Cheater plug on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
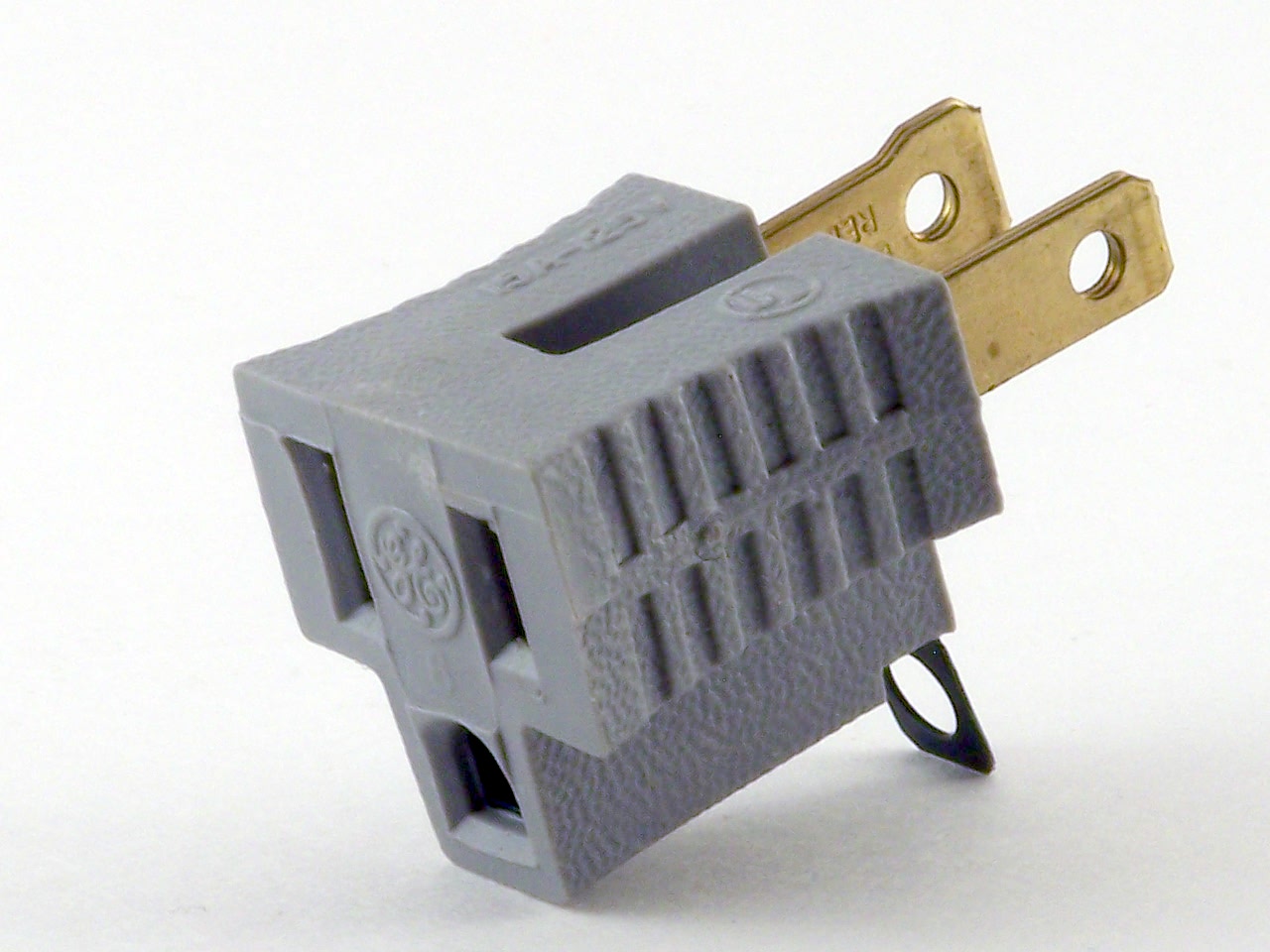 A cheater plug, AC ground lifter or three-prong/two-prong adapter is an adapter that allows a
A cheater plug, AC ground lifter or three-prong/two-prong adapter is an adapter that allows a
 A cheater plug, AC ground lifter or three-prong/two-prong adapter is an adapter that allows a
A cheater plug, AC ground lifter or three-prong/two-prong adapter is an adapter that allows a NEMA
The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) is the largest trade association of electrical equipment manufacturers in the United States. Founded in 1926, it advocates for the industry and publishes standards for electrical product ...
5-15P grounding-type plug (three prongs) to connect to a NEMA 1-15R non-grounding receptacle (two slots). They are needed to allow appliances with 3-wire power cords to plug into legacy ungrounded (two slot) receptacles found in older buildings. The use of such an adapter avoids the need to replace receptacles, but is potentially hazardous if the grounding tab is not connected to electrical ground. These adapters are illegal in some jurisdictions, in particular throughout Canada. A safer and more reliable alternative identified in the US and Canadian electrical codes is to replace the outlet with a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) breaker outlet.
Cheater plugs are also used to break ground loops in audio systems. This practice has been condemned as disregarding electrical safety. A safer and more reliable alternative is to use an isolation transformer made specifically for this purpose.
History
Cheater plugs were previously available with a short flexible grounding wire rather than a flat metal screw tab. This allowed use of the lower receptacle in a duplex outlet, which does not have a faceplate screw in the correct location for the screw tab. The grounding wire would be diverted around the adapter to reach the faceplate screw above it. However, this ground-wire style of cheater plug was discontinued when it was noted that a loose unattached grounding wire could accidentally become connected to the "hot" blade of a nearby outlet, potentially leading toelectric shock
An electrical injury (electric injury) or electrical shock (electric shock) is damage sustained to the skin or internal organs on direct contact with an electric current.
The injury depends on the Current density, density of the current, tissu ...
. As an additional failure mode, the thin flexible wire could break unnoticed inside the insulation. Lastly, most of the early adaptors allowed accidental reversal of hot and neutral connections, because they lacked the widened neutral blade to enforce correct plug orientation.
Modern cheater plugs lack a flexible wire which could be accidentally misconnected. The flat parallel plug blades are polarized to prevent the hot and the neutral connections from being reversed. In addition, many versions have a molded obstruction bump on top of the adapter, to block the grounding prong and thus physically prevent forcible insertion of a 3-prong plug in the wrong orientation.
Use in residences
Three-prong plugs do not fit into the older, two-prong receptacles. When used as intended, the ground pin of the 3-wire receptacle is to be connected to a grounded cover screw, or to an external ground. In 1969,Underwriters Laboratories
The UL enterprise is a global private safety company headquartered in Northbrook, Illinois, composed of three organizations, UL Research Institutes, UL Standards & Engagement and UL Solutions.
Established in 1894, the UL enterprise was founded a ...
mandated three-prong plugs on major appliance
A major appliance is a non-portable or semi-portable machine used for routine housekeeping tasks such as cooking, washing laundry, or food preservation. Such appliances are sometimes collectively known as white goods, as the products were trad ...
s for safety. At that time, only half of the receptacles in US homes were three-prong. Wiring in most homes did not include a grounding wire. The screws and outlet boxes were either connected to the neutral, or connected to nothing. Only in some jurisdictions where 2-wire non-metallic cable was restricted and armored cable
In electrical power distribution, armoured cable usually means steel wire armoured cable (SWA) which is a hard-wearing power cable designed for the supply of mains electricity. It is one of a number of armoured electrical cables – which include ...
was required (and still in good condition), do cheater plugs work safely as intended. In 1971, the US National Electrical Code
The National Electrical Code (NEC), or NFPA 70, is a regionally adoptable standard for the safe installation of electrical wiring and equipment in the United States. It is part of the National Fire Code series published by the National Fire Prote ...
(NEC) required grounded receptacles in all locations of the home (effective January 1, 1974).
Safety
In theprofessional audio
Professional audio, abbreviated as pro audio, refers to both an activity and a category of high-quality, studio-grade audio equipment. Typically it encompasses sound recording, sound reinforcement system setup and audio mixing, and studio mus ...
and video fields, the cheater plug has been identified as a serious safety problem. Its casual use as a method for avoiding ground loops in analog audio and video signals (to eliminate hums and buzzes) is dangerous. Bill Whitlock, president of Jensen Transformers, writes, "never, ever use devices such as 3 to 2-prong AC plug adapters, a.k.a. 'ground lifters', to solve a noise problem!" Whitlock relates how an electrical fault in one device that is connected to its electricity source through an ungrounded cheater plug will result in dangerous, high current flowing through audio or video cables. Whitlock notes that in 1997, consumer audio and video equipment electrocuted nine people.
The cheater plug is also recognized as a safety hazard in laboratory
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratories are found in a variety of settings such as schools ...
settings. For example, in August 2005, Tarun Mal, an associate professor at Cleveland State University
Cleveland State University (CSU) is a public research university in Cleveland, Ohio, United States. It was established in 1964 and opened for classes in 1965 after acquiring the entirety of Fenn College, a private school that had been in oper ...
, was electrocuted when he plugged a defective fluorescent lamp
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, to produce ultraviolet and make a phosphor ...
into a time switch
A time switch (also called a timer switch, or simply timer) is a device that operates an electric switch controlled by a timer.
Intermatic introduced its first time switch in 1945, which was used for "electric signs, store window lighting, apartm ...
using a cheater plug. Subsequently, the state of Ohio
Ohio ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the ...
issued seven citations to the university for unsafe electrical conditions. ''The Scientist'' notes that four of the University's seven environmental safety experts agreed that use of the cheater plug "is not uncommon in US university labs". Jim Kaufman, CEO of the Laboratory Safety Institute, says, "When you inspect labs, it's not unusual to find anywhere from one to seven that way."
Alternatives
There are several alternatives for connecting newer appliances to two-prong receptacles without rewiring the building: removing the grounding pin of the plug (unsafe), replacing the receptacle with a three-prong outlet (unsafe without proper ground), or replacing the receptacle with a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI). Removing the grounding pin of the appliance’s plug is unsafe, and leaves the appliance without proper grounding even when relocated and plugged into a properly grounded three-prong receptacle. Additionally, since most NEMA 5-15P plugs have both current-carrying prongs the same width and rely on the ground pin for correct orientation, removing it allows insertion of the plug with hot and neutral wires reversed, creating an additional hazard. In most cases it also invalidates the manufacturer's warranty against defects as an unsupported modification of the appliance. Replacing the receptacle with the three-prong type and leaving the ground screw unconnected is just as unsafe as using a cheater plug, but has the additional disadvantage that subsequent users of the outlet may not be aware that it is not properly grounded. Even worse, if the ground screw of the receptacle is connected to the neutral side, electric shock is possible even when the appliance is properly functioning. This is called a "false" or "bootleg" ground and is a serious safety hazard often undetected by common receptacle testers. Replacing the obsolete receptacle with a GFCI receptacle is the safest alternative, other than installing a new cable from the main circuit breaker panel. If a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter receptacle is properly functioning, it will interrupt dangerous current to limit the duration of a potentially lethalelectric shock
An electrical injury (electric injury) or electrical shock (electric shock) is damage sustained to the skin or internal organs on direct contact with an electric current.
The injury depends on the Current density, density of the current, tissu ...
from an appliance ''precisely when the receptacle is not the only conductor to electrical ground'' (this is a ground fault, by definition). For the purpose of protecting humans against electric shocks, the National Electrical Code
The National Electrical Code (NEC), or NFPA 70, is a regionally adoptable standard for the safe installation of electrical wiring and equipment in the United States. It is part of the National Fire Code series published by the National Fire Prote ...
permits such replacement if the installer labels the GFCI as having "No Equipment Ground". When installing the receptacle in this case, leave the ground connection unconnected. Note that an external GFCI receptacle tester may not make an ungrounded GFCI trip, as these testers use the ground connection to simulate a fault. But the test button integrated into the GFCI receptacle should function normally and cause the outlet to shut off until it is reset manually. If it does not, the outlet is not protected and should be replaced.
Certified standards and testing organizations
Testing and certification organizations, such as Underwriters Laboratories (UL), continue to evolve their safety standards to address new electrical safety concerns, including the risks posed by counterfeit plugs. UL now emphasizes the need for grounding adaptors to meet modern electrical safety protocols and ensures that alternative products, such as GFCI outlets (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter), provide equivalent or better protection for users. Additionally, laboratory safety standards for the use of cheater plugs in environments like universities and research labs have been updated in response to incidents involving electrical faults. In 2020, theNational Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the List of United States federal agencies, United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related occ ...
(NIOSH) revised its guidelines to emphasize the dangers of using cheater plugs in laboratories, recommending alternatives such as isolated power systems and dedicated circuits for grounding sensitive equipment.
References
{{reflist, 2 Mains power connectors