cell division on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger
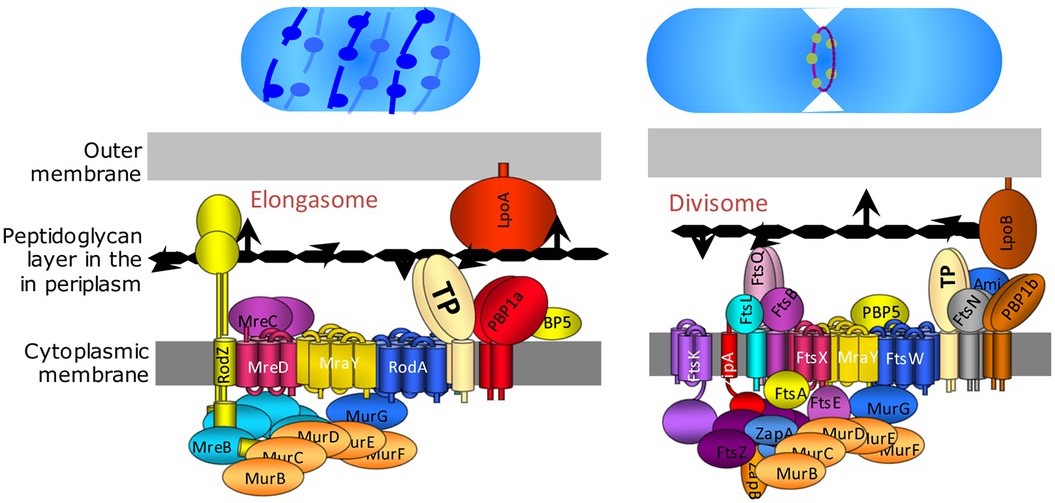 Bacterial cell division happens through
Bacterial cell division happens through

 Cells are broadly classified into two main categories: simple non-nucleated
Cells are broadly classified into two main categories: simple non-nucleated
Cell division: binary fission and mitosis
* McDougal, W. Scott, et al. ''Campbell-Walsh Urology Eleventh Edition Review''. Elsevier, 2016. * Th
Mitosis and Cell Cycle Control Section
from th
''Landmark Papers in Cell Biology''
(Gall JG, McIntosh JR, eds.) contains commentaries on and links to seminal research papers on mitosis and cell division. Published online in th
Image & Video Library
o
The American Society for Cell Biology
* Th
Image & Video Library
o
The American Society for Cell Biology
contains many videos showing the cell division. * Th
Cell Division
o
the Cell Image Library
– Flavon's Secret Flower Garden
Tyson's model of cell division
and
Description
on BioModels Database
WormWeb.org: Interactive Visualization of the ''C. elegans'' Cell Lineage
– Visualize the entire set of cell divisions of the nematode ''C. elegans'' {{Authority control Cell cycle Cellular processes Telomeres 1835 in science 1835 in the German Confederation
cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA re ...
in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
s, there are two distinct types of cell division: a vegetative division (mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
), producing daughter cells genetically identical to the parent cell, and a cell division that produces haploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for Autosome, autosomal and Pseudoautosomal region, pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the num ...
gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as s ...
s for sexual reproduction (meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
), reducing the number of chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
s from two of each type in the diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, ...
parent cell to one of each type in the daughter cells. Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA re ...
, in which, replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is preceded by the S stage of interphase
Interphase is the active portion of the cell cycle that includes the G1, S, and G2 phases, where the cell grows, replicates its DNA, and prepares for mitosis, respectively. Interphase was formerly called the "resting phase," but the cell i ...
(during which the DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all life, living organisms, acting as the most essential part of heredity, biolog ...
occurs) and is followed by telophase
Telophase () is the final stage in both meiosis and mitosis in a eukaryotic cell. During telophase, the effects of prophase and prometaphase (the nucleolus and nuclear membrane disintegrating) are reversed. As chromosomes reach the cell poles, ...
and cytokinesis
Cytokinesis () is the part of the cell division process and part of mitosis during which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell divides into two daughter cells. Cytoplasmic division begins during or after the late stages of nuclear division ...
; which divides the cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
, organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell (biology), cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as Organ (anatomy), organs are to th ...
s, and cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
of one cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis all together define the M phase of an animal cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA re ...
—the division of the mother cell into two genetically identical daughter cells.
To ensure proper progression through the cell cycle, DNA damage is detected and repaired at various checkpoints throughout the cycle. These checkpoints can halt progression through the cell cycle by inhibiting certain cyclin-CDK complexes. Meiosis undergoes two divisions resulting in four haploid daughter cells. Homologous chromosome
Homologous chromosomes or homologs are a set of one maternal and one paternal chromosome that pair up with each other inside a cell during meiosis. Homologs have the same genes in the same locus (genetics), loci, where they provide points along e ...
s are separated in the first division of meiosis, such that each daughter cell has one copy of each chromosome. These chromosomes have already been replicated and have two sister chromatids which are then separated during the second division of meiosis. Both of these cell division cycles are used in the process of sexual reproduction at some point in their life cycle. Both are believed to be present in the last eukaryotic common ancestor.
Prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Gree ...
s (bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
and archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
) usually undergo a vegetative cell division known as binary fission
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two values (0 and 1) for each digit
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical o ...
, where their genetic material is segregated equally into two daughter cells, but there are alternative manners of division, such as budding
Budding or blastogenesis is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site. For example, the small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is kno ...
, that have been observed. All cell divisions, regardless of organism, are preceded by a single round of DNA replication.
For simple unicellular
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and ...
microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s such as the amoeba
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; : amoebas (less commonly, amebas) or amoebae (amebae) ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of Cell (biology), cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by ...
, one cell division is equivalent to reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. There are two forms of reproduction: Asexual reproduction, asexual and Sexual ...
– an entire new organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
is created. On a larger scale, mitotic cell division can create progeny from multicellular organism
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organism ...
s, such as plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s that grow from cuttings. Mitotic cell division enables sexually reproducing
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete (haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote that d ...
organisms to develop from the one-celled zygote
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes.
The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individ ...
, which itself is produced by fusion of two gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as s ...
s, each having been produced by meiotic cell division. After growth from the zygote to the adult, cell division by mitosis allows for continual construction and repair of the organism. The human body experiences about 10 quadrillion cell divisions in a lifetime.
The primary concern of cell division is the maintenance of the original cell's genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
. Before division can occur, the genomic information that is stored in chromosomes must be replicated, and the duplicated genome must be cleanly divided between progeny cells. A great deal of cellular infrastructure is involved in ensuring consistency of genomic information among generations.
In bacteria
 Bacterial cell division happens through
Bacterial cell division happens through binary fission
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two values (0 and 1) for each digit
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical o ...
or through budding
Budding or blastogenesis is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site. For example, the small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is kno ...
. The divisome is a protein complex in bacteria that is responsible for cell division, constriction of inner and outer membranes during division, and remodeling of the peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like layer (sacculus) that surrounds the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. The sugar component consists of alternating ...
cell wall at the division site. A tubulin-like protein, FtsZ
FtsZ is a protein encoded by the ''ftsZ'' gene that assembles into a ring at the future site of bacterial cell division (also called the Z ring). FtsZ is a prokaryotic homologue of the eukaryotic protein tubulin. The initials FtsZ mean "Filame ...
plays a critical role in formation of a contractile ring for the cell division.
In eukaryotes
Cell division in eukaryotes is more complicated than in prokaryotes. If the chromosomal number is reduced, eukaryotic cell division is classified asmeiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
(reductional division). If the chromosomal number is not reduced, eukaryotic cell division is classified as mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
(equational division). A primitive form of cell division, called amitosis, also exists. The amitotic or mitotic cell divisions are more atypical and diverse among the various groups of organisms, such as protist
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancest ...
s (namely diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma'') is any member of a large group comprising several Genus, genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of Earth's B ...
s, dinoflagellate
The Dinoflagellates (), also called Dinophytes, are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered protists. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they are also commo ...
s, etc.) and fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
.
In the mitotic metaphase (see below), typically the chromosomes (each containing 2 sister chromatids that developed during replication in the S phase of interphase) align themselves on the metaphase plate. Then, the sister chromatids split and are distributed between two daughter cells.
In meiosis I, the homologous chromosomes are paired before being separated and distributed between two daughter cells. On the other hand, meiosis II is similar to mitosis. The chromatid
A chromatid (Greek ''khrōmat-'' 'color' + ''-id'') is one half of a duplicated chromosome. Before replication, one chromosome is composed of one DNA molecule. In replication, the DNA molecule is copied, and the two molecules are known as chrom ...
s are separated and distributed in the same way. In humans, other higher animals, and many other organisms, the process of meiosis is called gametic meiosis, during which meiosis produces four gametes. Whereas, in several other groups of organisms, especially in plants (observable during meiosis in lower plants, but during the vestigial stage in higher plants), meiosis gives rise to spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual reproduction, sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for biological dispersal, dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores fo ...
s that germinate
Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an flowering plant, angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the sp ...
into the haploid vegetative phase (gametophyte). This kind of meiosis is called " sporic meiosis."
Phases of eukaryotic cell division
Interphase
Interphase
Interphase is the active portion of the cell cycle that includes the G1, S, and G2 phases, where the cell grows, replicates its DNA, and prepares for mitosis, respectively. Interphase was formerly called the "resting phase," but the cell i ...
is the process through which a cell must go before mitosis, meiosis, and cytokinesis
Cytokinesis () is the part of the cell division process and part of mitosis during which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell divides into two daughter cells. Cytoplasmic division begins during or after the late stages of nuclear division ...
. Interphase consists of three main phases: G1, S, and G2. G1 is a time of growth for the cell where specialized cellular functions occur in order to prepare the cell for DNA replication. There are checkpoints during interphase that allow the cell to either advance or halt further development. One of the checkpoint is between G1 and S, the purpose for this checkpoint is to check for appropriate cell size and any DNA damage . The second check point is in the G2 phase, this checkpoint also checks for cell size but also the DNA replication. The last check point is located at the site of metaphase, where it checks that the chromosomes are correctly connected to the mitotic spindles. In S phase, the chromosomes are replicated in order for the genetic content to be maintained. During G2, the cell undergoes the final stages of growth before it enters the M phase, where spindles are synthesized. The M phase can be either mitosis or meiosis depending on the type of cell. Germ cell
A germ cell is any cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually. In many animals, the germ cells originate in the primitive streak and migrate via the gut of an embryo to the developing gonads. There, they unde ...
s, or gametes, undergo meiosis, while somatic cell
In cellular biology, a somatic cell (), or vegetal cell, is any biological cell forming the body of a multicellular organism other than a gamete, germ cell, gametocyte or undifferentiated stem cell. Somatic cells compose the body of an organism ...
s will undergo mitosis. After the cell proceeds successfully through the M phase, it may then undergo cell division through cytokinesis. The control of each checkpoint is controlled by cyclin
Cyclins are proteins that control the progression of a cell through the cell cycle by activating cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK).
Etymology
Cyclins were originally discovered by R. Timothy Hunt in 1982 while studying the cell cycle of sea urch ...
and cyclin-dependent kinase
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are a predominant group of serine/threonine protein kinases involved in the regulation of the cell cycle and its progression, ensuring the integrity and functionality of cellular machinery. These regulatory enzym ...
s. The progression of interphase is the result of the increased amount of cyclin. As the amount of cyclin increases, more and more cyclin dependent kinases attach to cyclin signaling the cell further into interphase. At the peak of the cyclin, attached to the cyclin dependent kinases this system pushes the cell out of interphase and into the M phase, where mitosis, meiosis, and cytokinesis occur. There are three transition checkpoints the cell has to go through before entering the M phase. The most important being the G1-S transition checkpoint. If the cell does not pass this checkpoint, it results in the cell exiting the cell cycle.
Prophase
Prophase
Prophase () is the first stage of cell division in both mitosis and meiosis. Beginning after interphase, DNA has already been replicated when the cell enters prophase. The main occurrences in prophase are the condensation of the chromatin retic ...
is the first stage of division. The nuclear envelope begins to be broken down in this stage, long strands of chromatin condense to form shorter more visible strands called chromosomes, the nucleolus disappears, and the mitotic spindle begins to assemble from the two centrosomes. Microtubules associated with the alignment and separation of chromosomes are referred to as the spindle and spindle fibers. Chromosomes
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most importa ...
will also be visible under a microscope and will be connected at the centromere. During this condensation and alignment period in meiosis, the homologous chromosomes undergo a break in their double-stranded DNA at the same locations, followed by a recombination of the now fragmented parental DNA strands into non-parental combinations, known as crossing over. This process is evidenced to be caused in a large part by the highly conserved Spo11
Spo11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SPO11'' gene. Spo11, in a complex with mTopVIB, creates double strand breaks to initiate meiotic recombination. Its active site contains a tyrosine which ligates and dissociates with DNA to p ...
protein through a mechanism similar to that seen with topoisomerase in DNA replication and transcription.
Prometaphase
Prometaphase
Prometaphase is the phase of mitosis following prophase and preceding metaphase in eukaryotic somatic cells. In prometaphase, the nuclear membrane breaks apart into numerous "membrane vesicles," and the chromosomes inside form protein structure ...
is the second stage of cell division. This stage begins with the complete breakdown of the nuclear envelope which exposes various structures to the cytoplasm. This breakdown then allows the spindle apparatus
In cell biology, the spindle apparatus is the cytoskeletal structure of eukaryotic cells that forms during cell division to separate sister chromatids between daughter Cell (biology), cells. It is referred to as the mitotic spindle during mitos ...
growing from the centrosome
In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum 'center' + Greek sōma 'body') (archaically cytocentre) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center (MTOC) of the animal cell, as well as a regulator of cell-cycle progre ...
to attach to the kinetochore
A kinetochore (, ) is a flared oblique-shaped protein structure associated with duplicated chromatids in eukaryotic cells where the spindle fibers, which can be thought of as the ropes pulling chromosomes apart, attach during cell division to ...
s on the sister chromatids. Stable attachment of the spindle apparatus to the kinetochores on the sister chromatids will ensure error-free chromosome segregation during anaphase. Prometaphase follows prophase and precedes metaphase.
Metaphase
Inmetaphase
Metaphase ( and ) is a stage of mitosis in the eukaryotic cell cycle in which chromosomes are at their second-most condensed and coiled stage (they are at their most condensed in anaphase). These chromosomes, carrying genetic information, alig ...
, the centromere
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fiber ...
s of the chromosomes align themselves on the ''metaphase plate'' (or ''equatorial plate''), an imaginary line that is at equal distances from the two centrosome
In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum 'center' + Greek sōma 'body') (archaically cytocentre) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center (MTOC) of the animal cell, as well as a regulator of cell-cycle progre ...
poles and held together by complexes known as cohesin
Cohesin is a protein complex that mediates Establishment of sister chromatid cohesion, sister chromatid cohesion, homologous recombination, and Topologically associating domain, DNA looping. Cohesin is formed of SMC3, SMC1A, SMC1, RAD21, SCC1 an ...
s. Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell by microtubule organizing center
The microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) is a structure found in eukaryotic cells from which microtubules emerge. MTOCs have two main functions: the organization of eukaryotic flagella and cilia and the organization of the mitotic and meiotic spi ...
s (MTOCs) pushing and pulling on centromeres of both chromatids thereby causing the chromosome to move to the center. At this point the chromosomes are still condensing and are currently one step away from being the most coiled and condensed they will be, and the spindle fibers have already connected to the kinetochores. During this phase all the microtubules, with the exception of the kinetochores, are in a state of instability promoting their progression toward anaphase. At this point, the chromosomes are ready to split into opposite poles of the cell toward the spindle to which they are connected.
Anaphase
Anaphase
Anaphase () is the stage of mitosis after the process of metaphase, when replicated chromosomes are split and the newly-copied chromosomes (daughter chromatids) are moved to opposite poles of the cell. Chromosomes also reach their overall maxim ...
is a very short stage of the cell cycle and it occurs after the chromosomes align at the mitotic plate. Kinetochores emit anaphase-inhibition signals until their attachment to the mitotic spindle. Once the final chromosome is properly aligned and attached the final signal dissipates and triggers the abrupt shift to anaphase. This abrupt shift is caused by the activation of the anaphase-promoting complex
Anaphase-promoting complex (also called the cyclosome or APC/C) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that marks target cell cycle proteins for degradation by the 26S proteasome. The APC/C is a large complex of 11–13 subunit proteins, including a cullin ...
and its function of tagging degradation of proteins important toward the metaphase-anaphase transition. One of these proteins that is broken down is securin Securin is a protein involved in control of the metaphase-anaphase transition and anaphase onset. Following bi-orientation of chromosome pairs and inactivation of the spindle checkpoint system, the underlying regulatory system, which includes securi ...
which through its breakdown releases the enzyme separase
Separase, also known as separin, is a cysteine protease responsible for triggering anaphase by hydrolysing cohesin, which is the protein responsible for binding sister chromatids during the early stage of anaphase. In humans, separin is encode ...
that cleaves the cohesin rings holding together the sister chromatids thereby leading to the chromosomes separating. After the chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell, the spindle fibers will pull them apart. The chromosomes are split apart while the sister chromatids move to opposite sides of the cell. As the sister chromatids are being pulled apart, the cell and plasma are elongated by non-kinetochore microtubules. Additionally, in this phase, the activation of the anaphase promoting complex through the association with Cdh-1 begins the degradation of mitotic cyclins.
Telophase
Telophase
Telophase () is the final stage in both meiosis and mitosis in a eukaryotic cell. During telophase, the effects of prophase and prometaphase (the nucleolus and nuclear membrane disintegrating) are reversed. As chromosomes reach the cell poles, ...
is the last stage of the cell cycle in which a cleavage furrow splits the cells cytoplasm (cytokinesis) and chromatin. This occurs through the synthesis of a new nuclear envelope that forms around the chromatin gathered at each pole. The nucleolus reforms as the chromatin reverts back to the loose state it possessed during interphase. The division of the cellular contents is not always equal and can vary by cell type as seen with oocyte formation where one of the four daughter cells possess the majority of the duckling.
Cytokinesis
The last stage of the cell division process iscytokinesis
Cytokinesis () is the part of the cell division process and part of mitosis during which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell divides into two daughter cells. Cytoplasmic division begins during or after the late stages of nuclear division ...
. In this stage there is a cytoplasmic division that occurs at the end of either mitosis or meiosis. At this stage there is a resulting irreversible separation leading to two daughter cells. Cell division plays an important role in determining the fate of the cell. This is due to there being the possibility of an asymmetric division. This as a result leads to cytokinesis producing unequal daughter cells containing completely different amounts or concentrations of fate-determining molecules.
In animals the cytokinesis ends with formation of a contractile ring and thereafter a cleavage. But in plants it happen differently. At first a cell plate is formed and then a cell wall develops between the two daughter cells.
In Fission yeast ( ''S. pombe'') the cytokinesis happens in G1 phase.
Variants
 Cells are broadly classified into two main categories: simple non-nucleated
Cells are broadly classified into two main categories: simple non-nucleated prokaryotic
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a single-celled organism whose cell lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'before', and (), meaning 'nut' ...
cells and complex nucleated eukaryotic
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
cells. Due to their structural differences, eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells do not divide in the same way. Also, the pattern of cell division that transforms eukaryotic stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can change into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell ...
s into gametes (sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
cells in males or egg
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the ...
cells in females), termed meiosis, is different from that of the division of somatic cells in the body.
In 2022, scientists discovered a new type of cell division called asynthetic fission found in the squamous epithelial cells in the epidermis of juvenile zebrafish. When juvenile zebrafish are growing, skin cells must quickly cover the rapidly increasing surface area of the zebrafish. These skin cells divide without duplicating their DNA (the S phase of mitosis) causing up to 50% of the cells to have a reduced genome size. These cells are later replaced by cells with a standard amount of DNA. Scientists expect to find this type of division in other vertebrates.
DNA damage repair in the cell cycle
DNA damage is detected and repaired at various points in the cell cycle. The G1/S checkpoint, G2/M checkpoint, and the checkpoint between metaphase and anaphase all monitor for DNA damage and halt cell division by inhibiting different cyclin-CDK complexes. The p53 tumor-suppressor protein plays a crucial role at the G1/S checkpoint and the G2/M checkpoint. Activated p53 proteins result in the expression of many proteins that are important in cell cycle arrest, repair, and apoptosis. At the G1/S checkpoint, p53 acts to ensure that the cell is ready for DNA replication, while at the G2/M checkpoint p53 acts to ensure that the cells have properly duplicated their content before entering mitosis. Specifically, when DNA damage is present, ATM and ATR kinases are activated, activating various checkpoint kinases. These checkpoint kinases phosphorylate p53, which stimulates the production of different enzymes associated with DNA repair. Activated p53 also upregulates p21, which inhibits various cyclin-cdk complexes. These cyclin-cdk complexesphosphorylate
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols:
:
This equation can be writt ...
the Retinoblastoma (Rb) protein, a tumor suppressor bound with the E2F family of transcription factors. The binding of this Rb protein ensures that cells do not enter the S phase prematurely; however, if it is not able to be phosphorylated by these cyclin-cdk complexes, the protein will remain, and the cell will be halted in the G1 phase of the cell cycle.
If DNA is damaged, the cell can also alter the Akt pathway in which BAD is phosphorylated and dissociated from Bcl2, thus inhibiting apoptosis. If this pathway is altered by a loss of function mutation in Akt or Bcl2, then the cell with damaged DNA will be forced to undergo apoptosis. If the DNA damage cannot be repaired, activated p53 can induce cell death by apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
. It can do so by activating the p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA). PUMA is a pro-apoptotic protein that rapidly induces apoptosis by inhibiting the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2
Bcl-2, encoded in humans by the ''BCL2'' gene, is the founding member of the Bcl-2 family of regulator proteins. BCL2 blocks programmed cell death (apoptosis) while other BCL2 family members can either inhibit or induce it. It was the first a ...
family members.
Degradation
Multicellular organisms replace worn-out cells through cell division. In some animals, however, cell division eventually halts. Inhuman
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s this occurs, on average, after 52 divisions, known as the Hayflick limit. The cell is then referred to as senescent. With each division the cells telomere
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes (see #Sequences, Sequences). Telomeres are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In ...
s, protective sequences of DNA on the end of a chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
that prevent degradation of the chromosomal DNA, shorten. This shortening has been correlated to negative effects such as age-related diseases and shortened lifespans in humans. Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
cells, on the other hand, are not thought to degrade in this way, if at all. An enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
complex called telomerase
Telomerase, also called terminal transferase, is a ribonucleoprotein that adds a species-dependent telomere repeat sequence to the 3' end of telomeres. A telomere is a region of repetitive sequences at each end of the chromosomes of most euka ...
, present in large quantities in cancerous cells, rebuilds the telomeres through synthesis of telomeric DNA repeats, allowing division to continue indefinitely.
History
At the beginning of the 19th century, various hypotheses circulated about cell proliferation, which became observable in plant and animal organisms as a result of advances in microscopy. While the proliferation of cells on the inner side of old cells, the attachment of vesicles to existing cells, or crystallization in the intercellular space were postulated as mechanisms of cell proliferation, cell division itself had to fight for its acceptance for decades. The Belgian botanistBarthélemy Charles Joseph Dumortier
Barthélemy Charles Joseph Dumortier (; 3 April 1797 – 9 July 1878) was a Belgians, Belgian who conducted a parallel career of botanist and Member of Parliament and is the first discoverer of biological cell division.
Over the course of his lif ...
must be regarded as the first discoverer of cell division. In 1832, he described cell division in simple aquatic plants (French 'conferve') as follows (translated from French to English):
"The development of the conferve is as simple as its structure; it takes place by the attachment of new cells to the old, and this attachment always takes place from the end. The terminal cell elongates more than the deeper cells; then the production of a lateral bisector takes place in the inner fluid, which tends to divide the cell into two parts, of which the deeper one remains stationary, while the terminal part elongates again, forms a new inner partition, and so on. Is the production of the middle partition originally double or single? It is impossible to determine this, but it is always true that it later appears double when united, and that when two cells naturally separate, each of them is closed at both ends."
In 1835, the German botanist and physician Hugo von Mohl described plant cell division in much greater detail in his dissertation on freshwater and seawater algae for his PhD thesis in medicine and surgery:
"Among the most obscure phenomena of plant life is the manner in which the newly developing cells are formed. ..and so there is no lack of manifold descriptions and explanations of this process. ..and that gaps that were found in the observations were filled in by overly bold conclusions and assumptions." (translated from German to English)
In 1838, the German physician and botanist Franz Julius Ferdinand Meyen confirmed the mechanism of cell division at the root tips of plants.
The German-Polish physician Robert Remak suspected that he had already discovered animal cell division in the blood of chicken embryos in 1841, but it was not until 1852 that he was able to confirm animal cell division for the first time in bird embryos, frog larvae and mammals.
In 1943, cell division was filmed for the first time by Kurt Michel using a phase-contrast microscope.
See also
*Cell fusion Cell fusion is an important cellular process in which several uninucleate cells (cells with a single nucleus) combine to form a multinucleate cell, known as a syncytium. Cell fusion occurs during differentiation of myoblasts, osteoclasts and ...
** gametic fusion
* Cell growth
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
* Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network
* Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization
* Electrochemical cell, a de ...
* Cyclin-dependent kinase
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are a predominant group of serine/threonine protein kinases involved in the regulation of the cell cycle and its progression, ensuring the integrity and functionality of cellular machinery. These regulatory enzym ...
* Labile cells, cells that constantly divide
* Mitotic catastrophe
Mitotic catastrophe has been defined as either a cellular mechanism to prevent potentially cancerous cells from proliferating or as a mode of cellular death that occurs following improper cell cycle progression or entrance. Mitotic catastrophe can ...
References
Further reading
* Morgan HI. (2007). "The Cell Cycle: Principles of Control" London: New Science Press. * J.M.Turner ''Fetus into Man'' (1978, 1989). Harvard University Press.Cell division: binary fission and mitosis
* McDougal, W. Scott, et al. ''Campbell-Walsh Urology Eleventh Edition Review''. Elsevier, 2016. * Th
Mitosis and Cell Cycle Control Section
from th
''Landmark Papers in Cell Biology''
(Gall JG, McIntosh JR, eds.) contains commentaries on and links to seminal research papers on mitosis and cell division. Published online in th
Image & Video Library
o
The American Society for Cell Biology
* Th
Image & Video Library
o
The American Society for Cell Biology
contains many videos showing the cell division. * Th
Cell Division
o
the Cell Image Library
– Flavon's Secret Flower Garden
Tyson's model of cell division
and
Description
on BioModels Database
WormWeb.org: Interactive Visualization of the ''C. elegans'' Cell Lineage
– Visualize the entire set of cell divisions of the nematode ''C. elegans'' {{Authority control Cell cycle Cellular processes Telomeres 1835 in science 1835 in the German Confederation