Bowline on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The bowline ( or ) is an ancient and simple
 A
A
this animation
There is a potential with beginners to wrongly tie the bowline. This faulty knot stems from an incorrect first step while tying the rabbit hole. If the loop is made backwards so that the end of the rope (the
File:Birmingham_Bowline_Loose.jpg, Two-loop Birmingham bowline before tightening and dressing the knot. Two turns taken around the standing part of the line form two loops.
File:Four knots.jpg, Bowline (1) and bowline-like knots (2 –
Video of the Lightning Method
YouTube animation of a Bowline knot
{{Knots
knot
A knot is an intentional complication in cordage which may be practical or decorative, or both. Practical knots are classified by function, including hitches, bends, loop knots, and splices: a ''hitch'' fastens a rope to another object; a ' ...
used to form a fixed loop at the end of a rope. It has the virtues of being both easy to tie and untie; most notably, it is easy to untie after being subjected to a load. The bowline is sometimes referred to as ''King of the knots'' because of its importance. Along with the sheet bend
The sheet bend (also known as becket bend, weaver's knot and weaver's hitch) is a bend. It is practical for joining lines of different diameter or rigidity.
It is quick and easy to tie, and is considered so essential it is the first knot given ...
and the clove hitch
The clove hitch is a type of knot. Along with the bowline and the sheet bend, it is often considered one of the most important knots. A clove hitch is two successive half-hitches around an object. It is most effectively used as a crossing kno ...
, the bowline is often considered one of the most essential knots.
The common bowline shares some structural similarity with the sheet bend. Virtually all end-to-end joining knots (i.e., bends) have a corresponding loop knot.
Although the bowline is generally considered a reliable knot, its main deficiencies are a tendency to work loose when not under load (or under cyclic loading), to slip when pulled sideways, and the bight
The word is derived from Old English ''byht'' (“bend, angle, corner; bay, bight”). In modern English, bight may refer to:
* Bight (geography), recess of a coast, bay, or other curved feature
* Bight (knot), a curved section, slack part, or loo ...
portion of the knot to capsize
Capsizing or keeling over occurs when a boat or ship is rolled on its side or further by wave action, instability or wind force beyond the angle of positive static stability or it is upside down in the water. The act of recovering a vessel fro ...
in certain circumstances. To address these shortcomings, a number of more secure variations of the bowline have been developed for use in safety-critical
A safety-critical system (SCS) or life-critical system is a system whose failure or malfunction may result in one (or more) of the following outcomes:
* death or serious injury to people
* loss or severe damage to equipment/property
* environme ...
applications, or by securing the knot with an overhand knot
The overhand knot is one of the most fundamental knots, and it forms the basis of many others, including the simple noose, overhand loop, angler's loop, reef knot, fisherman's knot, Half hitch, and water knot. The overhand knot is a stopper, e ...
backup.
History
The bowline's name has an earlier meaning, dating to theage of sail
The Age of Sail is a period that lasted at the latest from the mid-16th (or mid- 15th) to the mid- 19th centuries, in which the dominance of sailing ships in global trade and warfare culminated, particularly marked by the introduction of naval ...
. On a square-rigged ship, a bowline (sometimes spelled as two words, ''bow line'') is a rope that holds the edge of a square sail
A sail is a tensile structure—which is made from fabric or other membrane materials—that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails may ...
towards the bow of the ship and into the wind, preventing it from being taken aback. A ship is said to be on a "taut bowline" when these lines are made as taut as possible in order to sail close-hauled to the wind.
The bowline knot is thought to have been first mentioned in John Smith's
John Smith's Brewery in Tadcaster, North Yorkshire, England, produces beers including John Smith's, the highest selling bitter in the United Kingdom since the mid-1990s.
The majority of John Smith's sales are of the nitrogenated Extra Smooth ...
1627 work ''A Sea Grammar'' under the name Boling knot. Smith considered the knot to be strong and secure, saying, "The ''Boling knot'' is also so firmly made and fastened by the bridles into the cringle
A cringle is an eye through which to pass a rope. In nautical settings, the word refers to a small hole anywhere along the edge or in the corner of a sail, rimmed with stranded cordage and worked into the boltrope. Typically it encloses a meta ...
s of the sails, they will break, or the sail split before it will slip."
Another possible finding was discovered on the rigging of the Ancient Egyptian Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the an ...
Khufu's solar ship during an excavation in 1954.
Usage
The bowline is used to make a loop at one end of a line. It is tied with the rope'sworking end
A knot is an intentional complication in cordage which may be practical or decorative, or both. Practical knots are classified by function, including hitches, bends, loop knots, and splices: a ''hitch'' fastens a rope to another object; a ' ...
also known as the "tail" or "end". The loop may pass around or through an object during the making of the knot. The knot tightens when loaded at (pulled by) the standing part of the line.
The bowline is commonly used in sailing small craft, for example to fasten a halyard
In sailing, a halyard or halliard is a line (rope) that is used to hoist a ladder, sail, flag or yard. The term ''halyard'' comes from the phrase "to haul yards". Halyards, like most other parts of the running rigging, were classically made of ...
to the head of a sail or to tie a jib sheet
In sailing, a sheet is a line (rope, cable or chain) used to control the movable corner(s) ( clews) of a sail.
Terminology
In nautical usage the term "sheet" is applied to a line or chain attached to the lower corners of a sail for the purpos ...
to a clew
Sail components include the features that define a sail's shape and function, plus its constituent parts from which it is manufactured. A sail may be classified in a variety of ways, including by its orientation to the vessel (e.g. ''fore-and-a ...
of a jib
A jib is a triangular sail that sets ahead of the foremast of a sailing vessel. Its tack is fixed to the bowsprit, to the bows, or to the deck between the bowsprit and the foremost mast. Jibs and spinnakers are the two main types of headsail ...
. The bowline is well known as a rescue knot for such purposes as rescuing people who might have fallen down a hole, or off a cliff onto a ledge. This knot is particularly useful in such a situation because it is possible to tie with one hand. As such, a person needing rescue could hold onto the rope with one hand and use the other to tie the knot around their waist before being pulled to safety by rescuers. The Federal Aviation Administration
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is the largest transportation agency of the U.S. government and regulates all aspects of civil aviation in the country as well as over surrounding international waters. Its powers include air traffic m ...
recommends the bowline knot for tying down light aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines ...
.
A rope with a bowline retains approximately 2/3 of its strength, with variances depending upon the nature of the rope, as in practice the exact strength depends on a variety of factors.
In the United Kingdom, the knot is listed as part of the training objectives for the Qualified Firefighter Assessment.
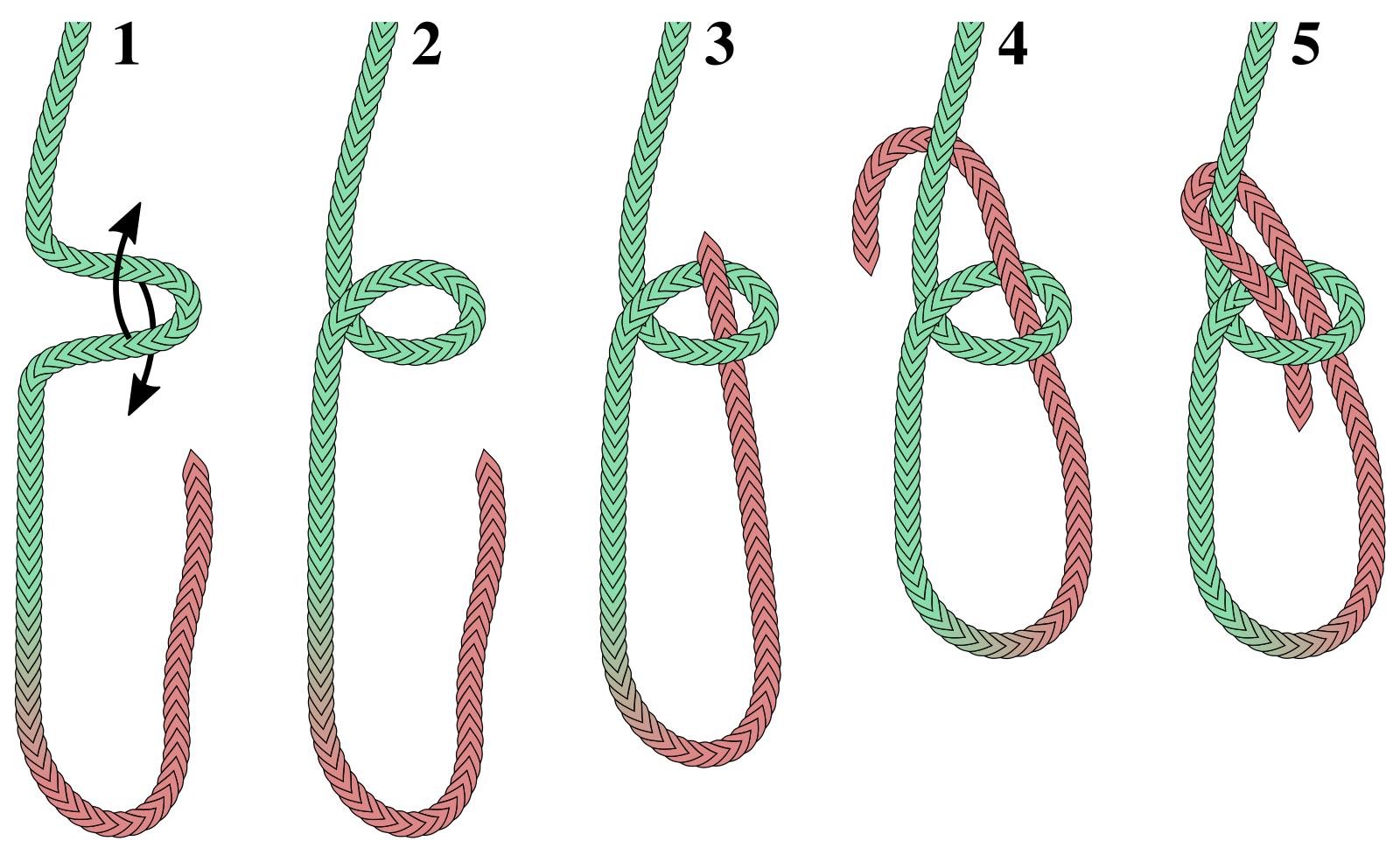
Tying

 A
A mnemonic
A mnemonic ( ) device, or memory device, is any learning technique that aids information retention or retrieval (remembering) in the human memory for better understanding.
Mnemonics make use of elaborative encoding, retrieval cues, and imag ...
used to teach the tying of the bowline is to imagine the working end of the rope as a rabbit.
* 1,2 – a loop is made into the standing part which will act as the rabbit's hole
* 3 – the "rabbit" comes up the hole,
* 4 – goes round the tree (standing part) right to left
* 5 – and back down the hole
This can be taught to children with the rhyme: "Up through the rabbit hole, round the big tree; down through the rabbit hole and off goes he."
A single handed method can also be used; sethis animation
There is a potential with beginners to wrongly tie the bowline. This faulty knot stems from an incorrect first step while tying the rabbit hole. If the loop is made backwards so that the end of the rope (the
bitter end
Bitter end or The Bitter End may refer to:
* Bitter end, the part of a rope used to form a knot
*The Bitter End, a nightclub in New York City
Geography
* Bitter End, Tennessee
*Bitter End, Virgin Gorda
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
...
) is on the bottom, the resulting knot will be the Eskimo bowline
The Eskimo bowline, Cossack knot (russian: Казачий узел), reverse bowline, or 'anti- bowline' is in a class of knots known as 'eye knots' or 'loop knots'. The eye is formed in the end of the rope to permit attachments/connections. ...
, looking like a sideways bowline, which is also a stable knot.
Security
As noted above, the simplicity of the bowline makes it a good knot for a general purpose end-of-line loop. However, in situations that require additional security, several variants have been developed:Round turn bowline
The round turn bowline is made by the addition of an extra turn in the formation of the "rabbit hole" before the working end is threaded through.Water bowline
Similar to the double bowline, the water bowline is made by forming aclove hitch
The clove hitch is a type of knot. Along with the bowline and the sheet bend, it is often considered one of the most important knots. A clove hitch is two successive half-hitches around an object. It is most effectively used as a crossing kno ...
before the working end is threaded through. It is said to be stronger and also more resistant to jamming than the other variations, especially when wet.
Yosemite bowline
In this variation the knot's working end is taken round the loop in the direction of the original round turn, then threaded back up through the original round turn before the knot is drawn tight. The Yosemite bowline is often used inclimbing
Climbing is the activity of using one's hands, feet, or any other part of the body to ascend a steep topographical object that can range from the world's tallest mountains (e.g. the eight thousanders), to small boulders. Climbing is done fo ...
.
Other variants
Thecowboy bowline
The cowboy bowline or left-hand bowline, is a variation of the bowline loop knot.
The cowboy bowline has the working end go around the standing part on the side closer to the loop and results with the working end outside the loop. In contrast, ...
(also called Dutch bowline), French bowline, and Portuguese bowline
The Portuguese bowline ( pt, Nó volta do calafate; also known as the French bowline and Lisbon surprise) is a variant of the bowline with two loops. The two loops are adjustable in size. Rope can be pulled from one loop into the other, even after ...
are variations of the bowline, each of which makes one loop. (Names of knots are mostly traditional and may not reflect their origins.) A running bowline
The running bowline is a knot consisting of a bowline looped around its own standing end to create a noose.
The running bowline is strong and secure. It slides easily and can be undone just as simply.
Tying
Tie a bowline
The bowline ( ...
can be used to make a noose which draws tighter as tension is placed on the standing part of the rope. The ''Birmingham bowline'' has two loops; the working part is passed twice around the standing part (the "rabbit" makes two trips out of the hole and around the tree). Other two-loop bowline knots include the Spanish bowline
The Spanish bowlineThe complete guide to knots and knot tying — Geoffrey Budworth — p.190 — is a double loop knot that can be used to lift a person. For a conscious person, each loop is placed around a leg and the person holds onto the sta ...
and the bowline on the bight
The bowline on a bight is a knot which makes a pair of fixed-size loops in the middle of a rope. Its advantage is that it is reasonably easy to untie after being exposed to load. This knot can replace the figure-eight loop knot when tying into a ...
; these can be tied in the middle of a rope without access to the ends. A triple bowline
The triple bowline knot is a variation of the bowline knot. The knot can be applied to emergency situations, such as mountain rescue.
Etymology
The name comes from the three loops that would be formed by tying this knot.
Tying
The knot is tied ...
is used to make three loops. A Cossack knot
The Eskimo bowline, Cossack knot (russian: Казачий узел), reverse bowline, or 'anti- bowline' is in a class of knots known as 'eye knots' or 'loop knots'. The eye is formed in the end of the rope to permit attachments/connections. ...
is a bowline where the running end goes around the loop-start rather than the main part and has a more symmetric triangular shaped knot. A slipped version of the Cossack knot is called Kalmyk loop
The Kalmyk Loop (russian: калмыцкий узел) is a fixed loop still largely unused in the West, but common in Russia and often used instead of the bowline.
The knot is named after the Kalmyks, a nomad ethnicity in Russia.
It is very q ...
. Tying video for Kalmyk loop
cowboy bowline
The cowboy bowline or left-hand bowline, is a variation of the bowline loop knot.
The cowboy bowline has the working end go around the standing part on the side closer to the loop and results with the working end outside the loop. In contrast, ...
, 3 – Eskimo bowline
The Eskimo bowline, Cossack knot (russian: Казачий узел), reverse bowline, or 'anti- bowline' is in a class of knots known as 'eye knots' or 'loop knots'. The eye is formed in the end of the rope to permit attachments/connections. ...
, 4 – Cossack knot
The Eskimo bowline, Cossack knot (russian: Казачий узел), reverse bowline, or 'anti- bowline' is in a class of knots known as 'eye knots' or 'loop knots'. The eye is formed in the end of the rope to permit attachments/connections. ...
) for comparison
File:Bowline to 6 2 knot.gif, If a bowline is tied and the two free ends of the rope are brought together in the simplest way, the mathematical knot
In mathematics, a knot is an embedding of the circle into three-dimensional Euclidean space, (also known as ). Often two knots are considered equivalent if they are ambient isotopic, that is, if there exists a continuous deformation of ...
obtained is the so-called 6₂ knot
In knot theory, the 62 knot is one of three prime knots with crossing number six, the others being the stevedore knot and the 63 knot. This knot is sometimes referred to as the Miller Institute knot, because it appears in the logo of the Mill ...
. The sequence of necessary moves is depicted here.
See also
*List of knots
This list of knots includes many alternative names for common knots and lashings. Knot names have evolved over time, and there are many conflicting or confusing naming issues. The overhand knot, for example, is also known as the thumb knot. The ...
*Karash double loop
Karash double loop is a common name for a knot forming two loops. This knot has been a known variant of the Bowline on a bight per the International Guild of Knot Tyers, referred to as ''bowline twist'' or ''twisted collar bowline on a bight''. ...
*Eye splice
The eye splice is a method of creating a permanent loop (an " eye") in the end of a rope by means of rope splicing.
The Flemish eye is a type of circular loop at the end of a thread. There are several techniques of creating the eye with its k ...
Notes
References
External links
Video of the Lightning Method
YouTube animation of a Bowline knot
{{Knots