cerebral circulation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cerebral circulation is the movement of

 The anterior cerebral circulation is the blood supply to the anterior portion of the brain including eyes. It is supplied by the following arteries:
* Internal carotid arteries: These large arteries are the medial branches of the common carotid arteries which enter the skull, as opposed to the external carotid branches which supply the facial tissues; the internal carotid artery branches into the
The anterior cerebral circulation is the blood supply to the anterior portion of the brain including eyes. It is supplied by the following arteries:
* Internal carotid arteries: These large arteries are the medial branches of the common carotid arteries which enter the skull, as opposed to the external carotid branches which supply the facial tissues; the internal carotid artery branches into the
 The posterior cerebral circulation is the blood supply to the posterior portion of the brain, including the occipital lobes,
The posterior cerebral circulation is the blood supply to the posterior portion of the brain, including the occipital lobes,
 Cerebral blood flow (CBF) is the blood supply to the
Cerebral blood flow (CBF) is the blood supply to the
Computer Model of the Cerebral Circulation for Training and Education
{{VeinsHeadNeck Neurology Cardiology
blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
through a network of cerebral arteries and veins supplying the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
. The rate of cerebral blood flow
Hemodynamics American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or haemodynamics are the Fluid dynamics, dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostasis, homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydrau ...
in an adult human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
is typically 750 milliliters per minute
A minute is a unit of time defined as equal to 60 seconds.
It is not a unit in the International System of Units (SI), but is accepted for use with SI. The SI symbol for minutes is min (without a dot). The prime symbol is also sometimes used i ...
, or about 15% of cardiac output. Arteries deliver oxygenated blood, glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
and other nutrients to the brain. Vein
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and feta ...
s carry "used or spent" blood back to the heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
, to remove carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
, lactic acid
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has the molecular formula C3H6O3. It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as wel ...
, and other metabolic
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the ...
products. The neurovascular unit regulates cerebral blood flow so that activated neurons can be supplied with energy in the right amount and at the right time. Because the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
would quickly suffer damage from any stoppage in blood supply, the cerebral circulatory system has safeguards including autoregulation of the blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s. The failure of these safeguards may result in a stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
. The volume
Volume is a measure of regions in three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch) ...
of blood in circulation is called the cerebral blood flow
Cerebral circulation is the movement of blood through a network of cerebral arteries and veins supplying the brain. The rate of cerebral blood flow in an adult human is typically 750 milliliters per minute, or about 15% of cardiac output. ...
. Sudden intense accelerations change the gravitational forces perceived by bodies and can severely impair cerebral circulation and normal functions to the point of becoming serious life-threatening conditions.
The following description is based on idealized human cerebral circulation. The pattern of circulation and its nomenclature
Nomenclature (, ) is a system of names or terms, or the rules for forming these terms in a particular field of arts or sciences. (The theoretical field studying nomenclature is sometimes referred to as ''onymology'' or ''taxonymy'' ). The principl ...
vary between organisms.
Anatomy

Blood supply
Blood supply to the brain is normally divided into anterior and posterior segments, relating to the different arteries that supply the brain. The two main pairs of arteries are the internal carotid arteries (supply the anterior brain) and vertebral arteries (supplying thebrainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
and posterior brain). The anterior and posterior cerebral circulations are interconnected via bilateral posterior communicating arteries. They are part of the circle of Willis, which provides backup circulation to the brain. In case one of the supply arteries is occluded, the circle of Willis provides interconnections between the anterior and the posterior cerebral circulation along the floor of the cerebral vault, providing blood to tissues that would otherwise become ischemic.
Anterior cerebral circulation
 The anterior cerebral circulation is the blood supply to the anterior portion of the brain including eyes. It is supplied by the following arteries:
* Internal carotid arteries: These large arteries are the medial branches of the common carotid arteries which enter the skull, as opposed to the external carotid branches which supply the facial tissues; the internal carotid artery branches into the
The anterior cerebral circulation is the blood supply to the anterior portion of the brain including eyes. It is supplied by the following arteries:
* Internal carotid arteries: These large arteries are the medial branches of the common carotid arteries which enter the skull, as opposed to the external carotid branches which supply the facial tissues; the internal carotid artery branches into the anterior cerebral artery
The anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes of the brain. The two anterior cerebral arteries arise from th ...
and continues to form the middle cerebral artery.
* Anterior cerebral artery
The anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes of the brain. The two anterior cerebral arteries arise from th ...
(ACA)
** Anterior communicating artery: Connects both anterior cerebral arteries, within and along the floor of the cerebral vault.
* Middle cerebral artery (MCA)
Posterior cerebral circulation
cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or eve ...
and brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
.
It is supplied by the following arteries:
* Vertebral arteries: These smaller arteries branch from the subclavian arteries which primarily supply the shoulders, lateral chest, and arms. Within the cranium the two vertebral arteries fuse into the basilar artery.
** Posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA)
* Basilar artery: Supplies the midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.
It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, mo ...
, cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or eve ...
, and usually branches into the posterior cerebral artery
The posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the occipital lobe, as well as the medial and inferior aspects of the temporal lobe of the human brain. The two arteries originate from the d ...
** Anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA)
** Pontine branches
** Superior cerebellar artery (SCA)
* Posterior cerebral artery
The posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the occipital lobe, as well as the medial and inferior aspects of the temporal lobe of the human brain. The two arteries originate from the d ...
(PCA)
* Posterior communicating artery
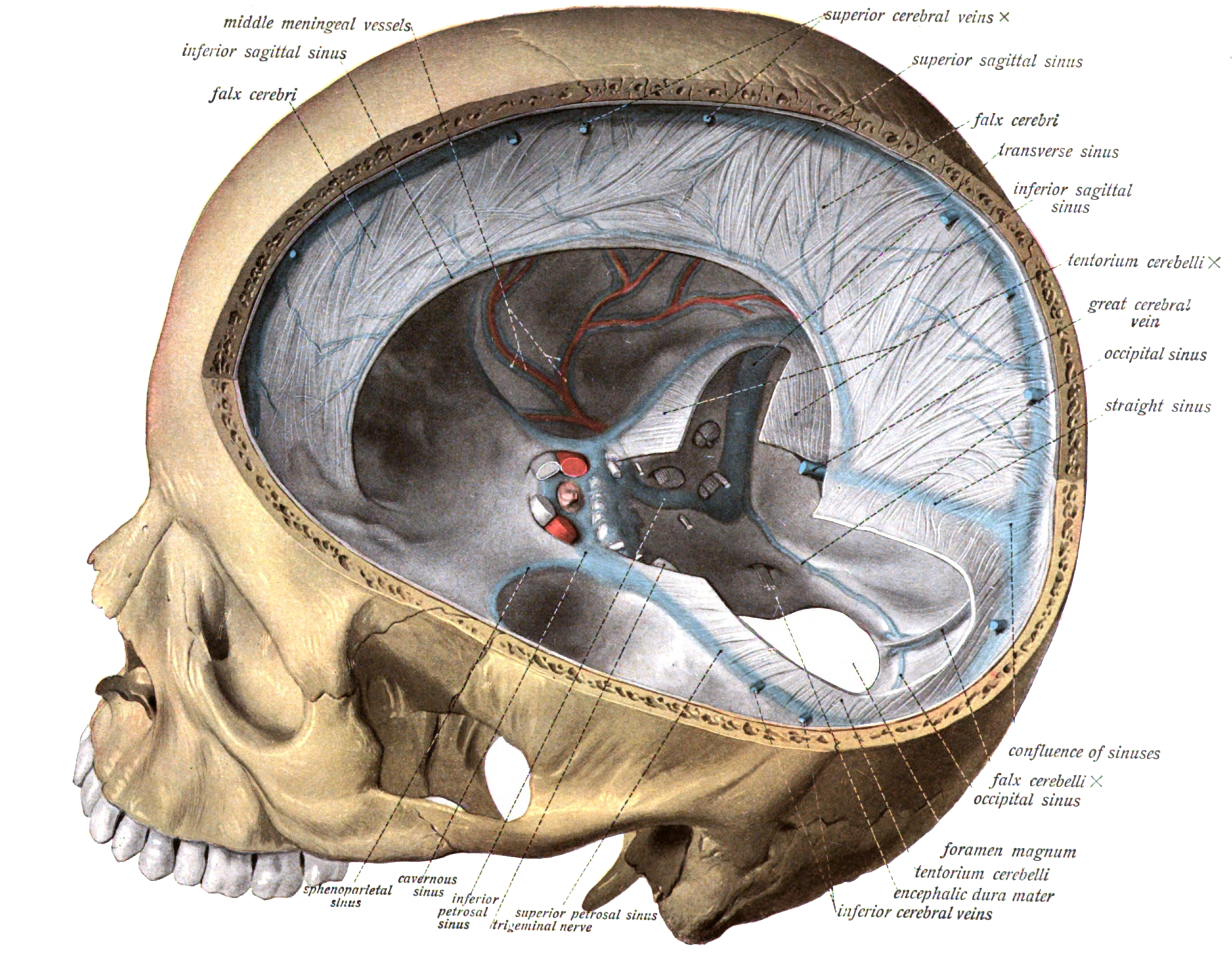
Venous drainage
The venous drainage of the cerebrum can be separated into two subdivisions: superficial and deep. ;The superficial system The superficial system is composed of dural venous sinuses, sinuses (channels) within the dura mater. The dural sinuses are therefore located on the surface of the cerebrum. The most prominent of these sinuses is the superior sagittal sinus which is located in the sagittal plane under the midline of the cerebral vault, posteriorly and inferiorly to the confluence of sinuses, where the superficial drainage joins with the sinus that primarily drains the deep venous system. From here, two transverse sinuses bifurcate and travel laterally and inferiorly in an S-shaped curve that forms thesigmoid sinuses
The sigmoid sinuses (sigma- or s-shaped hollow curve), also known as the , are paired dural venous sinuses within the skull that receive blood from posterior transverse sinuses.
Structure
The sigmoid sinus is a dural venous sinus situated within ...
which go on to form the two jugular veins. In the neck, the jugular veins parallel the upward course of the carotid arteries
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) () are arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external and internal carotid arteries.
Structure
The common carotid ...
and drain blood into the superior vena cava
The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vei ...
. The veins puncture the relevant dural sinus, piercing the arachnoid and dura mater as bridging veins that drain their contents into the sinus.
;The deep venous system
The deep venous system is primarily composed of traditional veins inside the deep structures of the brain, which join behind the midbrain to form the great cerebral vein (vein of Galen). This vein merges with the inferior sagittal sinus to form the straight sinus which then joins the superficial venous system mentioned above at the confluence of sinuses.
Maturation of cerebral blood vessels
The maturation of blood vessels in the brain is a critical process that occurs postnatally. It involves the acquisition of key barrier and contractile properties essential for brain function. During the early postnatal phase,endothelial cell
The endothelium (: endothelia) is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and th ...
s (ECs) and vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) undergo significant molecular and functional changes.
Endothelial cells begin to express P-glycoprotein, a crucial efflux transporter that helps protect the brain by expelling harmful substances. This efflux capacity is progressively acquired and becomes fully functional by the postnatal period. Additionally, VSMCs, which initially populate the arterial network, start to express contractile proteins such as smooth muscle actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ...
(SMA) and myosin-11, transforming VSMCs into contractile cells capable of regulating blood vessel tone and cerebral blood flow.
The expression of Myh11 in VSMCs acts as a developmental switch, with significant upregulation occurring from birth to the age of 2 to 5 years. This is a critical period needed for the establishment of vessel contractility and the overall functionality of the cerebral circulation.
Physiology
 Cerebral blood flow (CBF) is the blood supply to the
Cerebral blood flow (CBF) is the blood supply to the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
in a given period of time. In an adult, CBF is typically 750 millilitres per minute or 15.8 ± 5.7% of the cardiac output. This equates to an average perfusion
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ (anatomy), organ or a tissue (biology), tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion may also refer t ...
of 50 to 54 millilitres of blood per 100 grams of brain tissue per minute.
The ratio index of cerebral blood flow/cardiac output (CCRI) decreases by 1.3% per decade, even though cardiac output remains unchanged. Across the adult lifespan, women have a higher CCRI than men. CBF is inversely associated with body mass index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (Mass versus weight, weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the human body weight, body mass divided by the square (algebra), square of the human height, body height, and is ...
.
CBF is tightly regulated to meet the brain's metabolic
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the ...
demands. Too much blood (a clinical condition of a normal homeostatic response of hyperemia) can raise intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adu ...
(ICP), which can compress and damage delicate brain tissue. Too little blood flow (ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems ...
) results if blood flow to the brain is below 18 to 20 ml per 100 g per minute, and tissue death occurs if flow dips below 8 to 10 ml per 100 g per minute. In brain tissue, a biochemical cascade known as the ischemic cascade is triggered when the tissue becomes ischemic, potentially resulting in damage to and the death of brain cells. Medical professionals must take steps to maintain proper CBF in patients who have conditions like shock, stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
, cerebral edema, and traumatic brain injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity ranging from mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI/concussion) to severe traumati ...
.
Cerebral blood flow is determined by a number of factors, such as viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent drag (physics), resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for e ...
of blood, how dilated blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s are, and the net pressure of the flow of blood into the brain, known as cerebral perfusion pressure, which is determined by the body's blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
. Cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) is defined as the mean arterial pressure (MAP) minus the intracranial pressure (ICP). In normal individuals, it should be above 50 mm Hg. Intracranial pressure should not be above 15 mm Hg (ICP of 20 mm Hg is considered as intracranial hypertension). Cerebral blood vessels are able to change the flow of blood through them by altering their diameters in a process called cerebral autoregulation; they constrict when systemic blood pressure is raised and dilate when it is lowered. Arterioles also constrict and dilate in response to different chemical concentrations. For example, they dilate in response to higher levels of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
in the blood and constrict in response to lower levels of carbon dioxide.
For example, assuming a person with an arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide ( PaCO2) of 40 mmHg (normal range of 38–42 mmHg) and a CBF of 50 ml per 100g per min. If the PaCO2 dips to 30 mmHg, this represents a 10 mmHg decrease from the initial value of PaCO2. Consequently, the CBF decreases by 1ml per 100g per min for each 1mmHg decrease in PaCO2, resulting in a new CBF of 40ml per 100g of brain tissue per minute. In fact, for each 1 mmHg increase or decrease in PaCO2, between the range of 20–60 mmHg, there is a corresponding CBF change in the same direction of approximately 1–2 ml/100g/min, or 2–5% of the CBF value. This is why small alterations in respiration pattern can cause significant changes in global CBF, specially through PaCO2 variations.
CBF is equal to the cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) divided by the cerebrovascular resistance (CVR):
:CBF = CPP / CVR
Control of CBF is considered in terms of the factors affecting CPP and the factors affecting CVR. CVR is controlled by four major mechanisms:
# Metabolic
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the ...
control (or 'metabolic autoregulation')
# Pressure autoregulation
# Chemical control (by arterial pCO2 and pO2)
# Neural control
Role of intracranial pressure
Increasedintracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adu ...
(ICP) causes decreased blood perfusion of brain cells by mainly two mechanisms:
* Increased ICP constitutes an increased interstitial hydrostatic pressure that, in turn, causes a decreased driving force for capillary filtration from intracerebral blood vessels.
* Increased ICP compresses cerebral arteries, causing increased cerebrovascular resistance (CVR).
Cerebral perfusion pressure
Cerebral perfusion pressure is the netpressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
gradient causing cerebral blood flow
Cerebral circulation is the movement of blood through a network of cerebral arteries and veins supplying the brain. The rate of cerebral blood flow in an adult human is typically 750 milliliters per minute, or about 15% of cardiac output. ...
to the brain (brain perfusion
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ (anatomy), organ or a tissue (biology), tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion may also refer t ...
). It must be maintained within narrow limits; too little pressure could cause brain tissue to become ischemic (having inadequate blood flow), and too much could raise intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adu ...
.
Imaging
Arterial spin labeling (ASL), phase contrast magnetic resonance imaging (PC-MRI), andpositron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, r ...
(PET) are neuroimaging
Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the neuroanatomy, structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive ...
techniques that can be used to measure CBF. ASL and PET can also be used to measure regional CBF (rCBF) within a specific brain region.
rCBF at one location can be measured over time by thermal diffusion
References
External links
Computer Model of the Cerebral Circulation for Training and Education
{{VeinsHeadNeck Neurology Cardiology