Fujian
Fujian is a provinces of China, province in East China, southeastern China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its capital is Fuzhou and its largest prefe ...
to the mouth of the Liao River in Liaoning
)
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption = Clockwise: Mukden Palace in Shenyang, Xinghai Square in Dalian, Dalian coast, Yalu River at Dandong
, image_map = Liaoning in China (+all claims hatched).svg
, ...
.Tsang, Steve Yui-Sang Tsang. ''The Cold War's Odd Couple: The Unintended Partnership Between the Republic of China and the UK'', 1950–1958. (2006). I.B. Tauris. . pp. 155, 115–120, 139–145 Since mainland China's railroad network was underdeveloped, north–south trade depended heavily on sea lanes. ROC naval activity also caused severe hardship for mainland China fishermen.
During the retreat of the Republic of China to Taiwan, KMT troops, who could not retreat to Taiwan, were left behind to fight a guerrilla war
Guerrilla warfare is a form of unconventional warfare in which small groups of irregular military, such as rebels, partisans, paramilitary personnel or armed civilians, which may include recruited children, use ambushes, sabotage, terrorism ...
against the Communists. These KMT remnants were eliminated in what the PRC called the Campaign to Suppress Counterrevolutionaries
The Campaign to Suppress Counterrevolutionaries ( zh, c=鎮壓反革命運動, p=zhènyā fǎngémìng yùndòng, abbreviated as zh, c=鎮反, p=zhènfǎn, labels=no) was the first campaign of political repression launched by the People's Repu ...
and the Campaigns to Suppress Bandits. According to official statistics from the CCP in 1954, during the Campaign to Suppress Counterrevolutionaries, at least 2.6 million people were arrested, some 1.29 million people were imprisoned
Imprisonment or incarceration is the restraint of a person's liberty for any cause whatsoever, whether by authority of the government, or by a person acting without such authority. In the latter case it is considered " false imprisonment". Impri ...
, and 712,000 people were executed. Most of those killed were former Kuomintang officials, businessmen, former employees of Western companies and intellectuals whose loyalty was suspect.
Winning China proper in 1950, also after annexation of Tibet, the CCP controlled the entire mainland in late 1951 (excluding Kinmen
Kinmen, alternatively known as Quemoy, is a group of islands governed as a county by the Republic of China (Taiwan), only east from the city of Xiamen in Fujian, located at the southeastern coast of the People's Republic of China, from wh ...
and Matsu Islands
The Matsu Islands; Foochow Romanized: Mā-cū liĕk-dō̤ ( or ), officially Lienchiang County; Foochow Romanized: Lièng-gŏng-gâing (), are an archipelago of 36 islands and islets in the East China Sea governed by the Republic of China ...
). But a group of approximately 3,000 KMT Central soldiers retreated to Burma
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and ha ...
and continued launching guerrilla attacks into south China during the Kuomintang Islamic Insurgency in China (1950–1958) and Campaign at the China–Burma Border. Their leader, Li Mi, was paid a salary by the ROC government and given the nominal title of Governor of Yunnan
Yunnan; is an inland Provinces of China, province in Southwestern China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 47.2 million (as of 2020). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces ...
. Initially, the US-supported these remnants and the Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA; ) is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States tasked with advancing national security through collecting and analyzing intelligence from around the world and ...
provided them with military aid. After the Burmese government appealed to the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
in 1953, the US began pressuring the ROC to withdraw its loyalists. By the end of 1954 nearly 6,000 soldiers had left Burma and Li declared his army disbanded. However, thousands remained, and the ROC continued to supply and command them, even secretly supplying reinforcements at times to maintain a base close to China.
Following World War II, victory in the civil war and the establishment of the People's Republic of China in 1949, the Chinese communists supported Ho Chi Minh
(born ; 19 May 1890 – 2 September 1969), colloquially known as Uncle Ho () among other aliases and sobriquets, was a Vietnamese revolutionary and politician who served as the founder and first President of Vietnam, president of the ...
's Viet Minh
The Việt Minh (, ) is the common and abbreviated name of the League for Independence of Vietnam ( or , ; ), which was a Communist Party of Vietnam, communist-led national independence coalition formed at Pác Bó by Hồ Chí Minh on 19 May 1 ...
guerrillas against France. China, like the Eastern bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
, recognized the Hanoi government and began supplying military equipment in accordance with the agreement of April 1, 1950. By 1950, the Viet Minh had established full control over the Northern Free Zone and the common Sino-Vietnamese border, and the communists had consolidated their positions in Laos and Cambodia. This fact allowed the supply of materials and weapons to Vietnam, as well as the establishment of training camps and base areas. Chinese military aid played a key role in the Viet Minh's victory at the Battle of Dien Bien Phu
The Battle of Điện Biên Phủ was a climactic confrontation of the First Indochina War that took place between 13 March and 7 May 1954. It was fought between the forces of the French Union and Viet Minh.
The French began an operation to in ...
in 1954. The recognition of North Vietnam by the People's Republic of China and other Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
countries also forced the issue of creating an independent "State of Vietnam
The State of Vietnam (; chữ Hán: 國家越南; ) was a state in Southeast Asia that existed from 1949 until 1955, first as an associated state of the French Union and later as an independent state (from 20 July 1954 to 26 October 1955). The s ...
" in the south as a counterweight to the Democratic Republic of Vietnam in the north.
After the ROC complained to the United Nations against the Soviet Union for violating the Sino-Soviet Treaty of Friendship and Alliance
The Treaty of Friendship and Alliance (Traditional Chinese: 中 蘇 友好 同盟 條約; Russian: Договор о дружбе и союзе между СССР и Китайской Республикой) was a treaty signed by the Nati ...
to support the CCP, the UN General Assembly Resolution 505 was adopted on 1 February 1952, condemning the Soviet Union.
In the end, the Communist military forces suffered 1.3 million combat casualties in the 1945–1949 phase of the war: 260,000 killed, 190,000 missing, and 850,000 wounded, discounting irregulars. Nationalist casualties in the same phase were recorded after the war by the PRC 5,452,700 regulars and 2,258,800 irregulars.
After the formation of the PRC, the PRC government named the Western nations, led by the U.S., as the biggest threat to its national security. Basing this judgment on multiple factors, including the idea of a Chinese century of humiliation
The century of humiliation was a period in Chinese history beginning with the First Opium War (1839–1842), and ending in 1945 with China (then the Republic of China) emerging out of the Second World War as one of the Big Four and establishe ...
at the hands of Western powers beginning in the mid-19th century, U.S. support for the Nationalists during the Chinese Civil War, and the ideological struggles between revolutionaries and reactionaries, the PRC leadership believed that China would become a critical battleground in the U.S.'s crusade against Communism. As a countermeasure and to elevate China's standing among the worldwide Communist movements, the PRC leadership adopted a foreign policy that actively promoted Communist revolutions throughout territories on China's periphery.
Taiwan Strait tensions
Though viewed as a military liability by the US, the ROC viewed its remaining islands inFujian
Fujian is a provinces of China, province in East China, southeastern China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its capital is Fuzhou and its largest prefe ...
as vital for any future campaign to defeat the PRC and retake mainland China. On 3 September 1954, the First Taiwan Strait Crisis
The First Taiwan Strait Crisis (also known as the Formosa Crisis, the 1954–1955 Taiwan Strait Crisis, the Offshore Islands Crisis, the Quemoy-Matsu Crisis, and the 1955 Taiwan Strait Crisis) was a brief armed conflict between the People's Rep ...
started with the PRC shelling Kinmen
Kinmen, alternatively known as Quemoy, is a group of islands governed as a county by the Republic of China (Taiwan), only east from the city of Xiamen in Fujian, located at the southeastern coast of the People's Republic of China, from wh ...
. The PRC captured the Yijiangshan Islands on 19 January 1955, leading to the ROC abandoning the Dachen Islands
The Dachen Islands, Tachen Islands or Tachens form an island group off the coast of Taizhou, Zhejiang, China, in the East China Sea. They are administered by the Jiaojiang District of Taizhou.
Before the First Taiwan Strait Crisis in 1955, t ...
the following month. On 24 January 1955, the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature, legislative branch of the federal government of the United States. It is a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, including a Lower house, lower body, the United States House of Representatives, ...
passed the Formosa Resolution authorizing the President to defend the ROC's offshore islands. The First Taiwan Straits crisis ended in March 1955 when the PLA ceased its bombardment. The crisis ended during the Bandung conference
The first large-scale Asian–African or Afro–Asian Conference (), also known as the Bandung Conference, was a meeting of Asian and African states, most of which were newly independent, which took place on 18–24 April 1955 in Bandung, We ...
.
The Second Taiwan Strait Crisis
The Second Taiwan Strait Crisis, also known as the 1958 Taiwan Strait Crisis, was a conflict between the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the Taiwan, Republic of China (ROC). The PRC shelled the islands of Kinmen (Quemoy) and the Matsu Is ...
began on 23 August 1958 with air and naval engagements between PRC and ROC forces, leading to intense artillery bombardment of Kinmen by the PRC and Xiamen
Xiamen,), also known as Amoy ( ; from the Zhangzhou Hokkien pronunciation, zh, c=, s=, t=, p=, poj=Ē͘-mûi, historically romanized as Amoy, is a sub-provincial city in southeastern Fujian, People's Republic of China, beside the Taiwan Stra ...
by the ROC, and ended on November of the same year. PLA patrol boats blockaded the islands from ROC supply ships. Though the US rejected Chiang Kai-shek's proposal to bomb mainland China artillery batteries, it quickly moved to supply fighter jets and anti-aircraft missiles to the ROC. It also provided amphibious assault
Amphibious warfare is a type of offensive military operation that today uses naval ships to project ground and air power onto a hostile or potentially hostile shore at a designated landing beach. Through history the operations were conducte ...
ships to land supplies, as a sunken ROC naval vessel was blocking the harbor. On 7 September, the US escorted a convoy of ROC supply ships and the PRC refrained from firing.
The third crisis occurred in 1995–96. The PRC responded to Taiwanese President Lee Teng-hui's visit to the United States, and the U.S. recognition of Lee as a representative of Taiwan, with military exercises. The exercises were also meant to deter Taiwanese voters from supporting Lee in the 1996 election; Lee won the election. Two U.S. aircraft carriers were deployed during the crisis; they were not attacked and deescalation followed.
US Speaker of the House Nancy Pelosi
Nancy Patricia Pelosi ( ; ; born March 26, 1940) is an American politician who was the List of Speakers of the United States House of Representatives, 52nd speaker of the United States House of Representatives, serving from 2007 to 2011 an ...
's visit to Taiwan in August 2022 triggered PRC military exercises across the Taiwan Strait. She originally intended to travel to Taiwan in April 2022, but was delayed due to COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
. She rescheduled the trip to August as part of a wider Asian trip. The White House was reported to have been initially divided over the appropriateness of the trip but later affirmed Pelosi's right to visit Taiwan. As a result, the PLA announced four days of unprecedented military live-fire drills, in six zones that encircle the island on the busiest international waterways and aviation routes. In response to the announcement, ROC officials complained that the PRC's live-fire drills were an invasion of Taiwan's territorial space and a direct challenge to free air and sea navigation.
Political fallout
 On 25 October 1971, the
On 25 October 1971, the United Nations General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA or GA; , AGNU or AG) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as its main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ. Currently in its Seventy-ninth session of th ...
admitted the PRC and expelled the ROC, which had been a founding member of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
and was one of the five permanent members of the Security Council. Representatives of Chiang Kai-shek refused to recognise their accreditations as representatives of China and left the assembly. Recognition for the People's Republic of China soon followed from most other member nations, including the United States.
By 1984, PRC and ROC began to de-escalate their hostilities through diplomatic relations with each other, and cross-straits trade and investment has been growing ever since. The state of war was officially declared over by the ROC in 1991. Despite the end of the hostilities, the two sides have never signed any agreement or treaty to officially end the war. According to Mao Zedong, there were three ways of "staving off imperialist intervention in the short term" during the continuation of the Chinese Revolution. The first was through a rapid completion of the military takeover of the country, and through showing determination and strength against "foreign attempts at challenging the new regime along its borders". The second was by "formalising a comprehensive military alliance with the Soviet Union", which would dedicate Soviet power to directly defending China against its enemies; this aspect became extensively significant given the backdrop of the start of the Cold War. And finally, the regime had to "root out its domestic opponents: the heads of secret societies, religious sects, independent unions, or tribal and ethnic organisations". By destroying the basis of domestic reaction, Mao believed a safer world for the Chinese revolution to spread in would come into existence.
Under the new ROC president Lee Teng-hui
Lee Teng-hui (; pinyin: ''Lǐ Dēnghuī''; 15 January 192330 July 2020) was a Taiwanese politician and agricultural scientist who served as the fourth president of the Republic of China, president of the Taiwan, Republic of China (Taiwan) unde ...
, the Temporary Provisions Effective During the Period of Communist Rebellion
The Temporary Provisions Effective During the Period of National Mobilization for Suppression of the Communist Rebellion provisions of the Constitution of the Republic of China were effective from 1948 to 1991 and amended four times by the Centr ...
was renounced in May 1991, thus ending the chances of the Kuomintang's quest to retake the mainland. In July 1999, Lee announced a "special diplomatic relationship". China was furious again, but the military drills were stopped by the 921 earthquakes. It was the last tense moment of this civil war.
With the election in 2000 of Democratic Progressive Party
The Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) is a centre to centre-left Taiwanese nationalist political party in Taiwan. As the dominant party in the Pan-Green Coalition, one of the two main political camps in Taiwan, the DPP is currently the ...
candidate Chen Shui-bian
Chen Shui-bian ( zh, t=陳水扁; born 12 October 1950) is a Taiwanese former politician and lawyer who served as the fifth president of the Republic of China (Taiwan) from 2000 to 2008. Chen was the first president from the Democratic Progres ...
, a party other than the KMT gained the presidency for the first time in Taiwan. The new president did not share the Chinese nationalist ideology of the KMT and CCP. This led to tension between the two sides, although trade and other ties such as the 2005 Pan-Blue visit continued to increase.
With the election of pro-mainland President Ma Ying-jeou
Ma Ying-jeou ( zh, t=馬英九; pinyin: ''Mǎ Yīngjiǔ''; ; born 13 July 1950) is a Taiwanese politician, lawyer, and legal scholar who served as the sixth president of the Republic of China from 2008 to 2016. A member of the Kuomintang (KMT ...
(KMT) in 2008, significant warming of relations resumed between Taipei and Beijing, with high-level exchanges between the semi-official diplomatic organizations of both states such as the Chen-Chiang summit series. Although the Taiwan Strait
The Taiwan Strait is a strait separating the island of Taiwan and the Asian continent. The strait is part of the South China Sea and connects to the East China Sea to the north. The narrowest part is wide.
Names
Former names of the Tai ...
remains a potential flash point, regular direct air links were established in 2009.
Analysis
The Communist victory over the Nationalists is regarded as one of the most impressive twentieth century insurgent victories. Historians and political scientists cite a number of factors, including the CCP's success at mobilizing mass support and the shortcomings of the Nationalist government.Poor governance by Nationalists
Almost all studies of the failure of the Nationalist government identifyhyperinflation
In economics, hyperinflation is a very high and typically accelerating inflation. It quickly erodes the real versus nominal value (economics), real value of the local currency, as the prices of all goods increase. This causes people to minimiz ...
as a major factor in the government's collapse. The Nationalist military and the government's civilian employees were most impacted by hyperinflation which in turn prompted widespread corruption and pilfering. Little funding reached enlisted soldiers, who were typically malnourished and poorly equipped. Desertion was common.
The historian Rana Mitter
Rana Shantashil Rajyeswar Mitter (born 11 August 1969) is a British historian and political scientist of Indian descent who specialises in the History of the People's Republic of China. He is ST Lee Chair in US-Asia Relations at the Harvard ...
writes that a lack of trust in the Nationalist government developed, as it was increasingly seen as "corrupt, vindictive, and with no overall vision of what China under its rule should look like". Chiang wrote in his diary in June 1948: "After the fall of Kaifeng our conditions worsened and became more serious. I now realized that the main reason our nation has collapsed, time after time throughout our history, was not because of superior power used by our external enemies, but because of disintegration and rot from within."
Historian Odd Arne Westad
Odd Arne Westad FBA (born 5 January 1960) is a Norwegian historian specializing in the Cold War and contemporary East Asian history. He is the Elihu Professor of History and Global Affairs at Yale University, where he teaches in the Yale History ...
says the Communists won the Civil War because they made fewer military mistakes than Chiang Kai-shek and also because in his search for a powerful centralized government, Chiang antagonized too many interest groups in China. Furthermore, his party was weakened in the war against the Japanese. Meanwhile, the Communists targeted different groups, such as peasants, and brought them to their side. After 1945, the economy in the ROC areas collapsed because of hyperinflation and the failure of price controls
Price controls are restrictions set in place and enforced by governments, on the prices that can be charged for goods and services in a market. The intent behind implementing such controls can stem from the desire to maintain affordability of go ...
by the ROC government and financial reforms; the Gold Yuan depreciated sharply in late 1948 and resulted in the ROC government losing the support of the cities' middle class
The middle class refers to a class of people in the middle of a social hierarchy, often defined by occupation, income, education, or social status. The term has historically been associated with modernity, capitalism and political debate. C ...
es.
United States Secretary of State Dean Acheson
Dean Gooderham Acheson ( ; April 11, 1893October 12, 1971) was an American politician and lawyer. As the 51st United States Secretary of State, U.S. Secretary of State, he set the foreign policy of the Harry S. Truman administration from 1949 to ...
described the Nationalists as "corrupt, reactionary, and inefficient". He believed that the Nationalists had displayed both political inadequacy as well as "the grossest incompetence ever experienced by any military command," and that the Communists "did not create this condition", but skillfully exploited the opportunity it provided.
Popular support for Communists and cohesion
In the meantime, the Communists continued their land reform programs, winning the support of the population in the countryside. This was a decisive factor in the Communists' success. Millions of peasants who obtained land through the movement joined the People's Liberation Army or assisted in its logistical networks. According to historian Brian DeMare, land redistribution was a critical factor because it linked the interests of peasants in the north and northeast to the Communists' success. Ultimately, the Communists obtained the greatest popular support of any insurgency in modern history. An important advantage of the Communists was the "extraordinary cohesion" within its top leadership. This cohesion not only secured it from defections during difficult times but also facilitated "communications and top level debates over tactics". The charismatic style of leadership of Mao Zedong created a "unity of purpose" and a "unity of command" which the KMT lacked. Apart from that, the CCP had mastered the manipulation of local politics to their benefit; this was also derived from theirpropaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded l ...
skills that had also been decentralised successfully by portraying their opponents as "enemies of all groups of Chinese" and itself as "defenders of the nation" and people (given the backdrop of the war with Japan).
International factors
After the Second Sino-Japanese War ended, the United States government provided economic and military support exclusively to the Nationalists. As the United States increased aid to the Nationalists in 1947 and 1948, the Communists incorporated United States involvement into its political discourse and framed the conflict not as one between two Chinese sides, but between the Communists and "US imperialists and their puppets". Mao contended that the United States had provided US$5.9 billion to the Nationalists from 1945 to 1949 "to help Chiang Kai-shek slaughter several million Chinese". Strong American support for the Nationalists was hedged with the failure of the Marshall Mission, and then stopped completely mainly because of KMT corruption (such as the notorious Yangtze Development Corporation controlled by H. H. Kung and T. V. Soong's family) and KMT's military setback in Northeast China. Historians such as Jay Taylor, Robert Cowley, and Anne W. Carroll argue that the Nationalists' failure was largely caused by external reasons outside of the KMT's control, most notably the refusal of the Truman administration to support Chiang with the withdrawal of aid, the US armed embargo, the failed pursuit of a détente between the Nationalists and the communists, and the USSR's consistent support of the CCP in the Chinese Civil War. The better-trained Communist army's support from the USSR helped counter the American aid that the Nationalists received.Chen Yun
Chen Yun (13 June 1905 – 10 April 1995) was a statesman of the Chinese Communist Party and the People's Republic of China. He was one of the most prominent leaders during the periods when China was governed by Mao Zedong and later by Deng Xia ...
said: "They did their best to help us, we were backed by the Soviet Union and North Korea."
Atrocities
During the war, both the Nationalists and Communists carried out mass atrocities, with millions of non-combatants deliberately killed by both sides.Nationalist atrocities
Over several years after the 1927Shanghai massacre
The Shanghai massacre of 12 April 1927, the April 12 Purge or the April 12 Incident as it is commonly known in China, was the violent suppression of Chinese Communist Party (CCP) organizations and leftist elements in Shanghai by forces support ...
, the Kuomintang killed between 300,000 and one million people, primarily peasants, in anti-communist campaigns as part of the White Terror. During the White Terror, the Nationalists specifically targeted women with short hair who had not been subjected to foot binding
Foot binding (), or footbinding, was the Chinese custom of breaking and tightly binding the feet of young girls to change their shape and size. Feet altered by foot binding were known as lotus feet and the shoes made for them were known as lotus ...
, on the presumption that such "non-traditional" women were radicals. Nationalist forces cut off their breasts, shaved their heads, and displayed their mutilated bodies to intimidate the populace.
Torture, rape, and collective punishment were common Nationalist practices during its counter-insurgency campaigns. The Nationalists uprooted and moved entire communities in an effort to more easily monitor Communist activities.
From 1946 to 1949, the Nationalists arrested, tortured, and killed political dissidents via the Sino-American Cooperative Organization.
Communist atrocities
During the December 1930 Futian incident, the communists executed 2,000 to 3,000 members of the Futian battalion after its leaders had mutinied against Mao Zedong. Between 1931 and 1934 in theJiangxi–Fujian Soviet
The Jiangxi Soviet, sometimes referred to as the Jiangxi-Fujian Soviet, was a soviet area that existed between 1931 and 1934, governed by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). It was the largest component of the Chinese Soviet Republic and hom ...
, the communist authorities engaged in a widespread campaign of violence against civilians to ensure compliance with its policies and to stop defection to the advancing KMT, including mass executions, land confiscation and forced labor. According to Li Weihan
Li Weihan (; 2 June 1896 – 11 August 1984) was a Chinese Communist Party politician. After pursuing his studies in France in 1919–20, he returned to China for the first 1st National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party, National Congress o ...
, a high-ranking communist in Jiangxi at the time, in response to mass flight of civilians to KMT held areas, the local authorities would "usually to send armed squads after those attempting to flee and kill them on the spot, producing numerous mass grave
A mass grave is a grave containing multiple human corpses, which may or may Unidentified decedent, not be identified prior to burial. The United Nations has defined a criminal mass grave as a burial site containing three or more victims of exec ...
s throughout the CSR hinese Soviet Republic in Jiangxithat would later be uncovered by the KMT and its allies." Zhang Wentian
Zhang Wentian; 30 August 1900 – 1 July 1976), also known as Luo Fu ( zh, c=洛甫, w=Lo Fu (30 August 1900 – 1 July 1976) was a Chinese politician who was a high-ranking leader of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP).
Born in Nanhui District, ...
, another high-ranking communist, reported that "the policy of annihilating landlords as an exploiting class had degenerated into a massacre".
During the Siege of Changchun, the People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the military of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and the People's Republic of China (PRC). It consists of four Military branch, services—People's Liberation Army Ground Force, Ground Force, People's ...
implemented a military blockade on the KMT-held city of Changchun and prevented civilians from leaving the city during the blockade; this blockade caused the starvation of tensKoga, Yukiko (2016). ''Inheritance of Loss: China, Japan, and the Political Economy of Redemption After Empire''. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. . to 150 thousand civilians. The PLA continued to use siege tactics throughout Northeast China.
At the outbreak of the Chinese Civil War in 1946, Mao Zedong began to push for a return to radical policies to mobilize China against the landlord class, but protected the rights of middle peasants and specified that rich peasants were not landlords. The 7 July Directive of 1946 set off eighteen months of fierce conflict in which all rich peasant and landlord property of all types was to be confiscated and redistributed to poor peasants. CCP work teams went quickly from village to village and divided the population into landlords, rich, middle, poor, and landless peasants. Because the work teams did not involve villagers in the process, however, rich and middle peasants quickly returned to power. The Outline Land Law of October 1947 increased the pressure. Those condemned as landlords were buried alive, dismembered, strangled and shot.
In response to the aforementioned land reform campaign, the Kuomintang helped establish the "Huanxiang Tuan" (), or Homecoming Legion, which was composed of landlords who sought the return of their redistributed land and property from peasants and CCP guerrillas, as well as forcibly conscripted peasants and communist POWs. The Homecoming legion conducted its guerrilla warfare campaign against CCP forces and purported collaborators up until the end of the civil war in 1949.
See also
*Outline of the Chinese Civil War
The following is a topical outline of English Wikipedia articles about the history of the Chinese Civil War (1927–1949)
The Chinese Civil War was fought between the Kuomintang-led government of the Republic of China and the forces of the Chi ...
* Timeline of the Chinese Civil War
* List of wars involving the People's Republic of China
* Campaign to suppress bandits in northeast China
* Campaign to Suppress Bandits in Wuping
* Campaign to suppress bandits in southwestern China
The campaign to suppress bandits in southwestern China was a counterinsurgency campaign waged by the forces of the Chinese Communist Party against the Chinese Nationalist guerrillas, mostly consisting of bandits and regular nationalist forces ...
* Campaign to Suppress Bandits in Eastern China
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Summary of Chinese Civil War 1946–1949
Topographic maps of China Series L500, U.S. Army Map Service, 1954–
Operational Art in the Chinese PLA's Huai Hai Campaign
{{Authority control 20th-century conflicts Aftermath of World War II Civil wars in China Cross-strait conflict Interwar period Military history of the Republic of China (1912–1949) Proxy wars Revolutions in China Revolution-based civil wars Wars involving the Republic of China Wars involving the People's Republic of China