Cartesian coordinate robot on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A Cartesian coordinate robot (also called linear robot) is an
A Cartesian coordinate robot (also called linear robot) is an
 Robots have mechanisms consisting of rigid links connected together by
Robots have mechanisms consisting of rigid links connected together by
applied
for continuous parts loading and unloading on CNC lathes production lines, performing 3-axis ''(X, Y, Z)'' pick and place operations of heavy loads with high speed performance and high positioning accuracy. In general, overhead gantry Cartesian robots are suitable for many
 A Cartesian coordinate robot (also called linear robot) is an
A Cartesian coordinate robot (also called linear robot) is an industrial robot
An industrial robot is a robot system used for manufacturing. Industrial robots are automated, programmable and capable of movement on three or more axes.
Typical applications of robots include robot welding, welding, painting, assembly, Circu ...
whose three principal axes of control are linear (i.e. they move in a straight line rather than rotate) and are at right angle
In geometry and trigonometry, a right angle is an angle of exactly 90 Degree (angle), degrees or radians corresponding to a quarter turn (geometry), turn. If a Line (mathematics)#Ray, ray is placed so that its endpoint is on a line and the ad ...
s to each other. The three sliding joints correspond to moving the wrist up-down, in-out, back-forth. Among other advantages, this mechanical arrangement simplifies the robot control
Robotic control is the system that contributes to the movement of robots. This involves the mechanical aspects and programmable systems that makes it possible to control robots. Robotics can be controlled by various means including manual, wirele ...
arm solution. It has high reliability and precision when operating in three-dimensional space. As a robot coordinate system, it is also effective for horizontal travel and for stacking bins.
Configurations

 Robots have mechanisms consisting of rigid links connected together by
Robots have mechanisms consisting of rigid links connected together by joints
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
with either linear (prismatic ''P'') or rotary (revolute ''R'') motion, or combinations of the two. Active prismatic ''P'' and active revolute ''R'' joints are driven by motors under programmable control to manipulate objects to perform complex automated tasks. The linear motion of active prismatic ''P'' joints may be driven by rotary motors through gears or pulleys. Cartesian coordinate robots are controlled by mutually perpendicular
In geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at right angles, i.e. at an angle of 90 degrees or π/2 radians. The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the '' perpendicular symbol'', � ...
active prismatic ''P'' joints that are aligned with the ''X, Y, Z'' axes of a Cartesian coordinate system
In geometry, a Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane (geometry), plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point (geometry), point uniquely by a pair of real numbers called ''coordinates'', which are the positive and negative number ...
. Although not strictly ‘robots’, other types of manipulators, such as computer numerically controlled (CNC) machines, 3D printers or pen plotters
PEN may refer to:
* (National Ecological Party), former name of the Brazilian political party Patriota (PATRI)
*PEN International, a worldwide association of writers
**English PEN, the founding centre of PEN International
**PEN America, located in ...
, also have the same mechanical arrangement of mutually perpendicular active prismatic ''P'' joints.
Joint topology
A single chain of links and joints connects a moving object to a base ofserial manipulator Serial manipulators are the most common industrial robots and they are designed as a series of links connected by motor-actuated joints that extend from a base to an end-effector. Often they have an anthropomorphic arm structure described as havin ...
s. Multiple chains (limbs) connect the moving object to the base of parallel manipulator
A parallel manipulator is a mechanical system that uses several computer-controlled serial chains to support a single platform, or end-effector. Perhaps, the best known parallel manipulator is formed from six linear actuators that support a mo ...
s. Most Cartesian coordinate robots are fully serial or a combination of serial and parallel connected linkages. However, there are some Cartesian coordinate robots that are fully parallel-connected.
Degrees of freedom
Since they are driven by linear active prismatic ''P'' joints, Cartesian coordinate robots typically manipulate objects with only linear translation ''T''degrees of freedom
In many scientific fields, the degrees of freedom of a system is the number of parameters of the system that may vary independently. For example, a point in the plane has two degrees of freedom for translation: its two coordinates; a non-infinite ...
. However, some Cartesian coordinate robots also have rotational ''R'' degrees of freedom.
Construction
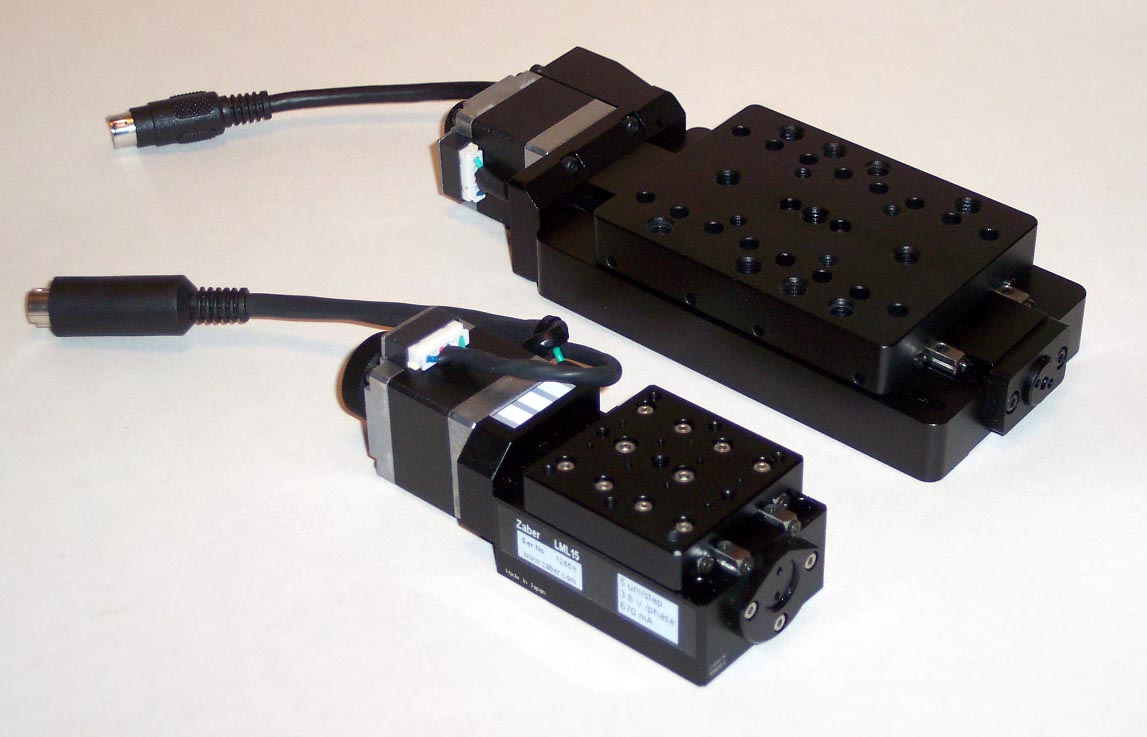
Each axis of a Cartesian coordinate robot typically is alinear stage
A linear stage or translation stage is a component of a precise motion system used to restrict an object to a single axis of motion. The term linear slide is often used interchangeably with "linear stage", though technically "linear slide" refer ...
consisting of a linear actuator
An actuator is a machine element, component of a machine that produces force, torque, or Displacement (geometry), displacement, when an electrical, Pneumatics, pneumatic or Hydraulic fluid, hydraulic input is supplied to it in a system (called an ...
geometrically parallel with linear bearings. The linear actuator is typically between two linear bearings spaced apart from each other to support moment loads. Two perpendicular linear stages stacked on top of each other form a XY table. Examples of XY tables include the XY axes of milling machines or precision positioning stages. At least one of the linear stages of cantilever
A cantilever is a rigid structural element that extends horizontally and is unsupported at one end. Typically it extends from a flat vertical surface such as a wall, to which it must be firmly attached. Like other structural elements, a cantilev ...
ed Cartesian coordinate robots is supported at only one end. Cantilevered construction provides accessibility to parts for pick-and-place applications such as laboratory automation for example. Cartesian coordinate robots with the horizontal member supported at both ends are sometimes called gantry robots; mechanically, they resemble gantry crane
A gantry crane is a Crane (machine), crane built atop a wikt:gantry, gantry, which is a structure used to straddle an object or workspace. They can range from enormous "full" gantry cranes, capable of lifting some of the heaviest loads in the wor ...
s, although the latter are not generally robots. Gantry robots are often quite large and may support heavy loads.
Applications
Popular applications for Cartesian coordinate robots are computer numerical control machines (CNC machine
Computer numerical control (CNC) or CNC machining is the automated control of machine tools by a computer. It is an evolution of numerical control (NC), where machine tools are directly managed by data storage media such as punched cards or ...
) and 3D printing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer ...
. The simplest application is used in milling machines and plotter
A plotter is a machine that produces vector graphics drawings. Plotters draw lines on paper using a pen, or in some applications, use a knife to cut a material like Polyvinyl chloride, vinyl or leather. In the latter case, they are sometimes k ...
s where a tool such as a router or pen translates across an ''X-Y'' plane and is raised and lowered onto a surface to create a precise design.
Pick and place machines are another application for Cartesian coordinate robots. For example, overhead gantry Cartesian robots arapplied
for continuous parts loading and unloading on CNC lathes production lines, performing 3-axis ''(X, Y, Z)'' pick and place operations of heavy loads with high speed performance and high positioning accuracy. In general, overhead gantry Cartesian robots are suitable for many
automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machine ...
systems.
See also
*List of 3D modeling software
Following is a list of notable software, computer programs, used to develop a mathematical representation of any ''three dimensional'' surface of objects, as 3D computer graphics, also called ''3D modeling''.
See also
* Comparison of computer- ...
* Robotic arm
A robotic arm is a type of mechanical arm, usually programmable, with similar functions to a human arm; the arm may be the sum total of the mechanism or may be part of a more complex robot. The links of such a manipulator are connected by join ...
* Cartesian parallel manipulators
References