Charlottetown Conference Delegates, September 1864 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Charlottetown is the capital and largest city of the
 During
During 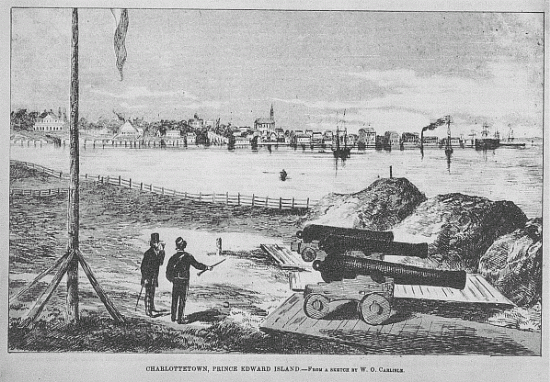 Prince Edward Island entered Confederation on July 1, 1873. Aside from being the seat of colonial government, the community came to be noted during the early nineteenth century for
Prince Edward Island entered Confederation on July 1, 1873. Aside from being the seat of colonial government, the community came to be noted during the early nineteenth century for
 To commemorate the centennial of the
To commemorate the centennial of the
 Downtown Charlottetown includes the city's historic five hundred lots, as surveyed by Captain Samuel Holland, as well as the waterfront facing the harbour and the Hillsborough River. Adjacent communities to the original downtown included Brighton, Spring Park, Sherwood and Parkdale. The areas to the west, north and east of downtown have been developed in recent decades with several residential and commercial/retail developments, although the outer regions of the city are still predominantly farmland, as is an area in the centre of the city where an Agriculture Canada experimental crop research station is located. The Agriculture Canada research station farm is the last remnant of the Queens Royalty common pasture lands and creates a large greenspace in the centre of the city, north of downtown. The development of the township of Queens Royalty, with its estates surveyed during the 18th and 19th centuries along a north–south axis forced early road networks into a grid.
21st-century Charlottetown landscape is dominated by urban development along the waterfront areas, suburban development to the west, north and east, as well as the airport to the north. Commercial development, aside from the central business district, is concentrated along several road corridors:
* University Avenue/Malpeque Road
* North River Road/Lower Malpeque Road
* St. Peter's Road
* Mount Edward Road
* Kensington Road
The downtown core is augmented by several feeder streets:
* Queen Street
* Water Street
* Grafton Street
Downtown Charlottetown includes the city's historic five hundred lots, as surveyed by Captain Samuel Holland, as well as the waterfront facing the harbour and the Hillsborough River. Adjacent communities to the original downtown included Brighton, Spring Park, Sherwood and Parkdale. The areas to the west, north and east of downtown have been developed in recent decades with several residential and commercial/retail developments, although the outer regions of the city are still predominantly farmland, as is an area in the centre of the city where an Agriculture Canada experimental crop research station is located. The Agriculture Canada research station farm is the last remnant of the Queens Royalty common pasture lands and creates a large greenspace in the centre of the city, north of downtown. The development of the township of Queens Royalty, with its estates surveyed during the 18th and 19th centuries along a north–south axis forced early road networks into a grid.
21st-century Charlottetown landscape is dominated by urban development along the waterfront areas, suburban development to the west, north and east, as well as the airport to the north. Commercial development, aside from the central business district, is concentrated along several road corridors:
* University Avenue/Malpeque Road
* North River Road/Lower Malpeque Road
* St. Peter's Road
* Mount Edward Road
* Kensington Road
The downtown core is augmented by several feeder streets:
* Queen Street
* Water Street
* Grafton Street
 Charlottetown has numerous parks and playing fields for soccer, baseball, softball, football, rugby, and field hockey. Cricket also has been gaining popularity after building a ground and a cricket pitch at Tea hill park in Stratford. There are also many outdoor tennis courts, recreational trails, and running tracks. Most public schools in the city have gymnasiums available for public use outside of school hours and there are community-owned and operated hockey arenas and swimming pools, as well as several privately operated fitness centres.
Amateur varsity team sports are prevalent for males and females in the city's two senior high schools, Colonel Gray and Charlottetown Rural, as well as the
Charlottetown has numerous parks and playing fields for soccer, baseball, softball, football, rugby, and field hockey. Cricket also has been gaining popularity after building a ground and a cricket pitch at Tea hill park in Stratford. There are also many outdoor tennis courts, recreational trails, and running tracks. Most public schools in the city have gymnasiums available for public use outside of school hours and there are community-owned and operated hockey arenas and swimming pools, as well as several privately operated fitness centres.
Amateur varsity team sports are prevalent for males and females in the city's two senior high schools, Colonel Gray and Charlottetown Rural, as well as the
 The city's municipal government is structured around a council comprising a
The city's municipal government is structured around a council comprising a
 Historically, Charlottetown was the centre of the province's railway network. Highway development in the latter part of the 20th century has resulted in the city being the focal point of several important routes in the province.
Historically, Charlottetown was the centre of the province's railway network. Highway development in the latter part of the 20th century has resulted in the city being the focal point of several important routes in the province.
 English public schooling (gr. K-12) in Charlottetown is provided by the Public Schools Branch. French public schooling (gr. K-12) in the city is provided by the
English public schooling (gr. K-12) in Charlottetown is provided by the Public Schools Branch. French public schooling (gr. K-12) in the city is provided by the
Canadian province
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Constitution of Canada, Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North Amer ...
of Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island is an island Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. While it is the smallest province by land area and population, it is the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
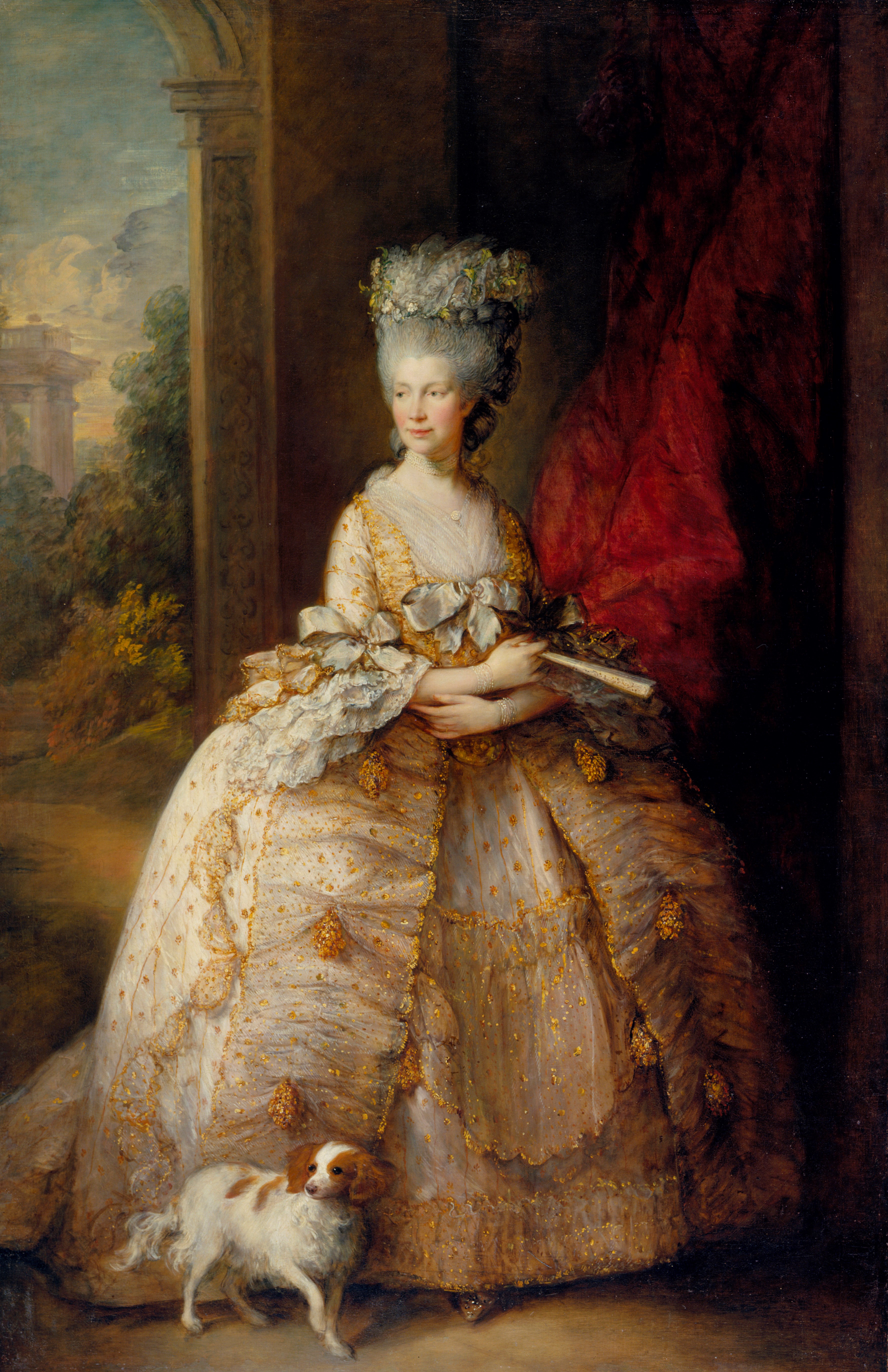
, and the county seat of Queens County. Named after Queen Charlotte
Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz (Sophia Charlotte; 19 May 1744 – 17 November 1818) was Queen of Great Britain and Ireland as the wife of King George III from their marriage on 8 September 1761 until her death in 1818. The Acts of Un ...
, Charlottetown was an unincorporated town until it was incorporated as a city in 1855.
It was the site of the famous Charlottetown Conference
The Charlottetown Conference (A Conference to discuss the Confederation of Canada) was held in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, for representatives from colonies of British North America to discuss Canadian Confederation. The conference to ...
in 1864, the first gathering of Canadian and Maritime statesmen to discuss the proposed Maritime Union
Maritime Union () is a proposed political union of the three Maritime provinces of Canada – New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island – to form a single new province.British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestown, ...
n colonies in 1867, which was the beginning of the Canadian confederation
Canadian Confederation () was the process by which three British North American provinces—the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick—were united into one federation, called the Name of Canada#Adoption of Dominion, Dominion of Ca ...
. Prince Edward Island, however, did not join Confederation until 1873. From this, the city adopted as its motto ''Cunabula Foederis'', "Birthplace of Confederation".
The population of Charlottetown is estimated to be 40,500 (2022); this forms the centre of a census agglomeration
The census geographic units of Canada are the census subdivisions defined and used by Canada's federal government statistics bureau Statistics Canada to conduct the country's quinquennial census. These areas exist solely for the purposes of stat ...
of 83,063 (2021), which is roughly half of the province's population (160,302).
History
Early history (1720–1900)
The first European settlers in the area were French; personnel fromFortress Louisbourg
The Fortress of Louisbourg () is a tourist attraction as a National Historic Site and the location of a one-quarter partial reconstruction of an 18th-century French fortress at Louisbourg on Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia. Its two sieges, espe ...
founded a settlement in 1720 named '' Port La Joye'' on the southwestern part of the harbour opposite the present-day city. This settlement was led by Michel Haché-Gallant, who used his sloop to ferry Acadian settlers from Louisbourg.
 During
During King George's War
King George's War (1744–1748) is the name given to the military operations in North America that formed part of the War of the Austrian Succession (1740–1748). It was the third of the four French and Indian Wars. It took place primarily in ...
, the British had taken over Prince Edward Island. French officer Jean-Baptiste Nicolas Roch de Ramezay
Jean-Baptiste Nicolas Roch, ''Seigneur de Ramezay'', (4 September 1708, in Montreal, New France – 7 May 1777, in Blaye, France) was an officer of the marines and colonial administrator for New France during the 18th century. Joining at age 1 ...
attacked with 500 men at the Battle at Port-la-Joye
The Battle at Port-la-Joye (also known as the ''Port-la-Joye Massacre'') was a battle in King George's War that took place with British against French troops and Mi'kmaq militia on the banks of present-day Hillsborough River, Prince Edward I ...
, resulting in a British defeat and the capture or death of all involved British troops.
In August 1758, at the height of the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War, 1754 to 1763, was a colonial conflict in North America between Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of France, France, along with their respective Native Americans in the United States, Native American ...
, a British fleet took control of the settlement and the rest of the island, promptly deporting those French settlers that they could find in the Ile Saint-Jean Campaign (this being fully three years after the initial Acadian Expulsion
The Expulsion of the Acadians was the forced removal of inhabitants of the North American region historically known as Acadia between 1755 and 1764 by Great Britain. It included the modern Canadian Maritime provinces of Nova Scotia, New Br ...
in Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
). British forces built ''Fort Amherst
Fort Amherst, in Medway, South East England, was constructed in 1756 at the southern end of the Brompton lines of defence to protect the southeastern approaches to Chatham Dockyard and the River Medway against a French invasion. Fort Amherst i ...
'' near the site of the abandoned ''Port La Joye'' settlement to protect the entrance to the harbour.
Charlottetown was selected as the site for the county seat of Queens County in the colonial survey of 1764 by Captain Samuel Holland of the Royal Engineers. A year later, Charlottetown was made the colonial capital of St. John's Island. Further surveys conducted between 1768 and 1771 established the street grid and public squares which can be seen in the city's historic district. The town was named in honour of Queen Charlotte
Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz (Sophia Charlotte; 19 May 1744 – 17 November 1818) was Queen of Great Britain and Ireland as the wife of King George III from their marriage on 8 September 1761 until her death in 1818. The Acts of Un ...
.
On November 17, 1775, during the American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
, the colony's new capital was ransacked by Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
-based privateers in the Raid on Charlottetown. During the attack, the colonial seal was stolen and several prisoners, including Phillips Callbeck
Phillips Callbeck ( – February 21, 1790) was a merchant, lawyer, and political figure in St. John's Island (later Prince Edward Island). He served as administrator for the island from 1775 to 1780.
Callbeck is likely to have been born in Engl ...
and Thomas Wright, were taken to Cambridge, Massachusetts
Cambridge ( ) is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. It is a suburb in the Greater Boston metropolitan area, located directly across the Charles River from Boston. The city's population as of the 2020 United States census, ...
and later released.
In 1793, land had been set aside by Governor Fanning on the western limits of the community for use by the "Administrator of Government" (the governor), and as such it became known informally as "Fanning's Bank" or just "Fanning Bank". On November 29, 1798, St. John's Island was renamed to Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island is an island Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. While it is the smallest province by land area and population, it is the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
in honour of Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn
Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn (Edward Augustus; 2 November 1767 – 23 January 1820) was the fourth son and fifth child of King George III and Queen Charlotte. His only child, Queen Victoria, Victoria, became Queen of the United Ki ...
, who was the Commander-in-Chief, North America
The office of Commander-in-Chief, North America was a military position of the British Army. Established in 1755 in the early years of the Seven Years' War, holders of the post were generally responsible for land-based military personnel and a ...
.
In 1805, the local British garrison constructed a harbour defence called "Fort Edward" to the west of the capital's waterfront and the "Prince Edward Battery" manned this facility. In 1835, "Government House
Government House is the name of many of the official residences of governors-general, governors and lieutenant-governors in the Commonwealth and British Overseas Territories. The name is also used in some other countries.
Government Houses in th ...
" was constructed at Fanning Bank as a residence for the colony's Governor
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the ...
. Today, it serves as the official residence for the Lieutenant Governor
A lieutenant governor, lieutenant-governor, or vice governor is a high officer of state, whose precise role and rank vary by jurisdiction. Often a lieutenant governor is the deputy, or lieutenant, to or ranked under a governor — a "second-in-comm ...
.
Between 1843 and 1847, a new legislative building was constructed in the community. Named the Colonial Building originally, following Confederation with Canada it gradually became known as " Province House". The completion of this structure with Isaac Smith as builder/architect
An architect is a person who plans, designs, and oversees the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to provide services in connection with the design of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the buildings that h ...
was an important milestone in the history of the capital and it is still in use today as the provincial legislature as well as a National Historic Site, and is currently the second-oldest legislative seat in Canada.
On April 17, 1855, Charlottetown was incorporated as a city, holding its first council meeting on August 11 of that year. The community had 6,500 residents at the time of incorporation.
Between September 1–8, 1864, Charlottetown hosted what is now termed the Charlottetown Conference
The Charlottetown Conference (A Conference to discuss the Confederation of Canada) was held in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, for representatives from colonies of British North America to discuss Canadian Confederation. The conference to ...
. Although many of the meetings and negotiations which would lead to Canadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation () was the process by which three British North American provinces—the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick—were united into one federation, called the Name of Canada#Adoption of Dominion, Dominion of Ca ...
were held in Province House, various social events spilled over into the surrounding community.
 Prince Edward Island entered Confederation on July 1, 1873. Aside from being the seat of colonial government, the community came to be noted during the early nineteenth century for
Prince Edward Island entered Confederation on July 1, 1873. Aside from being the seat of colonial government, the community came to be noted during the early nineteenth century for shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other Watercraft, floating vessels. In modern times, it normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation th ...
and its lumber industry as well as being a fishing port. The shipbuilding industry declined in the latter part of the nineteenth century.
On June 14, 1873 the "Government House Farm" at Fanning Bank was designated a municipal park, named Victoria Park in honour of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
.
In August 1874, the Prince Edward Island Railway
The Prince Edward Island Railway (PEIR) was a historic Canadian railway in Prince Edward Island (PEI). The railway ran tip-to-tip on the island, from Tignish in the west to Elmira in the east, with major spurs serving Borden-Carleton's train ...
opened its main line between Charlottetown and Summerside. The railway, along with the shipping industry, would continue to drive industrial development on the waterfront for several decades to come. The province's first health care facility, the Charlottetown Hospital
The Charlottetown Hospital is a former acute care hospital that was located in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island. Established in 1879 it was the first public hospital established in the province.
History Establishment
The facility was establis ...
, was opened by the Diocese of Charlottetown in 1879, which was followed by the publicly operated Prince Edward Island Hospital
The Prince Edward Island Hospital is a former acute care hospital that was located in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island. It was the first public general hospital established in the province and the largest such facility throughout its history.
...
in 1884.
Modern history (1900–present)
Religion played a central role in the development of Charlottetown's institutions with non-denominational (i.e. Protestant) and Roman Catholic public schools (Catholic Queen Square, Notre Dame, and St Joseph's vs. Protestant West Kent and Prince Street), hospitals (Prince Edward Island Hospital vs. Charlottetown Hospital), and post-secondary institutions (Prince of Wales College
Prince of Wales College (PWC) is a former university college, which was located in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada. PWC merged with St. Dunstan's University in 1969 to form the University of Prince Edward Island.
PWC traces its hi ...
vs. St. Dunstan's University) being instituted. St. Dunstan's was originally developed as a seminary for training priests, and the Maritime Christian College was founded in 1960 to train preachers for the Christian churches and churches of Christ
The group of churches known as the Christian Churches and Churches of Christ is a fellowship of congregations within the Restoration Movement (also known as the Stone–Campbell Movement and the Reformation of the 19th Century) that have no form ...
in Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island is an island Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. While it is the smallest province by land area and population, it is the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
and the Maritime Provinces
The Maritimes, also called the Maritime provinces, is a region of Eastern Canada consisting of three provinces: New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. The Maritimes had a population of 1,899,324 in 2021, which makes up 5.1% of ...
.
As with most communities in North America, the automobile
A car, or an automobile, is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of cars state that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, peopl ...
shaped Charlottetown's development in the latter half of the twentieth century, when outlying farms in rural areas of Brighton, Spring Park, and Parkdale saw increased housing developments. The Charlottetown airfield in the nearby rural community of Sherwood
Sherwood may refer to:
Places Australia
*Sherwood, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane
* Sherwood, South Australia, a locality
*Shire of Sherwood, a former local government area of Queensland
* Electoral district of Sherwood, an electoral district fr ...
was upgraded as part of the British Commonwealth Air Training Plan
The British Commonwealth Air Training Plan (BCATP), often referred to as simply "The Plan", was a large-scale multinational military aircrew training program created by the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia and New Zealand during the Second Wo ...
and operated for the duration of World War II as RCAF Station Charlottetown, in conjunction with RCAF Station Mount Pleasant and RCAF Station Summerside
Canadian Forces Base Summerside (CFB Summerside) was an air force base located in St. Eleanors, Prince Edward Island, Canada, now part of the city of Summerside.
RCAF Station Summerside World War II
The airfield was constructed by the Royal Ca ...
. After the war
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or between such organi ...
the airfield was designated Charlottetown Airport
Charlottetown Airport is located north of Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada. The airport is currently run by the Charlottetown Airport Authority, is owned by Transport Canada and forms part of the National Airports System.
The airpo ...
. Charlottetown's shipyards were used extensively during World War II, being used for refits and upgrades to numerous Royal Canadian Navy
The Royal Canadian Navy (RCN; , ''MRC'') is the Navy, naval force of Canada. The navy is one of three environmental commands within the Canadian Armed Forces. As of February 2024, the RCN operates 12 s, 12 s, 4 s, 4 s, 8 s, and several auxiliary ...
warships. Further post-war development continued to expand residential properties in adjacent outlying areas, particularly in the neighbouring farming communities of Sherwood, West Royalty, and East Royalty.
In 1959, the suburban village of Spring Park was amalgamated into the city, extending the city's northern boundary from Kirkwood Drive to Hermitage Creek and included the campus of St. Dunstan's University.
 To commemorate the centennial of the
To commemorate the centennial of the Charlottetown Conference
The Charlottetown Conference (A Conference to discuss the Confederation of Canada) was held in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, for representatives from colonies of British North America to discuss Canadian Confederation. The conference to ...
, the ten provincial governments and the Government of Canada contributed to a national monument to the "Fathers of Confederation". The Confederation Centre of the Arts
Confederation Centre of the Arts () is a cultural centre dedicated to the visual arts, visual and performing arts located in the city of Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada.
History
Construction of Confederation Centre, as it is commonly ...
, which opened in 1964, is a gift to the residents of Prince Edward Island, and contains a public library, nationally renowned art gallery, and a mainstage theatre which has played to the Charlottetown Festival The Charlottetown Festival is a seasonal Canadian musical theatre festival which has run from late May to mid-October every year since 1965.
The Charlottetown Festival is hosted in Confederation Centre of the Arts every year. Named after its host c ...
every summer since.
In the 1960s, new public schools were constructed in the community, and in 1969 the city became home to the amalgamated University of Prince Edward Island
The University of Prince Edward Island (UPEI) is a public university in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada, and the only university in the province. Founded in 1969, the enabling legislation is the ''University Act, R.S.P.E.I 2000.''
H ...
(UPEI), located on the campus of the former St. Dunstan's University. Together with the federal Department of Agriculture and Agri-Food's Charlottetown Experimental Farm (also known as ''Ravenwood Farm''), these properties comprise a large green space surrounded by the city. The Prince of Wales College downtown campus became part of a new provincial community college system named Holland College
Holland College is the provincial community college for the Canadian province of Prince Edward Island (PEI). It is named after the British Army engineer and surveyor Captain Samuel Holland. In 2024, about 30% of the college's enrolled student ...
, in honour of the island's famous surveyor. The PEI Comprehensive Development Plan in the late 1960s greatly contributed to the expansion of the provincial government in Charlottetown for the next decade.
The Queen Elizabeth Hospital opened in 1982. In 1983, the national headquarters of the federal Department of Veterans Affairs
The United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is a Cabinet-level executive branch department of the federal government charged with providing lifelong healthcare services to eligible military veterans at the 170 VA medical centers an ...
was moved to Charlottetown as part of a nationwide federal government decentralization programme. In 1986, UPEI expanded further with the opening of the Atlantic Veterinary College
The Atlantic Veterinary College (AVC) is an accredited and globally recognized veterinary school in the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine at University of Prince Edward Island, located in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada.
History
AVC ...
.
Throughout the 1970s and 1980s, there was increased commercial office and retail development. A waterfront hotel and convention centre was completed in 1982 and helped to encourage diversification and renewal in the area, leading to several residential complexes and downtown shopping facilities. The abandonment of rail service in the province by CN Rail
The Canadian National Railway Company () is a Canadian Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern and Southern United States.
CN is Canada's largest railway, in terms of both revenue an ...
in December 1989 led to the railway and industrial lands at the east end of the waterfront being transformed into parks and cultural attractions.
In the late 1990s and 2000s, the retail landscape changed with the opening of big box stores on the site of former traditional shopping centres and in new developments in the northern suburbs, particularly the neighbourhood of West Royalty, which is a key road junction.
On April 1, 1995, Charlottetown amalgamated with the Town of Parkdale and the incorporated communities of East Royalty, Hillsborough Park
Hillsborough Park is a large () parkland area in Hillsborough, Sheffield, South Yorkshire, England. It is situated three miles north-west of the city centre. It is owned by Sheffield City Council and is one of the 13 designated "City Parks".
...
, Sherwood
Sherwood may refer to:
Places Australia
*Sherwood, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane
* Sherwood, South Australia, a locality
*Shire of Sherwood, a former local government area of Queensland
* Electoral district of Sherwood, an electoral district fr ...
, West Royalty, and Winsloe. At the same time, the amalgamated Charlottetown annexed Queens Royalty. Today, the City of Charlottetown occupies parts of the Lot 33 and Lot 34 townships.
The central business district continues to undergo incremental expansion as government and private sector office space is constructed and new institutional space is built or retrofitted, however retail space in the CBD has suffered as a result of outlying big box retail construction in recent years.
On May 31, 2021, the Charlottetown City Council
The Charlottetown City Council is the governing body for the city of Charlottetown, the county seat of Queen's County, Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island is an island Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. While it ...
voted to remove a statue of John A. MacDonald
Sir John Alexander Macdonald (10 or 11January 18156June 1891) was the first prime minister of Canada, serving from 1867 to 1873 and from 1878 until his death in 1891. He was the dominant figure of Canadian Confederation, and had a political ...
, the first Prime Minister of Canada, following a year of vandalism in the wake of the George Floyd Protests
The George Floyd protests were a series of protests, riots, and demonstrations against police brutality that began in Minneapolis in the United States on May 26, 2020. The protests and civil unrest began in Minneapolis as Reactions to the mu ...
. The catalyst for the removal came following the discovery of a mass grave at the Kamloops Indian Residential School
The Kamloops Indian Residential School was part of the Canadian Indian residential school system. Located in Kamloops, British Columbia, it was once the largest residential school in Canada, with its enrolment peaking at 500 in the 1950s. The sc ...
in British Columbia.
The first video and sound recording of a meteorite striking the earth, the Charlottetown meteorite
The Charlottetown meteorite was a meteorite fall observed on July 25, 2024. It is notable as the first meteorite known with video and audio of the impact recorded and as the only known meteorite fall in Prince Edward Island, Canada.
The Charlott ...
, was captured in the neighborhood of Marshfield in 2024.
Geography
Charlottetown is situated on its namesakeharbour
A harbor (American English), or harbour (Commonwealth English; see American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, spelling differences), is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be Mooring, moored. The t ...
, which is formed by the confluence of three rivers in the central part of the island's south shore. The harbour opens onto the Northumberland Strait
The Northumberland Strait (French: ''détroit de Northumberland'') is a strait in the southern part of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence in eastern Canada. The strait is formed by Prince Edward Island and the gulf's eastern, southern, and western sho ...
. The city is roughly V-shaped (pointed to the south) and constrained by the North (Yorke) and the Hillsborough (East) Rivers to the west and east.
Climate
Charlottetown has ahumid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers, and cold ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (1951–2014), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author ...
''Dfb'') moderated partially by Prince Edward Island's location in the Gulf of Saint Lawrence
The Gulf of St. Lawrence is a gulf that fringes the shores of the provinces of Quebec, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, Newfoundland and Labrador, in Canada, plus the islands Saint-Pierre and Miquelon, possessions of France, in ...
. Winters are somewhat milder than many inland cities at a similar latitude: the January average is , and lows reach or below on an average 5.8 days per season. However, the coastal position means that winter precipitation, more often as snow, is frequent and at times heavy: the seasonal snow average is . Spring warming is gradual due to the ocean waters still being cold. Summers are mild, again due to the same maritime moderation: the July high is . Precipitation averages per year, with the greatest amounts falling in late fall and winter.
The highest temperature ever recorded in Charlottetown was on 19 August 1935.
The coldest temperature ever recorded was on 29 January 1877.
Cityscape

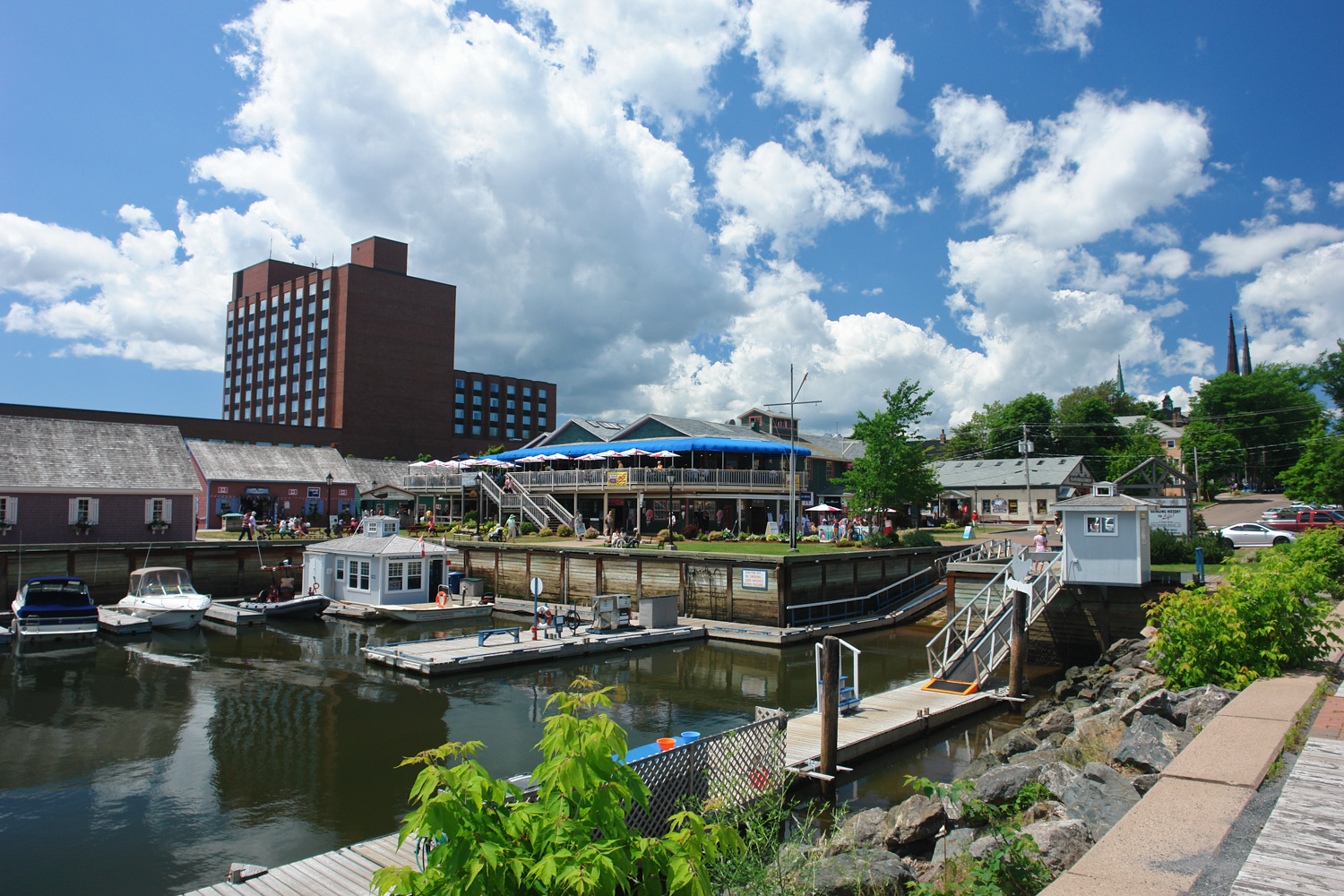
 Downtown Charlottetown includes the city's historic five hundred lots, as surveyed by Captain Samuel Holland, as well as the waterfront facing the harbour and the Hillsborough River. Adjacent communities to the original downtown included Brighton, Spring Park, Sherwood and Parkdale. The areas to the west, north and east of downtown have been developed in recent decades with several residential and commercial/retail developments, although the outer regions of the city are still predominantly farmland, as is an area in the centre of the city where an Agriculture Canada experimental crop research station is located. The Agriculture Canada research station farm is the last remnant of the Queens Royalty common pasture lands and creates a large greenspace in the centre of the city, north of downtown. The development of the township of Queens Royalty, with its estates surveyed during the 18th and 19th centuries along a north–south axis forced early road networks into a grid.
21st-century Charlottetown landscape is dominated by urban development along the waterfront areas, suburban development to the west, north and east, as well as the airport to the north. Commercial development, aside from the central business district, is concentrated along several road corridors:
* University Avenue/Malpeque Road
* North River Road/Lower Malpeque Road
* St. Peter's Road
* Mount Edward Road
* Kensington Road
The downtown core is augmented by several feeder streets:
* Queen Street
* Water Street
* Grafton Street
Downtown Charlottetown includes the city's historic five hundred lots, as surveyed by Captain Samuel Holland, as well as the waterfront facing the harbour and the Hillsborough River. Adjacent communities to the original downtown included Brighton, Spring Park, Sherwood and Parkdale. The areas to the west, north and east of downtown have been developed in recent decades with several residential and commercial/retail developments, although the outer regions of the city are still predominantly farmland, as is an area in the centre of the city where an Agriculture Canada experimental crop research station is located. The Agriculture Canada research station farm is the last remnant of the Queens Royalty common pasture lands and creates a large greenspace in the centre of the city, north of downtown. The development of the township of Queens Royalty, with its estates surveyed during the 18th and 19th centuries along a north–south axis forced early road networks into a grid.
21st-century Charlottetown landscape is dominated by urban development along the waterfront areas, suburban development to the west, north and east, as well as the airport to the north. Commercial development, aside from the central business district, is concentrated along several road corridors:
* University Avenue/Malpeque Road
* North River Road/Lower Malpeque Road
* St. Peter's Road
* Mount Edward Road
* Kensington Road
The downtown core is augmented by several feeder streets:
* Queen Street
* Water Street
* Grafton Street
Neighbourhoods
Charlottetown comprises the following neighbourhoods which were one-time independent municipalities: * Downtown Charlottetown * Brighton * Spring Park * Parkdale *Sherwood
Sherwood may refer to:
Places Australia
*Sherwood, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane
* Sherwood, South Australia, a locality
*Shire of Sherwood, a former local government area of Queensland
* Electoral district of Sherwood, an electoral district fr ...
(including Falconwood)
* East Royalty (including Hillsborough Park)
* West Royalty (including Lewis Point)
* Winsloe
The original municipal boundary between Charlottetown and the common area of the township of Queens Royalty was the northern edge of the original five hundred lots along present-day Euston Street. This boundary was extended north to Allen Street and Kirkwood Drive during the early twentieth century, taking in part of the rural community of Brighton west of the downtown. The village of Spring Park was amalgamated into the city in 1959, extending the city's boundary north to Hermitage Creek, which also formed the southern boundary of the village of West Royalty. Development filled in most vacant land in the Brighton and Spring Park neighbourhoods by the 1980s. Municipal amalgamation in 1996 saw the outlying independent municipalities of Parkdale (town), Sherwood, East Royalty, West Royalty and Winsloe (villages) merged into a larger city of Charlottetown at the same time as rural communities east and west of the city were amalgamated to form the towns of Stratford and Cornwall respectively.
A green belt
A green belt or greenbelt is a policy, and land-use zone designation used in land-use planning to retain areas of largely undeveloped, wilderness, wild, or agricultural landscape, land surrounding or neighboring urban areas. Similar concepts ...
is in place around the northern fringe of the municipal boundary, although it is poorly enforced by the provincial government, leading to suburban sprawl
Urban sprawl (also known as suburban sprawl or urban encroachment) is defined as "the spreading of urban developments (such as houses and shopping centers) on undeveloped land near a city". Urban sprawl has been described as the unrestricted ...
.
Culture
Attractions
The city's streetscape with a centrally planned downtown core containing many Victorian-era houses and buildings is an attraction, as well as the waterfront redevelopment project in recent decades which has seen walking trails and parks developed on former industrial lands. A newcruise ship
Cruise ships are large passenger ships used mainly for vacationing. Unlike ocean liners, which are used for transport, cruise ships typically embark on round-trip voyages to various ports of call, where passengers may go on Tourism, tours k ...
terminal was opened by the port authority in September 2007 which, proponents hope, will make the city a more attractive destination for the growing number of vessels operating in the Gulf of St. Lawrence.
Popular attractions within the city include the provincial legislature at Province House, which hosted the Charlottetown Conference
The Charlottetown Conference (A Conference to discuss the Confederation of Canada) was held in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, for representatives from colonies of British North America to discuss Canadian Confederation. The conference to ...
, as well as Founders Hall, a recently redeveloped railway maintenance building which now houses an interactive trip through history tracing the development of Canada as a nation.
The Confederation Centre of the Arts
Confederation Centre of the Arts () is a cultural centre dedicated to the visual arts, visual and performing arts located in the city of Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada.
History
Construction of Confederation Centre, as it is commonly ...
provides live theatre, including the Charlottetown Festival The Charlottetown Festival is a seasonal Canadian musical theatre festival which has run from late May to mid-October every year since 1965.
The Charlottetown Festival is hosted in Confederation Centre of the Arts every year. Named after its host c ...
during the summer months, as well as the Confederation Centre Art Gallery
The Confederation Centre Art Gallery (CCAG; ) is an art museum that forms a part of the Confederation Centre of the Arts in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada. The art museum pavilion forms the northeast portion of the Confederation Centre ...
. The Charlottetown Festival itself is headlined by Canada's most popular and longest-running musical, ''Anne of Green Gables - The Musical
''Anne Of Green Gables – The Musical'' is a musical based on the 1908 novel ''Anne of Green Gables'' by Lucy Maud Montgomery. The book was written by Don Harron exclusively, the music by Norman Campbell and the lyrics in a joint venture by Harr ...
'', an adaptation of Island author Lucy Maud Montgomery
Lucy Maud Montgomery (November 30, 1874 – April 24, 1942), published as L. M. Montgomery, was a Canadian author best known for a collection of novels, essays, short stories, and poetry beginning in 1908 with '' Anne of Green Gables''. Sh ...
's novel. Several other small theatres and galleries can be found immediately surrounding the Confederation centre including the Mac (MacKenzie theatre), the Arts Guild, and Pilar Shepard gallery.
There are 11 National Historic Sites of Canada
National Historic Sites of Canada () are places that have been designated by the federal Minister of the Environment on the advice of the Historic Sites and Monuments Board of Canada (HSMBC), as being of national historic significance. Parks C ...
located in Charlottetown, including Province House and the Confederation Centre of the Arts.
Sports
 Charlottetown has numerous parks and playing fields for soccer, baseball, softball, football, rugby, and field hockey. Cricket also has been gaining popularity after building a ground and a cricket pitch at Tea hill park in Stratford. There are also many outdoor tennis courts, recreational trails, and running tracks. Most public schools in the city have gymnasiums available for public use outside of school hours and there are community-owned and operated hockey arenas and swimming pools, as well as several privately operated fitness centres.
Amateur varsity team sports are prevalent for males and females in the city's two senior high schools, Colonel Gray and Charlottetown Rural, as well as the
Charlottetown has numerous parks and playing fields for soccer, baseball, softball, football, rugby, and field hockey. Cricket also has been gaining popularity after building a ground and a cricket pitch at Tea hill park in Stratford. There are also many outdoor tennis courts, recreational trails, and running tracks. Most public schools in the city have gymnasiums available for public use outside of school hours and there are community-owned and operated hockey arenas and swimming pools, as well as several privately operated fitness centres.
Amateur varsity team sports are prevalent for males and females in the city's two senior high schools, Colonel Gray and Charlottetown Rural, as well as the University of Prince Edward Island
The University of Prince Edward Island (UPEI) is a public university in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada, and the only university in the province. Founded in 1969, the enabling legislation is the ''University Act, R.S.P.E.I 2000.''
H ...
's varsity teams (the UPEI Panthers
The UPEI Panthers are the men's and women's athletic teams that represent the University of Prince Edward Island in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada. The UPEI Panthers have teams playing in the Atlantic University Sport (AUS) confere ...
) through the institution's affiliation with Canadian Interuniversity Sport
U Sports (stylized as U SPORTS) is the national sport governing body for universities in Canada, comprising the majority of degree-granting universities in the country and four regional conferences: Ontario University Athletics (OUA), Résea ...
. Holland College also has varsity teams, the Holland Hurricanes.
There is one junior
Junior or Juniors may refer to:
Aircraft
* Ekolot JK-05L Junior, a Polish ultralight aircraft
* PZL-112 Junior, a Polish training aircraft
* SZD-51 Junior, a Polish-made training and club glider
Arts and entertainment Characters
* Bowser Jr., ...
hockey team in the community: the Quebec Maritimes Junior Hockey League
The Quebec Maritimes Junior Hockey League (QMJHL; , LHJMQ), formerly the Quebec Major Junior Hockey League is one of the three major junior ice hockey leagues that constitute the Canadian Hockey League (CHL). The league includes teams in Quebec ...
's Charlottetown Islanders
The Charlottetown Islanders are a Canadian junior ice hockey team in the Quebec Maritimes Junior Hockey League (QMJHL) based in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island. They are members of the Maritimes Division, and play their home games at the ...
. The city is also home to the Island Storm
The Island Storm is an inactive Canadian professional basketball team based in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island. The team is a charter member of the National Basketball League of Canada that began play in the 2011–12 season. The Storm plays ...
of the National Basketball League of Canada
The National Basketball League of Canada (NBL Canada; ) was a Canadian professional men's minor league basketball organization. The NBL Canada was founded in 2011, when three existing Premier Basketball League teams joined with four new franchis ...
.
Other notable sporting events held by Charlottetown include:
* 1991 Canada Winter Games
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
* 2009 Canada Summer Games (Co-hosted with Summerside)
Demographics
In the2021 Canadian census
The 2021 Canadian census was a detailed enumeration of the Canada, Canadian population with a reference date of May 11, 2021. It follows the 2016 Canadian census, which recorded a population of 35,151,728. The overall response rate was 98%, whic ...
conducted by Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada (StatCan; ), formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and culture. It is headquartered in ...
, Charlottetown had a population of living in of its total private dwellings, a change of from its 2016 population of . With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2021.
In the 2021 census, children under five account for approximately 3.9% of the resident population of Charlottetown. This compares with 4.4% in Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island is an island Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. While it is the smallest province by land area and population, it is the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
, and 5.0% for Canada overall. 21.0% of the resident population in Charlottetown are of retirement age compared with 21.2% in Prince Edward Island and 19.0% in Canada. The median age is 40.8 years of age compared to 44.0 years of age for Prince Edward Island and 41.6 years of age for all of Canada.
There are 17,193 total private dwellings in Charlottetown with an occupancy rate of 93.6%. The median value of a private dwelling is $200,284 compared to $341,556 nationally. The population density is 814.1 per square kilometre.
The 2021 census reported that immigrants
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as permanent residents. Commuters, tourists, and other short- ...
(individuals born outside Canada) comprise 5,245 persons or 13.9% of the total population of Charlottetown. Of the total immigrant population, the top countries of origin were China (1,030 persons or 19.6%), India (530 persons or 10.1%), Vietnam (410 persons or 7.8%), Syria (345 persons or 6.6%), Philippines (310 persons or 5.9%), United States (280 persons or 5.3%), United Kingdom (245 persons or 4.7%), Lebanon (115 persons or 2.2%), Iran (110 persons or 2.1%), and Jamaica (95 persons or 1.8%).
Ethnicity
Charlottetown is approximately 76.2% white, 21.8% visible minorities and 2.0% Indigenous as of 2021. The largest visible minority groups in Charlottetown are South Asian (6.4%), Chinese (5.0%), Black (2.9%), Arab (2.3%), and Southeast Asian (2.0%).Language
78.6% of Charlottetown residents spoke English as their first language. Other common mother tongues are Chinese languages (4.3%), Punjabi (2.0%) French (1.8%), Arabic (1.7%), and Vietnamese (1.2%). 1.8% of residents listed both English and a non-official language as mother tongues.Religion
According to the 2021 census, religious groups in Charlottetown included: *Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
(21,665 persons or 57.6%)
*Irreligion
Irreligion is the absence or rejection of religious beliefs or practices. It encompasses a wide range of viewpoints drawn from various philosophical and intellectual perspectives, including atheism, agnosticism, religious skepticism, ...
(12,425 persons or 33.0%)
*Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
(1,265 persons or 3.4%)
*Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
(860 persons or 2.3%)
*Sikhism
Sikhism is an Indian religion and Indian philosophy, philosophy that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent around the end of the 15th century CE. It is one of the most recently founded major religious groups, major religio ...
(635 persons or 1.7%)
*Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
(350 persons or 0.9%)
*Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
(70 persons or 0.2%)
* Indigenous Spirituality (15 persons or <0.1%)
*Other (310 persons or 0.8%)
As of 2021, 57.6% of residents are Christians, down from 75.4% in 2011. 28.9% were Catholic, 16.9% were Protestant, 7.2% were Christian n.o.s, and 4.7% were other Christian denominations and Christian-related traditions. Non-religious or secular people are 33.0% of the population, up from 20.8% in 2011. There are also significant populations of Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
(3.4%) and Sikhs
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Sikh'' ...
(1.7%).
Economy
Charlottetown's economy is dominated by the public sector. The provincial, federal, and municipal levels of government are significant employers in the central part of Queens County, as are the health care and secondary and post-secondary education sectors. Technology companies have increased their share of the city's workforce, however the actual numbers are quite small once call-centres are excluded. Other significant economic activities include light manufacturing, such as chemicals, bio-technology, and machining.Government
mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a Municipal corporation, municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilitie ...
and ten councillor
A councillor, alternatively councilman, councilwoman, councilperson, or council member, is someone who sits on, votes in, or is a member of, a council. This is typically an elected representative of an electoral district in a municipal or re ...
s elected using the ward
Ward may refer to:
Division or unit
* Hospital ward, a hospital division, floor, or room set aside for a particular class or group of patients, for example the psychiatric ward
* Prison ward, a division of a penal institution such as a pris ...
system. The current mayor of the city is Philip Brown.
Charlottetown has seven seats (out of 27) in the Legislative Assembly of Prince Edward Island
The Legislative Assembly of Prince Edward Island () together with the Lieutenant Governor of Prince Edward Island, lieutenant governor of Prince Edward Island form the General Assembly of Prince Edward Island. The Legislative Assembly meets at ...
. Some of these electoral districts occupy adjacent rural areas that are not within the city's boundaries.
The city has a single seat in the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of ...
; the current Member of Parliament is Sean Casey.
Transportation
 Historically, Charlottetown was the centre of the province's railway network. Highway development in the latter part of the 20th century has resulted in the city being the focal point of several important routes in the province.
Historically, Charlottetown was the centre of the province's railway network. Highway development in the latter part of the 20th century has resulted in the city being the focal point of several important routes in the province. Route 1
The following highways are numbered 1.
For roads numbered A1, see list of A1 roads.
For roads numbered B1, see list of B1 roads.
For roads numbered M1, see List of M1 roads.
For roads numbered N1, see list of N1 roads.
For roads numbered S ...
, the Trans-Canada Highway
The Trans-Canada Highway (Canadian French, French: ; abbreviated as the TCH or T-Can) is a transcontinental federal–provincial highway system that travels through all ten provinces of Canada, from the Pacific Ocean on the west coast to the A ...
, partially bisects the northern suburbs, linking with Riverside Drive, the Hillsborough River Bridge and the North River Causeway/Bridge on a limited-access arterial highway linking the city with the Confederation Bridge
The Confederation Bridge () is a box girder bridge carrying the Trans-Canada Highway across the Abegweit Passage of the Northumberland Strait, linking the province of Prince Edward Island with the mainland province of New Brunswick. Opened ...
in the west and the Northumberland Ferries
Northumberland Ferries Limited (NFL) is a ferry company operating in eastern Canada and headquartered in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island. NFL is also the owner of subsidiary Bay Ferries Limited (which used to include the Bay Ferries Great La ...
terminal in the east. Route 2, the province's main east–west highway intersects with Route 1 in the city.
Charlottetown Airport
Charlottetown Airport is located north of Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada. The airport is currently run by the Charlottetown Airport Authority, is owned by Transport Canada and forms part of the National Airports System.
The airpo ...
is the province's only airport with scheduled passenger airline service, serving 280,000 passengers per year.
Charlottetown Transit was founded in 2005 and offers 10 bus routes around town.
The absence of public transit for many decades in Charlottetown resulted in a dependence on personal use of automobiles, with municipal governments constructing three large above-ground parking garages in the city's historic district to house vehicles of downtown workers. The city also had a statistically higher proportion of taxis than the Canadian average as taxi service became a last-resort for many residents without access to a vehicle.
The Charlottetown Harbour Authority operates the city's commercial port and is currently expanding a marine terminal which was formerly operated by the federal government. Importation of gravel for construction and petroleum products are the main port activities.
Education
 English public schooling (gr. K-12) in Charlottetown is provided by the Public Schools Branch. French public schooling (gr. K-12) in the city is provided by the
English public schooling (gr. K-12) in Charlottetown is provided by the Public Schools Branch. French public schooling (gr. K-12) in the city is provided by the Commission scolaire de langue française
The Commission scolaire de langue française is a school district in Abram-Village, Prince Edward Island, Canada.
The Commission scolaire de langue française is a Francophone district operating 6 public schools (gr. 1–12) across the province ...
.
The city also has two independent schools: Immanuel Christian School and Grace Christian School.
Charlottetown is home to the University of Prince Edward Island
The University of Prince Edward Island (UPEI) is a public university in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada, and the only university in the province. Founded in 1969, the enabling legislation is the ''University Act, R.S.P.E.I 2000.''
H ...
. UPEI has programs in Arts, Education, Science, Business, Nursing and Engineering. The provincial university also houses the Atlantic Veterinary College
The Atlantic Veterinary College (AVC) is an accredited and globally recognized veterinary school in the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine at University of Prince Edward Island, located in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada.
History
AVC ...
.
Charlottetown is also home to several campuses of Holland College
Holland College is the provincial community college for the Canadian province of Prince Edward Island (PEI). It is named after the British Army engineer and surveyor Captain Samuel Holland. In 2024, about 30% of the college's enrolled student ...
, the province's community college. In addition, there are various private training colleges in the city.
Media
Notable people
*Milton Acorn
Milton James Rhode Acorn (March 30, 1923 – August 20, 1986), nicknamed ''The People's Poet'' by his peers, was a Canadian poet, writer, and playwright.
Early life
He was born in Prince Edward Island, and grew up in Charlottetown. He joined the ...
, former poet
*Jared Connaughton
Jared Neal Connaughton (born July 20, 1985) is a Canadian former track athlete who specialized in the 100m and 200m. He is now a physical education cross country, and track and field coach at Fort Worth Country Day in Fort Worth, Texas.
Biograp ...
, Olympic athlete
* Dorothy Corrigan, first and only female mayor of Charlottetown
* Lloyd Duffy, jockey
*Mike Duffy
Michael Dennis Duffy (born May 27, 1946) is a former Canadian senator and Canadian television journalist. Prior to his appointment to the upper house in 2008, he was the Ottawa editor for CTV News Channel. Upon turning 75 on May 27, 2021, Duf ...
, Canadian senator and television journalist
* Kara Grant, Canadian pentathlon
A pentathlon is a contest featuring five events. The name is derived from Greek language, Greek: combining the words ''pente'' (five) and -''athlon'' (competition) (). The first pentathlon was documented in Ancient Greece and was part of the Anci ...
Olympian, 2004 Summer Olympics
The 2004 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the XXVIII Olympiad (), and officially branded as Athens 2004 (), were an international multi-sport event held from 13 to 29 August 2004 in Athens, Greece.
The Games saw 10,625 athletes ...
* Dylan Mohan Gray, filmmaker
*Vern Handrahan
James Vernon Handrahan (November 27, 1936 – November 2, 2016) was a Canadian professional baseball pitcher who played for the Kansas City Athletics of Major League Baseball (MLB) in 1964 and 1966. He is noted for being one of only three major- ...
, former professional baseball player, Kansas City Athletics
The Kansas City Athletics were a Major League Baseball team that played in Kansas City, Missouri, from 1955 to 1967, having previously played in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, as the Philadelphia Athletics. After moving in 1967, the team became the ...
* Wally Hennessey, harness racing driver
*Bonnie Henry
Bonnie J. Fraser Henry (born ) is a Canadian epidemiologist, physician, and public servant who has been the provincial health officer at the British Columbia Ministry of Health since 2014. Henry is also a clinical associate professor at the Unive ...
, provincial officer, British Columbia Ministry of Health
*Ross Johnston
Ross Johnston (born February 18, 1994) is a Canadian professional ice hockey forward for the Anaheim Ducks of the National Hockey League (NHL). He previously played for the New York Islanders.
Playing career
Johnston played junior ice hockey s ...
, professional ice hockey player, New York Islanders
The New York Islanders (colloquially known as the Isles) are a professional ice hockey team based in Elmont, New York. The Islanders compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Metropolitan Division in the Eastern Conference (N ...
*Lorie Kane
Lorie Kane, (born December 19, 1964, in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada) is a professional golfer on the LPGA Tour. She began her career on the LPGA Tour in 1996 and has four career victories and 99 top-10 finishes on the tour. She w ...
, professional LPGA
The Ladies Professional Golf Association (LPGA) is an American organization for female golfers. The organization is headquartered at LPGA International in Daytona Beach, Florida, and is best known for running the LPGA Tour, a series of weekly ...
golfer
* Joey Kitson, Celtic rock
Celtic rock is a genre of folk rock, as well as a form of Celtic fusion which incorporates Celtic music, instrumentation and themes into a rock music context. It has been prolific since the early 1970s and can be seen as a key foundation of the ...
musician and lead singer, Rawlins Cross
*Troy Little
Troy Little (born 7 March 1973) is a Canadian cartoonist working in comic books and animation. He began self publishing with ''Chiaroscuro (graphic novel), Chiaroscuro'', a graphic novel that was developed between 2000 and 2005 under his Meanwhile ...
, comic book artist, graphic designer, creator of ''Chiaroscuro
In art, chiaroscuro ( , ; ) is the use of strong contrasts between light and dark, usually bold contrasts affecting a whole composition. It is also a technical term used by artists and art historians for the use of contrasts of light to ach ...
''
* Whitney Rose, country musician
*Al MacAdam
Reginald Alan MacAdam (born March 16, 1952) is a Canadian former professional ice hockey player who spent 12 seasons in the National Hockey League (NHL) between 1973 and 1985, and was twice selected to play in the NHL All-Star Game. He is best kn ...
, former professional ice hockey player, Minnesota North Stars
The Minnesota North Stars were a professional ice hockey team in the National Hockey League (NHL) for 26 seasons, from 1967 to 1993. The North Stars played their home games at the Met Center in Bloomington, Minnesota, and the team's colors for ...
, Philadelphia Flyers
The Philadelphia Flyers are a professional ice hockey team based in Philadelphia. The Flyers compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Metropolitan Division in the Eastern Conference (NHL), Eastern Conference. The team play ...
, and Vancouver Canucks
The Vancouver Canucks are a professional ice hockey team based in Vancouver. The Canucks compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Pacific Division (NHL), Pacific Division in the Western Conference (NHL), Western Conferenc ...
* Amber MacArthur, television personality and author
* David MacEachern, Olympic gold medalist bobsled
Bobsleigh or bobsled is a winter sport in which teams of 2 to 4 athletes make timed speed runs down narrow, twisting, banked, iced tracks in a gravity-powered sleigh. International bobsleigh competitions are governed by the International Bobs ...
, 1998 Winter Olympics
The 1998 Winter Olympics, officially known as the and commonly known as Nagano 1998 (), were a winter multi-sport event held from 7 to 22 February 1998, mainly in Nagano, Nagano, Nagano, Nagano Prefecture, Japan, with some events ...
*Zack MacEwen
Zack MacEwen (born July 8, 1996) is a Canadian professional ice hockey forward for the Belleville Senators of the American Hockey League (AHL) while under contract to the Ottawa Senators of the National Hockey League (NHL). He previously played fo ...
, professional ice hockey player, Ottawa Senators
The Ottawa Senators (), officially the Ottawa Senators Hockey Club and colloquially known as the Sens, are a professional ice hockey team based in Ottawa. The Senators compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Atlantic Di ...
* Charles Andrew MacGillivary, Medal of Honor
The Medal of Honor (MOH) is the United States Armed Forces' highest Awards and decorations of the United States Armed Forces, military decoration and is awarded to recognize American United States Army, soldiers, United States Navy, sailors, Un ...
recipient for action with the U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of the United Stat ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
*Martha MacIsaac
Martha MacIsaac (born October 11, 1984) is a Canadian actress. She has appeared in several feature films, including ''Superbad (film), Superbad'' (2007), ''The Last House on the Left (2009 film), The Last House on the Left'' (2009), ''Dead Before ...
, actress
*Tara MacLean
Tara Margaret Charity MacLean (born October 25, 1973) is a Canadian musician, singer, and composer.
Her songs as a solo artist include "Evidence", "If I Fall (Tara MacLean song), If I Fall", and a cover of the Christmas song "Light of the Stabl ...
, singer-songwriter
* Cynthia MacLeod, fiddler
*Elizabeth S. MacLeod
Elizabeth Susan MacLeod (23 February 1842 – 15 January 1939) was a Scottish-born Canadian poet, called the "Island Poetess" in reference to her adopted home, Prince Edward Island.
Early life and education
Elizabeth Susan MacQueen was born in E ...
, poet
* Don McDougall, former president, Labatt Brewing Company
Labatt Brewing Company Limited () is a Anheuser-Busch InBev-owned brewery headquartered in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Founded in 1847, Labatt is the largest brewer in Canada.
In 1995, it was purchased by Belgian brewer Interbrew. In 2004, Interb ...
*Adam McQuaid
Adam McQuaid (born October 12, 1986) is a Canadian former professional ice hockey defenceman. He formerly played in the National Hockey League (NHL) with the Boston Bruins, New York Rangers and Columbus Blue Jackets. McQuaid was known primarily as ...
, former professional ice hockey player, Boston Bruins
The Boston Bruins are a professional ice hockey team based in Boston. The Bruins compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Atlantic Division (NHL), Atlantic Division in the Eastern Conference (NHL), Eastern Conference. The t ...
, Columbus Blue Jackets
The Columbus Blue Jackets (often simply referred to as the Jackets) are a professional ice hockey team based in Columbus, Ohio. The Blue Jackets compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Metropolitan Division in the Eastern C ...
, and New York Rangers
The New York Rangers are a professional ice hockey team based in New York City. The Rangers compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Metropolitan Division in the Eastern Conference (NHL), Eastern Conference. The team plays ...
* Sarah Newcomb Merrick, teacher, writer, businessperson, and physician
* Don Messer, fiddler and radio and TV show host, ''Don Messer's Jubilee''
*Lucy Maud Montgomery
Lucy Maud Montgomery (November 30, 1874 – April 24, 1942), published as L. M. Montgomery, was a Canadian author best known for a collection of novels, essays, short stories, and poetry beginning in 1908 with '' Anne of Green Gables''. Sh ...
, author
*Heather Moyse
Heather Moyse (born July 23, 1978) is a Canadian athlete and two-time Olympic gold medalist, representing Canada in international competition as a bobsledder, rugby union player, and track cyclist and competing at the Canadian intercollegiate ...
, Olympic gold medalist in bobsledding, 2010
The year saw a multitude of natural and environmental disasters such as the 2010 Haiti earthquake, the Deepwater Horizon oil spill, and the 2010 Chile earthquake. The 2009 swine flu pandemic, swine flu pandemic which began the previous year ...
and 2014 Winter Olympics
The 2014 Winter Olympics, officially called the XXII Olympic Winter Games () and commonly known as Sochi 2014 (), were an international winter multi-sport event that was held from 7 to 23 February 2014 in Sochi, Russia. Opening ro ...
*Chris Murphy
Christopher Scott Murphy (born August 3, 1973) is an American lawyer, author, and politician serving as the junior United States senator from the state of Connecticut since 2013. A member of the Democratic Party, he previously served in the U ...
, rock musician, Sloan
* Gary Simmons, former professional ice hockey player, California Golden Seals
The California Golden Seals were a professional ice hockey club that competed in the National Hockey League (NHL) from 1967–68 NHL season, 1967 to 1975–76 NHL season, 1976. Based in Oakland, California, they played their home games at the Oa ...
, Cleveland Barons, and Los Angeles Kings
The Los Angeles Kings are a professional ice hockey team based in Los Angeles. The Kings compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Pacific Division (NHL), Pacific Division in the Western Conference (NHL), Western Conference. ...
* Frederick Thornton Peters, Victoria Cross
The Victoria Cross (VC) is the highest and most prestigious decoration of the Orders, decorations, and medals of the United Kingdom, British decorations system. It is awarded for valour "in the presence of the enemy" to members of the British ...
recipient for action off the coast of Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
*Jackie Torrens
Jackie Torrens is a Canadian actress, writer and filmmaker based in Halifax, Nova Scotia. She was born in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island.
Acting
She began her career as an actress, most notably being cast as the frumpy but shrewd office mana ...
, comedian, '' Made in Canada'', actor, writer, and journalist
*Jonathan Torrens
Jonathan Ormond Torrens (born October 2, 1972) is a Canadian actor and television personality best known for his co-hosting of ''Street Cents'', his talk show ''Jonovision'', and his role as "J-Roc" in the popular Canadian mockumentary ''Trailer ...
, actor, writer, and producer
*Brian Tracy
Brian Tracy is a Canadian-American motivational public speaker and self-development author. He is the author of over eighty books that have been translated into dozens of languages. His popular books are ''Earn What You're Really Worth'', ''Eat ...
, self-development author and board member, The Heritage Foundation
The Heritage Foundation (or simply Heritage) is an American Conservatism in the United States, conservative think tank based in Washington, D.C. Founded in 1973, it took a leading role in the conservative movement in the 1980s during the Presi ...
*Rick Vaive
Richard Claude Vaive (; born May 14, 1959) is a Canadian former professional ice hockey player. He played in the final season of the World Hockey Association (WHA) and played in the National Hockey League (NHL) from 1979 to 1992. While with the T ...
, former professional ice hockey player, Toronto Maple Leafs
The Toronto Maple Leafs (officially the Toronto Maple Leaf Hockey Club and often referred to as the Leafs) are a professional ice hockey team based in Toronto. The Maple Leafs compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the A ...
and other teams
*William Henry Weeks
William Henry Weeks (1864–1936) was an early 20th-century architect who designed hundreds of buildings including many schools, banks, and libraries. He was best known for the monumental neoclassicism, neoclassical style of his public building ...
, former architect in California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
* James Wood, former Commander of the Royal Canadian Navy
Commander of the Royal Canadian Navy ( French: ''Commandant de la Marine royale canadienne'') is the title of the institutional head of the Royal Canadian Navy. This appointment also includes the title of Chief of the Naval Staff and is based at ...
See also
*Royal eponyms in Canada
In Canada, a number of sites and structures are named for royal individuals, whether a member of the past French royal family, British royal family, or present Canadian royal family thus reflecting the country's status as a constitutional mona ...
* Provinces and territories of Canada
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Constitution of Canada, Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North Amer ...
References
Notes
External links
* {{Authority control 1764 establishments in the British Empire Cities in Prince Edward Island Former colonial capitals in Canada Populated coastal places in Canada Populated places established in 1764