 Bengal ( ) is a historical geographical,
Bengal ( ) is a historical geographical, Etymology
The name of ''Bengal'' is derived from the ancient kingdom of Vanga Kingdom, Vanga (pronounced Bôngô), the earliest records of which date back to the ''Mahabharata'' epic in the first millennium BCE. The reference to 'Vangalam' is present in an inscription in the Brihadisvara Temple at Thanjavur, which is one of the oldest references to Bengal. The term ''Vangaladesa'' is used to describe the region in 11th-century South Indian records. The modern term ''Bangla'' is prominent from the 14th century, which saw the establishment of the Sultanate of Bengal, whose first ruler Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah was known as the ''Shah of Bangala''. The Portuguese Empire, Portuguese referred to the region as ''Bengala'' in the Age of Discovery.History
Antiquity
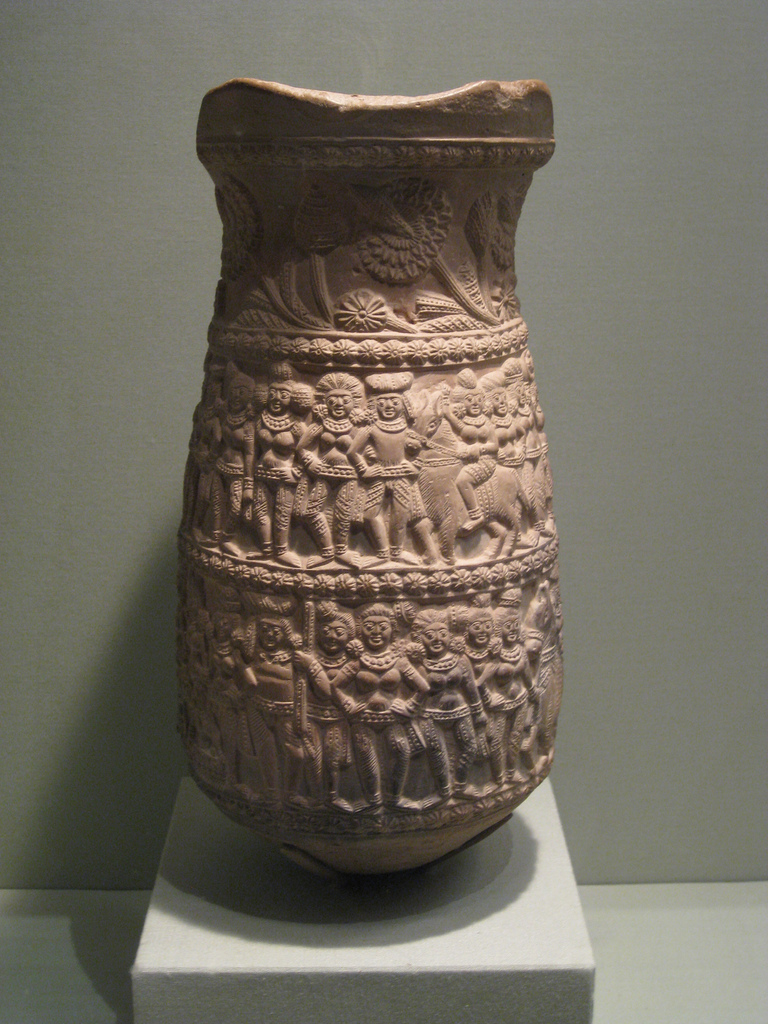

 Neolithic sites have been found in several parts of the region. In the second millennium BCE, rice-cultivating communities dotted the region. By the eleventh century BCE, people in Bengal lived in systematically aligned homes, produced copper objects, and crafted black and red pottery. Remnants of Copper Age settlements are located in the region. At the advent of the Iron Age, people in Bengal adopted iron-based weapons, tools and irrigation equipment. From 600 BCE, the second wave of urbanisation engulfed the north Indian subcontinent as part of the Northern Black Polished Ware culture. Ancient archaeological sites and cities in Dihar (archaeological site), Dihar, Pandu Rajar Dhibi, Mahasthangarh, Chandraketugarh and Wari-Bateshwar ruins, Wari-Bateshwar emerged. The Ganges, Brahmaputra and Meghna rivers were natural arteries for communication and transportation. Estuary, Estuaries on the
Neolithic sites have been found in several parts of the region. In the second millennium BCE, rice-cultivating communities dotted the region. By the eleventh century BCE, people in Bengal lived in systematically aligned homes, produced copper objects, and crafted black and red pottery. Remnants of Copper Age settlements are located in the region. At the advent of the Iron Age, people in Bengal adopted iron-based weapons, tools and irrigation equipment. From 600 BCE, the second wave of urbanisation engulfed the north Indian subcontinent as part of the Northern Black Polished Ware culture. Ancient archaeological sites and cities in Dihar (archaeological site), Dihar, Pandu Rajar Dhibi, Mahasthangarh, Chandraketugarh and Wari-Bateshwar ruins, Wari-Bateshwar emerged. The Ganges, Brahmaputra and Meghna rivers were natural arteries for communication and transportation. Estuary, Estuaries on the Sultanate period
 In 1204, the Ghurid Empire, Ghurid general Muhammad bin Bakhtiyar Khalji began the Islamic conquest of Bengal. The fall of Lakhnauti was recounted by historians circa 1243. Lakhnauti was the capital of the Sena dynasty. According to historical accounts, Ghurid cavalry swept across the Gangetic plains towards Bengal. They entered the Bengali capital disguised as horse traders. Once inside the royal compound, Bakhtiyar and his horsemen swiftly overpowered the guards of the Sena king who had just sat down to eat a meal. The king then hastily fled to the forest with his followers. The overthrow of the Sena king has been described as a coup d'état, which "inaugurated an era, lasting over five centuries, during which most of Bengal was dominated by rulers professing the Islamic faith. In itself this was not exceptional, since from about this time until the eighteenth century, Muslim sovereigns ruled over most of the Indian subcontinent. What was exceptional, however, was that among India's interior provinces only in Bengal—a region approximately the size of England and Scotland combined—did a majority of the indigenous population adopt the religion of the ruling class, Islam". Bengal became a province of the Delhi Sultanate. A coin featuring a horseman was issued to celebrate the Muslim conquest of Lakhnauti with inscriptions in Sanskrit and Arabic. An abortive Islamic invasion of Tibet was also mounted by Bakhtiyar. Bengal was under the formal rule of the Delhi Sultanate for approximately 150 years. Delhi struggled to consolidate control over Bengal. Rebel governors often sought to assert autonomy or independence. Sultan Iltutmish re-established control over Bengal in 1225 after suppressing the rebels. Due to the considerable overland distance, Delhi's authority in Bengal was relatively weak. It was left to local governors to expand territory and bring new areas under Muslim rule, such as through the Conquest of Sylhet in 1303.
In 1338, new rebellions sprung up in Bengal's three main towns. Governors in Lakhnauti, Satgaon and Sonargaon declared independence from Delhi. This allowed the ruler of Sonargaon, Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah, to annexe Chittagong to the Islamic administration. By 1352, the ruler of Satgaon, Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah, unified the region into an independent state. Ilyas Shah established his capital in Pandua, Malda, Pandua. The new breakaway state emerged as the Bengal Sultanate, which developed into a territorial, mercantile and maritime empire. At the time, the Islamic world stretched from Muslim Spain in the west to Bengal in the east.
The initial raids of Ilyas Shah saw the first Muslim army enter Nepal and stretched from Varanasi in the west to Orissa in the south to
In 1204, the Ghurid Empire, Ghurid general Muhammad bin Bakhtiyar Khalji began the Islamic conquest of Bengal. The fall of Lakhnauti was recounted by historians circa 1243. Lakhnauti was the capital of the Sena dynasty. According to historical accounts, Ghurid cavalry swept across the Gangetic plains towards Bengal. They entered the Bengali capital disguised as horse traders. Once inside the royal compound, Bakhtiyar and his horsemen swiftly overpowered the guards of the Sena king who had just sat down to eat a meal. The king then hastily fled to the forest with his followers. The overthrow of the Sena king has been described as a coup d'état, which "inaugurated an era, lasting over five centuries, during which most of Bengal was dominated by rulers professing the Islamic faith. In itself this was not exceptional, since from about this time until the eighteenth century, Muslim sovereigns ruled over most of the Indian subcontinent. What was exceptional, however, was that among India's interior provinces only in Bengal—a region approximately the size of England and Scotland combined—did a majority of the indigenous population adopt the religion of the ruling class, Islam". Bengal became a province of the Delhi Sultanate. A coin featuring a horseman was issued to celebrate the Muslim conquest of Lakhnauti with inscriptions in Sanskrit and Arabic. An abortive Islamic invasion of Tibet was also mounted by Bakhtiyar. Bengal was under the formal rule of the Delhi Sultanate for approximately 150 years. Delhi struggled to consolidate control over Bengal. Rebel governors often sought to assert autonomy or independence. Sultan Iltutmish re-established control over Bengal in 1225 after suppressing the rebels. Due to the considerable overland distance, Delhi's authority in Bengal was relatively weak. It was left to local governors to expand territory and bring new areas under Muslim rule, such as through the Conquest of Sylhet in 1303.
In 1338, new rebellions sprung up in Bengal's three main towns. Governors in Lakhnauti, Satgaon and Sonargaon declared independence from Delhi. This allowed the ruler of Sonargaon, Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah, to annexe Chittagong to the Islamic administration. By 1352, the ruler of Satgaon, Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah, unified the region into an independent state. Ilyas Shah established his capital in Pandua, Malda, Pandua. The new breakaway state emerged as the Bengal Sultanate, which developed into a territorial, mercantile and maritime empire. At the time, the Islamic world stretched from Muslim Spain in the west to Bengal in the east.
The initial raids of Ilyas Shah saw the first Muslim army enter Nepal and stretched from Varanasi in the west to Orissa in the south to Mughal period

 Mughal Bengal had the richest elite and was the wealthiest region in the subcontinent. Bengal's trade and wealth impressed the Mughals so much that it was described as the ''Paradise of the Nations'' by the Mughal Emperors. A new provincial capital was built in Dhaka. Members of the imperial family were appointed to positions in Mughal Bengal, including the position of governor (''subedar''). Dhaka became a centre of palace intrigue and politics. Some of the most prominent governors included Rajput general Man Singh I, Emperor Shah Jahan's son Prince Shah Shuja (Mughal prince), Shah Shuja, Emperor Aurangzeb's son and later Mughal emperor Muhammad Azam Shah, Azam Shah, and the influential aristocrat Shaista Khan. During the tenure of Shaista Khan, the Portuguese and Arakanese were expelled from the port of Chittagong in 1666. Bengal became the eastern frontier of the Mughal administration. By the 18th century, Bengal became home to a semi-independent aristocracy led by the Nawabs of Bengal. Bengal premier Murshid Quli Khan managed to curtail the influence of the governor due to his rivalry with Prince Azam Shah. Khan controlled Bengal's finances since he was in charge of the treasury. He shifted the provincial capital from Dhaka to Murshidabad.
In 1717, the Mughal court in Delhi recognised the hereditary monarchy of the Nawab of Bengal. The ruler was officially titled as the "Nawab of Bengal, Bihar and Orissa", as the Nawab ruled over the three regions in the eastern subcontinent. The Nawabs began issuing their own coins but continued to pledge nominal allegiance to the Mughal emperor. The wealth of Bengal was vital for the Mughal court because Delhi received its biggest share of revenue from the Nawab's court. The Nawabs presided over a period of unprecedented economic growth and prosperity, including an era of growing organisation in textiles, banking, a military-industrial complex, the production of fine quality handicrafts, and other trades. A process of proto-industrialisation was underway. Under the Nawabs, the streets of Bengali cities were filled with brokers, workers, peons, naibs, wakils, and ordinary traders. The Nawab's state was a major exporter of muslin trade in Bengal, Bengal muslin, silk, gunpowder and saltpetre. The Nawabs also permitted European trading companies to operate in Bengal, including the British East India Company, the John Law's Company, French East India Company, the Danish East India Company, the Austrian East India Company, the Ostend Company, and the Dutch East India Company. The Nawabs were also suspicious of the growing influence of these companies.
Under Mughal rule, Bengal was a centre of the worldwide muslin and silk trades. During the Mughal era, the most important centre of cotton production was Bengal, particularly around its capital city of Dhaka, leading to muslin being called "daka" in distant markets such as Central Asia.Richard Maxwell Eaton (1996)
Mughal Bengal had the richest elite and was the wealthiest region in the subcontinent. Bengal's trade and wealth impressed the Mughals so much that it was described as the ''Paradise of the Nations'' by the Mughal Emperors. A new provincial capital was built in Dhaka. Members of the imperial family were appointed to positions in Mughal Bengal, including the position of governor (''subedar''). Dhaka became a centre of palace intrigue and politics. Some of the most prominent governors included Rajput general Man Singh I, Emperor Shah Jahan's son Prince Shah Shuja (Mughal prince), Shah Shuja, Emperor Aurangzeb's son and later Mughal emperor Muhammad Azam Shah, Azam Shah, and the influential aristocrat Shaista Khan. During the tenure of Shaista Khan, the Portuguese and Arakanese were expelled from the port of Chittagong in 1666. Bengal became the eastern frontier of the Mughal administration. By the 18th century, Bengal became home to a semi-independent aristocracy led by the Nawabs of Bengal. Bengal premier Murshid Quli Khan managed to curtail the influence of the governor due to his rivalry with Prince Azam Shah. Khan controlled Bengal's finances since he was in charge of the treasury. He shifted the provincial capital from Dhaka to Murshidabad.
In 1717, the Mughal court in Delhi recognised the hereditary monarchy of the Nawab of Bengal. The ruler was officially titled as the "Nawab of Bengal, Bihar and Orissa", as the Nawab ruled over the three regions in the eastern subcontinent. The Nawabs began issuing their own coins but continued to pledge nominal allegiance to the Mughal emperor. The wealth of Bengal was vital for the Mughal court because Delhi received its biggest share of revenue from the Nawab's court. The Nawabs presided over a period of unprecedented economic growth and prosperity, including an era of growing organisation in textiles, banking, a military-industrial complex, the production of fine quality handicrafts, and other trades. A process of proto-industrialisation was underway. Under the Nawabs, the streets of Bengali cities were filled with brokers, workers, peons, naibs, wakils, and ordinary traders. The Nawab's state was a major exporter of muslin trade in Bengal, Bengal muslin, silk, gunpowder and saltpetre. The Nawabs also permitted European trading companies to operate in Bengal, including the British East India Company, the John Law's Company, French East India Company, the Danish East India Company, the Austrian East India Company, the Ostend Company, and the Dutch East India Company. The Nawabs were also suspicious of the growing influence of these companies.
Under Mughal rule, Bengal was a centre of the worldwide muslin and silk trades. During the Mughal era, the most important centre of cotton production was Bengal, particularly around its capital city of Dhaka, leading to muslin being called "daka" in distant markets such as Central Asia.Richard Maxwell Eaton (1996)''The Rise of Islam and the Bengal Frontier, 1204–1760'', page 202
University of California Press Domestically, much of India depended on Bengali products such as rice, silks and cotton textiles. Overseas, Europeans depended on Bengali products such as cotton textiles, silks and opium; Bengal accounted for 40% of Dutch East India Company, Dutch imports from Asia, for example, including more than 50% of textiles and around 80% of silks.Om Prakash (historian), Om Prakash,
Empire, Mughal
, ''History of World Trade Since 1450'', edited by John J. McCusker, vol. 1, Macmillan Reference USA, 2006, pp. 237–240, ''World History in Context''. Retrieved 3 August 2017 From Bengal, saltpetre was also shipped to Europe, opium was sold in Indonesia, raw silk was exported to Japan and the Netherlands, cotton and silk textiles were exported to Europe, Indonesia, and Japan,John F. Richards (1995)
''The Mughal Empire'', page 202
Cambridge University Press cotton cloth was exported to the Americas and the Indian Ocean. Bengal also had a large shipbuilding industry. In terms of shipbuilding tonnage during the 16th–18th centuries, economic historian Indrajit Ray estimates the annual output of Bengal at 223,250 tons, compared with 23,061 tons produced in nineteen colonies in North America from 1769 to 1771. Since the 16th century, European traders traversed the sea routes to Bengal, following the Portuguese conquests of Malacca and Goa. The Portuguese established a Portuguese Chittagong, settlement in Chittagong with permission from the Bengal Sultanate in 1528 but were later expelled by the Mughals in 1666. In the 18th-century, the Mughal Court rapidly disintegrated due to Nader Shah's invasion of India, Nader Shah's invasion and internal rebellions, allowing European colonial powers to set up trading posts across the territory. The British East India Company eventually emerged as the foremost military power in the region; and defeated the last independent Nawab of Bengal at the Battle of Plassey in 1757.
Colonial era (1757–1947)
The British East India Company began influencing and controlling the Nawab of Bengal from 1757 after the Battle of Plassey, thus signalling the start of British influence in India. British control of Bengal increased between 1757 and 1793 while the Nawab was reduced to a puppet figure. with the Presidency of Fort William asserting greater control over the entire province of Bengal and neighbouring territories. Kolkata, Calcutta was named the capital of British territories in India in 1772. The presidency was run by a military-civil administration, including the Bengal Army, and had the world's sixth earliest railway network. Between 1833 and 1854, the Governor of Bengal was concurrently the Governor-General of India for many years. Great Famines in India, Bengal famines struck several times during colonial rule (notably the Great Bengal famine of 1770 and Bengal famine of 1943). Under British rule, Bengal experienced the deindustrialisation of its pre-colonial economy. Company policies led to the deindustrialisation of Bengal's textile industry. The capital amassed by the East India Company in Bengal was invested in the emerging Industrial Revolution in United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, Great Britain, in industries such as Textile manufacture during the Industrial Revolution, textile manufacturing.Shombit SenguptaBengals plunder gifted the British Industrial Revolution
''The Financial Express (India), The Financial Express'', 8 February 2010 Economic mismanagement, alongside drought and a smallpox epidemic, directly led to the Great Bengal famine of 1770, which is estimated to have caused the deaths of between 1 million and 10 million people. In 1862, the British Bengal Legislative Council, Bengal Legislative Council was set up as the first modern List of legislatures in South Asia, legislature in India. Elected representation was gradually introduced during the early 20th century, including with the Morley-Minto reforms and the system of dyarchy. In 1937, the council became the upper chamber of the Bengali legislature while the Bengal Legislative Assembly (1937—1947), Bengal Legislative Assembly was created. Between 1937 and 1947, the chief executive of the government was the Prime Minister of Bengal. The Bengal Presidency was the largest administrative unit in the British Empire. At its height, it covered large parts of present-day India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Burma, Malaysia, and Singapore. In 1830, the British Straits Settlements on the coast of the Malacca Straits was made a residency of Bengal. The area included the erstwhile Prince of Wales Island (Malaysia), Prince of Wales Island, Province Wellesley, Malacca and Singapore. In 1867, Penang, Singapore and Malacca were separated from Bengal into the Straits Settlements. British Burma became a province of India and a later a Crown colony in itself. Western areas, including the Ceded and Conquered Provinces and Punjab Province (British India), The Punjab, were further reorganised. Northeastern areas became Colonial Assam. In 1876, about 200,000 people were killed in Bengal by the 1876 Bangladesh cyclone, Great Backerganj Cyclone of 1876 in the Barisal region. About 50 million were killed in Bengal due to massive plague outbreaks and famines which happened in 1895 to 1920, mostly in western Bengal.

 The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was initiated on the outskirts of Calcutta, and spread to Dhaka, Chittagong, Jalpaiguri, Sylhet and Agartala, in solidarity with revolts in North India. The failure of the rebellion led to the abolition of the Company Rule in India and establishment of direct rule over India by the British, commonly referred to as the British Raj. The late 19th and early 20th century Bengal Renaissance had a great impact on the cultural and economic life of Bengal and started a great advance in the literature and science of Bengal. Between 1905 and 1911, an abortive attempt was made to Partition of Bengal (1905), divide the province of Bengal into two: Bengal proper and the short-lived province of Eastern Bengal and Assam where the All India Muslim League was founded. In 1911, the Bengali poet and polymath Rabindranath Tagore became Asia's first Nobel laureate when he won the Nobel Prize in Literature.
Bengal played a major role in the Indian independence movement, in which Revolutionary movement for Indian independence, revolutionary groups were dominant. Armed attempts to overthrow the British Raj began with the rebellion of Titumir, and reached a climax when Subhas Chandra Bose led the Indian National Army against the British. Bengal was also central in the rising political awareness of the Muslim population—the All-India Muslim League was established in Dhaka in 1906. The Muslim homeland movement pushed for a sovereign state in eastern India with the Lahore Resolution in 1943. Hindu nationalism was also strong in Bengal, which was home to groups like the Hindu Mahasabha. In spite of a last-ditch effort by politicians Huseyn Shaheed Suhrawardy, Sarat Chandra Bose to form a United Bengal, when India History of the Republic of India, gained independence in 1947, Bengal was Partition of Bengal (1947), partitioned along religious lines. The western joined India (and was named West Bengal) while the eastern part joined Pakistan as a province called East Bengal (later renamed East Pakistan, giving rise to Bangladesh in 1971). The circumstances of partition were bloody, with widespread religious riots in Bengal.
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was initiated on the outskirts of Calcutta, and spread to Dhaka, Chittagong, Jalpaiguri, Sylhet and Agartala, in solidarity with revolts in North India. The failure of the rebellion led to the abolition of the Company Rule in India and establishment of direct rule over India by the British, commonly referred to as the British Raj. The late 19th and early 20th century Bengal Renaissance had a great impact on the cultural and economic life of Bengal and started a great advance in the literature and science of Bengal. Between 1905 and 1911, an abortive attempt was made to Partition of Bengal (1905), divide the province of Bengal into two: Bengal proper and the short-lived province of Eastern Bengal and Assam where the All India Muslim League was founded. In 1911, the Bengali poet and polymath Rabindranath Tagore became Asia's first Nobel laureate when he won the Nobel Prize in Literature.
Bengal played a major role in the Indian independence movement, in which Revolutionary movement for Indian independence, revolutionary groups were dominant. Armed attempts to overthrow the British Raj began with the rebellion of Titumir, and reached a climax when Subhas Chandra Bose led the Indian National Army against the British. Bengal was also central in the rising political awareness of the Muslim population—the All-India Muslim League was established in Dhaka in 1906. The Muslim homeland movement pushed for a sovereign state in eastern India with the Lahore Resolution in 1943. Hindu nationalism was also strong in Bengal, which was home to groups like the Hindu Mahasabha. In spite of a last-ditch effort by politicians Huseyn Shaheed Suhrawardy, Sarat Chandra Bose to form a United Bengal, when India History of the Republic of India, gained independence in 1947, Bengal was Partition of Bengal (1947), partitioned along religious lines. The western joined India (and was named West Bengal) while the eastern part joined Pakistan as a province called East Bengal (later renamed East Pakistan, giving rise to Bangladesh in 1971). The circumstances of partition were bloody, with widespread religious riots in Bengal.
Partition of Bengal (1947)
On 27 April 1947, the last Prime Minister of Bengal Huseyn Shaheed Suhrawardy held a press conference in New Delhi where he outlined his vision for an independent Bengal. Suhrawardy said "Let us pause for a moment to consider what Bengal can be if it remains united. It will be a great country, indeed the richest and the most prosperous in India capable of giving to its people a high standard of living, where a great people will be able to rise to the fullest height of their stature, a land that will truly be plentiful. It will be rich in agriculture, rich in industry and commerce and in course of time it will be one of the powerful and progressive states of the world. If Bengal remains united this will be no dream, no fantasy". On 2 June 1947, British Prime Minister Clement Attlee told the US Ambassador to the United Kingdom that there was a "distinct possibility Bengal might decide against partition and against joining either Hindustan or Pakistan". On 3 June 1947, the Mountbatten Plan outlined the partition of British India. On 20 June, the Bengal Legislative Assembly met to decide on the partition of Bengal. At the preliminary joint meeting, it was decided (126 votes to 90) that if the province remained united, it should join the Constituent Assembly of Pakistan. At a separate meeting of legislators fromGeography
Most of the Bengal region lies in the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta, but there are highlands in its north, northeast and southeast. The Ganges Delta arises from the confluence of the rivers Ganges, Brahmaputra River, Brahmaputra, and Meghna River, Meghna rivers and their respective tributaries. The total area of Bengal is —West Bengal is and Bangladesh . The flat and fertile Bangladesh Plain dominates the geography of Bangladesh. The Chittagong Hill Tracts and Sylhet region are home to most of the List of mountains in Bangladesh, mountains in Bangladesh. Most parts of Bangladesh are within above the sea level, and it is believed that about 10% of the land would be flooded if the sea level were to rise by . Because of this low elevation, much of this region is exceptionally vulnerable to seasonal flooding due to monsoons. The highest point in Bangladesh is in Mowdok range at . A major part of the coastline comprises a marshy jungle, the Sundarbans, the largest mangrove forest in the world and home to diverse flora and fauna, including the royal Bengal tiger. In 1997, this region was declared endangered. West Bengal is on the eastern bottleneck of India, stretching from the Himalayas in the north to the Bay of Bengal in the south. The state has a total area of . The Darjeeling Himalayan hill region in the northern extreme of the state belongs to the eastern Himalaya. This region contains Sandakfu ()—the highest peak of the state. The narrow Terai region separates this region from the plains, which in turn transitions into the Ganges delta towards the south. The Rarh region intervenes between the Ganges delta in the east and the western plateau and high lands. A small coastal region is on the extreme south, while the Sundarbans mangrove forests form a remarkable geographical landmark at the Ganges delta. At least nine districts in West Bengal and 42 districts in Bangladesh have Arsenic contamination of groundwater, arsenic levels in groundwater above the World Health Organization maximum permissible limit of 50 μg/L or 50 parts per billion and the untreated water is unfit for human consumption. The water causes arsenicosis, skin cancer and various other complications in the body.Geographic distinctions

North Bengal
North Bengal is a term used for the north-western part of Bangladesh and northern part of West Bengal. The Bangladeshi part comprises Rajshahi Division and Rangpur Division. Generally, it is the area lying west of Jamuna River (Bangladesh), Jamuna River and north of Padma River, and includes the Barind Tract. Politically, West Bengal's part comprises Jalpaiguri Division and most of Malda division (except Murshidabad district) together and Bihar's parts include Kishanganj district. Darjeeling Hilly are also part of North Bengal. The people of Jaipaiguri, Alipurduar and Cooch Behar usually identify themselves as North Bengali. North Bengal is divided into Terai and Dooars regions. North Bengal is also noted for its rich cultural heritage, including two UNESCO World Heritage Sites. Aside from the Bengali majority, North Bengal is home to many other communities including Nepalis, Santhal people, Lepchas and Rajbongshis.Northeast Bengal
 Northeast Bengal refers to the Sylhet region, which today comprises the Sylhet Division of Bangladesh and
Northeast Bengal refers to the Sylhet region, which today comprises the Sylhet Division of Bangladesh and Central Bengal
Central Bengal refers to the Dhaka Division of Bangladesh. It includes the elevated Madhupur tract with a large Sal (tree), Sal tree forest. The Padma River cuts through the southern part of the region, separating the greater Faridpur District, Faridpur region. In the north lies the greater Mymensingh and Tangail regions.South Bengal
South Bengal covers the southwestern Bangladesh and the southern part of the Indian state of West Bengal. The Bangladeshi part includes Khulna Division, Barisal Division and the proposed Faridpur Division The part of South Bengal of West Bengal includes Presidency division, Burdwan division and Medinipur division. The Sundarbans, a major biodiversity hotspot, is located in South Bengal. Bangladesh hosts 60% of the forest, with the remainder in India.Southeast Bengal
 Southeast Bengal refers to the hilly-coastal Chittagonian language, Chittagonian-speaking and coastal Bengali-speaking areas of Chittagong Division in southeastern Bangladesh. The region is noted for its thalassocracy, thalassocratic and seafaring heritage. The area was dominated by the Bengali Harikela and Samatata kingdoms in antiquity. It was known to Arab traders as ''Samandar'' in the 9th century. During the medieval period, the region was ruled by the Chandra dynasty, the sultanate of Bengal, the kingdom of Tripura, the kingdom of Mrauk U, the Portuguese Empire and the Mughal Empire, prior to the advent of British rule. The Chittagonian language, a sister of Bengali is prevalent in coastal areas of southeast Bengal. Along with its Bengali population, it is also home to Tibeto-Burman ethnic groups, including the Chakma people, Chakma, Marma people, Marma, Tanchangya people, Tanchangya and Bawm people, Bawm peoples.
Southeast Bengal is considered a bridge to Southeast Asia and the northern parts of Arakan are also historically considered to be a part of it.
Southeast Bengal refers to the hilly-coastal Chittagonian language, Chittagonian-speaking and coastal Bengali-speaking areas of Chittagong Division in southeastern Bangladesh. The region is noted for its thalassocracy, thalassocratic and seafaring heritage. The area was dominated by the Bengali Harikela and Samatata kingdoms in antiquity. It was known to Arab traders as ''Samandar'' in the 9th century. During the medieval period, the region was ruled by the Chandra dynasty, the sultanate of Bengal, the kingdom of Tripura, the kingdom of Mrauk U, the Portuguese Empire and the Mughal Empire, prior to the advent of British rule. The Chittagonian language, a sister of Bengali is prevalent in coastal areas of southeast Bengal. Along with its Bengali population, it is also home to Tibeto-Burman ethnic groups, including the Chakma people, Chakma, Marma people, Marma, Tanchangya people, Tanchangya and Bawm people, Bawm peoples.
Southeast Bengal is considered a bridge to Southeast Asia and the northern parts of Arakan are also historically considered to be a part of it.
Places of interest
There are four World Heritage Sites in the region, including the Sundarbans, the Somapura Mahavihara, the Mosque City of Bagerhat and the Darjeeling Himalayan Railway. Other prominent places include the Bishnupur, Bankura temple city, the Adina Mosque, the Katra Masjid, Caravanserai Mosque, numerous zamindar palaces (like Ahsan Manzil and Cooch Behar Palace), the Lalbagh Fort, the Bara Katra, Great Caravanserai ruins, the Choto Katra, Shaista Khan Caravanserai ruins, the Kolkata Victoria Memorial (Kolkata), Victoria Memorial, the Dhaka Parliament Building, archaeologically excavated ancient fort cities in Mahasthangarh, Mainamati, Chandraketugarh and Wari-Bateshwar, the Jaldapara National Park, the Lawachara National Park, the Teknaf Game Reserve and the Chittagong Hill Tracts. Cox's Bazar in southeastern Bangladesh is home to the longest natural sea beach in the world with an unbroken length of 120 km (75 mi). It is also a growing surfing destination. St. Martin's Island, off the coast of Chittagong Division, is home to the sole coral reef in Bengal.Other regions
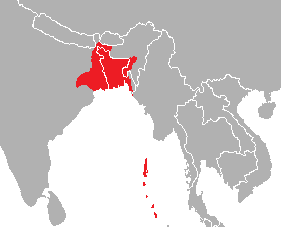 Bengal was a regional power of the Indian subcontinent. The administrative jurisdiction of Bengal historically extended beyond the territory of Bengal proper. In the 9th century, the Pala Empire of Bengal ruled large parts of northern India. The Bengal Sultanate controlled Bengal, Assam, Arakan, Bihar and Orissa at different periods in history. In Mughal Bengal, the Nawab of Bengal had a jurisdiction covering Bengal, Bihar and Orissa. Bengal's administrative jurisdiction reached its greatest extent under the British Empire, when the Bengal Presidency extended from the Straits of Malacca in the east to the Khyber Pass in the west. In the late-19th and early-20th centuries, administrative reorganisation drastically reduced the territory of Bengal.
Several regions bordering Bengal proper continue to have high levels of Bengali influence. The Indian state of Tripura has a Bengali majority population. Bengali influence is also prevalent in the Indian regions of Assam, Meghalaya, Bihar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands; as well as in Myanmar's Rakhine State.
Bengal was a regional power of the Indian subcontinent. The administrative jurisdiction of Bengal historically extended beyond the territory of Bengal proper. In the 9th century, the Pala Empire of Bengal ruled large parts of northern India. The Bengal Sultanate controlled Bengal, Assam, Arakan, Bihar and Orissa at different periods in history. In Mughal Bengal, the Nawab of Bengal had a jurisdiction covering Bengal, Bihar and Orissa. Bengal's administrative jurisdiction reached its greatest extent under the British Empire, when the Bengal Presidency extended from the Straits of Malacca in the east to the Khyber Pass in the west. In the late-19th and early-20th centuries, administrative reorganisation drastically reduced the territory of Bengal.
Several regions bordering Bengal proper continue to have high levels of Bengali influence. The Indian state of Tripura has a Bengali majority population. Bengali influence is also prevalent in the Indian regions of Assam, Meghalaya, Bihar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands; as well as in Myanmar's Rakhine State.
Arakan
 Arakan (now Rakhine State, Myanmar) has historically been under strong Bengali influence. Since antiquity, Bengal has influenced the culture of Arakan. The ancient Bengali script was used in Arakan. An Arakanese inscription recorded the reign of the Bengali Candra dynasty. Paul Wheatley (geographer), Paul Wheatley described the "Indianization" of Arakan.
According to Pamela Gutman, "Arakan was ruled by kings who adopted Indian titles and traditions to suit their own environment. Indian Brahmins conducted royal ceremonies, Buddhist monks spread their teachings, traders came and went and artists and architects used Indian models for inspiration. In the later period, there was also influence from the Islamic courts of Bengal and Delhi". Arakan emerged as a vassal state of the Bengal Sultanate. It later became an independent kingdom. The royal court and culture of the Kingdom of Mrauk U was heavily influenced by Bengal. Bengali Muslims served in the royal court as ministers and military commanders. Bengali Hindus and Bengali Buddhists served as priests. Some of the most important poets of medieval Bengali literature lived in Arakan, including Alaol and Daulat Qazi. In 1660, Shah Shuja (Mughal prince), Prince Shah Shuja, the governor of Mughal Bengal and a pretender of the Peacock Throne of India, was forced to seek asylum in Arakan. Bengali influence in the Arakanese royal court persisted until Burmese annexation in the 18th-century.
The modern-day Rohingya people, Rohingya population is a legacy of Bengal's influence on Arakan. The Rohingya genocide resulted in the displacement of over a million people between 2016 and 2017, with many being uprooted from their homes in Rakhine State.
Arakan (now Rakhine State, Myanmar) has historically been under strong Bengali influence. Since antiquity, Bengal has influenced the culture of Arakan. The ancient Bengali script was used in Arakan. An Arakanese inscription recorded the reign of the Bengali Candra dynasty. Paul Wheatley (geographer), Paul Wheatley described the "Indianization" of Arakan.
According to Pamela Gutman, "Arakan was ruled by kings who adopted Indian titles and traditions to suit their own environment. Indian Brahmins conducted royal ceremonies, Buddhist monks spread their teachings, traders came and went and artists and architects used Indian models for inspiration. In the later period, there was also influence from the Islamic courts of Bengal and Delhi". Arakan emerged as a vassal state of the Bengal Sultanate. It later became an independent kingdom. The royal court and culture of the Kingdom of Mrauk U was heavily influenced by Bengal. Bengali Muslims served in the royal court as ministers and military commanders. Bengali Hindus and Bengali Buddhists served as priests. Some of the most important poets of medieval Bengali literature lived in Arakan, including Alaol and Daulat Qazi. In 1660, Shah Shuja (Mughal prince), Prince Shah Shuja, the governor of Mughal Bengal and a pretender of the Peacock Throne of India, was forced to seek asylum in Arakan. Bengali influence in the Arakanese royal court persisted until Burmese annexation in the 18th-century.
The modern-day Rohingya people, Rohingya population is a legacy of Bengal's influence on Arakan. The Rohingya genocide resulted in the displacement of over a million people between 2016 and 2017, with many being uprooted from their homes in Rakhine State.
Assam
 The Indian state of
The Indian state of Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Bengali is the most spoken language among the population of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a strategically important archipelago which is controlled by India as a federal territory. The islands were once used as a British penal colony. During World War II, the islands were seized by the Japanese and controlled by the Provisional Government of Free India. Anti-British leader Subhash Chandra Bose visited and renamed the islands. Between 1949 and 1971, the Indian government resettled many Bengali Hindus in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.Bihar
 In antiquity, Bihar and Bengal were often part of the same kingdoms. The ancient region of Magadha (Mahajanapada), Magadha covered both Bihar and Bengal. Magadha was the birthplace or bastion of several pan-Indian empires, including the Mauryan Empire, the Gupta Empire and the
In antiquity, Bihar and Bengal were often part of the same kingdoms. The ancient region of Magadha (Mahajanapada), Magadha covered both Bihar and Bengal. Magadha was the birthplace or bastion of several pan-Indian empires, including the Mauryan Empire, the Gupta Empire and the Chittagong Hill Tracts
The Chittagong Hill Tracts is the southeastern frontier of Bangladesh. Its indigenous population includes Tibeto-Burman ethnicities, including the Chakma people, Bawm people and Mru people, Mro people among others. The region was historically ruled by tribal chieftains of the Chakma Circle and Bohmong Circle. In 1713, the Chakma Raja signed a treaty with Mughal Bengal after obtaining permission from Farrukhsiyar, Emperor Farrukhsiyar for trade with the plains of Chittagong. Like the kings of Arakan, the Chakma Circle began to fashion themselves using Mughal nomenclatures and titles. They initially resisted the Permanent Settlement and the activities of the East India Company. The tribal royal families of the region came under heavy Bengali influence. The Chakma queen Benita Roy was a friend of Rabindranath Tagore. The region was governed by the Chittagong Hill Tracts manual under colonial rule. The manual was significantly amended after the end of British rule; and the region became fully integrated with Bangladesh.Malay Archipelago
Through trade, settlements and the exchange of ideas; parts of Maritime Southeast Asia became linked with Bengal. Language, literature, art, governing systems, religions and philosophies in ancient Sumatra and Java were influenced by Bengal. Indianized kingdom, Hindu-Buddhist kingdoms in Southeast Asia depended on the Bay of Bengal for trade and ideas. Islam in Southeast Asia also spread through the Bay of Bengal, which was a bridge between the Malay Archipelago and Indo-Islamic states of the Indian subcontinent. A large number of wealthy merchants from Bengal were based in Malacca. Bengali ships were the largest ships in the waters of the Malay Archipelago during the 15th century. Between 1830 and 1867, the ports of Singapore and Malacca, the island of Penang, and a portion of the Malay Peninsula were ruled under the jurisdiction of the Bengal Presidency of the British Empire. These areas were known as the Straits Settlements, which was separated from the Bengal Presidency and converted into a Crown colony in 1867.Meghalaya
The Indian state of Meghalaya historically came under the influence of Shah Jalal, a Muslim missionary and conqueror from Sylhet. During British Raj, British rule, the city of Shillong was the summer capital of Eastern Bengal and Assam (modern Bangladesh and Northeast India). Shillong boasted the highest per capita income in British India.North India
The ancient Mauryan, Gupta and Pala Empire, Pala empires of the Magadha (Mahajanapada), Magadha region (Bihar and Bengal) extended into northern India. The westernmost border of the Bengal Sultanate extended towards Varanasi and Jaunpur district, Jaunpur. In the 19th century, Punjab Province (British India), Punjab and the Ceded and Conquered Provinces formed the western extent of the Bengal Presidency. According to the British historian Rosie Llewellyn-Jones, "The Bengal Presidency, an administrative division introduced by the East India Company, would later include not only the whole of northern India up to the Khyber Pass on the north-west frontier with Afghanistan, but would spread eastwards to Burma and Singapore as well".Odisha
Odisha, previously known as Orissa, has a significant Bengali minority. Historically, the region has faced invasions from Bengal, including an invasion by Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah. Parts of the region were ruled by the Bengal Sultanate and Mughal Bengal. The Nawab of Bengal was styled as the "Nawab of Bengal, Bihar and Orissa" because the Nawab was granted jurisdiction over Orissa by the Mughal Emperor.Tibet
During the Pala Empire, Pala dynasty, Tibet received missionaries from Bengal who influenced the emergence of Tibetan Buddhism. One of the most notable missionaries was Atisa. During the 13th century, Tibet experienced an Islamic invasion of Tibet, Islamic invasion by the forces of Bakhtiyar Khalji, the Muslim conqueror of Bengal.Tripura
The Tripura (princely state), princely state of Tripura was ruled by the Manikya dynasty until the 1949 Tripura Merger Agreement. Tripura was historically a vassal state of Bengal. After assuming the throne with military support from the Bengal Sultanate in 1464, Ratna Manikya I introduced administrative reforms inspired by the government of Bengal. The Tripura kings requested Sultan Ruknuddin Barbak Shah, Barbak Shah to provide manpower for developing the administration of Tripura. As a result, Bengali Hindu bureaucrats, cultivators and artisans began settling in Tripura. Today, the Indian state of Tripura has a Bengali-majority population. Modern Tripura is a gateway for trade and transport links betweenFlora and fauna
 The flat Bengal Plain, which covers most of Bangladesh and West Bengal, is one of the most Soil fertility, fertile areas on Earth, with lush vegetation and farmland dominating its landscape. Bengali villages are buried among groves of mango, jackfruit, betel nut and date palm. Rice, jute, mustard plant, mustard and sugarcane plantations are a common sight. Body of water, Water bodies and wetlands provide a habitat for many aquatic plants in the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta. The northern part of the region features Himalayan foothills (''Dooars'') with densely wooded Sal (tree), Sal and other tropical evergreen trees. Above an elevation of 1,000 metres (3,300 ft), the forest becomes predominantly subtropical, with a predominance of temperate-forest trees such as oaks, conifers and rhododendrons. Sal woodland is also found across central Bangladesh, particularly in the Bhawal National Park. The Lawachara National Park is a rainforest in northeastern Bangladesh. The Chittagong Hill Tracts in southeastern Bangladesh is noted for its high degree of biodiversity.
The littoral Sundarbans in the southwestern part of Bengal is the largest mangrove forest in the world and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The region has over List of mammals in Bangladesh, 89 species of mammals, List of birds of Bangladesh, 628 species of birds and List of fishes in Bangladesh, numerous species of fish. For Bangladesh, the Nymphaea, water lily, the oriental magpie-robin, the hilsa and mango tree are national symbols. For West Bengal, the white-throated kingfisher, the Alstonia, chatim tree and the night-flowering jasmine are state symbols. The Bengal tiger is the national animal of Bangladesh and India. The fishing cat is the state animal of West Bengal.
The flat Bengal Plain, which covers most of Bangladesh and West Bengal, is one of the most Soil fertility, fertile areas on Earth, with lush vegetation and farmland dominating its landscape. Bengali villages are buried among groves of mango, jackfruit, betel nut and date palm. Rice, jute, mustard plant, mustard and sugarcane plantations are a common sight. Body of water, Water bodies and wetlands provide a habitat for many aquatic plants in the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta. The northern part of the region features Himalayan foothills (''Dooars'') with densely wooded Sal (tree), Sal and other tropical evergreen trees. Above an elevation of 1,000 metres (3,300 ft), the forest becomes predominantly subtropical, with a predominance of temperate-forest trees such as oaks, conifers and rhododendrons. Sal woodland is also found across central Bangladesh, particularly in the Bhawal National Park. The Lawachara National Park is a rainforest in northeastern Bangladesh. The Chittagong Hill Tracts in southeastern Bangladesh is noted for its high degree of biodiversity.
The littoral Sundarbans in the southwestern part of Bengal is the largest mangrove forest in the world and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The region has over List of mammals in Bangladesh, 89 species of mammals, List of birds of Bangladesh, 628 species of birds and List of fishes in Bangladesh, numerous species of fish. For Bangladesh, the Nymphaea, water lily, the oriental magpie-robin, the hilsa and mango tree are national symbols. For West Bengal, the white-throated kingfisher, the Alstonia, chatim tree and the night-flowering jasmine are state symbols. The Bengal tiger is the national animal of Bangladesh and India. The fishing cat is the state animal of West Bengal.
Politics
Today, the region of Bengal proper is divided between the sovereign state of the Bangladesh, People's Republic of Bangladesh and theBangladeshi Republic
The state of Bangladesh is a parliamentary republic based on the Westminster system, with a Constitution of Bangladesh, written constitution and a President of Bangladesh, President elected by parliament for mostly ceremonial purposes. The Government of Bangladesh, government is headed by a Prime Minister, who is appointed by the President from among the popularly elected 300 Members of Parliament in the Jatiyo Sangshad, the national parliament. The Prime Minister is traditionally the leader of the single largest party in the Jatiyo Sangshad. Under the constitution, while recognising Islam as the country's established religion, the constitution grants freedom of religion to non-Muslims. Between 1975 and 1990, Bangladesh had a presidential system of government. Since the 1990s, it was administered by non-political technocratic Caretaker government of Bangladesh, caretaker governments on four occasions, the last being under military-backed emergency rule in 2007 and 2008. The Awami League and the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) were the two most dominant political parties in Bangladesh until the July Revolution (Bangladesh), July Revolution of 2024, which led to the ousting of Sheikh Hasina following mass protests and a nationwide uprising. In the aftermath, a non-partisan Yunus Ministry, interim government was formed under Nobel laureate Muhammad Yunus to restore democratic governance and oversee institutional reforms. Much like the technocratic caretaker governments between 1990 and 2008, this interim administration pledged neutrality and began preparations for constitutional changes and future elections. Bangladesh is a member of the United Nations, UN, World Trade Organization, WTO, International Monetary Fund, IMF, the World Bank, Asian Development Bank, ADB, Organization of Islamic Cooperation, OIC, Islamic Development Bank, IDB, South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation, SAARC, Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation, BIMSTEC and the Islamic Military Counter Terrorism Coalition, IMCTC. Bangladesh has achieved significant strides in List of countries by Human Development Index, human development compared to its neighbours.Indian Bengal
West Bengal is a constituent state of the India, Republic of India, with local State governments of India, executives and Vidhan Sabha, assemblies- features shared with other states in the Indian federal system. The president of India appoints a governor as the ceremonial representative of the Government of India, union government. The governor appoints the chief minister on the nomination of the legislative assembly. The chief minister is the traditionally the leader of the party or coalition with most seats in the assembly. President's rule is often imposed in Indian states as a direct intervention of the union government led by the prime minister of India. The Bengali-speaking zone of India carries 48 seats in the lower house of India, Lok Sabha. Each state has popularly elected members in the Indian lower house of parliament, the Lok Sabha. Each state nominates members to the Indian upper house of parliament, the Rajya Sabha. The state legislative assemblies also play a key role in electing the ceremonial president of India. The former president of India, Pranab Mukherjee, was a native of West Bengal and a leader of the Indian National Congress. The former Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha, leader of opposition of India, Adhir Ranjan Chowdhury is fromCrossborder relations
India and Bangladesh are the world's first and eighth most populous countries respectively. Bangladesh-India relations began on a high note in 1971 when India played a major role in the liberation of Bangladesh, with the Indian Bengali populace and media providing overwhelming support to the independence movement in the former East Pakistan. The two countries had a twenty five-year friendship treaty between 1972 and 1996. However, differences over river sharing, border security and access to trade have long plagued the relationship. In more recent years, a consensus has evolved in both countries on the importance of developing good relations, as well as a strategic partnership in South Asia and beyond. Commercial, cultural and defence co-operation have expanded since 2010, when Prime Ministers Sheikh Hasina and Manmohan Singh pledged to reinvigorate ties. The Bangladesh High Commission in New Delhi operates a Deputy High Commission in Kolkata and a consular office in Agartala. India has a High Commission in Dhaka with consulates in Chittagong and Rajshahi. Frequent international air, bus and rail services connect major cities in Bangladesh and Indian Bengal, particularly the three largest cities- Dhaka, Kolkata and Chittagong. Undocumented immigration of Bangladeshi workers is a controversial issue championed by right-wing nationalist parties in India but finds little sympathy in West Bengal. India has since fenced the border which has been criticised by Bangladesh.Economy
The Ganges Delta provided advantages of fertile soil, ample water, and an abundance of fish, wildlife, and fruit. Living standards for Bengal's elite were relatively better than other parts of theStock markets
*Dhaka Stock Exchange *Chittagong Stock Exchange *Calcutta Stock ExchangePorts and harbours
*Port of Chittagong *Port of Kolkata *Port of Mongla *Haldia Port, Port of Haldia *Port of Payra *Port of Pangaon *Farakka Port, Port of Farakka *Port of Narayanganj *Port of Ashuganj *Port of Barisal *Matarbari Port *Land port of Benapole-PetrapoleChambers of commerce
*Bengal Chamber of Commerce and Industry *Bengal National Chamber of Commerce & Industry *Federation of Bangladesh Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FBCCI) *Chittagong Chamber of Commerce & Industry *Dhaka Chamber of Commerce & Industry (DCCI) *Metropolitan Chamber of Commerce and Industry, Dhaka, Metropolitan Chamber of Commerce and Industry (MCCI)Intra-Bengal trade
Bangladesh and India are the largest trading partners in South Asia, with two-way trade valued at an estimated US$16 billion. Most of this trade relationship is centred on some of the world's busiest land ports on the Bangladesh-India border. The Bangladesh Bhutan India Nepal Initiative seeks to boost trade through a Regional Motor Vehicles Agreement.Demographics
The Bengal region is one of the Population density, most densely populated areas in the world. With a population of 300 million, Bengalis are the third largest ethnic group in the world after the Han Chinese and Arabs. According to provisional results of 2011 Bangladesh census, the population of Bangladesh was 149,772,364; however, CIA's ''The World Factbook'' gives 163,654,860 as its population in a July 2013 estimate. According to the provisional results of the 2011 Indian national census, West Bengal has a population of 91,347,736. "So, the Bengal region, , has at least 241.1 million people. This figures give a population density of 1003.9/km2; making it among the most densely populated areas in the world.World Bank Group, World Bank Development Indicators Database, 2006. Bengali language, Bengali is the main language spoken in Bengal. Many phonological, lexical, and structural differences from the standard variety occur in peripheral varieties of Bengali across the region. Other regional languages closely related to Bengali include Sylheti language, Sylheti, Chittagonian language, Chittagonian, Chakma language, Chakma, Rangpuri language, Rangpuri/Rajbangshi, Hajong language, Hajong, Rohingya language, Rohingya, and Tangchangya language, Tangchangya. According to the 2011 Indian census, 18% of the Bengali-speakers are bilingual of whom half can speak Hindi, and 5% are trilingual. In general, Bengalis are followers of Islam, Hinduism, Christianity and Buddhism with a significant number are Irreligion, Irreligious. In addition, several minority ethnolinguistic groups are native to the region. These include speakers of other Indo-Aryan languages (e.g., Bishnupriya Manipuri language, Bishnupriya Manipuri, Sadri language, Oraon Sadri, various Bihari languages), Tibeto-Burman languages (e.g., A'Tong language, A'Tong, Chak language, Chak, Koch language, Koch, Garo language, Garo, Megam language, Megam, Meitei language, Meitei (officially called "Manipuri language, Manipuri"), Mizo language, Mizo, Mru language, Mru, Pangkhua language, Pangkhua, Rakhine language, Rakhine/Marma Language, Marma, Kok Borok language, Kok Borok, Reang language, Riang, Tippera language, Tippera, Usoi language, Usoi, various Chin languages), Austroasiatic languages (e.g., Khasi language, Khasi, Koda language, Koda, Mundari language, Mundari, Pnar language, Pnar, Santali language, Santali, War language, War), and Dravidian languages (e.g., Kurukh language, Kurukh, Sauria Paharia language, Sauria Paharia). Life expectancy is around 72.49 years for Bangladesh and 70.2 for West Bengal. In terms of literacy, West Bengal leads with 77% literacy rate, in Bangladesh the rate is approximately 72.9%. The level of poverty in West Bengal is at 19.98%, while in Bangladesh it stands at 12.9% West Bengal has one of the lowest total fertility rates in India. West Bengal's TFR of 1.6 roughly equals that of Canada.Major cities
The Bengal region is home to the some of List of urban areas by population, major urban areas of the world, Dhaka is the List of urban areas by population, 4th largest urban areas of the world. Kolkata is List of urban areas by population, 17th largest urban area.Other major cities in West Bengal
Other important cities of West Bengal region such as Howrah, Kalyani, West Bengal, Kalyani, Basirhat, Kharagpur, Durgapur, Coochbehar, Malda, West Bengal, Malda, Chandannagar, Bardhaman, Darjeeling etc.Other major cities in Bangladesh
Other important cities in Bangladesh such as Sylhet, Khulna, Jessore, Rajshahi, Rangpur, Bangladesh, Rangpur, Cox's Bazar etc.Culture
Language
Currency
Literature
 Bengali literature has a rich heritage. It has a history stretching back to the 3rd century BCE, when the main language was Sanskrit written in the brahmi script. The Bengali language and Bengali–Assamese script, script evolved from Magadhi Prakrit. Bengal has a long tradition in folk literature, evidenced by the ''Charyapada, Chôrjapôdô'', ''Mangalkavya'', ''Shreekrishna Kirtana'', ''Maimansingha Gitika'' or ''Thakurmar Jhuli''. Bengali literature in the medieval age was often either religious (e.g. Chandidas), or adaptations from other languages (e.g. Alaol). During the Bengal Renaissance of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, Bengali literature was modernised through the works of authors such as Michael Madhusudan Dutta, Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar, Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay, Rabindranath Tagore, Sarat Chandra Chattopadhyay, Kazi Nazrul Islam, Satyendranath Dutta, Begum Rokeya and Jibanananda Das. In the 20th century, prominent modern Bengali writers included Syed Mujtaba Ali, Jasimuddin, Manik Bandopadhyay, Tarasankar Bandyopadhyay, Bibhutibhushan Bandyopadhyay, Buddhadeb Bose, Sunil Gangopadhyay and Humayun Ahmed.
Prominent contemporary Bengali writers in English include Amitav Ghosh, Tahmima Anam, Jhumpa Lahiri and Zia Haider Rahman among others.
Bengali literature has a rich heritage. It has a history stretching back to the 3rd century BCE, when the main language was Sanskrit written in the brahmi script. The Bengali language and Bengali–Assamese script, script evolved from Magadhi Prakrit. Bengal has a long tradition in folk literature, evidenced by the ''Charyapada, Chôrjapôdô'', ''Mangalkavya'', ''Shreekrishna Kirtana'', ''Maimansingha Gitika'' or ''Thakurmar Jhuli''. Bengali literature in the medieval age was often either religious (e.g. Chandidas), or adaptations from other languages (e.g. Alaol). During the Bengal Renaissance of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, Bengali literature was modernised through the works of authors such as Michael Madhusudan Dutta, Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar, Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay, Rabindranath Tagore, Sarat Chandra Chattopadhyay, Kazi Nazrul Islam, Satyendranath Dutta, Begum Rokeya and Jibanananda Das. In the 20th century, prominent modern Bengali writers included Syed Mujtaba Ali, Jasimuddin, Manik Bandopadhyay, Tarasankar Bandyopadhyay, Bibhutibhushan Bandyopadhyay, Buddhadeb Bose, Sunil Gangopadhyay and Humayun Ahmed.
Prominent contemporary Bengali writers in English include Amitav Ghosh, Tahmima Anam, Jhumpa Lahiri and Zia Haider Rahman among others.
Personification
The Bangamata is a female national personification, personification of Bengal which was created during the Bengali Renaissance and later adopted by the Bengali nationalism, Bengali nationalists. Hindu nationalism, Hindu nationalists adopted a modified Bharat Mata as a national personification of India. The Mother Bengal represents not only biological motherness but its attributed characteristics as well – protection, never ending love, consolation, care, the beginning and the end of life. In Amar Sonar Bangla, the national anthem of Bangladesh, Rabindranath Tagore has used the word "Maa" (Mother) numerous times to refer to the motherland i.e. Bengal.Art
Architecture
 Classical Bengali architecture features terracotta buildings. Ancient Bengali kingdoms laid the foundations of the region's architectural heritage through the construction of monasteries and temples (for example, the Somapura Mahavihara). During the Bengal Sultanate, sultanate period, a distinct and glorious Islamic style of architecture developed the region. Most Islamic buildings were small and highly artistic terracotta mosques with multiple domes and no minarets. Bengal was also home to the largest mosque in South Asia at Adina Mosque,
Adina. Bengali vernacular architecture is credited for inspiring the popularity of the bungalow.
The Bengal region also has a rich heritage of Indo-Saracenic architecture, including numerous zamindar palaces and mansions. The most prominent example of this style is the Victoria Memorial, Kolkata.
In the 1950s, Muzharul Islam pioneered the modernist terracotta style of architecture in South Asia. This was followed by the design of the Jatiyo Sangshad Bhaban by the renowned American architect Louis Kahn in the 1960s, which was based on the aesthetic heritage of Bengali architecture and geography.
Classical Bengali architecture features terracotta buildings. Ancient Bengali kingdoms laid the foundations of the region's architectural heritage through the construction of monasteries and temples (for example, the Somapura Mahavihara). During the Bengal Sultanate, sultanate period, a distinct and glorious Islamic style of architecture developed the region. Most Islamic buildings were small and highly artistic terracotta mosques with multiple domes and no minarets. Bengal was also home to the largest mosque in South Asia at Adina Mosque,
Adina. Bengali vernacular architecture is credited for inspiring the popularity of the bungalow.
The Bengal region also has a rich heritage of Indo-Saracenic architecture, including numerous zamindar palaces and mansions. The most prominent example of this style is the Victoria Memorial, Kolkata.
In the 1950s, Muzharul Islam pioneered the modernist terracotta style of architecture in South Asia. This was followed by the design of the Jatiyo Sangshad Bhaban by the renowned American architect Louis Kahn in the 1960s, which was based on the aesthetic heritage of Bengali architecture and geography.
Sciences
 The Gupta dynasty, which is believed to have originated in North Bengal, pioneered the invention of chess, the concept of zero, the heliocentrism, theory of Earth orbiting the Sun, the study of Sun, solar and Moon, lunar eclipses and the flourishing of Sanskrit literature and Sanskrit drama, drama.
The educational reforms during the British Raj gave birth to many distinguished scientists in Bengal. Sir Jagadish Chandra Bose pioneered the investigation of radio and microwave optics, made significant contributions to plant science, and laid the foundations of experimental science in the Indian subcontinent. IEEE named him one of the People known as the father or mother of something, fathers of radio science. He was the first person from the Indian subcontinent to receive a United States patent law, US patent, in 1904. In 1924–25, while researching at the University of Dhaka, Satyendra Nath Bose well known for his works in quantum mechanics, provided the foundation for Bose–Einstein statistics and the theory of the Bose–Einstein condensate. Meghnad Saha was the first scientist to relate a star's spectrum to its temperature, developing thermal ionization equations (notably the Saha ionization equation) that have been foundational in the fields of astrophysics and astrochemistry. Amal Kumar Raychaudhuri was a physicist, known for his research in general relativity and cosmology. His most significant contribution is the eponymous Raychaudhuri equation, which demonstrates that singularities arise inevitably in general relativity and is a key ingredient in the proofs of the Penrose–Hawking singularity theorems.
In the United States, the Bangladeshi-American engineer Fazlur Rahman Khan emerged as the "father of tubular designs" in skyscraper construction. Ashoke Sen is an Indian theoretical physicist whose main area of work is string theory. He was among the first recipients of the Fundamental Physics Prize "for opening the path to the realisation that all string theories are different limits of the same underlying theory".
The Gupta dynasty, which is believed to have originated in North Bengal, pioneered the invention of chess, the concept of zero, the heliocentrism, theory of Earth orbiting the Sun, the study of Sun, solar and Moon, lunar eclipses and the flourishing of Sanskrit literature and Sanskrit drama, drama.
The educational reforms during the British Raj gave birth to many distinguished scientists in Bengal. Sir Jagadish Chandra Bose pioneered the investigation of radio and microwave optics, made significant contributions to plant science, and laid the foundations of experimental science in the Indian subcontinent. IEEE named him one of the People known as the father or mother of something, fathers of radio science. He was the first person from the Indian subcontinent to receive a United States patent law, US patent, in 1904. In 1924–25, while researching at the University of Dhaka, Satyendra Nath Bose well known for his works in quantum mechanics, provided the foundation for Bose–Einstein statistics and the theory of the Bose–Einstein condensate. Meghnad Saha was the first scientist to relate a star's spectrum to its temperature, developing thermal ionization equations (notably the Saha ionization equation) that have been foundational in the fields of astrophysics and astrochemistry. Amal Kumar Raychaudhuri was a physicist, known for his research in general relativity and cosmology. His most significant contribution is the eponymous Raychaudhuri equation, which demonstrates that singularities arise inevitably in general relativity and is a key ingredient in the proofs of the Penrose–Hawking singularity theorems.
In the United States, the Bangladeshi-American engineer Fazlur Rahman Khan emerged as the "father of tubular designs" in skyscraper construction. Ashoke Sen is an Indian theoretical physicist whose main area of work is string theory. He was among the first recipients of the Fundamental Physics Prize "for opening the path to the realisation that all string theories are different limits of the same underlying theory".
Music
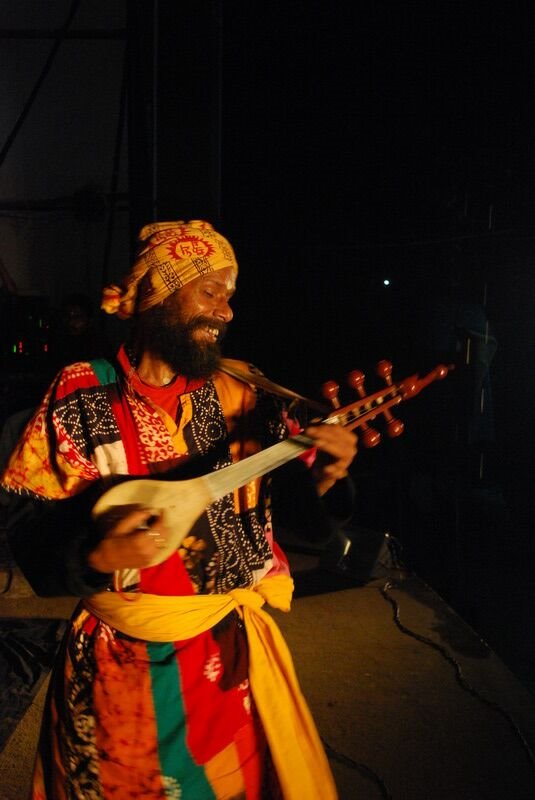 The Baul tradition is a unique heritage of Bengali folk music. The 19th century mystic poet Lalon Shah is the most celebrated practitioner of the tradition. Other folk music forms include Gombhira, Bhatiali and Bhawaiya. Hason Raja is a renowned folk poet of the Sylhet region. Folk music in Bengal is often accompanied by the ektara, a one-stringed instrument. Other instruments include the dotara, dhol, flute, and tabla. The region also has a rich heritage in Hindustani classical music, North Indian classical music.
The Baul tradition is a unique heritage of Bengali folk music. The 19th century mystic poet Lalon Shah is the most celebrated practitioner of the tradition. Other folk music forms include Gombhira, Bhatiali and Bhawaiya. Hason Raja is a renowned folk poet of the Sylhet region. Folk music in Bengal is often accompanied by the ektara, a one-stringed instrument. Other instruments include the dotara, dhol, flute, and tabla. The region also has a rich heritage in Hindustani classical music, North Indian classical music.
Cuisine
Bengali cuisine is the only traditionally developed multi-course tradition from the Indian subcontinent. Rice and fish are traditional favourite foods, leading to a saying that "fish and rice make a Bengali". Bengal's vast repertoire of fish-based dishes includes Hilsa preparations, a favourite among Bengalis. Bengalis make distinctive confectionery, sweetmeats from milk products, including ''Rasgulla, Rôshogolla'', ''Chômchôm'', and several kinds of ''Pithe''. The old city of Dhaka is noted for its distinct Indo-Islamic cuisine, including biryani, bakarkhani and kebab dishes.Boats
 There are 150 types of Bengali country boats plying the List of rivers in Bangladesh, 700 rivers of the Bengal delta, the vast floodplain and many oxbow lakes. They vary in design and size. The boats include the dinghy and sampan among others. Country boats are a central element of Bengali culture and have inspired generations of artists and poets, including the ivory artisans of the Mughal era. The country has a long shipbuilding tradition, dating back many centuries. Wooden boats are made of timber such as ''Jarul'' (dipterocarpus turbinatus),'' sal'' (shorea robusta), ''sundari'' (heritiera fomes), and ''Teak, Burma teak'' (tectons grandis). Medieval Bengal was shipbuilding hub for the Mughal Empire, Mughal and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman navies. The British Royal Navy later utilised Bengali shipyards in the 19th century, including for the Battle of Trafalgar.
There are 150 types of Bengali country boats plying the List of rivers in Bangladesh, 700 rivers of the Bengal delta, the vast floodplain and many oxbow lakes. They vary in design and size. The boats include the dinghy and sampan among others. Country boats are a central element of Bengali culture and have inspired generations of artists and poets, including the ivory artisans of the Mughal era. The country has a long shipbuilding tradition, dating back many centuries. Wooden boats are made of timber such as ''Jarul'' (dipterocarpus turbinatus),'' sal'' (shorea robusta), ''sundari'' (heritiera fomes), and ''Teak, Burma teak'' (tectons grandis). Medieval Bengal was shipbuilding hub for the Mughal Empire, Mughal and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman navies. The British Royal Navy later utilised Bengali shipyards in the 19th century, including for the Battle of Trafalgar.
Attire
 Bengali women commonly wear the ''sari, shaŗi'' , often distinctly designed according to local cultural customs. In urban areas, many women and men wear Western-style attire. Among men, European dressing has greater acceptance. Men also wear traditional costumes such as the ''panjabi'' with ''dhoti'' or ''pyjama'', often on religious occasions. The lungi, a kind of long skirt, is widely worn by Bangladeshi men.
Bengali women commonly wear the ''sari, shaŗi'' , often distinctly designed according to local cultural customs. In urban areas, many women and men wear Western-style attire. Among men, European dressing has greater acceptance. Men also wear traditional costumes such as the ''panjabi'' with ''dhoti'' or ''pyjama'', often on religious occasions. The lungi, a kind of long skirt, is widely worn by Bangladeshi men.
Festivals
For Bengali Muslims, the major religious festivals are Eid al-Fitr, Eid al-Adha, Mawlid, Muharram, and Barat Night, Shab-e-Barat. For Bengali Hindus, the major religious festivals include Durga Puja, Kali Puja, Janmashtami and Rath Yatra. In honour of Bengali Buddhists and Bengali Christians, both Buddha's Birthday and Christmas are public holidays in the region. The Bengali New Year is the main secular festival of Bengali culture celebrated by people regardless of religious and social backgrounds. The biggest congregation in Bengal is the Bishwa ijtema, which is also the world's second largest Islamic congregation. Other Bengali festivals include the Pohela Falgun, first day of spring and the Nabanna harvest festival in autumn.Media
Bangladesh has a diverse, outspoken and privately owned News media, press. English-language titles are popular in the urban readership. West Bengal had 559 published newspapers in 2005, of which 430 were in Bengali, with the largest circulated Bengali-language newspapers, Bengali language newspapers and magazines in the world. Cinema of Bangladesh, Bengali cinema is divided between the media hubs of Dhaka and Kolkata.Sports
Cricket and association football, football are popular sports in the Bengal region. Local games include sports such as Kho Kho and Kabaddi, the latter being the national sport of Bangladesh. An Indo-Bangladesh ''Bengali Games'' has been organised among the athletes of the Bengali speaking areas of the two countries.See also
* Bangladeshi diaspora * List of Bengalis * ZeratNotes
References
External links
{{Authority control Bengal, Regions of Asia Geography of South Asia Geography of Bangladesh History of Bengal, B Regions of India Historical Indian regions Subdivisions of British India Historical regions