Bogart–Bacall syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bogart–Bacall syndrome (BBS) is a voice disorder that is caused by abuse or overuse of the vocal cords.
 People who speak or sing outside their normal vocal range can develop BBS; symptoms are chiefly an unusually deep or rough voice, or
People who speak or sing outside their normal vocal range can develop BBS; symptoms are chiefly an unusually deep or rough voice, or
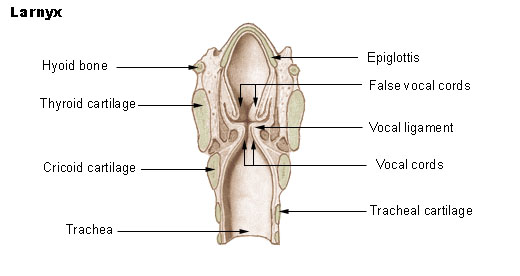
 People who speak or sing outside their normal vocal range can develop BBS; symptoms are chiefly an unusually deep or rough voice, or
People who speak or sing outside their normal vocal range can develop BBS; symptoms are chiefly an unusually deep or rough voice, or dysphonia
A hoarse voice, also known as dysphonia or hoarseness, is when the voice involuntarily sounds breathy, raspy, or strained, or is softer in volume or lower in pitch. A hoarse voice can be associated with a feeling of unease or scratchiness in the ...
, and vocal fatigue. The people most commonly affected are those who speak in a low-pitched voice, particularly if they have poor breath and vocal control. The syndrome can affect both men and women.
In 1988, an article was published describing a discrete type of vocal dysfunction which results in men sounding like actor Humphrey Bogart
Humphrey DeForest Bogart ( ; December 25, 1899 – January 14, 1957), nicknamed Bogie, was an American actor. His performances in classic Hollywood cinema made him an American cultural icon. In 1999, the American Film Institute selected Bogart ...
and women sounding like actress Lauren Bacall
Betty Joan Perske (September 16, 1924 – August 12, 2014), professionally known as Lauren Bacall ( ), was an American actress. She was named the AFI's 100 Years...100 Stars, 20th-greatest female star of classic Hollywood cinema by the America ...
; Bogart and Bacall were married to each other and made several films together. BBS is now the medical term for an ongoing hoarseness that often affects actors, singers or TV/radio voice workers who routinely speak in a very low pitch.
Treatment usually involves voice therapy by a speech language pathologist.
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms of Bogart–Bacall Syndrome can appear differently depending on the vocal use of the individual. In singers, symptoms may appear more subtly due to their extreme sensitivity to small changes in the laryngeal mechanism and being able to control their laryngeal muscles more than the average person. This vocal control can compensate for irritation, weakness, or change in vibration patterns for the vocal folds. Signs and symptoms will vary on a case-by-case basis and will depend on vocal strain and the degree of daily use. Women are also more susceptible than men to experience heightened symptoms due to their increased likelihood of speaking at a lower pitch in professional settings. Signs and symptoms of Bogart–Bacall include the following: * Vocal fatigue * Unnaturally deep or rough voice *Hoarseness
A hoarse voice, also known as dysphonia or hoarseness, is when the voice involuntarily sounds breathy, raspy, or strained, or is softer in volume or lower in pitch. A hoarse voice can be associated with a feeling of unease or scratchiness in the ...
* Sore larynx (tightness or muscle aches in the throat)
* Sudden breaks or fading of the voice
* Loss of vocal range when singing
* Feeling the need to clear the throat often
* Experiencing loss of speech
Cause
The cause of Bogart–Bacall syndrome is most commonly identified as abuse or overuse of the vocal cords. Individuals who speak or sing outside of their normal range can develop BBS over a long period of misuse. Individuals who develop this syndrome tend to speak or perform with poor breath support and laryngeal muscle tension. Causes include speech and communication disorders, throat conditions, and work-related conditions. Speech and communication disorders refers to issues involving language and related areas such as oral motor function. Some examples includeexpressive language disorder
Expressive language disorder is one of the "specific developmental disorders of speech and language" recognized by the tenth edition of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10). As of the eleventh edition (ICD-11, current 1 January 20 ...
, receptive-expressive language disorder, phonologic disorder, and stuttering
Stuttering, also known as stammering, is a speech disorder characterized externally by involuntary repetitions and prolongations of sounds, syllables, words, or phrases as well as involuntary silent pauses called blocks in which the person who ...
.
Throat conditions can be any one of the following:
* Vocal cord paralysis
* Vocal cord polyps
* Laryngitis
Laryngitis is inflammation of the larynx (voice box). Symptoms often include a hoarse voice and may include fever, cough, pain in the front of the neck, and trouble swallowing. Typically, these last under 2 weeks.
Causes
Laryngitis is cat ...
* Achalasia
Esophageal achalasia, often referred to simply as achalasia, is a failure of smooth muscle fibers to relax, which can cause the lower esophageal sphincter to remain closed. Without a modifier, "achalasia" usually refers to achalasia of the esopha ...
* Throat cancer
Head and neck cancer is a general term encompassing multiple cancers that can develop in the head and neck region. These include cancers of the mouth, tongue, gums and lips ( oral cancer), voice box ( laryngeal), throat ( nasopharyngeal, orophar ...
* Hypopharyngeal cancer
Hypopharyngeal cancer is a disease in which malignant cells grow in the hypopharynx (also known as the ''laryngopharynx'') the area where the larynx and esophagus meet.
It first forms in the outer layer (epithelium) of the hypopharynx (last part ...
* Larynx cancer
Laryngeal cancer is a kind of cancer that can develop in any part of the larynx (voice box). It is typically a squamous-cell carcinoma, reflecting its origin from the epithelium of the larynx.
The prognosis is affected by the location of the tum ...
.
Work-related conditions typically affect individuals whose professions require extensive use or overuse of their vocal cords. Some examples include news and television broadcasters, radio hosts, as well as singers or actors. Teachers may also be susceptible to BBS depending on their volume and how much they talk on a regular basis.
Mechanism
There are many plausible reasons for how Bogart–Bacall and other vocal disorders occur, but it can not be determined for certain due to the many factors that play a role in speech production. Voice production requires the coordination of many muscles and other structures in the larynx. Many factors can cause the larynx to become tensed which changes the position of larynx. This affects thecartilaginous
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. Semi-transparent and non-porous, it is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints ...
structures within the larynx leading to abnormal phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defi ...
. Bogart–Bacall refers to an unnaturally deep voice, so when lowering their voice, individuals may continue to speak even when the air in their lungs has been almost entirely expelled. Due to the effort exerted in lowering the pitch range, the muscles involved in respiration become tensed and strained along with speech.
Bogart–Bacall syndrome is considered a secondary muscle tension dysphonia disorder, meaning that there is an abnormality in the voice box that causes the overuse of muscles to help produce your voice. This abnormality can be caused by an underlying medical reason or a physical exertion. By lowering vocal pitch, the larynx compresses the vocal folds which regulate air flow and production of the sounds used in speech which can cause damage to these muscles over time. Vocal fold lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by injury or diseases. The term ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin meaning "injury". Lesions may occur in both plants and animals.
Types
There is no de ...
s or nodule
Nodule may refer to:
* Nodule (geology), a small rock or mineral cluster
* Manganese nodule, a metallic concretion found on the seafloor
*Nodule (medicine), a small aggregation of cells
*Root nodule
Root nodules are found on the roots of plants, ...
s can cause changes in the vocal fold mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It ...
which leads to increased tension in the larynx, ultimately causing dysphonia.

Diagnosis
A speech-language pathology evaluation will need to be conducted to be conscious vocal use history as well examination of the throat and larynx. This evaluation potentially involves imaging to visualize the vocal cords. Imaging options can include alaryngoscope
Laryngoscopy () is endoscopy of the larynx, a part of the throat. It is a medical procedure that is used to obtain a view, for example, of the vocal folds and the glottis. Laryngoscopy may be performed to facilitate tracheal intubation during ge ...
, videostroboscopy, or laryngeal electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyo ...
. Diagnosis of Bogart–Bacall can be difficult due to the variance in symptom presentation and vocal use.
Videostroboscopy provides a magnified, slow-motion view of the vocal cords and larynx in action which allows professionals to see any abnormal movement. Videostroboscopy can be used to visualize any swelling of the vocal folds, irritation, or polyps and growth. Occasionally, redness or bumps can be seen on vocal cords which is useful in making a correct diagnosis.
Laryngeal electromyography is a test that measures the electrical signals from the voice box muscles (laryngeal muscles) during speaking, breathing, and swallowing. This evaluation is to check if vocal issues are related to any one of the following: partial paralysis resulting in muscle weakness, paralysis
Paralysis (: paralyses; also known as plegia) is a loss of Motor skill, motor function in one or more Skeletal muscle, muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory d ...
resulting in loss of muscle function, and the functionality of the motor unit of the laryngeal muscles. Laryngeal electromyography plays an important role in determining whether or not a nerve problem is the cause of a vocal disorder.
Prevention and treatment
Prevention of Bogart–Bacall syndrome aims to target the two main symptoms of this disorder,dysphonia
A hoarse voice, also known as dysphonia or hoarseness, is when the voice involuntarily sounds breathy, raspy, or strained, or is softer in volume or lower in pitch. A hoarse voice can be associated with a feeling of unease or scratchiness in the ...
and vocal fatigue. Having effective posture allows a person to shift the tension between the muscles allowing free movement of the larynx without blockage leading to effective voice production. Improvement of breath control with a professional vocal coach
A vocal coach, also known as a voice coach (though this term often applies to those working with speech and communication rather than singing), is a music teacher, usually a piano accompanist, who helps singers prepare for a performance, often al ...
is also important for individuals who may have work-related conditions that require continuous strain on the vocal cords and larynx.
Speech therapy
Speech is the use of the human voice as a medium for language. Spoken language combines vowel and consonant sounds to form units of meaning like words, which belong to a language's lexicon. There are many different intentional speech acts, suc ...
with a speech-language pathologist is a very common method of treatment to return speaking level to its normal pitch range. Consultation with a speech-language pathologist will determine what levels of rest, fluid, and performance corrections are needed for the vocal cords and larynx to sustain a healthy voice. If there is a particular underlying cause of the condition that can be treated with medication, this can be coupled with speech therapy as a form of treatment.
Individuals with persistent symptoms after speech therapy may require more invasive treatment. Invasive treatment may require the removal of lesions, nodules, or masses on the vocal cords if visualized during diagnostic imaging. If the disorder is found to be nerve related through electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyo ...
the nerve in question may need to be replaced or the vocal cords can be pushed together with a bulk injection or thyroplasty. A bulk injection involves adding a filler substance to the paralyzed vocal cord to have it vibrate closer to the functioning vocal cord. Thyroplasty involves the insertion of an implant against the paralyzed vocal cord moving it closer to the other vocal cord.
Prognosis
Individuals with Bogart–Bacall syndrome that do not have an underlying condition are typically expected to make a vocal recovery through voice therapy. Having a form of muscle tension dysphonia go untreated, can cause further long-term disorders that require additional forms of treatment.Epidemiology
Bogart–Bacall syndrome can develop in individuals at any age. It is more likely to develop in individuals who work in voice performance which can range from singers, actors, teachers or radio and television broadcasters. Women are more likely than men to develop BBS due to the tendency of lowering their voices in a professional environment. This syndrome is also more prevalent in the 40–50-year-old-age group as their vocal cords thin. Vocal disorders are prevalent in roughly 10% of the population and can range from muscle tension dysphonia to speech and language disorders.Research directions
Further studies need to be conducted to further examine the long-term effects of Bogart–Bacall syndrome if left untreated. Studies that are currently ongoing aim to understand what the best course of treatment may be for individuals with muscle tension dysphonia, which includes individuals with Bogart–Bacall. It is currently understood that an interdisciplinary approach to target the causes such as poor breath support, overuse, and inappropriate intensity is most effective. Vocal disorders and misuse are currently being researched depending on work conditions and professions. A study based on over 1,200 teachers has indicated that voice disorders play a significant role in their profession. The study found that a substantial number of teachers have needed to take time off work or seek medical attention due to voice issues or to seek treatment. The study also found that women are more likely to develop these disorders over their male counterparts. There is more research available on vocal disorders and how they may be effected by additional lifestyle factors. A study was conducted to understand how reflux effected vocal disorders such as dysphonia in singers withbulimia
Bulimia nervosa, also known simply as bulimia, is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating (eating large quantities of food in a short period of time, often feeling out of control) followed by compensatory behaviors, such as self-induc ...
. Singers tend to overuse their vocal cords which makes them very susceptible to a variety of vocal disorders. Dysphonia associated with bulimia has been linked to vocal fold edema
Edema (American English), also spelled oedema (British English), and also known as fluid retention, swelling, dropsy and hydropsy, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. S ...
and polypoid changes. The aim was to understand if bulimia was linked to laryngopharyngeal reflux as a plausible cause of dysphonia. In preliminary results, it was understood that reflux was the case in every singer with bulimia and dysphonia, indicating it may be a contributing factor to their vocal disorder.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Bogart-Bacall syndrome Human voice Medical terminology Voice disorders Syndromes