CW Leonis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
CW Leonis or IRC +10216 is a variable
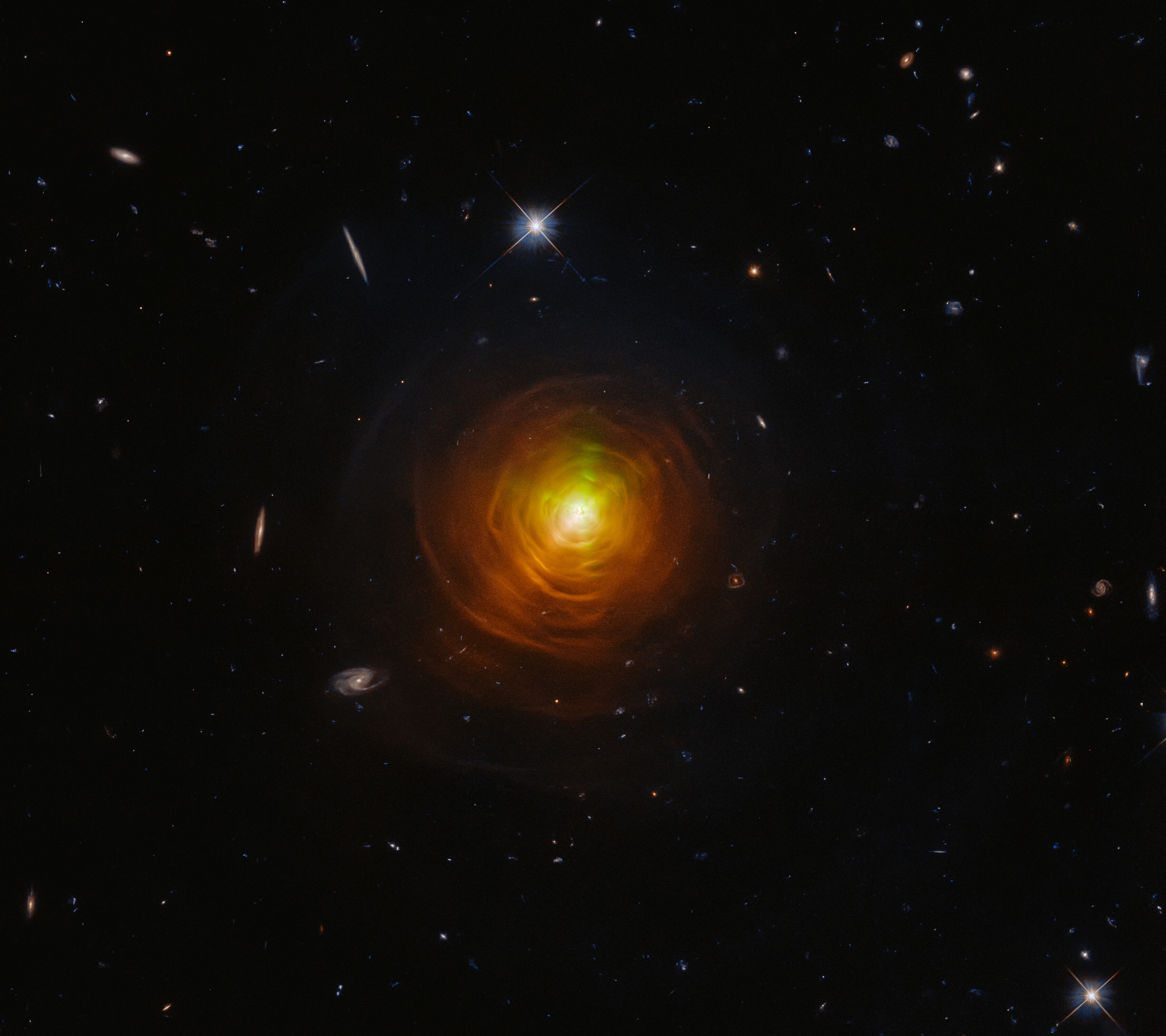
 CW Leonis is believed to be in a late stage of its life, blowing off its own sooty atmosphere to form a
CW Leonis is believed to be in a late stage of its life, blowing off its own sooty atmosphere to form a
 If the distance to this star is assumed to be at the lower end of the estimate range, 120 pc, then the
If the distance to this star is assumed to be at the lower end of the estimate range, 120 pc, then the
Water Found Around Nearby Star CW Leonis
Astronomy Picture of the Day July 16, 2001
revealed by aperture masking interferometry * http://jumk.de/astronomie/special-stars/cw-leonis.shtml * {{Stars of Leo Carbon stars Protoplanetary nebulae Leo (constellation) ? Mira variables Leonis, CW IRAS catalogue objects J09475740+1316435 Emission-line stars
carbon star
A carbon star (C-type star) is typically an asymptotic giant branch star, a luminous red giant, whose Stellar atmosphere, atmosphere contains more carbon than oxygen. The two elements combine in the upper layers of the star, forming carbon monox ...
that is embedded in a thick dust envelope. It was first discovered in 1969 by a group of astronomers led by Eric Becklin, based upon infrared observations made with the 62-inch Caltech Infrared Telescope at Mount Wilson Observatory
The Mount Wilson Observatory (MWO) is an Observatory#Astronomical observatories, astronomical observatory in Los Angeles County, California, United States. The MWO is located on Mount Wilson (California), Mount Wilson, a peak in the San Gabrie ...
. Its energy is emitted mostly at infrared wavelengths. At a wavelength of 5 μm, it was found to have the highest flux of any object outside the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
.
Properties
 CW Leonis is believed to be in a late stage of its life, blowing off its own sooty atmosphere to form a
CW Leonis is believed to be in a late stage of its life, blowing off its own sooty atmosphere to form a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a Compact star, stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very density, dense: in an Earth sized volume, it packs a mass that is comparable to the Sun. No nuclear fusion takes place i ...
. Based upon isotope ratios of magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
, the initial mass of this star has been constrained to lie between 3–5 solar mass
The solar mass () is a frequently used unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxie ...
es. The mass of the star's core, and the final mass of the star once it becomes a white dwarf, is about 0.7–0.9 solar masses. Its bolometric luminosity
Luminosity is an absolute measure of radiated electromagnetic energy per unit time, and is synonymous with the radiant power emitted by a light-emitting object. In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of electromagnetic energy emitted per ...
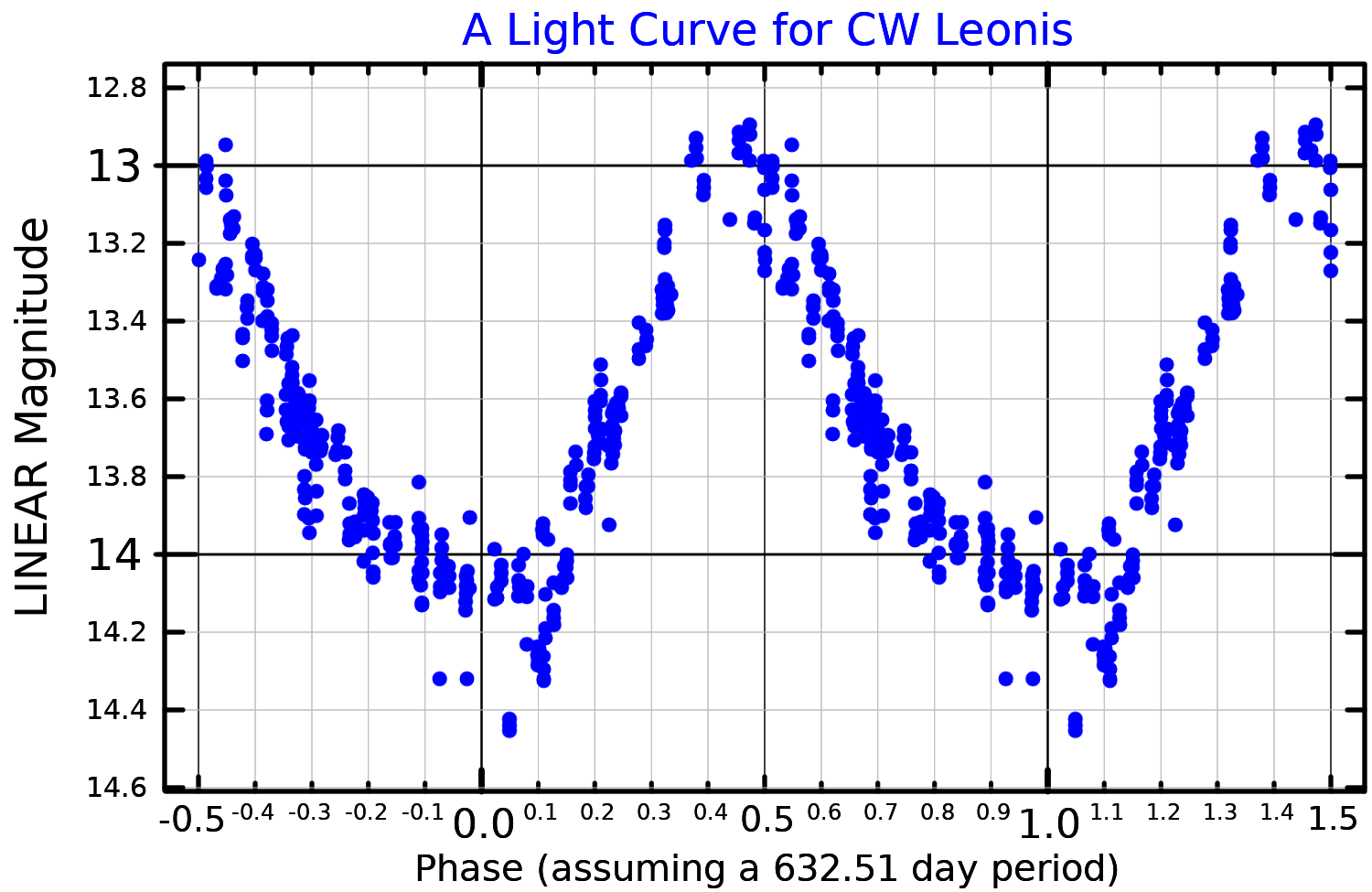
varies over the course of a 649-day pulsation cycle, ranging from a minimum of about 6,250 times the Sun's luminosity up to a peak of around 15,800 times. The overall output of the star is best represented by a luminosity of . The brightness of the star varies by about two magnitudes over its pulsation period, and may have been increasing over a period of years. One study finds an increase in the mean brightness of about a magnitude between 2004 and 2014. Many studies of this star are done at infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
wavelengths because of its very red colour; published visual magnitudes are uncommon and often dramatically different. The Guide Star Catalog from 2006 gives an apparent visual magnitude of 19.23. The ASAS-SN variable star catalog based on observations from 2014 to 2018 reports a mean magnitude of 17.56 and an amplitude of 0.68 magnitudes. An even later study gives a mean magnitude of 14.5 and an amplitude of 2.0 magnitudes.
The carbon-rich gaseous envelope surrounding this star is at least 69,000 years old and the star is losing about solar mass
The solar mass () is a frequently used unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxie ...
es per year. The extended envelope contains at least 1.4 solar mass
The solar mass () is a frequently used unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxie ...
es of material. Speckle observations from 1999 show a complex structure to this dust envelope, including partial arcs and unfinished shells. This clumpiness may be caused by a magnetic cycle in the star that is comparable to the solar cycle
The Solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of Modern Maximum, variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun ...
in the Sun and results in periodic increases in mass loss.
Various chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
s and about 50 molecules
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry ...
have been detected in the outflows from CW Leonis, among others nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
, oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
and water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
, silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
, and iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
. One theory was that the star was once surrounded by comets that melted once the star started expanding, but water is now thought to form naturally in the atmospheres of all carbon stars.
Distance
 If the distance to this star is assumed to be at the lower end of the estimate range, 120 pc, then the
If the distance to this star is assumed to be at the lower end of the estimate range, 120 pc, then the astrosphere
A stellar-wind bubble is a cavity light-years across filled with hot gas blown into the interstellar medium by the high-velocity (several thousand km/s) stellar wind from a single massive star of type O or B. Weaker stellar winds also blow bub ...
surrounding the star spans a radius of about 84,000 AU. The star and its surrounding envelope are advancing at a velocity of more than 91 km/s through the surrounding interstellar medium
The interstellar medium (ISM) is the matter and radiation that exists in the outer space, space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as cosmic dust, dust and cosmic rays. It f ...
. It is moving with a space velocity of , V, W
The comma is a punctuation mark that appears in several variants in different languages. Some typefaces render it as a small line, slightly curved or straight, but inclined from the vertical; others give it the appearance of a miniature fille ...
= , km s−1.
Companion
Several papers have suggested that CW Leonis has a closebinary
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two values (0 and 1) for each digit
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical op ...
companion. ALMA
Alma or ALMA may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Alma'' (film), a 2009 Spanish short animated film
* ''Alma'', an upcoming film by Sally Potter
* ''Alma'' (Oswald de Andrade novel), 1922
* ''Alma'' (Le Clézio novel), 2017
* ''Alma'' ( ...
and astrometric
Astrometry is a branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other celestial bodies. It provides the kinematics and physical origin of the Solar System and this galaxy, the Milky Way.
History ...
measurements may show orbital motion. The astrometric measurements, combined with a model including the companion, provide a parallax measurement showing that CW Leonis is the closest carbon star
A carbon star (C-type star) is typically an asymptotic giant branch star, a luminous red giant, whose Stellar atmosphere, atmosphere contains more carbon than oxygen. The two elements combine in the upper layers of the star, forming carbon monox ...
to the Earth.
See also
*List of largest known stars
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but ...
References
External links
Water Found Around Nearby Star CW Leonis
Astronomy Picture of the Day July 16, 2001
revealed by aperture masking interferometry * http://jumk.de/astronomie/special-stars/cw-leonis.shtml * {{Stars of Leo Carbon stars Protoplanetary nebulae Leo (constellation) ? Mira variables Leonis, CW IRAS catalogue objects J09475740+1316435 Emission-line stars