Bottleneck (engineering) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
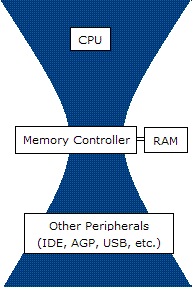 In
In
Jean-Yves Le Boudec (EPFL Lausanne) "Rate adaptation, Congestion Control and Fairness: A Tutorial" Nov 2005
/ref> Note that this definition is substantially different from a common meaning of a ''bottleneck''. Also note, that this definition does not forbid a single link to be a bottleneck for multiple flows. A data rate allocation is max-min fair if and only if a data flow between any two nodes has at least one bottleneck link.
 In
In engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
, a bottleneck is a phenomenon by which the performance or capacity of an entire system is severely limited by a single component. The component is sometimes called a bottleneck point. The term is metaphorically derived from the neck of a bottle, where the flow speed of the liquid is limited by its neck.
Formally, a bottleneck lies on a system's critical path and provides the lowest throughput. Bottlenecks are usually avoided by system designers, also a great amount of effort is directed at locating and tuning them. Bottleneck may be for example a processor, a communication link, a data processing software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
, etc.
Bottlenecks in software
Incomputer programming
Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called computer program, programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of proc ...
, tracking down bottlenecks (sometimes known as "hot spots" - sections of the code that execute most frequently - i.e. have the highest execution count) is called performance analysis. Reduction is usually achieved with the help of specialized tools, known as performance analyzers or profilers. The objective being to make those particular sections of code perform as fast as possible to improve overall algorithmic efficiency
In computer science, algorithmic efficiency is a property of an algorithm which relates to the amount of computational resources used by the algorithm. Algorithmic efficiency can be thought of as analogous to engineering productivity for a repea ...
.
Bottlenecks in max-min fairness
In a communication network, sometimes a max-min fairness of the network is desired, usually opposed to the basic first-come first-served policy. With max-min fairness, data flow between any two nodes is maximized, but only at the cost of ''more or equally expensive'' data flows. To put it another way, in case of network congestion any data flow is only impacted by smaller or equal flows. In such context, a ''bottleneck link'' for a given data flow is a link that is fully utilized (is ''saturated'') and of all the flows sharing this link, the given data flow achieves maximum data rate network-wide./ref> Note that this definition is substantially different from a common meaning of a ''bottleneck''. Also note, that this definition does not forbid a single link to be a bottleneck for multiple flows. A data rate allocation is max-min fair if and only if a data flow between any two nodes has at least one bottleneck link.
See also
* Fairness measure ** Max-min fairness *Optimization (computer science)
In computer science, program optimization, code optimization, or software optimization is the process of modifying a software system to make some aspect of it work more algorithmic efficiency, efficiently or use fewer resources. In general, a com ...
* Performance engineering
Performance engineering encompasses the techniques applied during a systems development life cycle to ensure the non-functional requirements for performance (such as throughput, latency, or memory usage) will be met. It may be alternatively refe ...
* Profiling (computer programming)
In software engineering, profiling (program profiling, software profiling) is a form of dynamic program analysis that measures, for example, the space (memory) or time complexity of a program, the usage of particular instructions, or the freque ...
* Route capacity
* Theory of constraints
The theory of constraints (TOC) is a management paradigm that views any manageable system as being limited in achieving more of its goals by a very small number of constraints. There is always at least one constraint, and TOC uses a focusing p ...
References
{{Reflist Network performance