Bois-Brûlés on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Bois-Brûlés (''burnt wood'') are
Bois-Brûlés (''burnt wood'') are
Dictionary of Canadian Biography (DICKSON, JAMES, self-styled “Liberator of the Indian Nations”)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Bois-Brules Métis people First Nations in Manitoba Métis in the United States


Métis
The Métis ( , , , ) are a mixed-race Indigenous people whose historical homelands include Canada's three Prairie Provinces extending into parts of Ontario, British Columbia, the Northwest Territories and the northwest United States. They ha ...
. The name is most frequently associated with the French-speaking Métis
The Métis ( , , , ) are a mixed-race Indigenous people whose historical homelands include Canada's three Prairie Provinces extending into parts of Ontario, British Columbia, the Northwest Territories and the northwest United States. They ha ...
of the Red River Colony
The Red River Colony (or Selkirk Settlement), also known as Assiniboia, was a colonization project set up in 1811 by Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk, on of land in British North America. This land was granted to Douglas by the Hudson's Bay ...
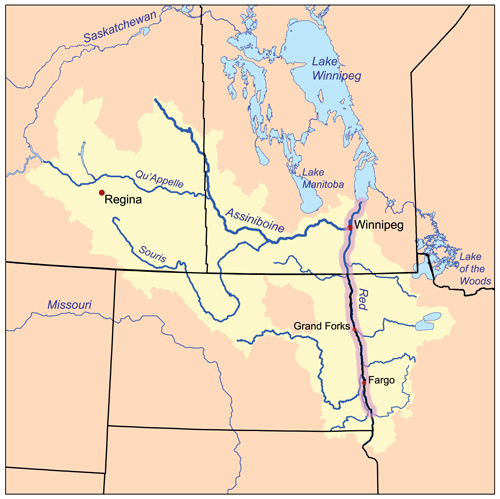
in the Red River valley
The Red River Valley is a region in central North America that is drained by the Red River of the North; it is part of both Canada and the United States. Forming the border between Minnesota and North Dakota when these territories were admitted ...
of Canada and the United States.
The Bois-Brûlés, led by their leader Cuthbert Grant, took part in the Battle of Seven Oaks (1816). The "Chanson de la Grenouillère", composed in 1816 by Métis bard Pierre Falcon in honour of the Battle of Seven Oaks, also called "Falcon's Song" or "la Bataille des sept chênes", refers to the Métis participants as victorious "Bois-Brûlés", and the song remained central to Métis lore for generations. In 1837 Pierre Falcon also wrote "The Dickson Song" or "''Ballade du Général Dickson''". The song is about "General" James Dickson who planned to raise an army of Bois-Brûlés for the purpose of setting up a kingdom in California.
William H. Keating described a group of Métis buffalo hunt
The Métis ( , , , ) are a mixed-race Indigenous people whose historical homelands include Canada's three Prairie Provinces extending into parts of Ontario, British Columbia, the Northwest Territories and the northwest United States. They hav ...
ers he encountered at Pembina by the Red River of the North in 1823 as ''Bois brulés''.
Later in the 19th century, the people in 1869 came into temporary prominence during the Riel Rebellion in the Red River area. They were alternatively called Métis
The Métis ( , , , ) are a mixed-race Indigenous people whose historical homelands include Canada's three Prairie Provinces extending into parts of Ontario, British Columbia, the Northwest Territories and the northwest United States. They ha ...
; historically the majority were descendants of French Canadian
French Canadians, referred to as Canadiens mainly before the nineteenth century, are an ethnic group descended from French people, French colonists first arriving in Canada (New France), France's colony of Canada in 1608. The vast majority of ...
men and First Nations
First nations are indigenous settlers or bands.
First Nations, first nations, or first peoples may also refer to:
Indigenous groups
*List of Indigenous peoples
*First Nations in Canada, Indigenous peoples of Canada who are neither Inuit nor Mé ...
women.
The name Bois-Brûlés seems to have waned in popularity and general use after the merger of the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), originally the Governor and Company of Adventurers of England Trading Into Hudson’s Bay, is a Canadian holding company of department stores, and the oldest corporation in North America. It was the owner of the ...
and North West Company
The North West Company was a Fur trade in Canada, Canadian fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in the regions that later became Western Canada a ...
in 1821. The young Canadian adventurer Martin McLeod, later a fur trader and Minnesota Territory politician in the United States, referred to the "Brules" in 1837 in his journal of travel to the Red River of the North
The Red River (), also called the Red River of the North () to differentiate it from the Red River of the South, Red River in the south of the continent, is a river in the north-central United States and central Canada. Originating at the confl ...
region with James Dickson, who had a dream of an Indian empire.Grace L. Nute, "James Dickson, A Filibuster in Minnesota in 1836," in ''Mississippi Valley Historical Review'', 10: 127-140 (September 1923) As late as 1900, the American author Jack London
John Griffith London (; January 12, 1876 – November 22, 1916), better known as Jack London, was an American novelist, journalist and activist. A pioneer of commercial fiction and American magazines, he was one of the first American authors t ...
used the term in his short story, "An Odyssey of the North".
See also
* Turtle Mountain Band of Chippewa IndiansReferences
External links
Dictionary of Canadian Biography (DICKSON, JAMES, self-styled “Liberator of the Indian Nations”)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Bois-Brules Métis people First Nations in Manitoba Métis in the United States