Blue Screens Of Death on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The blue screen of death (BSoD) or blue screen error, blue screen, fatal error, bugcheck, and officially known as a stop erroris a critical error screen displayed by the
The blue screen of death (BSoD) or blue screen error, blue screen, fatal error, bugcheck, and officially known as a stop erroris a critical error screen displayed by the
 Blue screen errors have been around since the very first version of Windows in 1985. In the Beta Release of
Blue screen errors have been around since the very first version of Windows in 1985. In the Beta Release of  The first BSoD to indicate a critical system error appeared in
The first BSoD to indicate a critical system error appeared in
 The
The
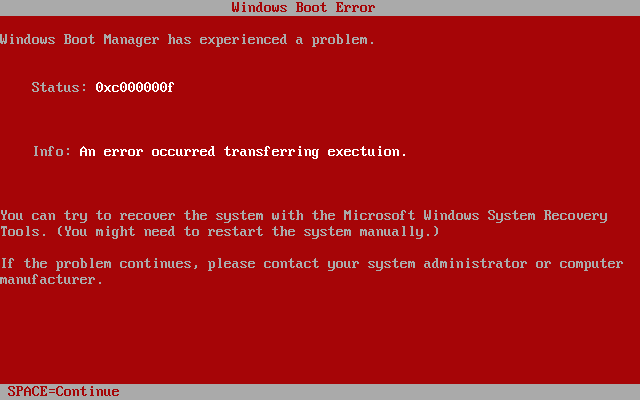 In some cases, a differently-colored error screen is used.
In some cases, a differently-colored error screen is used. 
Bug Check Code Reference
SysInternals BlueScreen Screen Saver v3.2
Blue Screen of Death
on MalWiki. {{Error messages Computer errors Windows administration Screens of death
 The blue screen of death (BSoD) or blue screen error, blue screen, fatal error, bugcheck, and officially known as a stop erroris a critical error screen displayed by the
The blue screen of death (BSoD) or blue screen error, blue screen, fatal error, bugcheck, and officially known as a stop erroris a critical error screen displayed by the Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
s to indicate a system crash, in which the operating system reaches a critical condition where it can no longer operate safely.
The name comes from the blue colored background used predominately on the error screens found in the majority of Windows releases. Possible issues contributing to a BSoD may include hardware failures, an issue with or without a device driver, viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almo ...
, malware
Malware (a portmanteau of ''malicious software'')Tahir, R. (2018)A study on malware and malware detection techniques . ''International Journal of Education and Management Engineering'', ''8''(2), 20. is any software intentionally designed to caus ...
, and other factors such as intentional user action.
__TOC__
History
 Blue screen errors have been around since the very first version of Windows in 1985. In the Beta Release of
Blue screen errors have been around since the very first version of Windows in 1985. In the Beta Release of Windows 1.0
Windows 1.0 is the first major release of Microsoft Windows, a family of graphical operating systems for personal computers developed by Microsoft. It was first released to manufacturing in the United States on November 20, 1985, while the E ...
, if it detected a version of DOS
DOS (, ) is a family of disk-based operating systems for IBM PC compatible computers. The DOS family primarily consists of IBM PC DOS and a rebranded version, Microsoft's MS-DOS, both of which were introduced in 1981. Later compatible syste ...
that is newer than the OS expects, the boot screen would have the text "Incorrect DOS version" alongside other messages detailing what check failed to pass appended into it before starting normally. This behavior remains in the final version released to retail (version 1.01), however the remaining text messages were removed during development in the lead up to Windows 1.0's release, displaying mojibake
Mojibake (; , 'character transformation') is the garbled or gibberish text that is the result of text being decoded using an unintended character encoding. The result is a systematic replacement of symbols with completely unrelated ones, often ...
instead. Contrary to popular belief, this is not a system crash screen; when the operating system actually crashed, it either freezes or unexpectedly exits to DOS. This behavior was retained in Windows 2.0 and Windows 2.1.
Windows 3.0
Windows 3.0 is the third major release of Microsoft Windows, launched on May 22, 1990. It introduces a new graphical user interface (GUI) that represents applications as clickable icons, instead of the list of file names in its predecessors. ...
uses a text-mode screen for displaying important system messages, usually from digital device drivers in 386 Enhanced Mode
Windows 3.0 is the third major release of Microsoft Windows, launched on May 22, 1990. It introduces a new graphical user interface (GUI) that represents applications as clickable icons, instead of the list of file names in its predecessors. ...
or other situations where a program could not run. Windows 3.1
Windows 3.1 is a major release of Microsoft Windows. It was released to manufacturing on April 6, 1992, as a successor to Windows 3.0. Like its predecessors, the Windows 3.1 series run as a shell on top of MS-DOS; it was the last Windows 1 ...
changed the color of this screen from black to blue. It also displays a blue screen when the user presses the Ctrl+Alt+Delete key combination to bring up a rudimentary task manager
In operating systems, a task manager is a system monitor program used to provide information about the processes and applications running on a computer, as well as the general status of the computer. Some implementations can also be used t ...
, reserved for quitting any unresponsive programs if they are available. Like previous versions of Windows before 3.0, Windows 3.x exits to DOS if an error condition is severe enough.
 The first BSoD to indicate a critical system error appeared in
The first BSoD to indicate a critical system error appeared in Windows NT 3.1
Windows NT 3.1 is the first major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft, released on July 27, 1993. It marked the company's entry into the corporate computing environment, designed to support large networks and to be ...
(the first version of the Windows NT
Windows NT is a Proprietary software, proprietary Graphical user interface, graphical operating system produced by Microsoft as part of its Windows product line, the first version of which, Windows NT 3.1, was released on July 27, 1993. Original ...
family, released in 1993). The error screens initially started with *** STOP: in its earlier iterations, hence it became known as a "stop error." This format was used on all Windows operating systems released afterwards, with various differences in later versions. Despite popular belief, there are no known genuine equivalents of a BSoD in the Windows Embedded Compact
Windows CE, later known as Windows Embedded CE and Windows Embedded Compact, is a discontinued operating system developed by Microsoft for Mobile device, mobile and Embedded system, embedded devices. It was part of the Windows Embedded family an ...
(formerly known as Windows CE) line of embedded operating systems.
BSoDs can be caused by poorly written device driver
In the context of an operating system, a device driver is a computer program that operates or controls a particular type of device that is attached to a computer or automaton. A driver provides a software interface to hardware devices, enabli ...
s or malfunctioning hardware, such as faulty memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembe ...
, power supply problems, overheating of components, or hardware running beyond its specification limits. In the Windows 9x
Windows 9x is a generic term referring to a line of discontinued Microsoft Windows operating systems released from 1995 to 2000 and supported until 2006, which were based on the kernel introduced in Windows 95 and modified in succeeding version ...
line of operating systems, incompatible DLLs or bugs in the operating system kernel
Kernel may refer to:
Computing
* Kernel (operating system), the central component of most operating systems
* Kernel (image processing), a matrix used for image convolution
* Compute kernel, in GPGPU programming
* Kernel method, in machine learnin ...
could also cause BSoDs. Because of the general instability and lack of memory protection in Windows 9x, BSoDs were much more common.
Attribution
On September 4, 2014, several online journals such as ''Business Insider
''Business Insider'' (stylized in all caps: BUSINESS INSIDER; known from 2021 to 2023 as INSIDER) is a New York City–based multinational financial and business news website founded in 2007. Since 2015, a majority stake in ''Business Inside ...
'', ''DailyTech
DailyTech was an online daily publication of technology news, founded by ex-AnandTech editor Kristopher Kubicki on January 1, 2005. The site featured a prominent "comments" section that acted as the forums for the publication. Users were able t ...
'', ''Engadget
Engadget ( ) is a technology news, reviews and analysis website offering daily coverage of gadgets, consumer electronics, video games, gaming hardware, apps, social media, streaming, AI, space, robotics, electric vehicles and other potentially ...
'', ''Gizmodo
''Gizmodo'' () is a design, technology, science, and science fiction website. It was originally launched as part of the Gawker Media network run by Nick Denton. ''Gizmodo'' also includes the sub-blogs ''io9'' and ''Earther'', which focus on pop ...
'', ''Lifehacker
''Lifehacker'' is a weblog about life hacks and software that launched on 31 January 2005. The site was originally launched by Gawker Media and is owned by Ziff Davis. The blog posts cover a wide range of topics including Microsoft Windows, M ...
'', ''Neowin
Neowin is a technology news website. Editorial focus is predominantly on Microsoft-related news, but the site also offers analysis and reporting on mobile news, tech trends, gadgets and new technological developments, as well as in-depth produc ...
'', ''Softpedia
Softpedia is a software and tech news website based in Romania. It indexes, reviews and hosts downloadable software and reports news on technology and science topics. It is ranked as among of the top download portals on the internet.
History
So ...
'', ''TechSpot'', ''Boy Genius Report
Boy Genius Report (also referred to as BGR) is a technology-influenced website and covers topics ranging from consumer gadgets to entertainment, gaming, and science. Founded in October 2006 by anonymous web personality Boy Genius (also referred t ...
'' (''BGR''), ''The Register
''The Register'' (often also called El Reg) is a British Technology journalism, technology news website co-founded in 1994 by Mike Magee (journalist), Mike Magee and John Lettice. The online newspaper's Nameplate_(publishing), masthead Logo, s ...
'', and ''The Verge
''The Verge'' is an American Technology journalism, technology news website headquarters, headquartered in Lower Manhattan, New York City and operated by Vox Media. The website publishes news, feature stories, guidebooks, product reviews, cons ...
'', as well as print and non-English sources like ''PC Authority'' and Austrian tech site ''FutureZone'' all attributed the creation of the Blue Screen of Death to Steve Ballmer
Steven Anthony Ballmer (; March 24, 1956) is an American businessman and investor who served as chief executive officer of Microsoft from 2000 to 2014. He is the owner of the Los Angeles Clippers of the National Basketball Association (NBA). He i ...
, the former CEO
A chief executive officer (CEO), also known as a chief executive or managing director, is the top-ranking corporate officer charged with the management of an organization, usually a company or a nonprofit organization.
CEOs find roles in variou ...
of Microsoft. The articles specifically cited a blog post by Microsoft employee Raymond Chen
Raymond Tsong-he Chen (born 1968) is an American lawyer who has served as a United States circuit judge of the United States Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit since 2013.
Early life and education
Chen was born in 1968 in New York City ...
entitled "Who wrote the text for the Ctrl+Alt+Del dialog in Windows 3.1?", which focused on the creation of the first rudimentary task manager in Windows 3.x. The aforementioned task manager shared some visual similarities with a BSOD, with Ballmer writing the messages that appeared on the screen.
Chen took notice of the widespread misinformation and addressed the issue himself in a blog post on September 9, 2014. According to Chen, he was scathing on his evaluation of major tech news sites that had picked up on the incorrect story and performed poor or non-existent research that demonstrated complete ignorance of his original account. He indicated that, in addition to the faulty base story, over half a dozen significant sites had included other embellished or invented details in their stories, including incorrectly naming Chen as a Microsoft executive, treating Chen as an "official company spokesperson", and using unrelated images from Windows NT or Windows 95 as illustrations. In addition, he also pointed out a very special mention for the worst single distortion out of any misinformations, which belonged to ''BGR'' (Boy Genius Report), who "fabricated a scenario and posited it as real" in a rhetorical question to readers. He also found that several sources had conflated the creation of the BSoD with the fact that they occur, thus inverting cause and effect
Causality is an influence by which one event, process, state, or object (''a'' ''cause'') contributes to the production of another event, process, state, or object (an ''effect'') where the cause is at least partly responsible for the effect, ...
by implying that the invention of BSoDs ''caused'' fatal errors to occur instead of their actual, helpful function of giving the user information about a fatal error ''after'' the system has already become unrecoverable (such incorrect sources transitively blamed Ballmer for the existence of all fatal crashes in Windows). A day after his initial complaint, Chen would follow this up with another blog post on September 10, 2014, claiming responsibility for revising the BSoD in Windows 95
Windows 95 is a consumer-oriented operating system developed by Microsoft and the first of its Windows 9x family of operating systems, released to manufacturing on July 14, 1995, and generally to retail on August 24, 1995. Windows 95 merged ...
. His post said in detail that he was the one who "sort of" created the BSoD in its first modern incarnation in Windows 95.
According to former Microsoft employee Dave Plummer
David William Plummer (born August 9, 1968) is a Canadian-American programmer and entrepreneur. He created the Task Manager for Windows, the '' Space Cadet Pinball'' ports to Windows NT, Zip file support for Windows, HyperCache for the Amiga an ...
, the BSoD in the Windows NT family
Windows NT is a proprietary graphical operating system produced by Microsoft as part of its Windows product line, the first version of which, Windows NT 3.1, was released on July 27, 1993. Originally made for the workstation, office, and ser ...
was not based on the rudimentary task manager screen of Windows 3.x, but was actually designed by Microsoft developer John Vert. Additionally, Vert has also stated the reason why the error screens were given the color blue was because the universal color palette of the video hardware at that time was very rudimentary, and he personally used a MIPS OS box and SlickEdit for programming so that both the firmware and editor displayed white text on a blue background, making for a more consistent programming experience.
Formats
BSoDs originally showedsilver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
text on a royal blue
Royal blue is a deep and vivid shade of blue. It is said to have been created by a consortium of mills in Rode, Wiltshire (in Somerset as of 1937), which won a competition to make a robe for Queen Charlotte, consort of King George III. I ...
background with information about current memory values and register values. Starting with Windows Server 2012 (released in September 2012), Windows adopted a cerulean
The color cerulean (American English) or caerulean (British English, Commonwealth English), is a variety of the hue of blue that may range from a light azure blue to a more intense sky blue. Cerulean may also be mixed with the hue of green. ...
background. Earlier versions of Windows 11
Windows 11 is a version of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system, released on October 5, 2021, as the successor to Windows 10 (2015). It is available as a free upgrade for devices running Windows 10 that meet the #System requirements, Windo ...
used a black background, which was changed to dark blue starting with build 22000.348 and then back to black with build 26120.3653. Preview builds of Windows 10, Windows 11, and Windows Server
Windows Server (formerly Windows NT Server) is a brand name for Server (computing), server-oriented releases of the Windows NT operating system (OS) that have been developed by Microsoft since 1993. The first release under this brand name i ...
(available from the Windows Insider
Windows Insider is an open software testing program by Microsoft that allows users globally who own a valid license of Windows 11, Windows 10, or Windows Server to register for pre-release builds of the operating system previously only accessible ...
program) feature a dark green background instead of a blue one. Windows 3.1, 95, and 98 supports customizing the color of the screen whereas the color is hard-coded in the Windows NT family
Windows NT is a proprietary graphical operating system produced by Microsoft as part of its Windows product line, the first version of which, Windows NT 3.1, was released on July 27, 1993. Originally made for the workstation, office, and ser ...
.
Windows 95, 98, and Me render their BSoDs in the 80×25 text mode
Text mode is a computer display mode in which content is internally represented on a computer screen in terms of characters rather than individual pixels. Typically, the screen consists of a uniform rectangular grid of ''character cells'', ea ...
with a 720×400 screen resolution
The display resolution or display modes of a digital television, computer monitor, or other display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resoluti ...
. BSoDs in the Windows NT family initially used the 80×50 text mode with a 720×400 screen resolution, but changed to use the 640×480 screen resolution starting with Windows 2000 up to 7. BSoDs on Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 are rendered in higher resolutions than previous versions of Windows, where it uses the highest screen resolution available on UEFI machines. On legacy BIOS machines, they use the 1024×768 resolution by default, but they can also be configured to use the highest resolution available (via the 'highestmode' parameter in Boot Configuration Data
The Windows Boot Manager (BOOTMGR) is the bootloader provided by Microsoft for Windows NT versions starting with Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008. It is the first program launched by the BIOS or UEFI of the computer and is responsible for ...
). Windows 95, 98, Me, and NT versions prior to Windows 2000 used text mode fonts provided by the graphics adapter, Windows 2000 used its built-in kernel mode font, Windows XP, Vista, and 7 use the Lucida Console
Lucida (pronunciation: ) is an extended family of related typefaces designed by Charles Bigelow (type designer), Charles Bigelow and Kris Holmes and released from 1984 onwards. The family is intended to be extremely legible when printed at small ...
font, and Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 onwards use the Segoe UI
Segoe ( ) is a typeface, or family of fonts, that is best known for its use by Microsoft. The company uses Segoe in its online and printed marketing materials, including recent logos for a number of products. Additionally, the Segoe UI font su ...
font.
Windows 10 builds 14316 and up uses the same format as Windows 8, but has a QR code which leads to a Microsoft Support web page that tries to help users troubleshoot the issue step-by-step. This format was retained in Windows 11, however build 26120.3653 changes the layout to be more consistent with that of Windows 11's UI, removing the QR code among other changes.
Windows NT
In theWindows NT
Windows NT is a Proprietary software, proprietary Graphical user interface, graphical operating system produced by Microsoft as part of its Windows product line, the first version of which, Windows NT 3.1, was released on July 27, 1993. Original ...
family of operating systems, the blue screen of death (referred to as "bug check
Bug or BUG may refer to:
Common uses
* A terrestrial arthropod animal, usually with at least six legs
** Insect, a six-legged arthropod
***Hemiptera, the true bugs
* A colloquialism for most minibeasts including arthropods, gastropods and worms. ...
" in the Windows software development kit
A software development kit (SDK) is a collection of software development tools in one installable package. They facilitate the creation of applications by having a compiler, debugger and sometimes a software framework. They are normally specific t ...
and driver development kit documentation) occurs when the kernel or a driver running in kernel mode
In computer science, hierarchical protection domains, often called protection rings, are mechanisms to protect data and functionality from faults (by improving fault tolerance) and malicious behavior (by providing computer security).
Computer ...
encounters an error from which it cannot recover. This is usually caused by an illegal operation being performed. The only safe action the operating system can take in this situation is to restart the computer. Because of this, data loss may occur since the restart is unplanned, and the user is not given an opportunity to save their work.
The text on the error screen contains the code of the error and its symbolic name (e.g. "0x0000001E, KMODE_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED") along with four error-dependent values in parentheses that are there to help software engineers fix the problem that occurred. Depending on the error code, it may display the address where the problem occurred, along with the driver which is loaded at that address. Under Windows NT, the second and third sections of the screen may contain information on all loaded drivers and a stack dump, respectively. The driver information is in three columns; the first lists the base address of the driver, the second lists the driver's creation date (as a Unix time
Unix time is a date and time representation widely used in computing. It measures time by the number of non-leap seconds that have elapsed since 00:00:00 Coordinated Universal Time, UTC on 1 January 1970, the Unix Epoch (computing), epoc ...
stamp), and the third lists the name of the driver. By default, Windows will create a memory dump
In computing, a core dump, memory dump, crash dump, storage dump, system dump, or ABEND dump consists of the recorded state of the working memory of a computer program at a specific time, generally when the program has crashed or otherwise termin ...
file when a stop error occurs. Depending on the OS version, there may be several formats this can be saved in, ranging from a 64kB "minidump" (introduced in Windows 2000) to a "complete dump" which is effectively a copy of the entire contents of physical memory (RAM
Ram, ram, or RAM most commonly refers to:
* A male sheep
* Random-access memory, computer memory
* Ram Trucks, US, since 2009
** List of vehicles named Dodge Ram, trucks and vans
** Ram Pickup, produced by Ram Trucks
Ram, ram, or RAM may also ref ...
). The resulting memory dump file may be debugged later, using a kernel debugger
A debugger is a computer program used to test and debug other programs (the "target" programs). Common features of debuggers include the ability to run or halt the target program using breakpoints, step through code line by line, and display ...
. For Windows, WinDBG or KD debuggers from Debugging Tools for Windows are used. A debugger is necessary to obtain a stack
Stack may refer to:
Places
* Stack Island, an island game reserve in Bass Strait, south-eastern Australia, in Tasmania’s Hunter Island Group
* Blue Stack Mountains, in Co. Donegal, Ireland
People
* Stack (surname) (including a list of people ...
trace, and may be required to ascertain the true cause of the problem; as the information on-screen is limited and thus possibly misleading, it may hide the true source of the error. By default, Windows XP is configured to save only a 64kB minidump when it encounters a stop error, and to then automatically reboot the computer. Because this process happens very quickly, the blue screen may be seen only for an instant or not at all. Users have sometimes noted this as a random reboot rather than a traditional stop error, and are only aware of an issue after Windows reboots and displays a notification that it has recovered from a serious error. This happens only when the computer has a function called "Auto Restart" enabled, which can be disabled in the Control Panel which in turn shows the stop error.
Microsoft Windows can also be configured to send live debugging information to a kernel debugger running on a separate computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
. If a stop error is encountered while a live kernel debugger is attached to the system, Windows will halt execution and cause the debugger to break in, rather than displaying the BSoD. The debugger can then be used to examine the contents of memory and determine the source of the problem.
A BSoD can also be caused by a critical boot loader error, where the operating system is unable to access the boot partition due to incorrect storage drivers, a damaged file system or similar problems. The error code in this situation is STOP: 0x0000007B (INACCESSIBLE_BOOT_DEVICE). In such cases, there is no memory dump saved. Since the system is unable to boot from the hard drive in this situation, correction of the problem often requires using the repair tools found on the Windows installation disc.
Details
Earlier versions (NT, 2000, XP, Vista, 7)
BSoDs in the Windows NT family before the release ofWindows 8
Windows 8 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was Software release life cycle#Release to manufacturing (RTM), released to manufacturing on August 1, 2012, made available for download via Microsoft ...
and Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012, codenamed "Windows Server 8", is the ninth major version of the Windows NT operating system produced by Microsoft to be released under the Windows Server brand name. It is the server version of Windows based on Windows ...
displayed the error name in uppercase (e.g. APC_INDEX_MISMATCH) and its respective hexadecimal error number (e.g. 0x00000001), along with four parameters. This is shown together in the following format:
Depending on the error number and its nature, all, some, or even none of the parameters contain data pertaining to what went wrong, and/or where it happened. In addition, starting with Windows 2000
Windows 2000 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft, targeting the server and business markets. It is the direct successor to Windows NT 4.0, and was Software release life cycle#Release to manufacturing (RT ...
onwards, the error screens showed up to four paragraphs of general explanation and advice and may have included other technical data such the file name of the culprit and memory addresses.
In rare cases, the BSOD would be truncated, sometimes not showing the error name, codes, or the four paragraphs of advice. Instead, it would often show different formats of the error screen depending on the type of error that occurred. For instance, BSoDs related to the termination of the Winlogon
Winlogon (Windows Logon) is the component of Microsoft Windows operating systems that is responsible for handling the secure attention sequence, loading the user profile on logon, creates the desktops for the window station, and optionally locki ...
process (e.g. "0xC000021A, WINLOGON_FATAL_ERROR") displayed the following message in this format:
On Windows 2000, the above message is sometimes displayed alongside the four paragraphs of general instructions and advice, the latter of which are absent on Windows XP to Windows 7.
Another example is that when Windows finds a corrupt registry file that is critical to the operating system (e.g. "0xC0000218, STATUS_CANNOT_LOAD_REGISTRY_FILE"), it would display the following message:
Also, hardware errors that can prevent Windows from booting properly will also display this rare message (This example is 0x00000080 (NMI_HARDWARE_FAILURE); note that the error code is not shown in this example below):
Additionally, when the system is performing a memory dump on the BSoD, the following message is displayed after the memory dump is done (after the "Physical memory dump complete" sentence):
From Windows XP
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct successor to Windows 2000 for high-end and business users a ...
to Windows 7
Windows 7 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was Software release life cycle#Release to manufacturing (RTM), released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009, and became generally available on October 22, ...
, the layout of the BSoD was slightly altered, specifically the hexadecimal error number and the four parameters were moved to the bottom of the screen after the four paragraphs under the label "Technical information:". The error screens also began with the following infamous message:
On BSoDs with error code 0x000000F4 (CRITICAL_OBJECT_TERMINATION), which determines that a critical process has been exited or terminated unexpectedly by various factors (including intentional action by the user), the following message would be displayed in place of the error name:
Additionally, on 64-bit versions of Windows XP, Vista and 7, the BSoD would oftentimes have the four parameters extended, where the parameters are extended to about 16 characters long ("0x0000000000000000") instead of 8 ("0x00000000"). This applies to all future versions of Windows using the 64-bit architecture.
Later versions (Server 2012 and 8 onwards)
With the release of Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012, the BSoD was changed. It removed all of the above in favor of the error name and a concise description. Windows 8 also adds a sad emoticon to the error screen, which is absent from Japanese releases or its Windows Server counterparts. The hexadecimal error code and parameters can still be found in the Windows Event Log or inmemory dump
In computing, a core dump, memory dump, crash dump, storage dump, system dump, or ABEND dump consists of the recorded state of the working memory of a computer program at a specific time, generally when the program has crashed or otherwise termin ...
s, however some BSoDs which used a truncated format from previous BSoDs such as those relating to Winlogon termination may have the aforementioned hexadecimal error code in place of the error name. Hardware errors causing an BSoD also uses the same format as the normal BSoD, including the use of the error name instead of an error code. One such example are BSoDs with the error name "NMI_HARDWARE_FAILURE" (error code 0x00000080).
This format was retained in Windows 10 and Windows 11 (as well as its Server counterparts). Windows 10 build 14316 adds a QR code to the screen for quick troubleshooting, and all references to "PC" were changed to the word "device" starting from Windows 10 v2004 onwards. The BSoD was once again changed starting with Windows 11 build 26120.3653, which included the removal of the QR code and the sad emoticon from the error screen as well as changes to the layout to be more consistent with that of Windows 11.
Windows 9x
 The
The Windows 9x
Windows 9x is a generic term referring to a line of discontinued Microsoft Windows operating systems released from 1995 to 2000 and supported until 2006, which were based on the kernel introduced in Windows 95 and modified in succeeding version ...
line of operating systems used the Blue Screen of Death as the main way for virtual device drivers to report errors to the user. This version of the BSoD, internally referred to as "_VWIN32_FaultPopup", gives the user the option either to restart the computer or to continue using Windows, allowing the user to save their work before any data could be lost. Depending on the type of situation it may have occurred, however, the options to either continue or restart may or may not work at all. This is in contrast to the Windows NT version of BSoDs, which prevented the user from using the computer until it has been powered off or restarted (usually automatic for the latter).
The most common BSoD is displayed on an 80×25 text-mode screen, which is the operating system's way of reporting an interrupt caused by a processor exception; it is a more serious form of the general protection fault
A general protection fault (GPF) in the x86 instruction set architectures (ISAs) is a fault (a type of interrupt) initiated by ISA-defined protection mechanisms in response to an access violation caused by some running code, either in the kern ...
dialog boxes. The memory address of the error is given and the error type is a hexadecimal number from 00 to 11 (0 to 17 decimal). The error codes are as follows:
* 00: Division fault
* 01: Startup Error
* 02: Non-Maskable Interrupt
In computing, a non-maskable interrupt (NMI) is a hardware interrupt that standard interrupt-masking techniques in the system cannot ignore. It typically occurs to signal attention for non-recoverable hardware errors. Some NMIs may be masked, but ...
* 03: Shutdown Error
* 04: Overflow Trap
* 05: Bounds Check Fault
* 06: Invalid Opcode Fault
* 07: "Coprocessor
A coprocessor is a computer processor used to supplement the functions of the primary processor (the CPU). Operations performed by the coprocessor may be floating-point arithmetic, graphics, signal processing, string processing, cryptography or ...
Not Available" Fault
* 08: Double Fault
* 09: Coprocessor Segment Overrun
* 0A: Invalid Task State Segment Fault
* 0B: Not Present Fault
* 0C: Stack Fault
* 0D: General Protection Fault
A general protection fault (GPF) in the x86 instruction set architectures (ISAs) is a fault (a type of interrupt) initiated by ISA-defined protection mechanisms in response to an access violation caused by some running code, either in the kern ...
* 0E: Page Fault
In computing, a page fault is an exception that the memory management unit (MMU) raises when a process accesses a memory page without proper preparations. Accessing the page requires a mapping to be added to the process's virtual address space ...
* 0F: Error Message Limit Exceed
* 10: Coprocessor Error Fault
* 11: Alignment Check Fault
Reasons for BSoDs include:
* Problems that occur with incompatible versions of DLLs: Windows loads these DLLs into memory when they are needed by application programs; if versions are changed, the next time an application loads the DLL it may be different from what the application expects. These incompatibilities increase over time as more new software is installed. It is one of the many reasons why some people said that a clean install of Windows is more stable than an "old" one (or an in-place upgrade).
* Faulty or poorly written device driver
In the context of an operating system, a device driver is a computer program that operates or controls a particular type of device that is attached to a computer or automaton. A driver provides a software interface to hardware devices, enabli ...
s.
* Hardware incompatibilities.
* Damaged hardware may also cause a BSoD.
In Windows 95 and 98, a BSoD occurs when the system attempts to access the file "c:\con\con", "c:\aux\aux", or "c:\prn\prn" on the hard drive. This could be inserted on a website to crash visitors' machines as a prank. In reality, however, they are reserved device names for DOS systems; attempting to access them from Windows causes a crash, which in turn brings up said BSoD. Creating the aforementioned directories within Windows will also not work and may cause the same BSOD to occur. On March 16, 2000, Microsoft released a security update
A patch is data that is intended to be used to modify an existing software resource such as a program or a file, often to fix bugs and security vulnerabilities. A patch may be created to improve functionality, usability, or performance. A pa ...
to resolve this issue.
One famous instance of a Windows 9x BSoD occurred during a presentation of a Windows 98 beta
Beta (, ; uppercase , lowercase , or cursive ; or ) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive . In Modern Greek, it represe ...
given by Bill Gates
William Henry Gates III (born October 28, 1955) is an American businessman and philanthropist. A pioneer of the microcomputer revolution of the 1970s and 1980s, he co-founded the software company Microsoft in 1975 with his childhood friend ...
at COMDEX on April 20, 1998: The demo PC crashed with a BSoD when his assistant, Chris Capossela, connected a scanner to the PC to demonstrate Windows 98's support for Plug and Play
In computing, a plug and play (PnP) device or computer bus is one with a specification that facilitates the recognition of a hardware component in a system without the need for physical device configuration or user intervention in resolving reso ...
devices. This event brought thunderous applause from the crowd and Gates replied (after a nervous pause): "That must be why we're not shipping Windows 98 yet."
Similar screens
Stop errors are comparable tokernel panic
A kernel panic (sometimes abbreviated as KP) is a safety measure taken by an operating system's Kernel (operating system), kernel upon detecting an internal Fatal system error, fatal error in which either it is unable to safely recover or con ...
s in macOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
, Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
, and other Unix-like
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X, *nix or *NIX) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Uni ...
systems, and to bugchecks in OpenVMS
OpenVMS, often referred to as just VMS, is a multi-user, multiprocessing and virtual memory-based operating system. It is designed to support time-sharing, batch processing, transaction processing and workstation applications. Customers using Op ...
.
A black screen of death can occur upon hardware or software failures. Windows 3.1
Windows 3.1 is a major release of Microsoft Windows. It was released to manufacturing on April 6, 1992, as a successor to Windows 3.0. Like its predecessors, the Windows 3.1 series run as a shell on top of MS-DOS; it was the last Windows 1 ...
displays a black screen of death instead of a blue one. Some versions of macOS (notably OS X Lion
OS X Lion, also known as Mac OS X Lion, (version 10.7) is the eighth major release of macOS, Apple's desktop and server operating system for Mac computers.
A preview of OS X 10.7 Lion was publicly shown at the "Back to the Mac" Apple Speci ...
) display a black screen of death instead of a kernel panic, usually pointed to a graphics card or sleep/wake issue, it may also display a black screen when the operating system fails to boot properly. The Xbox
Xbox is a video gaming brand that consists of four main home video game console lines, as well as application software, applications (games), the streaming media, streaming service Xbox Cloud Gaming, and online services such as the Xbox networ ...
series of consoles (which includes the original Xbox, Xbox 360
The Xbox 360 is a home video game console developed by Microsoft. As the successor to the Xbox (console), original Xbox, it is the second console in the Xbox#Consoles, Xbox series. It was officially unveiled on MTV on May 12, 2005, with detail ...
, Xbox One
The Xbox One is a home video game console developed by Microsoft. Announced in May 2013, it is the successor to Xbox 360 and the third console in the Xbox#Consoles, Xbox series. It was first released in North America, parts of Europe, Austra ...
and the Xbox Series X/S
The Xbox Series X and Xbox Series S are the fourth generation of consoles in the Xbox series, succeeding the previous generation's Xbox One. Released on November 10, 2020, the higher-end Xbox Series X and lower-end Xbox Series S are part o ...
) also display a black screen when a hardware or software error occurs.
 In some cases, a differently-colored error screen is used.
In some cases, a differently-colored error screen is used. Beta version
The software release life cycle is the process of developing, testing, and distributing a software product (e.g., an operating system). It typically consists of several stages, such as pre-alpha, alpha, beta, and release candidate, before the fi ...
s of Windows 98
Windows 98 is a consumer-oriented operating system developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows 9x family of Microsoft Windows operating systems. It was the second operating system in the 9x line, as the successor to Windows 95. It was Software ...
display a red error screen raised by the Advanced Configuration and Power Interface
Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) is an open standard that operating systems can use to discover and configure computer hardware components, to perform power management (e.g. putting unused hardware components to sleep), auto con ...
(ACPI) when the host computer's BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is a type of firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization d ...
encounters a problem. The bootloader
A bootloader, also spelled as boot loader or called bootstrap loader, is a computer program that is responsible for booting a computer and booting an operating system. If it also provides an interactive menu with multiple boot choices then it's o ...
of the first beta version of Windows Vista
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, released five years earlier, which was then the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft W ...
originally displayed a red screen background in the event of a boot failure, which was changed to black afterwards. As mentioned earlier, the insider builds of Windows 10
Windows 10 is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. The successor to Windows 8.1, it was Software release cycle#Release to manufacturing (RTM), released to manufacturing on July 15, 2015, and later to retail on July 2 ...
and later, as well as Windows Server 2016
Windows Server 2016 is the eleventh major version of the Windows NT operating system produced by Microsoft to be released under the Windows Server brand name. It was developed alongside Windows 10 and is the successor to the Windows 8.1-based ...
and later, display a green screen instead of blue. Windows 10 and later (and Windows Server 2016 and later) also display an orange screen in an extremely rare case where a hardware issue with the GPU or a graphics driver problem is encountered.

ReactOS
ReactOS is a Free and open-source software, free and open-source operating system for i586/amd64 personal computers that is intended to be binary-code compatibility, binary-compatible with computer programs and device drivers developed for Wind ...
, an open-source operating system designed to achieve binary compatibility with Windows, implements a version of the Blue Screen of Death similar to that used in Windows NT operating systems. systemd
systemd is a software suite that provides an array of system components for Linux operating systems. The main aim is to unify service configuration and behavior across Linux distributions. Its primary component is a "system and service manage ...
, a software suite providing system components for Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
operating systems, also implements a version of the Blue Screen of Death similar to that of Windows, albeit not as a replacement to the kernel panic in Linux (see above), but rather was used in the event of a bootup failure. This iteration uses systemd-bsod, which was added on December 6, 2023 starting with version 255 of systemd.
See also
* Screen of death ** Guru Meditation **Kernel panic
A kernel panic (sometimes abbreviated as KP) is a safety measure taken by an operating system's Kernel (operating system), kernel upon detecting an internal Fatal system error, fatal error in which either it is unable to safely recover or con ...
** Purple Screen of Death
** Sad Mac
The Macintosh startup sequence for Apple Macintosh (or Mac) computers includes hardware tests and diagnostics which can trigger the startup chimes and/or other instances of success or failure of the startup routines.
The startup sequence provid ...
** Black screen of death
* Red Ring of Death
* Hang (computing)
In computing, a hang or freeze occurs when either a process or system ceases to respond to inputs. A typical example is when computer's graphical user interface (such as Microsoft Windows) no longer responds to the user typing on the keyboard o ...
* Machine-check exception
A machine check exception (MCE) is a type of computer error that occurs when a problem involving the computer's hardware is detected. With most mass-market personal computers, an MCE indicates faulty or misconfigured hardware.
The nature and ...
(MCE)
* Windows Hardware Error Architecture
Windows Hardware Error Architecture (WHEA) is an operating system hardware error handling mechanism introduced with Windows Vista SP1 and Windows Server 2008 as a successor to Machine Check Architecture (MCA) on previous versions of Windows. ...
(WHEA)
References
External links
Bug Check Code Reference
SysInternals BlueScreen Screen Saver v3.2
Blue Screen of Death
on MalWiki. {{Error messages Computer errors Windows administration Screens of death