Battle Of Jieting on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle of Jieting was fought between the states of
Cao Wei
Wei ( Hanzi: 魏; pinyin: ''Wèi'' < : *''ŋjweiC'' < and
Shu Han
Han (; 221–263), known in historiography as Shu Han ( ) or Ji Han ( "Junior Han"), or often shortened to Shu (; pinyin: ''shŭ'' <
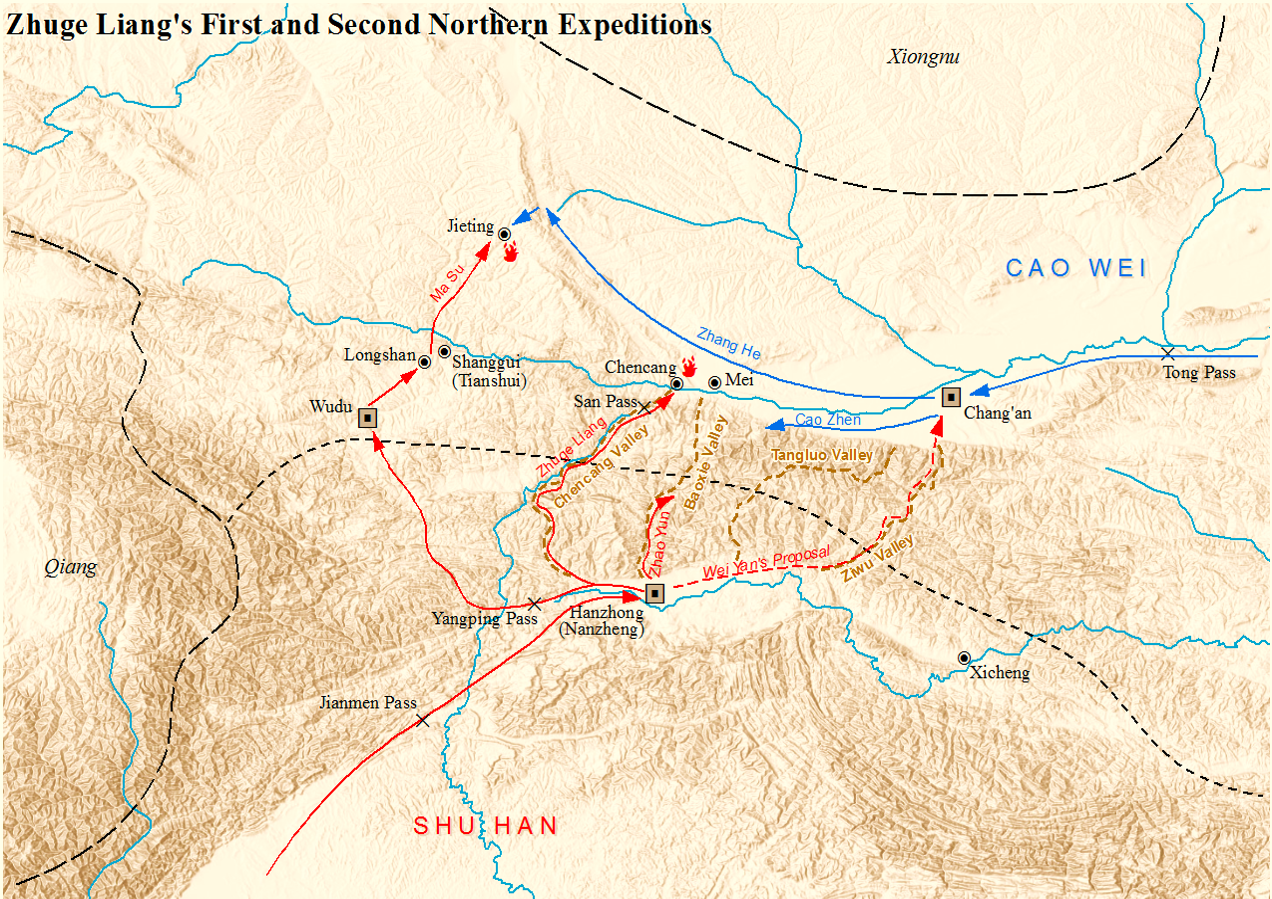 Jieting was a crucial region for the securing of supplies, and Zhuge Liang sent Ma Su and Wang Ping to guard the region. Ma Su went accompanied by Wang Ping but did not listen to his sound military advice. Relying purely on books of military tactics, Ma Su chose to "take the high ground" and set his base on the mountains instead of in a city, ignoring Wang Ping's advice to make camp in a valley well supplied with water. Wang Ping, however, managed to persuade Ma Su to give him command of a portion of the troops, and later Wang set up his base camp near Ma's camp, in order to offer assistance when Ma was in danger.
Due to this tactical mistake, the Wei army led by Zhang He encircled the hill and cut off the water supply to the Shu troops and defeated them. Amidst the panic, Ma Su is recorded to have left his post leaving the army with no commander. Wang Ping rallied Ma Su's army and with only a handful of soldiers did his best to keep the retreat organized and ordered his soldiers to beat their drums loudly to create the impression that reinforcements had arrived. Zhang He believed this to possibly be a sign of an ambush and so he did not pursue. When Zhuge Liang arrived, he attempted to defeat Zhang He however he didn't find a way to take a position and so the Shu army had to retreat to Hanzhong.
Though he survived the battle, Ma Su's army suffered a heavy defeat (Wang Ping was able to regroup Ma Su's remaining troops and gather the Shu army's scattered supplies.), so he was soon arrested and sentenced to execution by a reluctant and tearful Zhuge Liang.
Jieting was a crucial region for the securing of supplies, and Zhuge Liang sent Ma Su and Wang Ping to guard the region. Ma Su went accompanied by Wang Ping but did not listen to his sound military advice. Relying purely on books of military tactics, Ma Su chose to "take the high ground" and set his base on the mountains instead of in a city, ignoring Wang Ping's advice to make camp in a valley well supplied with water. Wang Ping, however, managed to persuade Ma Su to give him command of a portion of the troops, and later Wang set up his base camp near Ma's camp, in order to offer assistance when Ma was in danger.
Due to this tactical mistake, the Wei army led by Zhang He encircled the hill and cut off the water supply to the Shu troops and defeated them. Amidst the panic, Ma Su is recorded to have left his post leaving the army with no commander. Wang Ping rallied Ma Su's army and with only a handful of soldiers did his best to keep the retreat organized and ordered his soldiers to beat their drums loudly to create the impression that reinforcements had arrived. Zhang He believed this to possibly be a sign of an ambush and so he did not pursue. When Zhuge Liang arrived, he attempted to defeat Zhang He however he didn't find a way to take a position and so the Shu army had to retreat to Hanzhong.
Though he survived the battle, Ma Su's army suffered a heavy defeat (Wang Ping was able to regroup Ma Su's remaining troops and gather the Shu army's scattered supplies.), so he was soon arrested and sentenced to execution by a reluctant and tearful Zhuge Liang.
Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms () from 220 to 280 AD was the tripartite division of China among the dynastic states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The Three Kingdoms period was preceded by the Han dynasty#Eastern Han, Eastern Han dynasty and wa ...
period in China. The battle was part of the first Northern Expedition led by Shu's chancellor
Chancellor ( la, cancellarius) is a title of various official positions in the governments of many nations. The original chancellors were the of Roman courts of justice—ushers, who sat at the or lattice work screens of a basilica or law cou ...
-regent, Zhuge Liang
Zhuge Liang ( zh, t=諸葛亮 / 诸葛亮) (181 – September 234), courtesy name Kongming, was a Chinese statesman and military strategist. He was chancellor and later regent of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period. He is r ...
, to attack Wei. The battle concluded with a decisive victory for Wei.
Opening moves
Zhuge Liang first sent generalsZhao Yun
Zhao Yun ( ) (died 229), courtesy name Zilong (), was a military general who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty and early Three Kingdoms period of China. Originally a subordinate of the northern warlord Gongsun Zan, Zhao Yun later came ...
and Deng Zhi
Deng Zhi (178 - 251), courtesy name Bomiao, was a government official, diplomat and military general of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period of China. A descendant of Deng Yu, Deng Zhi started his career in the late Eastern Han ...
to attack Wei, while he personally led a force towards Mount Qi. Cao Rui
Cao Rui () (204 or 206 – 22 January 239), courtesy name Yuanzhong, was the second emperor of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period. His parentage is in dispute: his mother, Lady Zhen, was Yuan Xi's wife, but she later remarr ...
, the emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
of Wei, moved to Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin Shi ...
and sent Zhang He
Zhang He () (died July or August 231), courtesy name Junyi, was a military general serving under the warlord Cao Cao in the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He continued serving in the state of Cao Wei under its first two rulers, Cao Pi and ...
to attack Zhuge Liang while Cao Zhen
Cao Zhen (died April or May 231), courtesy name Zidan, was a military general of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He was an adopted son of Cao Cao, a warlord who rose to power in the late Eastern Han dynasty and l ...
would oppose Zhao Yun. Zhuge Liang chose generals Ma Su
Ma Su (190–228), courtesy name Youchang, was a military general and strategist of the state of Shu Han in the Three Kingdoms period of China. Ma Su had conspicuous talent in military theories and was admired by the Shu chancellor Zhuge Liang. ...
as the vanguard commander along with Wang Ping to intercept Zhang He, rather than the suggested veterans officers Wei Yan
Wei Yan () (died October 234), courtesy name Wenchang, was a Chinese military general and politician of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period of China. Originally a subordinate of the warlord Liu Bei in the late Eastern Han dyna ...
or Wu Yi.
The battle
 Jieting was a crucial region for the securing of supplies, and Zhuge Liang sent Ma Su and Wang Ping to guard the region. Ma Su went accompanied by Wang Ping but did not listen to his sound military advice. Relying purely on books of military tactics, Ma Su chose to "take the high ground" and set his base on the mountains instead of in a city, ignoring Wang Ping's advice to make camp in a valley well supplied with water. Wang Ping, however, managed to persuade Ma Su to give him command of a portion of the troops, and later Wang set up his base camp near Ma's camp, in order to offer assistance when Ma was in danger.
Due to this tactical mistake, the Wei army led by Zhang He encircled the hill and cut off the water supply to the Shu troops and defeated them. Amidst the panic, Ma Su is recorded to have left his post leaving the army with no commander. Wang Ping rallied Ma Su's army and with only a handful of soldiers did his best to keep the retreat organized and ordered his soldiers to beat their drums loudly to create the impression that reinforcements had arrived. Zhang He believed this to possibly be a sign of an ambush and so he did not pursue. When Zhuge Liang arrived, he attempted to defeat Zhang He however he didn't find a way to take a position and so the Shu army had to retreat to Hanzhong.
Though he survived the battle, Ma Su's army suffered a heavy defeat (Wang Ping was able to regroup Ma Su's remaining troops and gather the Shu army's scattered supplies.), so he was soon arrested and sentenced to execution by a reluctant and tearful Zhuge Liang.
Jieting was a crucial region for the securing of supplies, and Zhuge Liang sent Ma Su and Wang Ping to guard the region. Ma Su went accompanied by Wang Ping but did not listen to his sound military advice. Relying purely on books of military tactics, Ma Su chose to "take the high ground" and set his base on the mountains instead of in a city, ignoring Wang Ping's advice to make camp in a valley well supplied with water. Wang Ping, however, managed to persuade Ma Su to give him command of a portion of the troops, and later Wang set up his base camp near Ma's camp, in order to offer assistance when Ma was in danger.
Due to this tactical mistake, the Wei army led by Zhang He encircled the hill and cut off the water supply to the Shu troops and defeated them. Amidst the panic, Ma Su is recorded to have left his post leaving the army with no commander. Wang Ping rallied Ma Su's army and with only a handful of soldiers did his best to keep the retreat organized and ordered his soldiers to beat their drums loudly to create the impression that reinforcements had arrived. Zhang He believed this to possibly be a sign of an ambush and so he did not pursue. When Zhuge Liang arrived, he attempted to defeat Zhang He however he didn't find a way to take a position and so the Shu army had to retreat to Hanzhong.
Though he survived the battle, Ma Su's army suffered a heavy defeat (Wang Ping was able to regroup Ma Su's remaining troops and gather the Shu army's scattered supplies.), so he was soon arrested and sentenced to execution by a reluctant and tearful Zhuge Liang.
Aftermath
Ma Su was sentenced to death by Zhuge Liang, along with his deputies Zhang Xiu () and Li Sheng () as a way to soothe the masses. Before his execution Ma Su wrote a letter to Zhuge Liang: Many among the army wept greatly for Ma Su's death. Because of the loss of Jieting, the supply situation became dire for Zhuge Liang's army and he had to retreat to his main base at Hanzhong. In addition, the defeat at Jieting caused the First Northern Expedition to result in failure.Location
The exact location of the battle is not certain, according to research by theGansu Daily
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibe ...
newspaper, there are several plausible locations.
* Jieting village, Maiji District
Maiji District () is a district of the prefecture-level city of Tianshui in the southeast of Gansu, Gansu Province, China, bordering Shaanxi, Shaanxi Province to the east. It is best known for, and named after, the Maijishan Grottoes. Before 2005 ...
, southeast of Tianshui
Tianshui is the second-largest cities in Gansu, city in Gansu list of Chinese provinces, Province, China. The city is located in the southeast of the province, along the upper reaches of the Wei River and at the boundary of the Loess Plateau and ...
* Gongmen town, east of Zhangjiachuan County
The Zhangjiachuan Hui Autonomous County (, Xiao'erjing: ) is a county in the east of Gansu Province of the People's Republic of China, bordering Shaanxi Province to the east. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Tianshui ...
* Jieting Mountain in Mian County
Mian County or Mianxian () is a county of Hanzhong, in Shaannan, the southwest of Shaanxi province, China, bordering Gansu province to the northwest. Its area measures , and its total population as of 2020 was 429,000 people. During the Qin dynast ...
, Shaanxi Province
* Longcheng town, east of Qin'an County
Qin'an County () is a county in the east of Gansu province of the People's Republic of China. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Tianshui. Its postal code is 741600, and in 1999 its population was 567,553 people. As of 2 ...
, Gansu
* Other locations named by some are Huating and Zhuanglang
A memorial of the battle is located in Longcheng town. Topographical evidence and weapons found suggest that Longcheng is the most likely location, although there is no consensus among experts.
In ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms''
In the 14th-century historical novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms
''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' () is a 14th-century historical novel attributed to Luo Guanzhong. It is set in the turbulent years towards the end of the Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period in Chinese history, starting in 184 AD and ...
'', Ma Su was executed on the order of a tearful Zhuge Liang, whose continued high appraisal for Ma's intelligence made that a very reluctant decision. The scene has also been reenacted in Chinese opera
Traditional Chinese opera (), or ''Xiqu'', is a form of musical theatre in China with roots going back to the early periods in China. It is an amalgamation of various art forms that existed in ancient China, and evolved gradually over more tha ...
. A Chinese proverb, "wiping away tears and executing Ma Su" (), refers specifically to this incident, meaning "punishing a person for his wrongdoings regardless of relations or his abilities. A Japanese equivalent is .
In the novel, the loss of Jieting exposed Zhuge Liang's current location, the defenceless Xicheng (西城). Zhuge Liang used the Empty Fort Strategy
The Empty Fort Strategy is the 32nd of the Chinese Thirty-Six Stratagems. The strategy involves using reverse psychology (and luck) to deceive the enemy into thinking that an empty location is full of traps and ambushes, and therefore induce the en ...
to ward off the enemy before retreating.
In many stories, including the novel, the battle includes Sima Yi
Sima Yi ( ; 179 CE – 7 September 251 CE), courtesy name Zhongda, was a Chinese military general, politician, and regent of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China.
He formally began his political career in 208 un ...
on the Wei side, but this event is impossible according to his biography in the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms''. Moss Roberts comments on this in his fourth volume of his English translation of ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' on (page 2179 under Chapter 95 Notes, fourth and last paragraph of the chapter notes):
::''The historical Sima Yi was not at the western front for the "vacant city ruse" but at the more important southern front with the Southland u Sima Yi did not come to the western front until Kongming's huge Liangfourth offensive attle of Mount Qi The fictional tradition tends to attach more importance to the Wei-Shu conflict than the Wei-Wu conflict, and Three Kingdoms accordingly builds up the Kongming-Sima Yi rivalry and the events of AD 228.''
In the abstract theory above, Roberts explains and compares historic history with fictional tales and the most likely reason Sima Yi was included before the Battle of Mount Qi
The Battle of Mount Qi was a military conflict which took place around Mount Qi (祁山; the mountainous regions around present-day Li County, Gansu) between the states of Cao Wei and Shu Han in 231 during the Three Kingdoms period of China. I ...
. Based on Robert's view of the fictional novel's tendency to build up the rivalry between Sima Yi and Zhuge Liang, and the contradiction of Sima Yi's location at the time of this event, some share Robert's opinion that the event did not happen. However, many historians agree that Sima Yi's absence alone cannot disprove the occurrence. The historical basis for the event comes from an anecdote shared by Guo Chong (郭沖) in the early Jin dynasty (266–420). The anecdote is translated as follows:
"Zhuge Liang garrisoned at Yangping (陽平; around present-day Hanzhong, Shaanxi) and ordered Wei Yan to lead the troops east. He left behind only 10,000 men to defend Yangping. Sima Yi led 200,000 troops to attack Zhuge Liang and he took a shortcut, bypassing Wei Yan's army and arriving at a place 60 li away from Zhuge Liang's location. Upon inspection, Sima Yi realised that Zhuge Liang's city was weakly defended. Zhuge Liang knew that Sima Yi was near, so he thought of recalling Wei Yan's army back to counter Sima Yi, but it was too late already and his men were worried and terrified. Zhuge Liang remained calm and instructed his men to hide all flags and banners and silence the war drums. He then ordered all the gates to be opened and told his men to sweep and dust the ground. Sima Yi was under the impression that Zhuge Liang was cautious and prudent, and he was baffled by the sight before him and suspected that there was an ambush. He then withdrew his troops. The following day, Zhuge Liang clapped his hands, laughed, and told an aide that Sima Yi thought that there was an ambush and had retreated. Later, his scouts returned and reported that Sima Yi had indeed retreated. Sima Yi was very upset when he found out later."
Later, in the fifth century, Pei Songzhi added the anecdote as an annotation to Zhuge Liang's biography in the Sanguozhi. Since Zhuge Liang wrote on the use of this tactic in his compilation work, "Thirty Six Stratagems", going so far as to detail how the psychology employed works, and why:
"When the enemy is superior in numbers and your situation is such that you expect to be overrun at any moment, then drop all pretense of military preparedness, act calmly, and taunt the enemy, so that the enemy will think you have a huge ambush hidden for them. It works best by acting calm and at ease when your enemy expects you to be tense. This ploy is only successful if in most cases you do have a powerful hidden force and only sparsely use the empty fort strategy."
Also worthy of note is that Zhuge Liang wrote this passage in his sixth chapter, titled "Desperate Stratagems", (敗戰計/败战计, Bài zhàn jì), further supporting the implication that he had experience in using this tactic, and his description does match the situation described by Guo Chong. However, there are a number of texts that dispute the accuracy of Guo Chong's anecdote.In popular culture
The battle is featured as a playable stage inKoei
Koei Co., Ltd. was a Japanese video game publisher, developer, and distributor founded in 1978. The company is known for its ''Dynasty Warriors'' games based on the novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'', as well as simulation games based on p ...
's video game series ''Dynasty Warriors
is a series of Japanese hack and slash action video games created by Omega Force and Koei (now is Koei Tecmo). The series is a spin-off of Koei's turn-based strategy '' Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' series, based upon the Chinese novel of ...
'' for the PlayStation 2
The PlayStation 2 (PS2) is a home video game console developed and marketed by Sony Computer Entertainment. It was first released in Japan on 4 March 2000, in North America on 26 October 2000, in Europe on 24 November 2000, and in Australia on 3 ...
. If the player is playing on the Wei side, he has the option of following history to win the stage easily. On the other hand, if the player is playing on the Shu side, he will encounter a higher level of difficulty since one of his major objectives is to ensure the survival of Ma Su.
In the collectible card game ''Magic: The Gathering
''Magic: The Gathering'' (colloquially known as ''Magic'' or ''MTG'') is a Tabletop game, tabletop and Digital collectible card game, digital Collectible card game, collectable card game created by Richard Garfield. Released in 1993 by Wizards ...
'' there is a card named Empty City Ruse in reference to the Empty Fort Strategy
The Empty Fort Strategy is the 32nd of the Chinese Thirty-Six Stratagems. The strategy involves using reverse psychology (and luck) to deceive the enemy into thinking that an empty location is full of traps and ambushes, and therefore induce the en ...
described in the 14th-century historical novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms
''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' () is a 14th-century historical novel attributed to Luo Guanzhong. It is set in the turbulent years towards the end of the Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period in Chinese history, starting in 184 AD and ...
''.
Notes
References
*Chen Shou
Chen Shou (; 233–297), courtesy name Chengzuo (), was a Chinese historian, politician, and writer who lived during the Three Kingdoms period and Jin dynasty of China. Chen Shou is most known for his most celebrated work, the ''Records of the ...
. ''Records of Three Kingdoms
The ''Records or History of the Three Kingdoms'', also known by its Chinese name as the Sanguo Zhi, is a Chinese historical text which covers the history of the late Eastern Han dynasty (c. 184–220 AD) and the Three Kingdoms period (220– ...
'', Volume 17, Biography of Zhang He
Zhang He () (died July or August 231), courtesy name Junyi, was a military general serving under the warlord Cao Cao in the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He continued serving in the state of Cao Wei under its first two rulers, Cao Pi and ...
.
*Luo Guanzhong
Luo Ben (c. 1330–1400, or c.1280–1360), better known by his courtesy name Guanzhong (Mandarin pronunciation: ), was a Chinese writer who lived during the Ming dynasty. He was also known by his pseudonym Huhai Sanren (). Luo was attri ...
. ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms
''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' () is a 14th-century historical novel attributed to Luo Guanzhong. It is set in the turbulent years towards the end of the Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period in Chinese history, starting in 184 AD and ...
'', Chapters 95-96.
{{coord, 35.0020074, N, 105.9718660, E, source:wikidata, display=title
Jieting
Jieting 228
228
Military history of Gansu