Buccal Object Rule on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
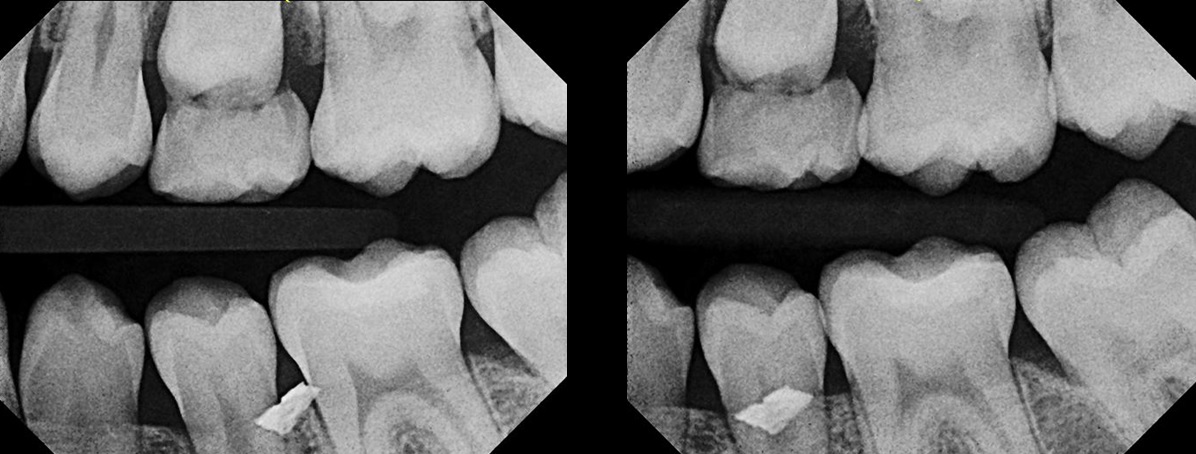 The buccal object/SLOB rule is a method used to determine the relative position of two objects in the
The buccal object/SLOB rule is a method used to determine the relative position of two objects in the
SLOB rule
'', as a complicated set of three radiographs, but which can be simplified as follows using just two: :Expose another film while angle of the x-ray beam has been changed. If an object moves in the ''same'' direction as the source of the x-ray beam, it is ''
 In 1952, Richards amended this rule using only 2 radiographs,Richards AG. The buccal object rule. ''Journal of the Tennessee State Dental Association'' 1953;33:263-268 asserting that the object positioned more buccally will move more relative to the object positioned more palatally or lingually.
As a generalization, but not specifically stated as part of Richards' buccal object rule, the ''more buccal'' an object is (i.e. the closer it is to the x-ray source) the ''more it will move'' in the second radiograph when repositioning the x-ray source.
At the
In 1952, Richards amended this rule using only 2 radiographs,Richards AG. The buccal object rule. ''Journal of the Tennessee State Dental Association'' 1953;33:263-268 asserting that the object positioned more buccally will move more relative to the object positioned more palatally or lingually.
As a generalization, but not specifically stated as part of Richards' buccal object rule, the ''more buccal'' an object is (i.e. the closer it is to the x-ray source) the ''more it will move'' in the second radiograph when repositioning the x-ray source.
At the
 The buccal object/SLOB rule is a method used to determine the relative position of two objects in the
The buccal object/SLOB rule is a method used to determine the relative position of two objects in the oral cavity
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on t ...
using projectional dental radiography.
Clark's Rule
In 1909, Charles A. Clark described a radiographic procedure for localizing impacted teeth to determining their relative antero-posterior position. If the two teeth (or, by extension, any two objects, such as a tooth and a foreign object) are located in front of one another relative to the x-ray beam, they will appear superimposed on one another on a dental radiograph, but it will be impossible to know which one is in front of the other. To determine which is in front and which is behind, Clark proposed his 'SLOB rule
'', as a complicated set of three radiographs, but which can be simplified as follows using just two: :Expose another film while angle of the x-ray beam has been changed. If an object moves in the ''same'' direction as the source of the x-ray beam, it is ''
lingual
Lingual may refer to:
* Tongue, a muscular hydrostat on the floors of the mouths of most vertebrates which manipulates food for mastication
* Lingual, in palaeontology, the side of the teeth that faces the tongue
* Lingual artery arises from the e ...
'' to the other object. If the object moves in the ''opposite'' direction of the source, it is '' buccal'' to the other object.
:Same Lingual; Opposite Buccal
SLOB rule in Dentistry Video Tutorial
The video below shows a 5 minute illustration describing SLOB rule in dentistry https://www.youtube.com/embed/AzjvFPlZtZgBuccal Object Rule
 In 1952, Richards amended this rule using only 2 radiographs,Richards AG. The buccal object rule. ''Journal of the Tennessee State Dental Association'' 1953;33:263-268 asserting that the object positioned more buccally will move more relative to the object positioned more palatally or lingually.
As a generalization, but not specifically stated as part of Richards' buccal object rule, the ''more buccal'' an object is (i.e. the closer it is to the x-ray source) the ''more it will move'' in the second radiograph when repositioning the x-ray source.
At the
In 1952, Richards amended this rule using only 2 radiographs,Richards AG. The buccal object rule. ''Journal of the Tennessee State Dental Association'' 1953;33:263-268 asserting that the object positioned more buccally will move more relative to the object positioned more palatally or lingually.
As a generalization, but not specifically stated as part of Richards' buccal object rule, the ''more buccal'' an object is (i.e. the closer it is to the x-ray source) the ''more it will move'' in the second radiograph when repositioning the x-ray source.
At the University of Alabama School of Dentistry
The University of Alabama School of Dentistry is the public dental school located at the University of Alabama in Birmingham, Alabama, United States. The dental school was founded in 1948 and is the only dental school in Alabama.
History
T ...
, this rule is referred to as the BAMA rule: buccal always moves away.
References
{{reflist Dentistry