branch dock on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A branch dock is a
A branch dock is a 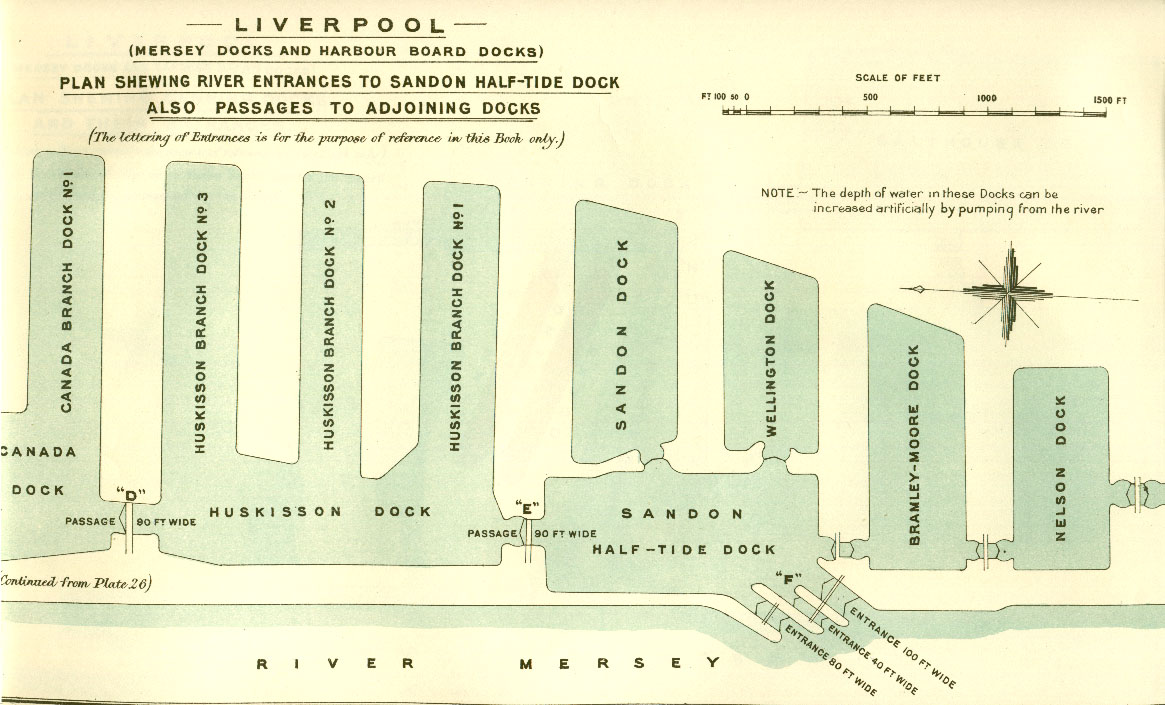 Branch docks are terminal branches of a main
Branch docks are terminal branches of a main
 A branch dock is a
A branch dock is a dock
A dock (from Dutch ''dok'') is the area of water between or next to one or a group of human-made structures that are involved in the handling of boats or ships (usually on or near a shore) or such structures themselves. The exact meaning va ...
that forms part of a large harbour system of interlinked docks.
 Branch docks are terminal branches of a main
Branch docks are terminal branches of a main floating dock
Floating may refer to:
* a type of dental work performed on horse teeth
* use of an isolation tank
* the guitar-playing technique where chords are sustained rather than scratched
* ''Floating'' (play), by Hugh Hughes
* Floating (psychological phe ...
. They are ''not'' isolated from the main dock by gate
A gate or gateway is a point of entry to or from a space enclosed by walls. The word derived from old Norse "gat" meaning road or path; But other terms include '' yett and port''. The concept originally referred to the gap or hole in the wal ...
s or locks and they share the same water level. Where docks join other docks or basins through gates, these are usually given a distinct name rather than being termed a 'branch'. Floating docks that are separated from tidal waters by a half tide dock commonly have related names such as Sandon Dock and Sandon Half Tide Dock. Branch docks are usually numbered, following the name of their main dock, i.e. ' Gladstone Number Three Branch Dock', rather than individually named.
The purpose of a branch dock is to increase the quay
A wharf, quay (, also ), staith, or staithe is a structure on the shore of a harbour or on the bank of a river or canal where ships may dock to load and unload cargo or passengers. Such a structure includes one or more berths ( mooring locati ...
side frontage and space for warehouse
A warehouse is a building for storing goods. Warehouses are used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, wholesalers, transport businesses, customs, etc. They are usually large plain buildings in industrial parks on the outskirts of cities, ...
s, for a given volume of water,The cost of excavation for a dock is roughly proportional to its volume. and without requiring the cost and complexity of more locks.
Branch docks first appeared in the 18th century, but their heyday was in the middle of the 19th century when major Victorian port cities such as Liverpool
Liverpool is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the List of English districts by population, 10th largest English district by population and its E ...
were constructing their dock systems. Complex floating harbours were being built that allowed more ships to enter or leave on each tide. The increased number of ships required more space for loading than a simple rectangular dock
When ships began to increase in size after World War II and cargo began to be handled by either bulk carrier
A bulk carrier or bulker is a merchant ship specially designed to transport unpackaged bulk cargo — such as grains, coal, ore, steel coils, and cement — in its cargo holds. Since the first specialized bulk carrier was built in 1852, ec ...
s or container
A container is any receptacle or enclosure for holding a product used in storage, packaging, and transportation, including shipping.
Things kept inside of a container are protected on several sides by being inside of its structure. The term ...
s, the need for warehouses at docks was reduced. Many older docks became obsolete and were closed in the 1970s and 1980s. These branch docks were often infilled to create more land within the dock complex; either to provide parking and marshalling space for container trucks, or to build new dock features such as specialist bulk loading facilities or other ancillaries.The infilled Sandon Dock now contains a sewage plant.
Notes
References
Docks (maritime) {{Water-transport-stub