changwat on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The provinces of Thailand are administrative divisions of the
National Administration Act 1991 and its amendments
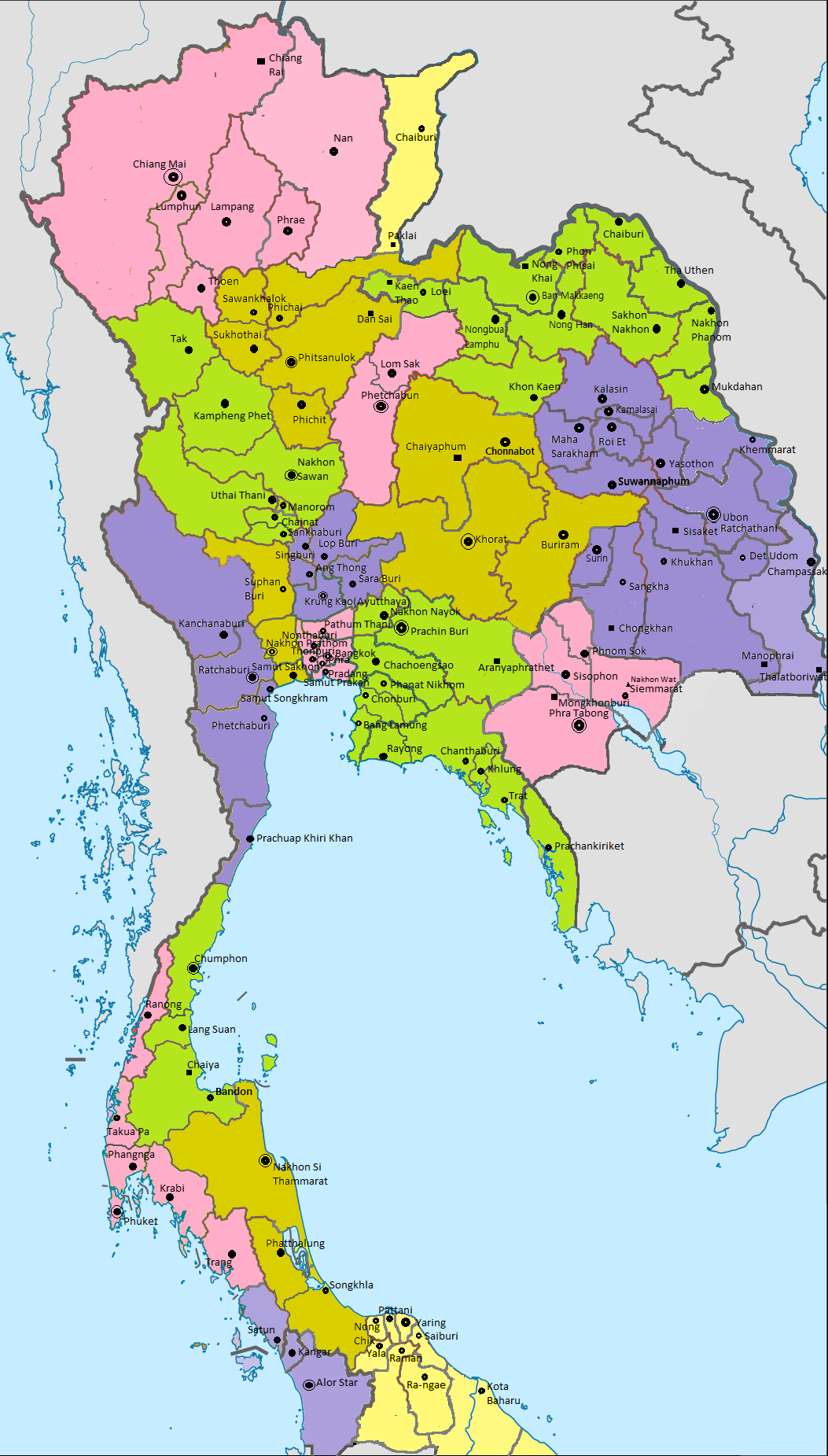
The country is divided into 76
 At the end of the 19th century King
At the end of the 19th century King  When Prince Damrong resigned in 1915, the whole country was divided into 19 monthon (including the area around Bangkok, which was under the responsibility of another ministry until 1922), with 72 provinces.
In December 1915 King
When Prince Damrong resigned in 1915, the whole country was divided into 19 monthon (including the area around Bangkok, which was under the responsibility of another ministry until 1922), with 72 provinces.
In December 1915 King
File:Map of Ayutthaya Kingdom in 1468.jpg, Ayutthaya administrative division in 1468 ( Borommarachathirat III)
File:Map of Ayutthaya Kingdom in 1767.jpg, Ayutthaya administrative division in 1767 ( Borommaracha III)
File:Map of Thonburi Kingdom in 1780.jpg, Thonburi administrative division in 1780 ( Borommaracha IV)
File:Map of Rattanakosin Kingdom in 1800.jpg, Rattanakosin administrative division in 1800 (
Department of Provincial Administration
Pronunciation of provinces in Thailand at www.forvo.com
{{DEFAULTSORT:Provinces Of Thailand Subdivisions of Thailand Thailand geography-related lists Thailand 1 Provinces, Thailand Thailand, provinces by area
government of Thailand
Government of Thailand, officially the Royal Thai Government (RTG; , , ), is the central executive authority of the Kingdom of Thailand. The government is led by the prime minister of Thailand, prime minister (Paetongtarn Shinawatra since 14 ...
.Office of the Council of State of ThailandNational Administration Act 1991 and its amendments
The country is divided into 76
province
A province is an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire, Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
s (, , ) proper, with one additional special administrative area (the capital, Bangkok). They are the primary local government units and act as juristic persons
A juridical person is a legal person that is not a natural person but an organization recognized by law as a fictitious person such as a corporation, government agency, non-governmental organisation, or international organization (such as the Eu ...
. They are divided into amphoe
An amphoe (sometimes also ''amphur'', , )—usually translated as "district"—is the second level administrative subdivision of Thailand. Groups of ''amphoe'' or districts make up the Provinces of Thailand, provinces, and are analogous to count ...
(districts) which are further divided into tambon
''Tambon'' (, ) is a local governmental unit in Thailand. Below district (''amphoe'') and province ('' changwat''), they form the third administrative subdivision level. there were 7,255 tambons, not including the 180 ''khwaeng'' of Bangkok, whi ...
(sub districts), the next lower level of local government.
All provinces form part of the partially devolved central government, or the regional government (ราชการส่วนภูมิภาค ). Majority of public services, including police, prison, transport, public relation and others are still overseen and managed by the province on behalf of the central government. In 1938–1996, the Royal Thai Government proposed that each province should have a council, elected from people resided within that province. The council acts as an advisory and auditing body to the governor (ผู้ว่าราชการจังหวัด ), who is appointed by the central government. In 1997, each province has its own provincial administrative organization (องค์การบริหารส่วนจังหวัด ), presided over by the president. The PAO manages some public services related to the province. It was expected that the PAO president will become the elected governor (instead of a centrally-appointed one), but the full devolution of the government has not happened. The PAO as well as other municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality' ...
form part of the local self-governing government (ราชการส่วนท้องถิ่น ).
Bangkok, the sole special administrative area, combines the tasks of the provinces with that of a municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality' ...
, including having an elected governor. The average area of the 76 provinces of Thailand plus Bangkok is about , while its average population of all 77 divisions of Thailand is about 908,064 people.
76 provinces in Thailand
* The total population of Thailand is 65,951,000 as of December 2024. * The total land area of Thailand is 517,646 km2 in 2013. * The total land area of Chiang Mai province is 22,311 sq.km * HS – Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System. * FIPS code is replaced on 31 December 2014 with ISO 3166.Governance
Thailand's national government organisation is divided into three types: central government (ministries
Ministry may refer to:
Government
* Ministry (collective executive), the complete body of government ministers under the leadership of a prime minister
* Ministry (government department), a department of a government
Religion
* Christian mi ...
, bureaus and departments), provincial government (provinces and districts
A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions ...
) and local government (Bangkok, Pattaya
Pattaya is a city in Eastern Thailand, the second-largest city in Chonburi province and the List of municipalities in Thailand, eighth-largest city in Thailand. It is on the east coast of the Gulf of Thailand, about southeast of Bangkok, and h ...
, provincial administrative organisations, etc.).
A province, as part of the provincial government, is administered by a governor (ผู้ว่าราชการจังหวัด) who is appointed by the Minister of Interior. Bangkok, as part of the local government, is administered by a corporation called Bangkok Metropolitan Administration
The Bangkok Metropolitan Administration (BMA) is the local government of Bangkok, which includes the capital of Thailand. The government is composed of two branches: the executive (or the Governor of Bangkok) and the legislative (or Bangkok Metro ...
. The corporation is led by the Governor of Bangkok (ผู้ว่าราชการกรุงเทพมหานคร) who is directly elected by the citizens of Bangkok.
The provinces are named after their original main city, which may not necessarily still be the most populous city within the province today. Also, in several provinces the administration has been moved into a new building outside the city.
History
Before 1892
Many provinces date back to semi-independent local chiefdoms or kingdoms, which made up theAyutthaya Kingdom
The Ayutthaya Kingdom or the Empire of Ayutthaya was a Thai people, Thai kingdom that existed in Southeast Asia from 1351 to 1767, centered around the city of Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya (city), Ayutthaya, in Siam, or present-day Thailand. Europe ...
. The provinces were created around a capital city (''mueang
Mueang ( Ahom: 𑜉𑜢𑜤𑜂𑜫; ''mɯ̄ang'', ), Muang ( ''mɯ́ang'', ), Möng ( Tai Nuea: ᥛᥫᥒᥰ ''möeng''; ''móeng'', ), Meng ( zh, c=猛 or 勐) or Mường (Vietnamese) were pre-modern semi-independent city-states or princip ...
''), and included surrounding villages or satellite towns. The provinces were administered either by a governor, who was appointed by the king or by a local ruling family, who were descendants of the old kings and princes of that area and had been given this privilege by the central king. De facto the king did not have much choice but to choose someone from the local nobility or an economically strong man, as against these local power groups the administration would have become impossible. The governor was not paid by the king, but instead financed himself and his administration by imposing local taxes himself. Every province was required to send an annual tribute to Bangkok.
The provinces were divided into four different classes. The first-class were the border provinces. The second-class were those that once had their own princely house. Third-class were provinces that were created by splitting them from other provinces. Fourth-class were provinces near the capital. Additionally tributary states like the principalities of Lan Na
The Lan Na kingdom or the Kingdom of Lanna (, , "Kingdom of a Million Rice Fields"; , , ), also known as Lannathai, was an Indianized state centered in present-day Northern Thailand from the 13th to the 18th centuries.
The cultural developmen ...
, the Laotian kingdoms of Vientiane
Vientiane (, ) is the capital city, capital and largest city of Laos. Situated on the banks of the Mekong, Mekong River at the Thailand, Thai border, it comprises the five urban districts of Vientiane Prefecture and had a population of 840,000 ...
and Luang Prabang
Luang Prabang (Lao language, Lao: wikt:ຫຼວງພະບາງ, ຫຼວງພະບາງ, pronounced ), historically known as Xieng Thong (ຊຽງທອງ) and alternatively spelled Luang Phabang or Louangphabang, is the capital of Lu ...
, Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
, or the Malay sultanate Kedah
Kedah (), also known by its honorific Darul Aman (Islam), Aman (دار الأمان; Arabic for 'The Safe Abode') and historically as Queda, is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Malaysia, located in the northwestern part of ...
were also part of the country, but with more autonomy than the provinces. In this Mandala system the semi-independent countries sometimes were tributary to more than one country.
New provinces were created when the population of an area outgrew the administration, but also for political reasons. If a governor became too dominant in a region former satellite cities were elevated to provincial status, as was the case with Maha Sarakham province.
Reforms of the provincial administration started in the 1870s under increased pressure from the colonial states of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
and France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
. Agents were sent, especially to border areas, to impose more control on the provinces or tributary states.
Administrative reform of 1892
 At the end of the 19th century King
At the end of the 19th century King Chulalongkorn
Chulalongkorn (20 September 1853 – 23 October 1910), posthumously honoured as King Chulalongkorn the Great, was the fifth king of Siam from the Chakri dynasty, titled Rama V. Chulalongkorn's reign from 1868 until his death in 1910 was cha ...
reformed the central government. In 1892 the ministry, which previously had many overlapping responsibilities, was reorganized with clear missions as in Western administrations. Prince Damrong Rajanubhab
Prince Tisavarakumara, the Prince Damrong Rajanubhab (; Full transcription is "Somdet Phrachao Borommawongthoe Phra-ongchao Ditsawarakuman Kromphraya Damrongrachanuphap" (สมเด็จพระเจ้าบรมวงศ์เธอ พ� ...
became minister of the Ministry of the North ('' Mahatthai''), originally responsible for the northern administration. When the Ministry of the South (''Kalahom
Chatusadom or Catustambha ( , literally "Four Pillars" from Sanskrit language, Sanskrit ''Catur'' "Four" + ''Stambha'' "Pillars") was the Thai system of central executive governance during the Ayutthaya Kingdom, Thonburi Kingdom and Rattanakosin ...
'') was dissolved in 1894, Prince Damrong became Minister of the Interior, responsible for the provincial administration of the whole country.
Starting in 1893 the already existing commissionaireships in some parts of the country were renamed "superintendent commissioner" (''khaluang Thesaphiban''), and their area of responsibility was called a ''monthon
''Monthon'' (), also known as ''Monthon Thesaphiban'' (; Mṇṯhl Theṣ̄āp̣hibāl; , ), were Administrative divisions of Thailand, administrative subdivisions of Thailand at the beginning of the 20th century. The Thai word ''monthon'' is a tr ...
''. In strategically important areas the monthon were created first, while in other areas the provinces kept their independence a bit longer. Several smaller provinces were reduced in status to an ''amphoe'' (district) or even lower to a ''tambon'' (sub-district) and included in a neighboring province, sometimes for administrative reasons, but sometimes to remove an uncooperative governor.
In some regions rebellions broke out against the new administrative system, usually induced by the local nobility fearing their loss of power. The most notable was the Holy Man Rebellion in 1902 in Isan
Northeast Thailand or Isan (Isan language, Isan/, ; ; also written as Isaan, Isarn, Issarn, Issan, Esan, or Esarn; from Pāli ''isāna'' or Sanskrit ईशान्य ''īśānya'' "northeast") consists of 20 provinces in northeastern Thai ...
. It was initially a messianic doomsday sect, but it also attacked government representatives in the northeast. The provincial town Khemarat was even burned by the rebels. After a few months the rebellion was beaten back.
After 1916, the word ''changwat'' became common to use for the provinces, partly to distinguish them from the provincial capital city (''mueang'' or ''amphoe mueang''), but also to stress the new administrative structure of the provinces.
 When Prince Damrong resigned in 1915, the whole country was divided into 19 monthon (including the area around Bangkok, which was under the responsibility of another ministry until 1922), with 72 provinces.
In December 1915 King
When Prince Damrong resigned in 1915, the whole country was divided into 19 monthon (including the area around Bangkok, which was under the responsibility of another ministry until 1922), with 72 provinces.
In December 1915 King Vajiravudh
Vajiravudh (1 January 188126 November 1925) was the sixth Monarchy of Thailand, king of Siam from the Chakri dynasty, titled Rama VI. He reigned from 1910 until his death in 1925. King Vajiravudh is best known for his efforts to create and pro ...
announced the creation of regions (''phak''), each administered by a viceroy (''upparat''), to cover several monthon. Until 1922 four regions were established; however, in 1925 they were dissolved again. At the same time several monthon were merged, in an attempt to streamline administration and reduce costs.
Since 1932
The monthons were dissolved when Thailand transformed from an absolute monarchy into a constitutional monarchy in 1932, making the provinces the top level administrative division again. Several smaller provinces were also abolished at that time. During World War II, several provinces around Bangkok were merged. These changes were undone after the war. Also the occupied area from French Indochina was organized into four provinces: Phra Tabong, Phibunsongkhram, Nakhon Champasak and Lan Chang. The current province of Sukhothai was at first known as Sawankhalok. It was renamed Sukhothai in 1939 (which is why the railway system goes to Sawankhalok city and not Sukhothai city). The province, Kalasin, was reestablished in 1947 after having been dissolved in 1932. In 1972 Phra Nakhon and Thonburi provinces were merged to form the special administrative area of Bangkok, which combines the tasks of the provinces with that of amunicipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality' ...
, including having an elected governor.
Starting in the second half of the 20th century some provinces were newly created by splitting them off from bigger provinces. In 1975, Yasothon province was split off from Ubon Ratchathani. In 1977, Phayao province was created from districts formerly part of Chiang Rai. In 1982, Mukdahan was split off from Nakhon Phanom. In 1993 three provinces were created: Sa Kaeo (split from Prachinburi), Nong Bua Lamphu province (split from Udon Thani), and Amnat Charoen
Amnat Charoen (, ) is a town in Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. Wi ...
(split from Ubon Ratchathani). The newest province is Bueng Kan
Bueng Kan (, ) is a town municipality ('' thesaban mueang'') in Mueang Bueng Kan district, in Bueng Kan province, Isan (northeastern Thailand). It is the district capital and is on the Mekong River, opposite the Laotian town of Pakxan of Bol ...
, which was split off from Nong Khai effective 23 March 2011.
Former provinces and administrative areas
Former provinces merged into other provinces
Conceded territories (including protectorates)
Map of Siam in early 1893
Historic administrative divisions of Thailand
Rama I
Phutthayotfa Chulalok (born Thongduang; 20 March 1737 – 7 September 1809), also known by his regnal name Rama I, was the founder of the Rattanakosin Kingdom (now Thailand) and the first King of Siam from the reigning Chakri dynasty. He asc ...
)
File:Map of Rattanakosin Kingdom in 1805.jpg, Rattanakosin administrative division in 1805 (Rama I
Phutthayotfa Chulalok (born Thongduang; 20 March 1737 – 7 September 1809), also known by his regnal name Rama I, was the founder of the Rattanakosin Kingdom (now Thailand) and the first King of Siam from the reigning Chakri dynasty. He asc ...
)
File:Map of Rattanakosin Kingdom in 1824.jpg, Rattanakosin administrative division in 1824 (Rama II
Phutthaloetla Naphalai (born Chim; 24 February 1767 or 1768 – 21 July 1824), also known by his regnal name Rama II, was the second King of Siam from the Chakri dynasty, ruling from 1809 to 1824. In 1809, Itsarasunthon succeeded his father R ...
)
File:Map of Rattanakosin Kingdom in 1837.jpg, Rattanakosin administrative division in 1837 ( Rama III)
File:Map of Rattanakosin Kingdom in 1850.jpg, Rattanakosin administrative division in 1850 ( Rama III)
File:Map of Rattanakosin Kingdom in 1882.jpg, Rattanakosin administrative division in 1882 (Rama V
Chulalongkorn (20 September 1853 – 23 October 1910), posthumously honoured as King Chulalongkorn the Great, was the fifth Monarchy of Thailand, king of Siam from the Chakri dynasty, titled Rama V. Chulalongkorn's reign from 1868 until his ...
)
File:Map of Siamese Kingdom in 1890.jpg, Siamese administrative division in 1890 (Rama V
Chulalongkorn (20 September 1853 – 23 October 1910), posthumously honoured as King Chulalongkorn the Great, was the fifth Monarchy of Thailand, king of Siam from the Chakri dynasty, titled Rama V. Chulalongkorn's reign from 1868 until his ...
)
File:Map of Siamese Kingdom in 1893.jpg, Siamese administrative division in 1893 (Rama V
Chulalongkorn (20 September 1853 – 23 October 1910), posthumously honoured as King Chulalongkorn the Great, was the fifth Monarchy of Thailand, king of Siam from the Chakri dynasty, titled Rama V. Chulalongkorn's reign from 1868 until his ...
)
File:Map of Siamese Kingdom in 1900.jpg, Siamese administrative division in 1900 (Rama V
Chulalongkorn (20 September 1853 – 23 October 1910), posthumously honoured as King Chulalongkorn the Great, was the fifth Monarchy of Thailand, king of Siam from the Chakri dynasty, titled Rama V. Chulalongkorn's reign from 1868 until his ...
)
File:Map of Siamese Kingdom in 1906.jpg, Siamese administrative division in 1906 (Rama V
Chulalongkorn (20 September 1853 – 23 October 1910), posthumously honoured as King Chulalongkorn the Great, was the fifth Monarchy of Thailand, king of Siam from the Chakri dynasty, titled Rama V. Chulalongkorn's reign from 1868 until his ...
)
File:Map of Siamese Kingdom in 1908.jpg, Siamese administrative division in 1908 (Rama V
Chulalongkorn (20 September 1853 – 23 October 1910), posthumously honoured as King Chulalongkorn the Great, was the fifth Monarchy of Thailand, king of Siam from the Chakri dynasty, titled Rama V. Chulalongkorn's reign from 1868 until his ...
)
File:Map of Siamese Kingdom in 1916.jpg, Siamese administrative division in 1916 ( Rama VI)
File:Map of Thai Kingdom in 1932.jpg, Siamese administrative division in 1932 ( Rama VII)
File:Map of Siam Kingdom in 1941.jpg, Thai administrative division in 1941 ( Rama VIII)
File:Map of Thai Kingdom in 1945.jpg, Thai administrative division in 1945 ( Rama VIII)
File:Map of Thai Kingdom in 1950.jpg, Thai administrative division in 1950 (Rama IX
Bhumibol Adulyadej (5 December 192713 October 2016), titled Rama IX, was King of Thailand from 1946 until Death and funeral of Bhumibol Adulyadej, his death in 2016. His reign of 70 years and 126 days is the longest of any List of Thai mo ...
)
File:Map of Thai Kingdom in 1973.jpg, Thai administrative division in 1973 (Rama IX
Bhumibol Adulyadej (5 December 192713 October 2016), titled Rama IX, was King of Thailand from 1946 until Death and funeral of Bhumibol Adulyadej, his death in 2016. His reign of 70 years and 126 days is the longest of any List of Thai mo ...
)
File:Map of Thai Kingdom in 2023.jpg, Thai administrative division in 2023 (Rama X
Vajiralongkorn (born 28 July 1952) is King of Thailand. He is the tenth Thai monarch of the Chakri dynasty since ascending the throne in 2016 with the regnal name Rama X.
The only son of King Bhumibol Adulyadej (Rama IX) and Queen Sirik ...
)
See also
* ISO 3166-2:TH * List of districts of Thailand * List of Thai provinces by GPP * Nationality, religion, and language data for the provinces of Thailand *Organization of the government of Thailand
Thailand is a unitary state in Southeast Asia. The administrative services of the executive branch of the government are regulated by the ''National Government Organisation Act, BE 2534 (1991)'' (พระราชบัญญัติระเ ...
* Seals of the provinces of Thailand
This is a list of the seals of the provinces of Thailand ().
Current provinces
This list includes all the seal (emblem), seals of the provinces of Thailand. It also includes the special administrative area of the capital, Bangkok.
Former provinc ...
* Administrative divisions of Thailand
Thailand is a unitary state, which means the territories are separated into central co-dependencies, with the central government deciding everything for the provinces. The kingdom is separated into multiple levels including regions, provinces, a ...
References
Further reading
*External links
Department of Provincial Administration
Pronunciation of provinces in Thailand at www.forvo.com
{{DEFAULTSORT:Provinces Of Thailand Subdivisions of Thailand Thailand geography-related lists Thailand 1 Provinces, Thailand Thailand, provinces by area
Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
Geography of Thailand